AP Environmental Science: Earth Systems, Plate Tectonics, Soil, Atmosphere, and Climate Patterns
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
What is the core of the Earth composed of?
A dense mass of solid nickel, iron, and radioactive elements that release heat.
What layer surrounds the Earth's core?
The mantle, which is a liquid layer of magma.
What is the asthenosphere?
The solid, flexible outer layer of the mantle beneath the lithosphere.
What is the lithosphere?
The thin, brittle layer of rock floating on top of the mantle, broken into tectonic plates.
What is the crust?
The very outer layer of the lithosphere, which is Earth's surface.
What occurs at a convergent plate boundary?
Plates move towards each other, leading to subduction.
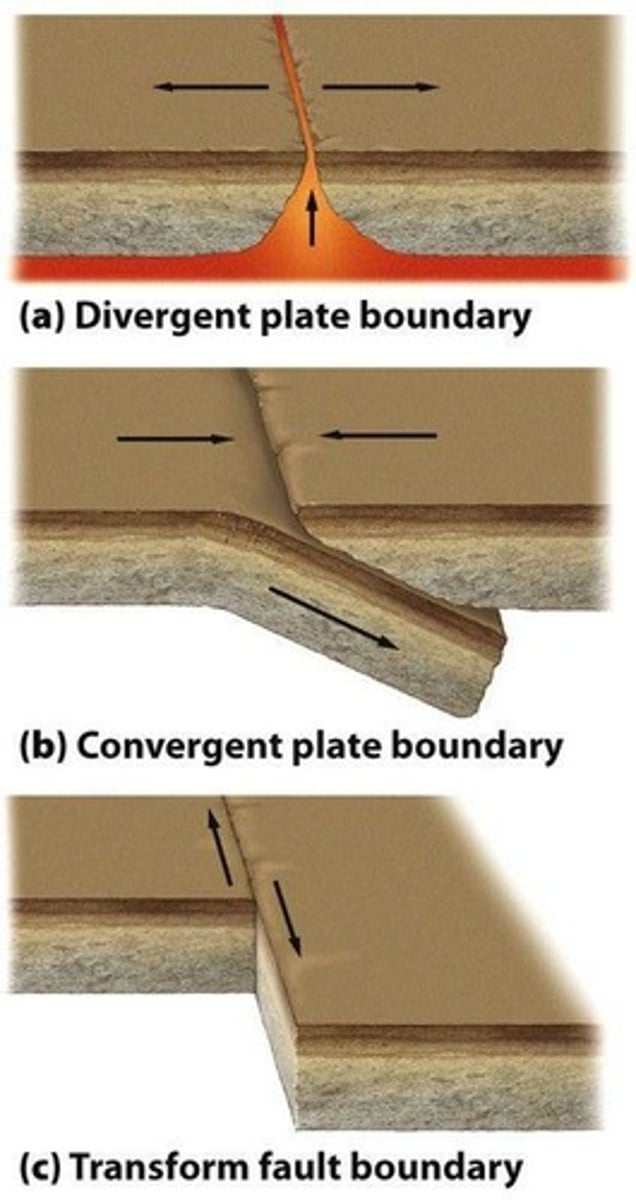
What is formed at a divergent plate boundary?
Mid-oceanic ridges, volcanoes, sea-floor spreading, and rift valleys.
What is the result of a transform fault plate boundary?
Plates slide past each other, commonly causing earthquakes.
What drives convection cycles in the Earth's mantle?
Magma heated by the Earth's core rises towards the lithosphere.
