Knowt 7.2 - Primate Behavior
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Part 2 - Reproductive Behaviors and Modeling Evolution
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Reproductive Strategies
Behaviors that have been naturally selected to increase individual reproductive success.
r/K selection Theory (i.e., K-selected vs. r-selected species)
Life history traits more important
r-selected species
Minimize parental investment with many offspring
K-selected species
Maximize parental investment with one to two offspring
Parental Care
Mother-Infant connection is the basis of all primate social groupings
Fathers rarely help rear offspring, b/c uncertainty
"Mothering” is a learned behavior (not innate)
Sexual Selection
The competition for mates that leads to evolution of certain traits
Dimorphism
The existence of two distinct forms within a species
Two Types of Sexual Selection
Intersexual Selection
Intrasexual Selection
Intersexual selection
Mate choice, often females
exaggerated (ornamental) traits
Between different sex
Intrasexual Selection
Competition for mates, often between males
Males typically much larger than females
Between same sex
Infanticide
The killing of young offspring
Infanticide Info
Male more common perpetrator
Frequently occurs when unfamiliar males enter a new group
Other possible explanations:
Competition for resources?
Accidental killing?
Alloparenting
The practice of caring for other’s offspring
Alloparenting Info
Also considered an affiliative behavior
Why alloparent?
To teach juvenile females
direct reciprocity (cohension)
Increase indirect fitness
Mothering
Model Development
Examining behavior
Drawing correlations
Development hypothesis
Examining Behavior
Patterns that have evolved as adaptive responses
Drawing Correlations
Between those behaviors and human behavior
Developing hypotheses
To test the ecological and genetic factors that produced modern human behaviors
Encephalization
Larger brain weight relative to body mass over time
Index of Encephalization
The predictable relationship between brain and body size
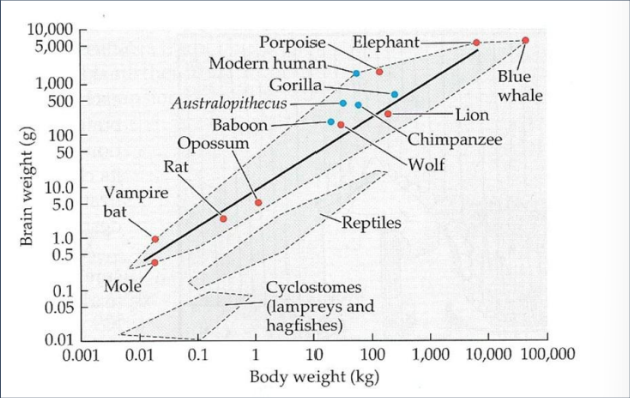
Hominin Brains developed in response to….
DietProvisioning strategies
Process, think, engage, create, innovate
Social Living
Higher fitness, larger brains
Language
A standardized system of arbitrary vocal sounds, written symbols ,and
gestures used in communication.
NHP’s Call Systems
Patterned sounds and utterances that convey meaning
NHP’s Call Systems Info
Limited
Stimuli-dependent
