Phylogeny and Evolutionary Relationships: Tree Analysis and Applications(Week 4 Slides)
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
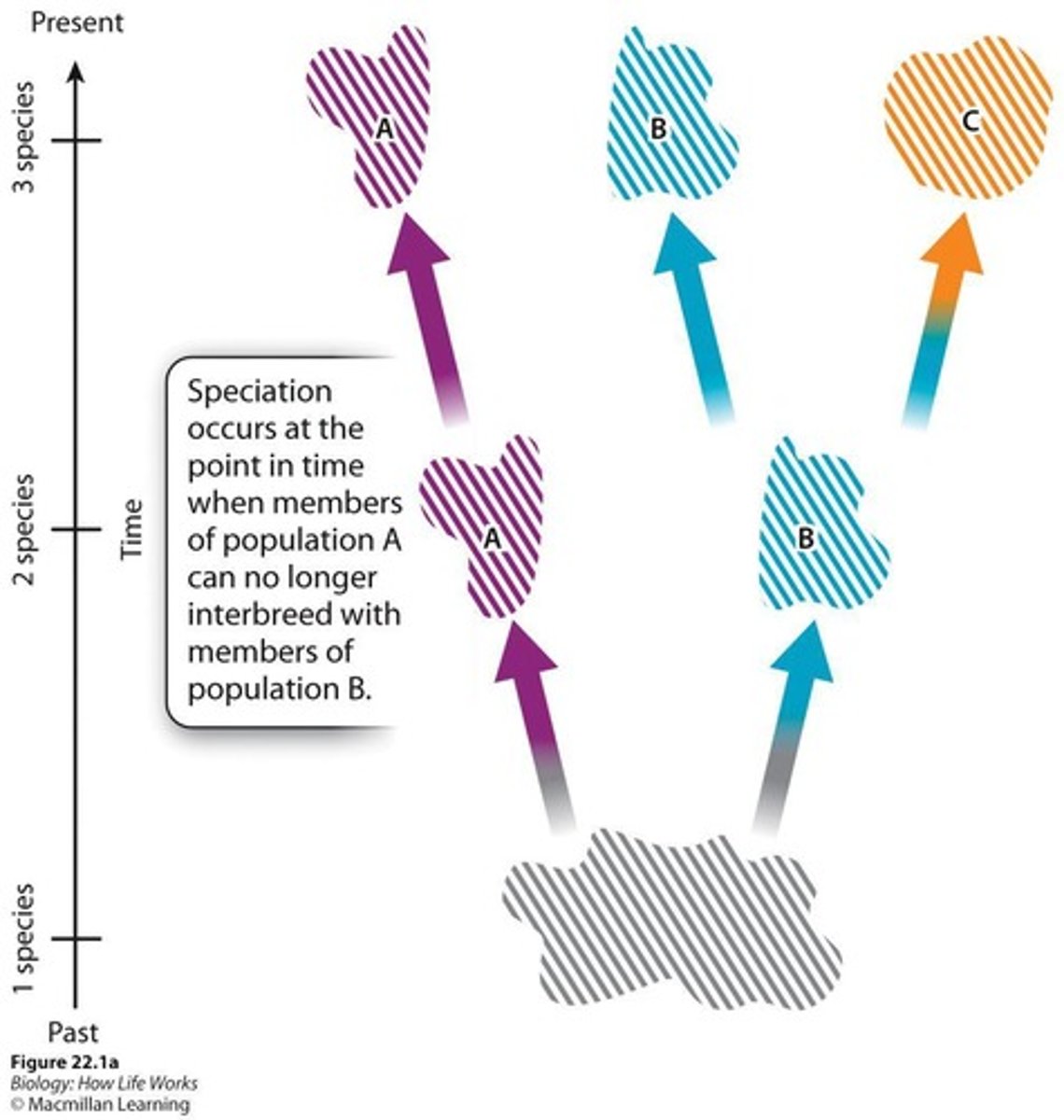
Speciation
Results in a nested branching pattern of evolutionary relationships among different lineages.
Phylogenetic trees
Represent evolution and show patterns of descent.