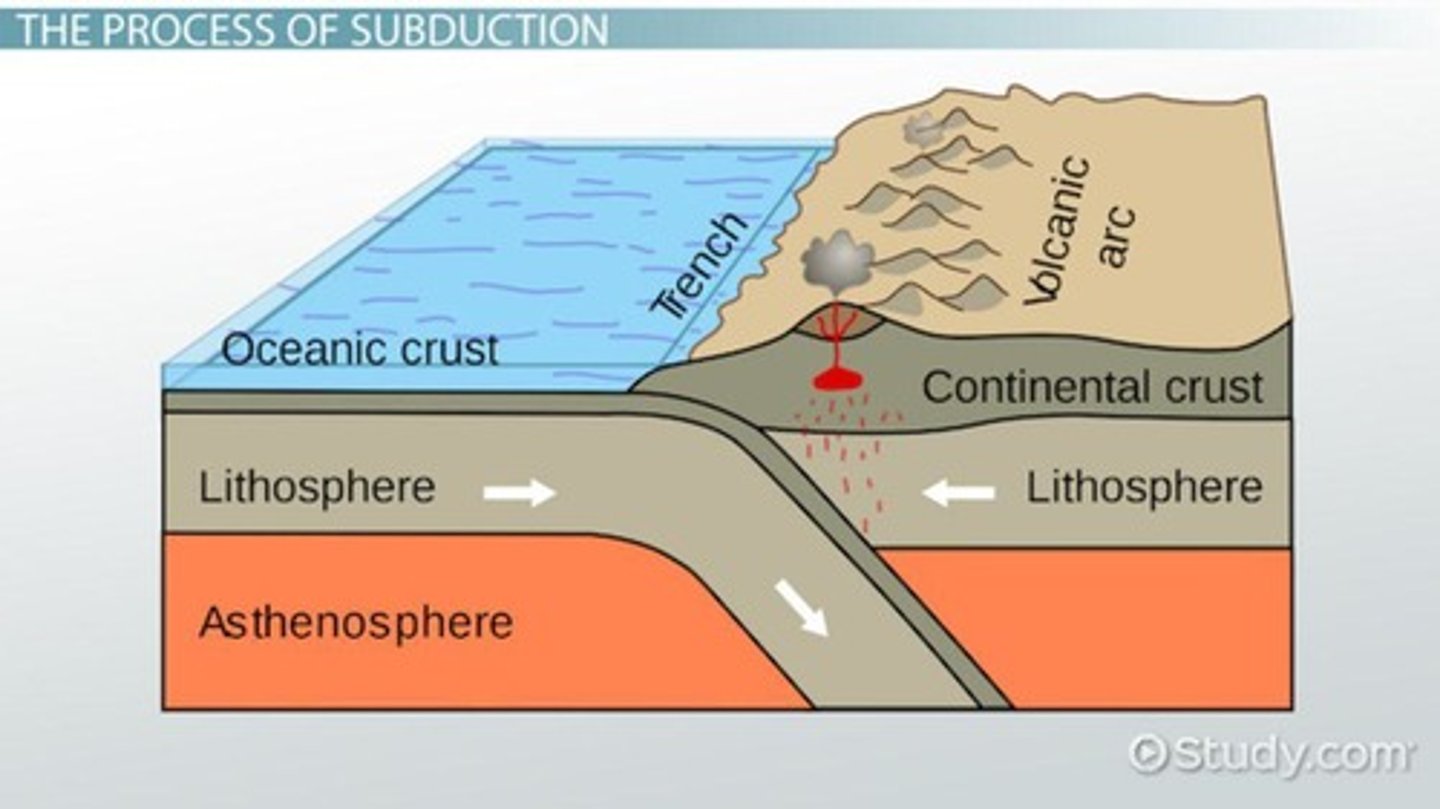
What happens during subduction?
One tectonic plate is forced beneath another, leading to volcanic activity.
What is soil composed of?
A mix of geologic (rock) and organic (living) components.
What role do plants play in soil formation?
They anchor roots, provide water, shelter, and nutrients for growth.
What is humus?
The main organic part of soil, consisting of broken down biomass.
What is the difference between weathering and erosion?
Weathering is the breakdown of rocks, while erosion is the transport of weathered fragments.
