CH3: Statistics
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Continuous scale
Theoretically possible to divide any values of the scale (e.g., height, depression).
Discrete scales
Categorical values (e.g., male or female).
Error
Collective influence of all factors on a test score beyond those specifically measured by the test.
Nominal Scales
Involve classification or categorization based on one or more distinguishing characteristics (e.g., DSM-4 diagnoses, degree program).
Ordinal Scale
Involve classifications like nominal scales but allow rank ordering (e.g., Olympian medalists, Likert scales).
Interval Scale
Contain equal intervals between numbers; each unit on the scale is equal to any other unit (e.g., IQ scores, temperature).
Ratio Scale
Interval scales with a true zero point; zero represents something (e.g., height & weight, reaction time).
Ordinal, Interval
Psychological disorders are naturally _ but are treated as _
Distributions
A set of test scores arrayed for recording or study.
Raw score
Straightforward, unmodified accounting of performance, usually represented by a number.
Histogram
A graph with vertical lines drawn at the true limits of each test score forming a series of contiguous rectangles.
Y-axis, X-axis
In a Bar graph, numbers of indicative frequency appear on the _ and reference to some categorization appears on _
J shaped curve
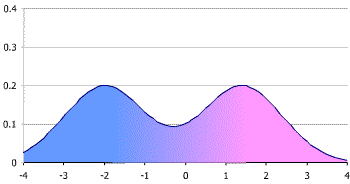
Identify the type of distribution.
Bimodal distribution
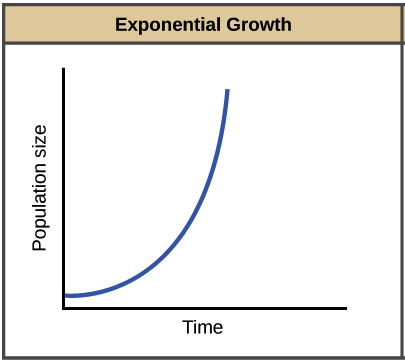
Identify the type of distribution
Positively skewed distribution
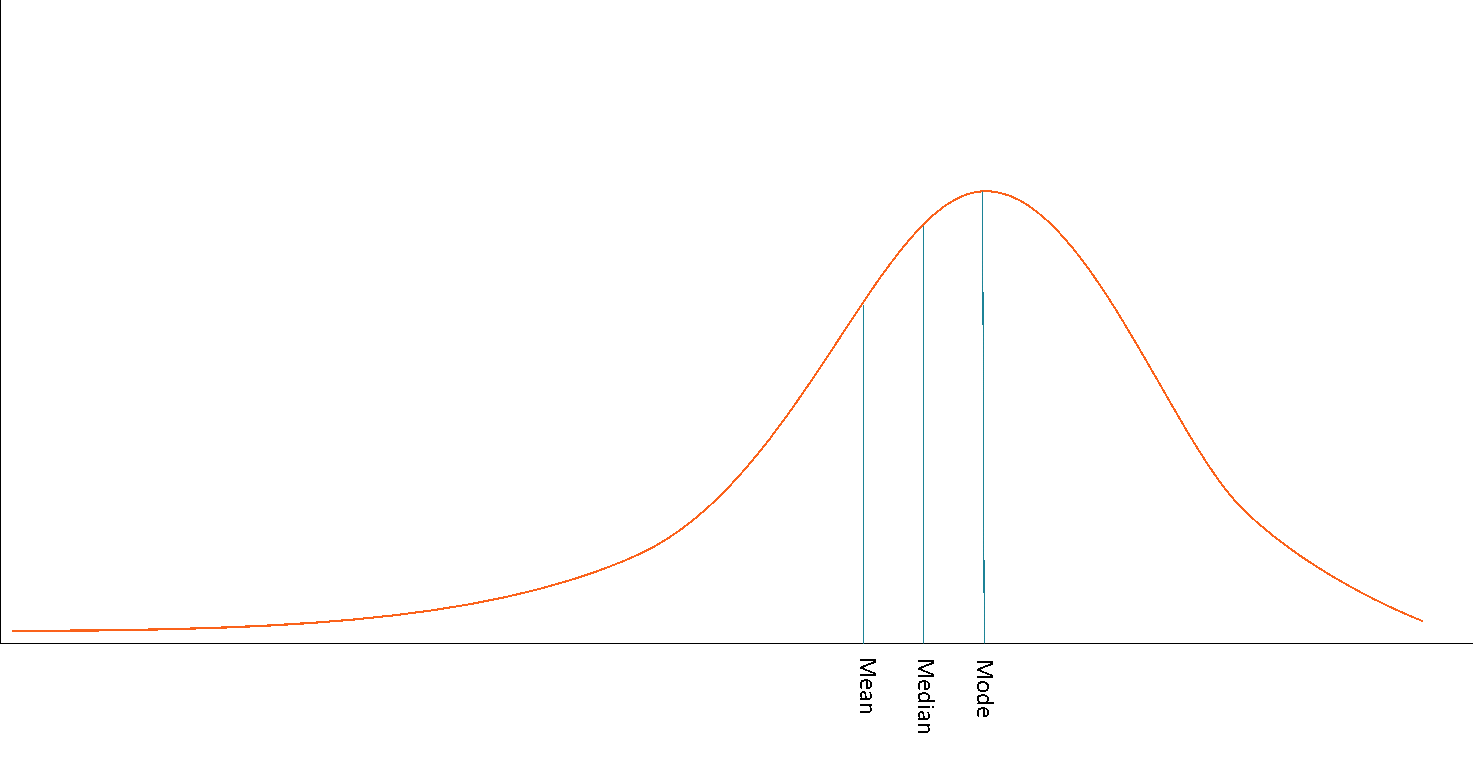
Identify the type of distribution.
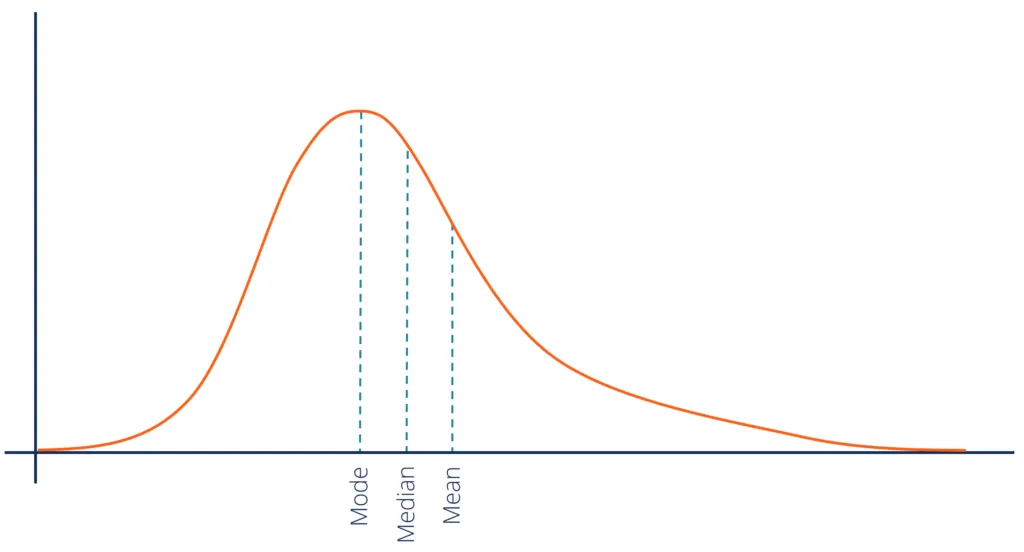
Negatively skewed distribution
Identify the type of distribution.
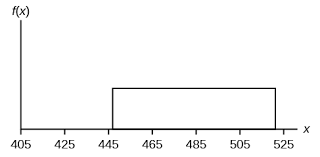
Rectangular distribution
Identify the type of distribution.
Central Tendency
A statistic that indicates the average or midmost score between extreme scores in a distribution.
Mean
Sum of observations divided by the number of observations.
Median
Middle score in a distribution.
Mode
Most frequently occurring score in a distribution.
Variability
Indication of the degree to which scores are scattered or dispersed in a distribution.
Range
Difference between the highest and lowest scores.
Interquartile range
Difference between 3rd and 1st quartile.
Semi-Interquartile Range
Interquartile range divided by 2.
Variance
Arithmetic mean of the squares of the differences between the scores in a distribution and their mean.
Standard deviation
The square root of the average squared deviations about the mean.
Kurtosis
Steepness of a distribution in the center.