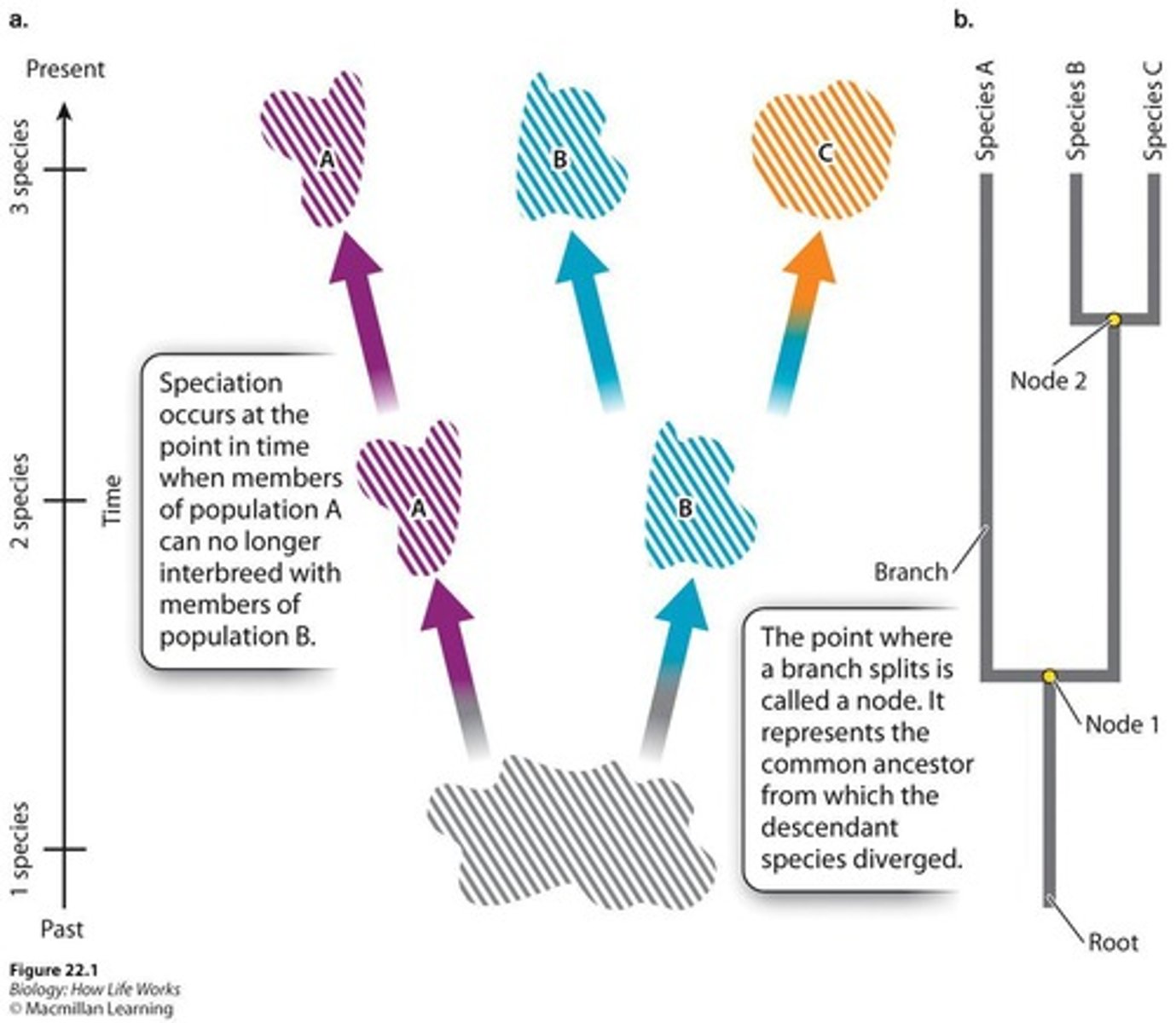
Branch point/Node
Represents the divergence of two evolutionary lineages from a common ancestor.
Sister taxa
Groups that share an immediate common ancestor not shared by any other group.
