Maintenance: Fluid & Salt Balance
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 10: Tuesday, October 28th: Maintenance: Fluid & Salt Balance; Week 10: Week 10: Thursday, October 30th: Maintenance: Fluid & Salt Balance (cont.); Maintenance: Calcium Balance
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
in a hypertonic cell, if there’s too much salt outside, water inside will leave, causing what to happen to the cell?
shrinkage
in a hypotonic cell, if there’s too much salt inside, water outside will enter, causing what to happen to the cell?
swelling
eating salt, digesting food, and drinking water cause a/an _______ (increase or decrease) in water/salt extracellularly
increase
sweating, urination, defecation blood loss, water loss causes a/an _______ (increase or decrease) in water/salt extracellularly
decrease
_______ is caused by excessive water drinking
polydipsia
_______ is caused by excessive sweating
hyperventilation
_______ is caused by excessive urination
polyuria
_______ is caused by excessive defecation
diarrhea
_______ is caused by excessive blood loss
hemorrhage
_______ is caused by excessive water loss
dehydration
_______ is needed to release angiotensin 2, which recruits _______ to specifically pull sodium in
renin, aldosterone
_______ specifically pulls water in, and is recruited by angiotensin 2
_______ is a local constrictor that works like ADH; it pulls water in
endothelin
_______ is released from the atria to decrease/push salt and fluid
atrial natriuretic peptide
_______ works with ANP to push water out and prevent high blood pressure
adrenomedulin
ANP and adrenomedulin have what effect on water levels? (increase or decrease?)
decrease water
vasopressin and aldosterone have what effect on water levels? (increase or decrease?)
increases water
angiotensin 2 and aldosterone have what effect on water and salt levels? (increase or decrease?)
increases water and salt
angiotensin 2 and vasopressin have what effect on thirst and ADH levels? (increase or decrease?)
increases thirst and ADH
vasopressin adn endothelin have what effect on blood pressure? (increase or decrease?)
increases blood pressure
renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) regulates _______ via vasoconstriction and increased blood volume
blood pressure
in the RAAS system, kidneys detect low fluid/salt/blood pressure, and release _______ from juxtaglomerular cells
renin
in the RAAS system, renin converts _______ released from the liver into angiotensin 1
angiotensinogen
in the RAAS system, angiotensin 1 is converted into angiotensin 2 using _______ released by the lungs in pulmonary blood
angiotensin converting enzymes (ACE)
angiotensin 2 recruits ______ and _______ to constrict blood vessels and increase blood pressure
aldosterone and vasopressint