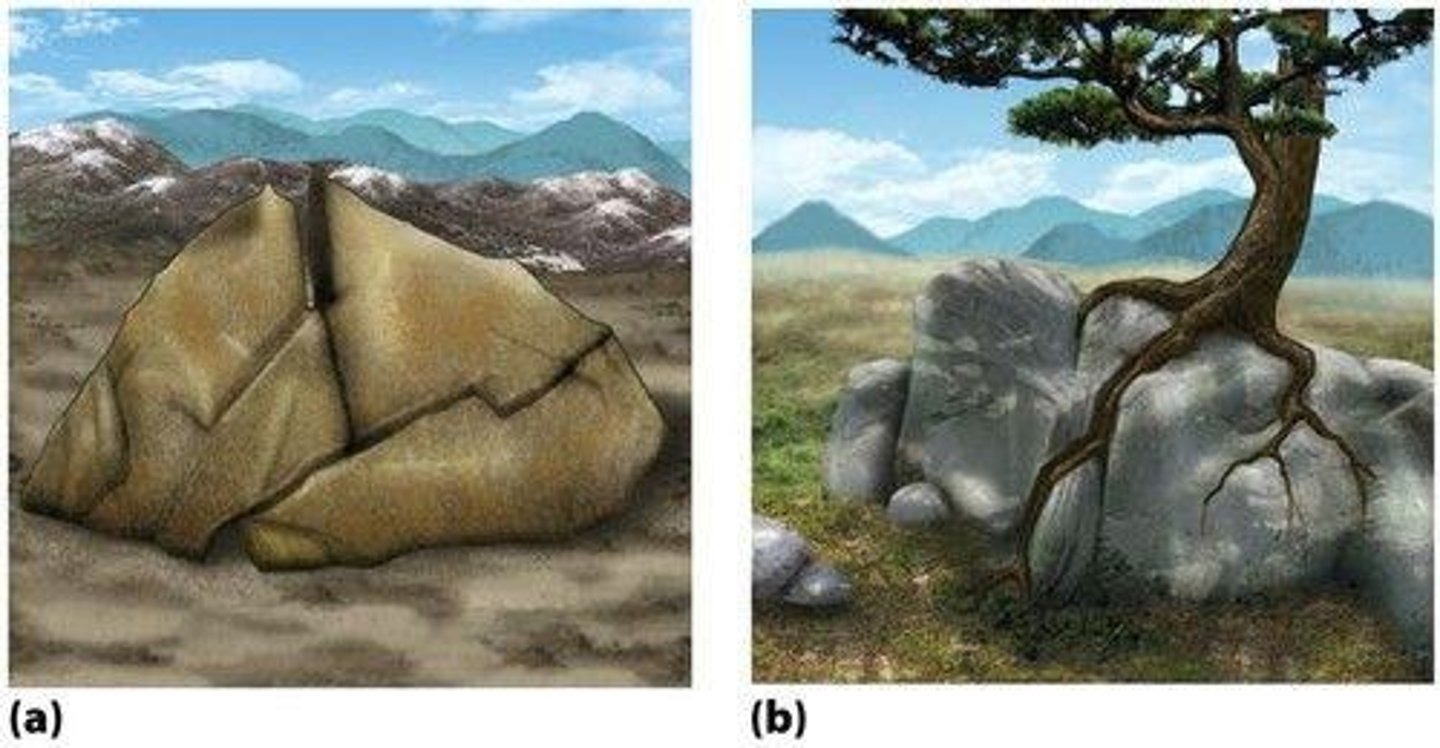
What factors affect soil formation?
Parent material, topography, and climate.
What is the O-Horizon in soil?
The layer of organic matter on top of the soil, providing nutrients.
What is the A-Horizon also known as?
Topsoil, which contains humus and minerals with high biological activity.
What does the B-Horizon consist of?
Subsoil, a lighter layer mostly made of minerals with little organic matter.
What is the C-Horizon?
The least weathered soil closest to the parent material, sometimes called bedrock.
What causes soil degradation?
Loss of topsoil, compaction, and nutrient depletion.
How does compaction affect soil?
It reduces the soil's ability to hold moisture.
What is nutrient depletion in soil?
The removal of key nutrients from soil due to repeated crop growth.
What is the impact of dry soil on plant growth?
It erodes more easily and supports less plant growth.
What is the Ring of Fire?
A pattern of volcanoes surrounding the Pacific Plate.