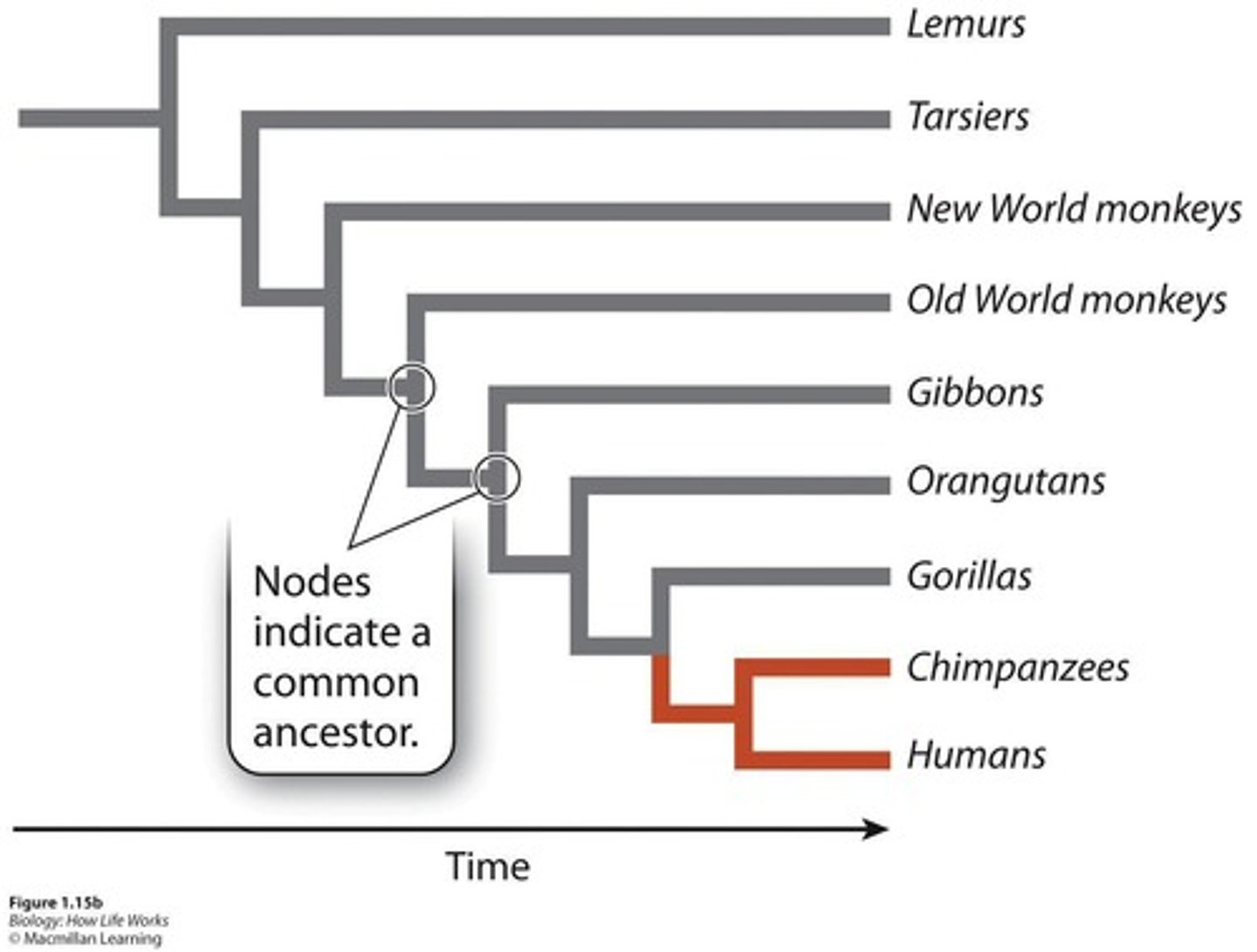
Basal taxon
A lineage that diverges from all members of its group early in the group's history.
Root
The common ancestor from which all members of a phylogenetic tree descend.
Evolutionary relationships
Described by the patterns shown in phylogenetic trees.
Common ancestor
The ancestor from which two or more species have diverged.
Monophyletic groups
Only these groups reflect evolutionary relationships.
Taxa
The groups of organisms that are represented at the branch tips of a phylogenetic tree.