the hypothamalus has two osmoreceptors to control fluid & salt levels and detect blood salt concentration, which are the:
organum vasculosum and subforical organ
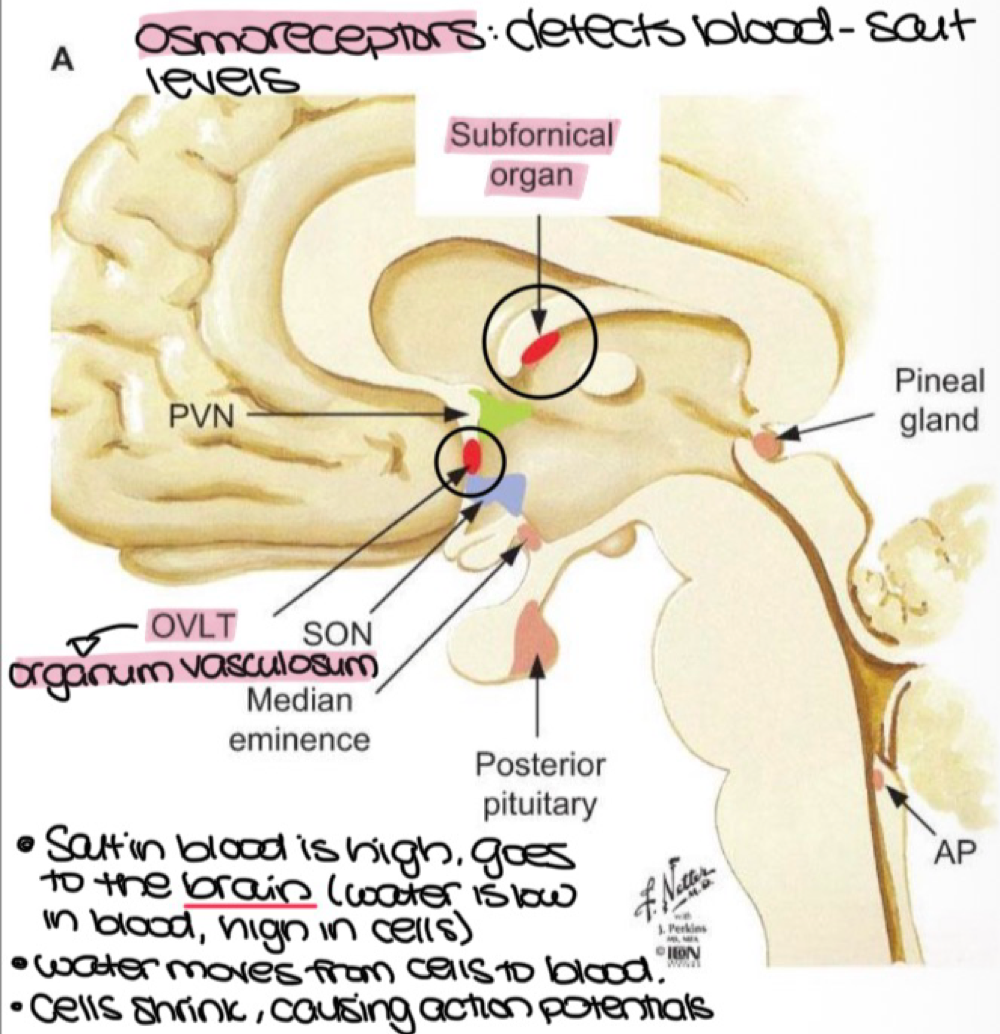
in the brain, when blood salt concentration is high, water is low ______ but high in _______
blood, water
in the brain, cell shrinkage of the osmoreceptors causes depolarization and signals the release of ________ from the neurohypopsis
ADH
angiotensin 2 _______ osmoreceptor detection, but ANP _______ it (increases or decreases)
decreases, increases
_______ is excessive fluid loss (blood, water, sodium)
hypovolemia
in the event of hypovolemia, low blood volume lowers pressure sensed by _______, which signal the hypothalamus to signal the neurohypopsus to release ADH
baroreceptorsv
ADH retains water and solutes, and raises blood pressure via what two organs?
kidneys and blood vessels
in the kidneys, ADH binds to _______ to trigger the G alpha S receptor pathway (atp → cAMP → PKA) and increase _______ in the cell
V2 receptors, aquaporin
in the kidneys, AVP increases ion channels, so more NA+, K+, and Cl- are _______ and ________
reaborbed, retained
in blood vessels, AVP binds to _______ to trigger the G alpha q receptor pathway (PLC → IP3 →Ca2+) to cause _______ and _______
V1 receptors, smooth muscle contractions and vasoconstriction
in blood vessels, AVP increases total peripheral constriction to redirect blood to vital organs and increase _______
blood pressure
the heart uses _______ to detect changesin blood volume via vessel expansion adn blood pressure
baroreceptors
the kidneys use their blood vessels and _______ to detect change sin blood volume adn salt levels
juxtaglomerular cells
low fluid and salt causes the adrenal cortex to _______ aldosterone release
increase
low fluid and salt causes the kidneys to _______ renin release
increase
low fluid and salt causes blood vessels to _______ endothelin release
increase
low fluid and salt causes the brain to _______ AVP and thus blood pressure
increaseh
high fluid and salt causes the heart to _______ ANP
increase
high fluid and salt causes blood vessels to _______ adrenomedulin
increase
high fluid and salt causes the kidneys/adrenal cortex to _______ renin and aldosterone
decreasea
aldosterone is stimulated by _______ and _______
angiotensin 2, ACTH
in the kidneys, aldosterone will _______ Na+ aborption and _______ K+ in the collecting ducts
increase, decrease
ANP _______ fluid and salt, so it opposed the RAAS system
decreases
ANP _______ renin, angiotensin 2, aldosterone, ADH, and thirst, and salt appetite
inhibits
endothelin and andrenomedulin are released during _______ for repair
tissue injury/inflammation
endothelin acts as an _______ for hypertension and kidney disease
antagonists
adrenomedulin _______ urine and interstitial fluid, but _______ ACTH and aldosterone
increases, decreases