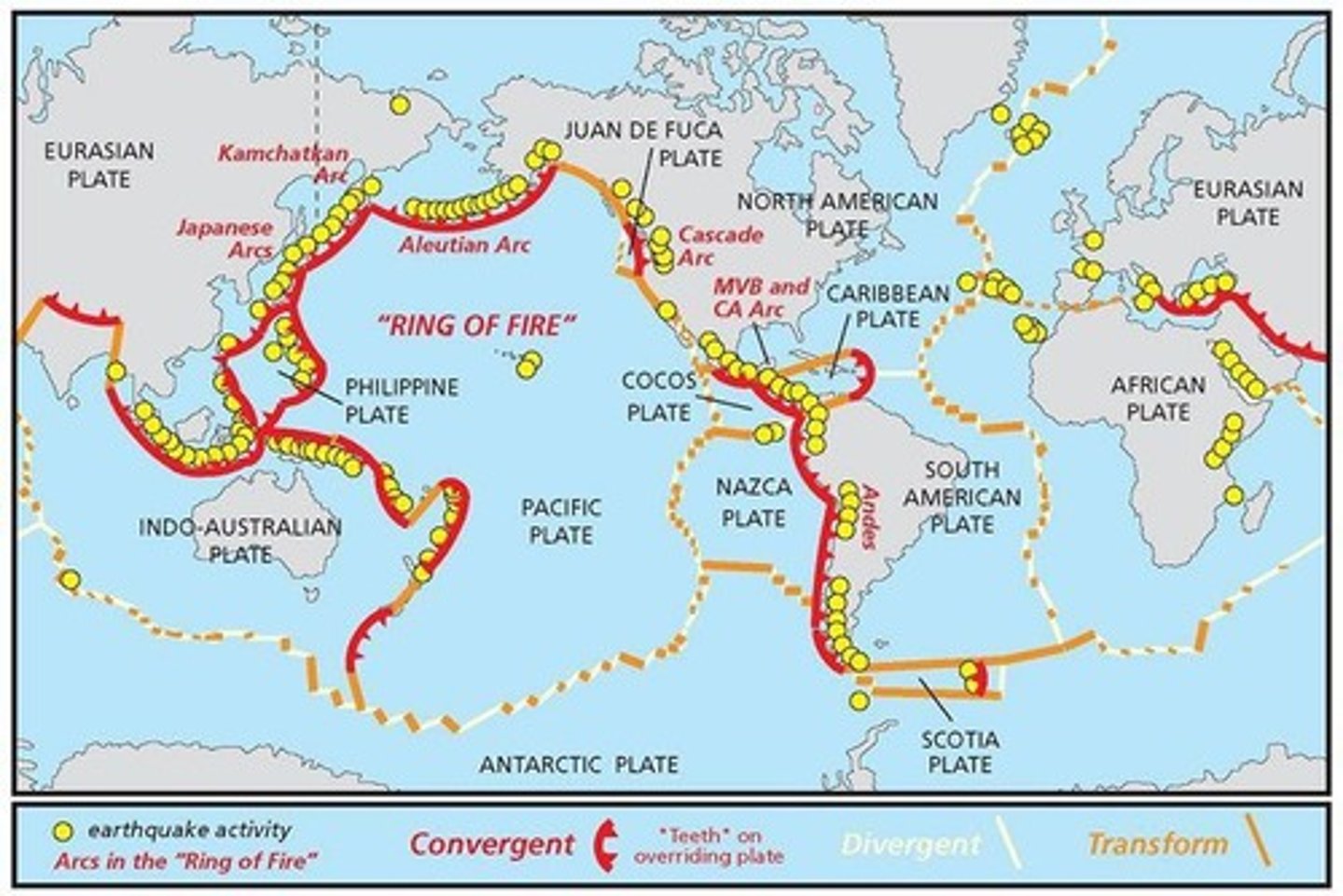
What are hotspots in geology?
Areas of especially hot magma rising up to the lithosphere.
What is the role of decomposers in soil?
They break down dead organic matter and return nutrients to the soil.
What is the effect of climate on soil formation?
Climate influences the rate of organic matter breakdown and weathering.
What are the three main particles that make up the geologic portion of soil?
Sand, silt, and clay (from largest to smallest)
What is soil texture?
The percentage of sand, silt, and clay in a soil, which always adds up to 100%.
How does sand affect porosity and permeability?
Sand has larger pores, allowing air and water to enter easily, resulting in higher porosity and permeability.
What effect does clay have on porosity and permeability?
Clay has smaller pores, making it harder for air and water to enter, resulting in lower porosity and permeability.
What is the ideal soil texture for most plant growth?
Loam, which balances porosity and water holding capacity.
What factors can increase soil nutrients?
Aerated soil, compost/humus/organic matter, clay content, and root structure.
What factors can decrease soil nutrients?
Compacted soil, topsoil erosion, sand, root loss, and excessive rain.
How can you test soil texture?
By letting soil settle in a jar of water and measuring the three layers that form (sand, silt, clay).
What does permeability measure in soil?
How easily water drains through soil.
What is the relationship between porosity and permeability?
Higher porosity generally leads to higher permeability.
What is the effect of organic matter on soil nutrients?
Organic matter can release nutrients and improve soil fertility.
What does a higher nutrient level in soil indicate?
It indicates better potential for plant growth.
What is the significance of soil pH?