Divergence of populations
The process by which new species arise from a common ancestor.
Evolutionary tree
A diagram that shows the evolutionary relationships among various biological species.
Phylogenetic tree limitations
Do not generally show how old lineages are or how much they have changed.
Inference of evolution
It should not be assumed that a taxon evolved from the taxon next to it.
Sister groups
Two groups that are more closely related to each other than either is to anything else on the tree.
Trace most recent common ancestors
A method to address evolutionary relationships by tracing branches.
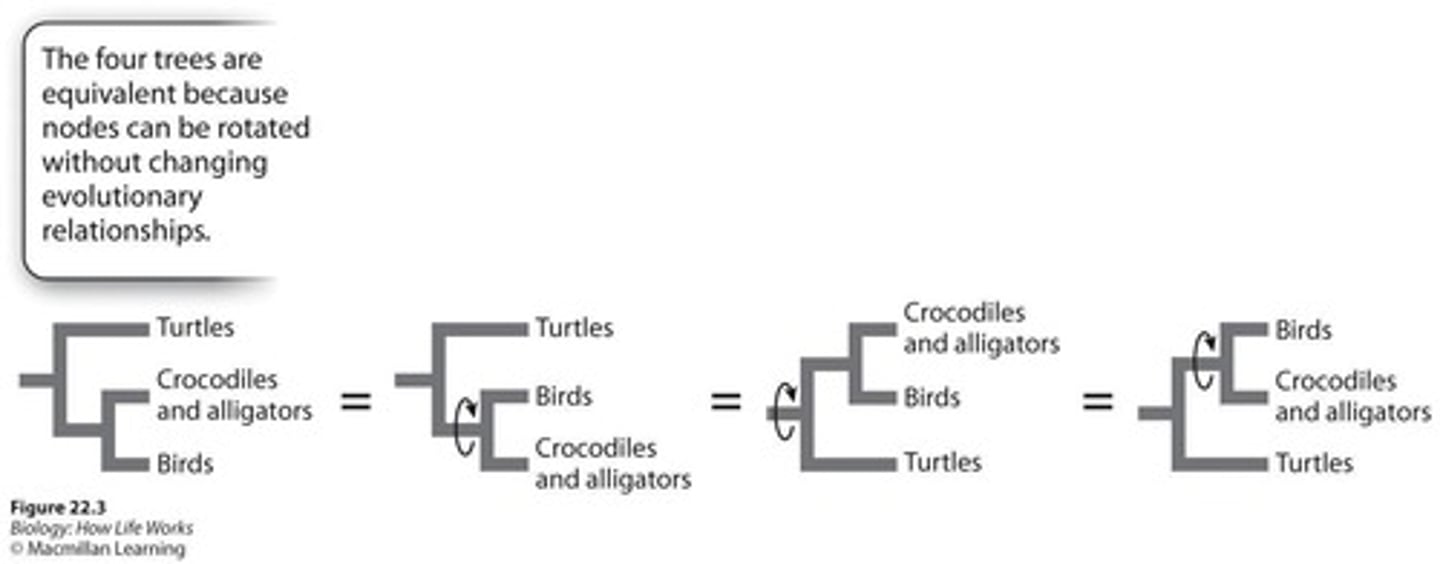
Branch movement
Branches can freely move around nodes without influencing the evolutionary relationships.
Evolutionary relationships inference
We can only infer that taxa evolved from a recent common ancestor.
Order of taxa appearance
Does not represent the sequence of evolution in a phylogenetic tree.
Patterns of descent
Shown by phylogenetic trees.
Evolutionary tree question
Which group shares a more recent common ancestor with turtles?
Evolutionary relationships question
Which statement best reflects the evolutionary relationships among the organisms?
Monophyletic group
Also called a clade, it shows the evolutionary path a group has taken since its origin.
Paraphyletic group
A group that includes an ancestor and some, but not all, of its descendants.