Discrete meanings
Nearly-identical species wide
NHP’s Info
They cannot speak, but they can learn and use language
Examples
Washoe and Loulis - ASL
Sarah - Arbitrary markers as signs
Chantek - used ASL to refer to out-of-view
Sherman and Austin - symbolic categories
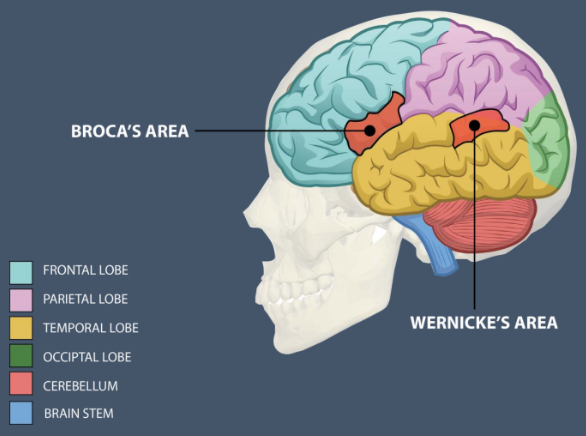
Broca’s Area
Frontal Lobe
Speech Production
Translates inputs into muscle movements
Broca’s Aphasia (“non-fluent aphasia”)
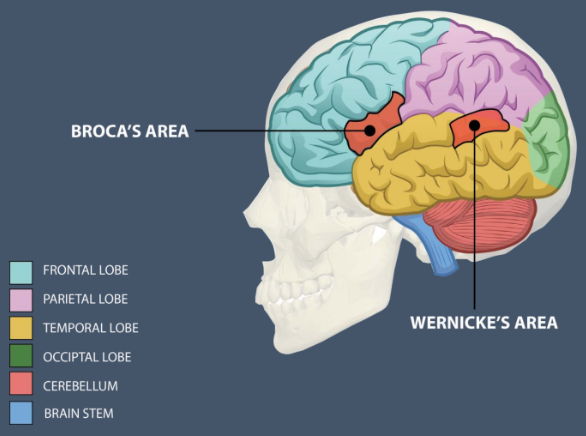
Wernicke’s Area
Temporal lobe
Language comprehension
Wernicke’s aphasia (“fluent aphasia”)
Aphasia
A language disorder that affects a person’s ability to communicate
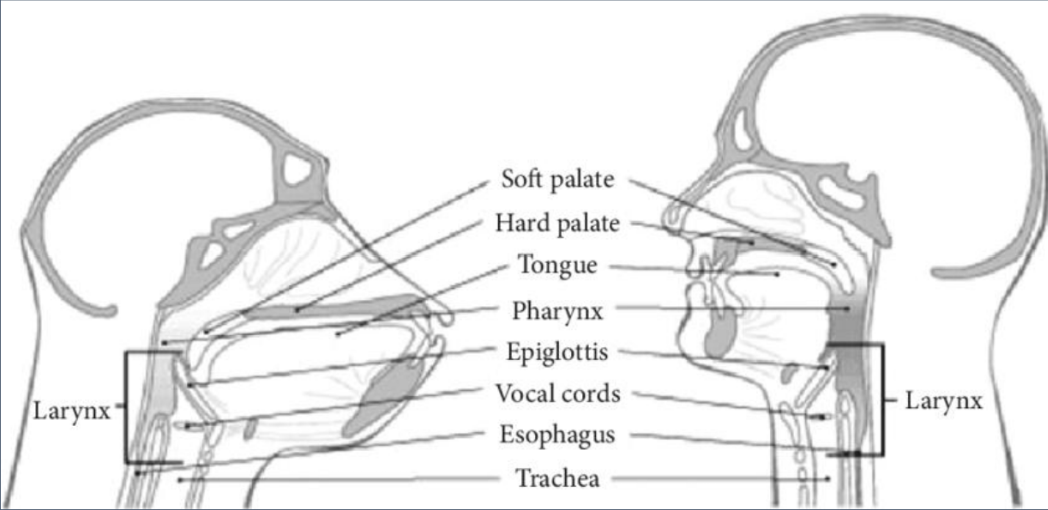
FOXP2 Gene
Regulatory gene
Highly conservative
Chromosome 7
Human & Primate Comparison Image
Cultural Behaviors
Behaviors that are learned and transmitted
E.g. Japanese macaques and their taters (you know, '“po-tay-toes”)
Variation observed between groups
E.g. Orangutans and chimpanzees
Tool Use
Implies Planning and forethought
preconceived ideas
The Evolution of Prosocial behaviors
actions that benefit other individuals or the group
includes assistance, sharing, caregiving, and compassion
Altruism
Empathy
Altruism
Helping others at great risk to oneself
Empathy
The ability to identify with the feeling and thoughts of another individual
Why? - The evolution of prosocial behaviors:
To ensure offspring or relative lives to reproductive age
Reciprocation
Kin selection ("for the good of the family!")
Group selection ("for the good of the group!")
Main Ideas
Some behaviors increase an individual's reproductive success – we call these behaviors"strategies"
reproductive strategies depend largely on life history traits and other ecological factors
primates are described as K-selected species; females give birth to very few highly dependent offspring over the course of their lives
sexual selection and dimorphism is the result of different strategies
infanticide is a strategy often perpetrated by males entering new groups
alloparenting is another reproductive behavior with positive impacts on an individual's reproductive success
anthropologists develop models by making observations, comparisons, and hypotheses.
models to explain the difference between human and nonhuman primate characters that can be tested as hypotheses about human evolution
examples include encephalization, symbolic thought, language, and culture
our goal is to apply knowledge gained in the present to our understanding of hominin evolution in the past