It indicates how acidic or basic the soil is, affecting nutrient availability.
What is the role of humus in soil?
Humus holds and releases nutrients, improving soil fertility.
What is a watershed?
All of the land that drains into a specific body of water (river, lake, bay, etc.).
What determines the boundaries of a watershed?
The slope of the land and ridges that divide watersheds.
What is the relationship between soil texture and water holding capacity?
More porous/permeable soils have lower water holding capacity.
What happens to soil that is too sandy?
It drains water too quickly for roots, leading to dryness.
What is the consequence of clay-heavy soil?
It can prevent water from draining to roots, leading to waterlogging.
What is the importance of the temperature gradient in atmospheric layers?
It affects the density and behavior of air in different layers of the atmosphere.
What gases make up Earth's atmosphere?
Nitrogen (~78%), Oxygen (~21%), Argon (~0.93%), Carbon Dioxide (~0.04%), and Water Vapor (~0-4%).
What is the role of the stratosphere?
It contains the ozone layer, which absorbs harmful UV radiation.
What is the Coriolis effect?
The deflection of objects traveling through the atmosphere due to the Earth's rotation.
How does temperature change with altitude in the troposphere?
Temperature decreases as altitude increases.
What is the significance of the thermosphere?
It is the hottest layer of the atmosphere, absorbing solar radiation.
What factors influence how watersheds drain?
Vegetation, soil composition, and slope.
How does vegetation affect groundwater recharge?
More vegetation leads to more infiltration and groundwater recharge.
What is the effect of greater slope on runoff?
Greater slope results in faster velocity of runoff and more soil erosion.
What determines runoff versus infiltration rates?
Soil permeability determines runoff versus infiltration rates.
What human activities impact water quality in watersheds?
Agriculture, clearcutting, urbanization, dams, and mining.
What is the Chesapeake Bay Watershed?
A 6-state region that drains into a series of streams/rivers and eventually into Chesapeake Bay.
What makes estuary habitats in Chesapeake Bay productive?
A mix of fresh and salt water along with nutrients in sediment.
List some ecosystem services provided by estuaries and wetlands.
Tourism revenue, water filtration, habitats for food sources, and storm protection.
What causes eutrophication in Chesapeake Bay?
Nutrient pollution (nitrogen and phosphorus) leads to algae blooms, reducing sunlight and causing hypoxia.
What are major sources of nitrogen and phosphorus pollution?
Discharge from sewage treatment plants, animal waste from CAFOs, and synthetic fertilizers.
What are the effects of clearcutting on watersheds?
Increased soil erosion, sediment deposits in streams, and warmer water temperatures.
How does deforestation affect water quality?
Deforestation can lead to increased sedimentation and warmer water temperatures.
What is insolation?
The amount of solar radiation reaching an area, measured in Watts/m².
How does solar intensity vary with latitude?
Solar intensity depends on the angle of sunlight and the amount of atmosphere the rays pass through.
What happens during the June and December solstices?
One hemisphere is maximally tilted toward the sun, resulting in summer or winter.
What is albedo?
The proportion of light that is reflected by a surface.
How does albedo affect surface temperature?
Surfaces with lower albedo absorb more sunlight and heat, while higher albedo surfaces reflect more light.
What is the Urban Heat Island effect?
Urban areas are hotter than surrounding rural areas due to low albedo of surfaces like blacktop.
What is thermohaline circulation?
A global ocean circulation pattern that mixes salt, nutrients, and temperature throughout the oceans.
What is the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO)?
A pattern of shifting atmospheric pressure and ocean currents in the Pacific Ocean affecting weather globally.
What are the effects of El Niño?
Suppressed upwelling, warmer winters in North America, increased precipitation and flooding.
What are the effects of La Niña?
Stronger upwelling, better fisheries in South America, cooler and drier weather in the Americas.
What causes rain shadow effects?
Mountains disrupt wind patterns, causing moist air to rise and cool, leading to rain on the windward side and dry conditions on the leeward side.
How does geography influence climate?
Geography affects climate through factors like mountains disrupting wind and oceans moderating temperature.
What is the impact of high pressure at 30° latitude?
High pressure leads to dry, descending air, contributing to arid conditions.
What role do global wind patterns play in ocean currents?
Global wind patterns create gyres and influence the direction of ocean currents.
What is the significance of upwelling zones?
Upwelling zones bring nutrients to the surface, supporting productive fisheries.