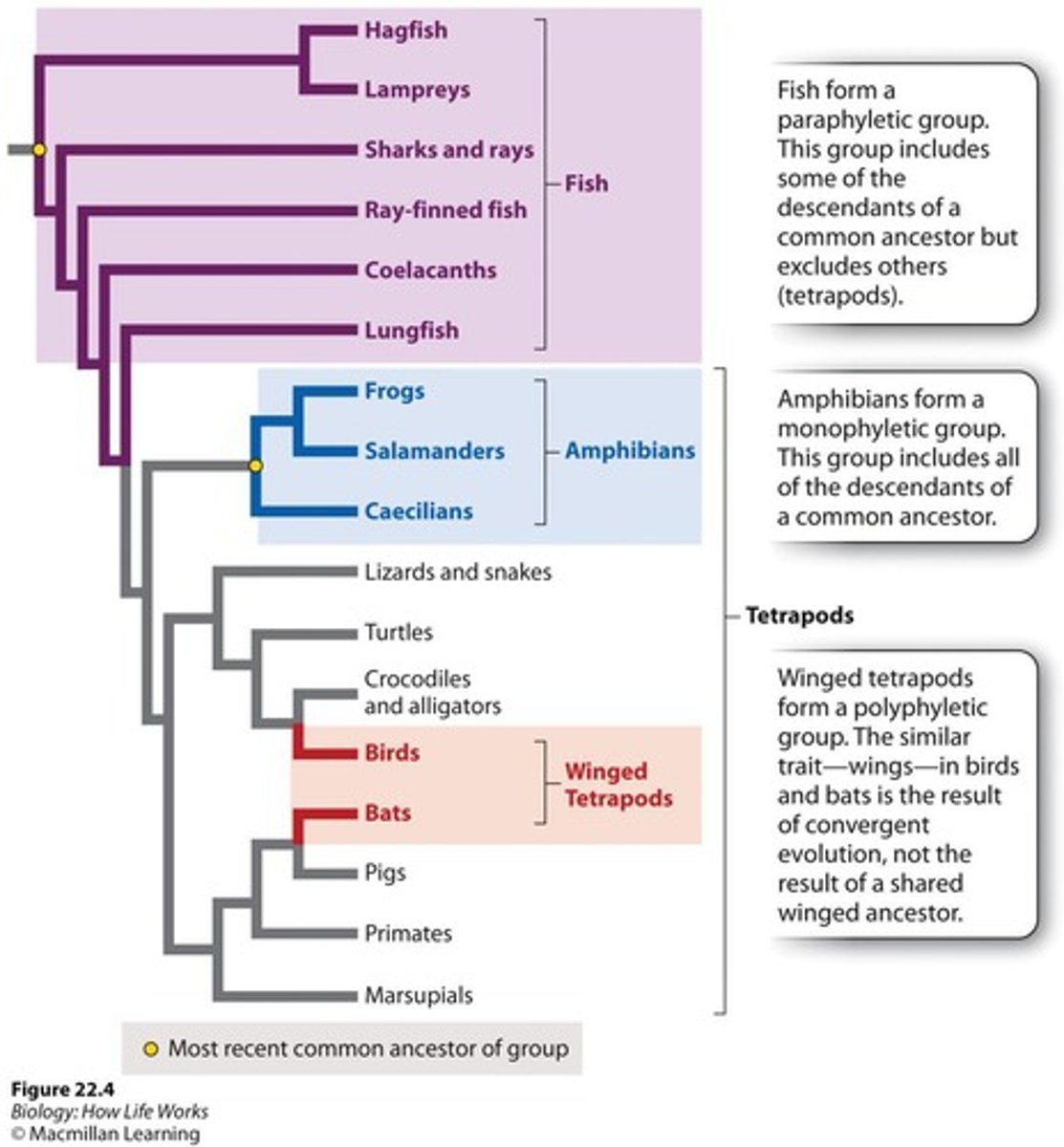
Polyphyletic group
A group that does not include the most recent common ancestor of its members.
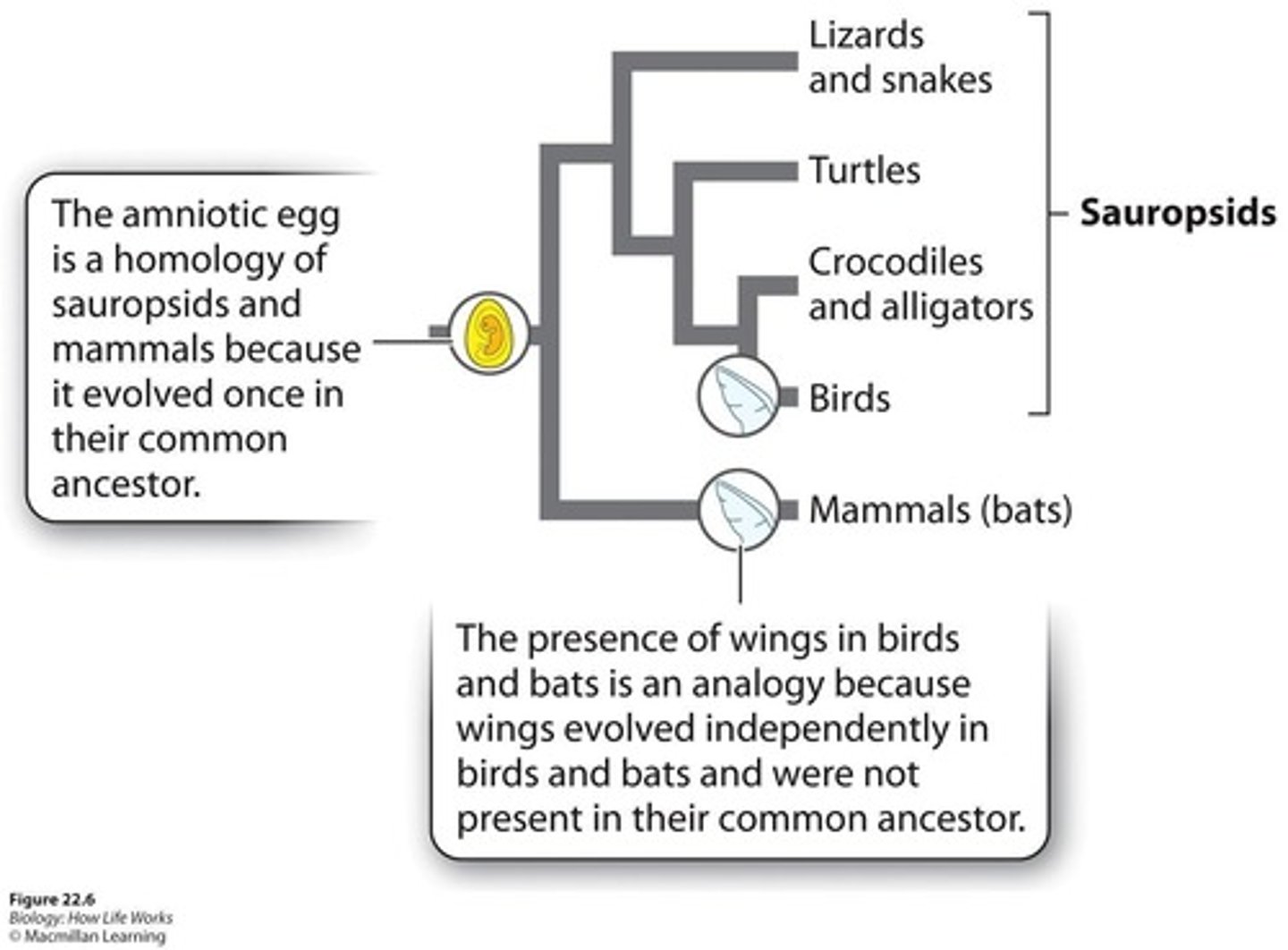
Homologous traits
Traits that are similar because of inheritance from a common ancestor.
Analogous traits
Traits that are similar due to convergent evolution, not inheritance.
Shared derived characteristics
Characteristics that are shared by all the lineages of a particular monophyletic group, but are absent in the sister taxa of the group.
Synapomorphies
Shared derived characteristics that help build phylogenetic trees.
Bipedalism
A shared derived trait in humans indicating the ability to walk on two legs.
Cranial capacity
A shared derived trait in humans referring to the size of the braincase.
Phylogenetic tree
A diagram that shows the evolutionary relationships among various biological species.
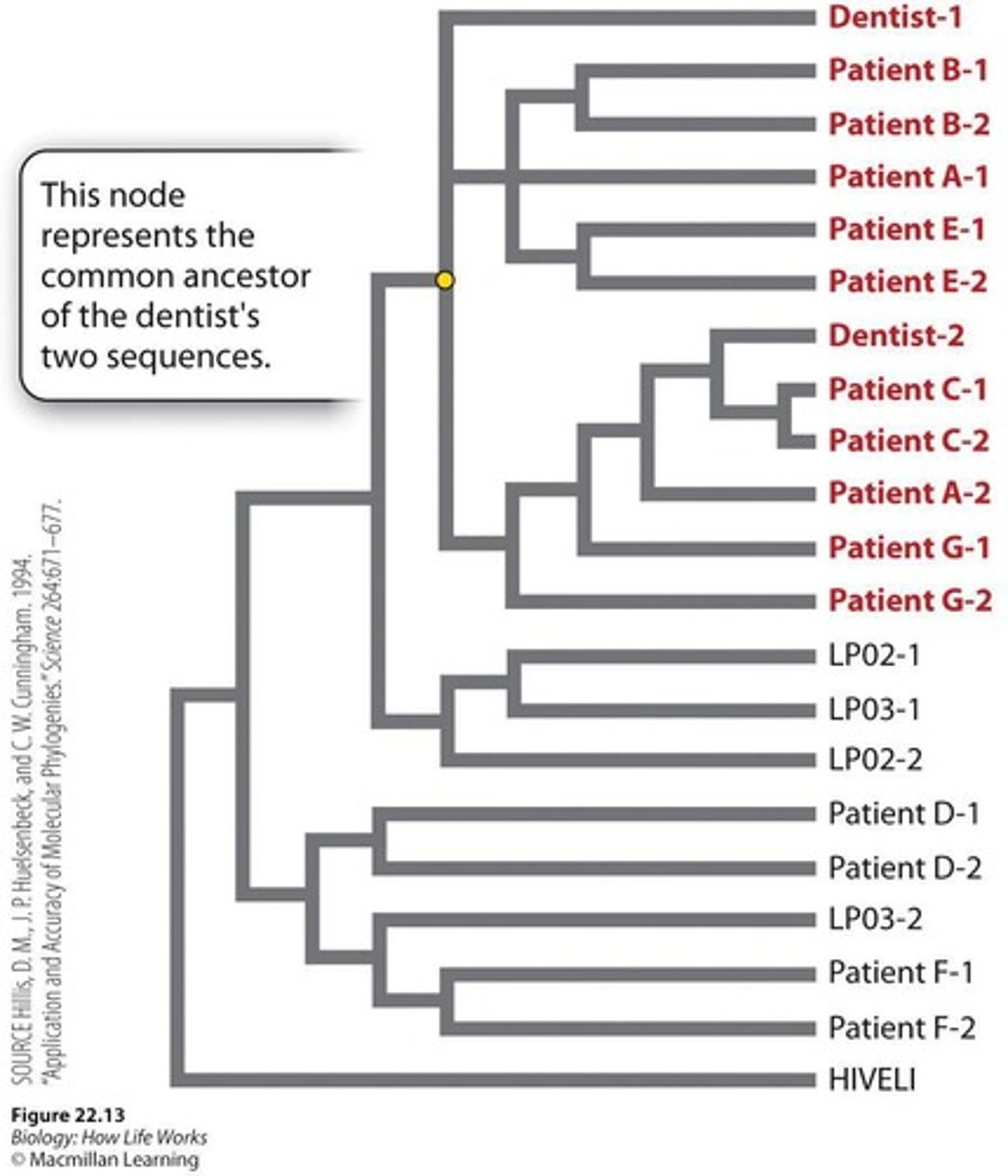
Evidence of HIV transmission
Phylogenetic analysis showed that a dentist gave HIV to his patients in the 1980s.
mtDNA
Mitochondrial DNA used to identify species and track biological material.
Illegal harvesting
The act of capturing species, such as whales, that are not legal to harvest.
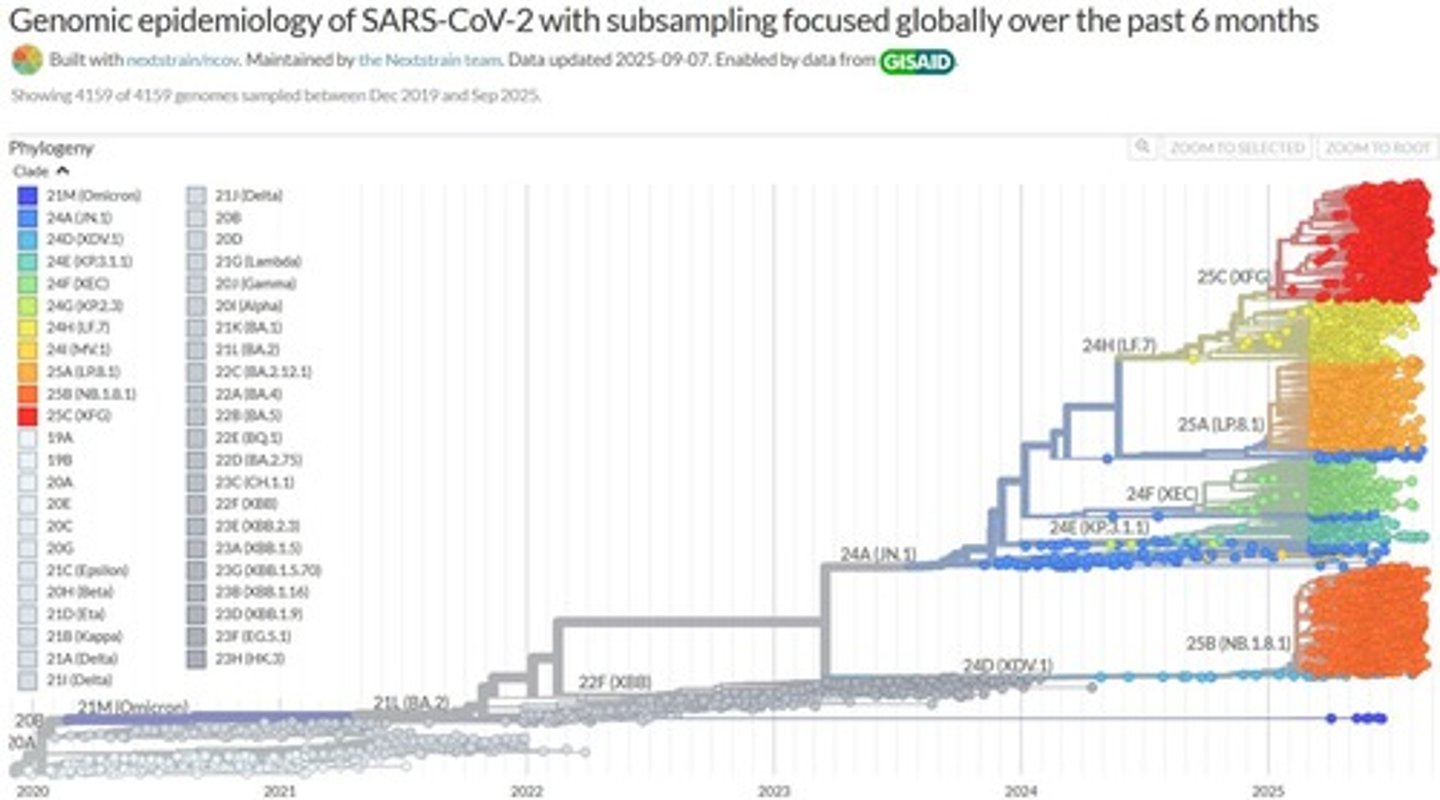
COVID-19 strain tracking
Using phylogenetic trees to track the spread of COVID-19 strains across the globe.
Convergent evolution
The process where organisms not closely related independently evolve similar traits.
Ancestral lineage
The lineage from which traits are inherited or evolved.
Selection pressures
Environmental factors that influence the evolution of traits.
Phylogenetic analyses
Methods used to study the evolutionary relationships and origins of species.
Morphological features
Physical characteristics used to identify shared derived traits.
Genetic characteristics
DNA traits that can be used to determine evolutionary relationships.