midterm
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/232
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
233 Terms
1
New cards
population
a group of organisms of the same species populating a given area
-species make up populations which then make up communities
-studied by examining geographic range, growth rate, density/distribution, & age structure
-species make up populations which then make up communities
-studied by examining geographic range, growth rate, density/distribution, & age structure
2
New cards
population distribution
describe the way individuals are spaced out across their range
3
New cards
clumped population distribution
-packed closely together
-can help animals avoid predators
-school fish, flocking birds
-can help animals avoid predators
-school fish, flocking birds

4
New cards
uniform population distribution
-individuals are evenly spaced
-individuals compete w/ one another for space or resources
-orchard, penguins
-individuals compete w/ one another for space or resources
-orchard, penguins
5
New cards
random population distribution
-individuals spaced out unevenly
-when the location of an individual in a population is independent of others
-trees, dandelions
-when the location of an individual in a population is independent of others
-trees, dandelions

6
New cards
limiting factor
anything that constrains a population's size and slows or stops it from growing
7
New cards
density dependent factors
limiting factor that depends on population size
-competition
-predation
-parasitism and disease
-food/resource availability
-competition
-predation
-parasitism and disease
-food/resource availability
8
New cards
density independent factors
limiting factor that affects all populations, regardless of population size
-unusual weather (affects food chains and food webs)
-natural disasters (tornadoes, hurricanes, etc.)
-human activity (destruction of habitat, introduction to non-native species)
-unusual weather (affects food chains and food webs)
-natural disasters (tornadoes, hurricanes, etc.)
-human activity (destruction of habitat, introduction to non-native species)
9
New cards
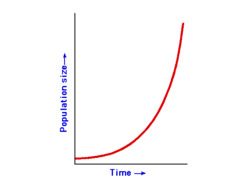
exponential growth
occurs when population size increases dramatically over time
10
New cards
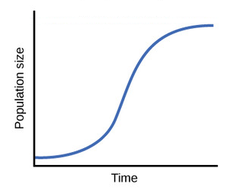
logistic growth
begins with period of slow growth followed by a brief exponential growth before leveling off at a stable size
11
New cards
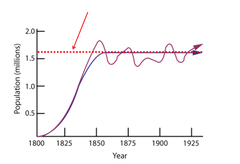
carrying capacity
the largest population that an area can support
-when a population goes over carrying capacity, density-dependent factors affect it greatly.
-when a population goes over carrying capacity, density-dependent factors affect it greatly.
12
New cards
population growth
determined by the birth rate, death rate, immigration rate, and emigration rate.
13
New cards
population +/- equation
birth+immigration - death+emigration
14
New cards
birth/death rate
-more deaths = population decrease
-more births = population increases
-more births = population increases
15
New cards
immigration
movement of individuals into an area w/ an existing population
-more immigration = population increase
-speed of immigration/emigration depends on species' speed, travel distance, & if human activity moves them around/
(squirrels immigrating in search of food, population +)
-more immigration = population increase
-speed of immigration/emigration depends on species' speed, travel distance, & if human activity moves them around/
(squirrels immigrating in search of food, population +)
16
New cards
emigration
movement of individuals out of a population
-more emigration + population decrease
-speed of immigration/emigration depends on species' speed, travel distance, & if human activity moves them around/
(local food shortage causing emigration, population -)
-more emigration + population decrease
-speed of immigration/emigration depends on species' speed, travel distance, & if human activity moves them around/
(local food shortage causing emigration, population -)
17
New cards
biotic factors
are living factors in an ecosystem (plants, animals, insects, fungi, bacteria, etc.)
-predation
-parasites
-predation
-parasites
18
New cards
abiotic factors
nonliving factors in an ecosystem (terrain, temperature, humidity, precipitation, etc.)
-weather
-weather
19
New cards
niche
range of physical and biological conditions under which a species lives (its role in the community)
-how it uses all its resources
-how it uses all its resources
20
New cards
human population growth
exponential growth
21
New cards
keystone species
species that exert strong effects on the community
(wolves in yellowstone, coral)
(wolves in yellowstone, coral)
22
New cards
tolerance
range of conditions an organism can survive & reproduce in (can be true for animals, plants, etc.)
23
New cards
neutral relationship
neither species directly affects the other
(fox on grass)
(fox on grass)
24
New cards
interspecific competition
competition between members of different species for limited supply of resources (food, shelters, mates, etc.)
25
New cards
resource partioning
two species divide a niche to avoid competition
-interspecific competition
-negative effect on both species
(anteaters)
-interspecific competition
-negative effect on both species
(anteaters)
26
New cards
competitive exclusion
two species in the same community cannot share the exact same niche
-interspecific competition
-negative effect on both species
(lion vs hyena)
-interspecific competition
-negative effect on both species
(lion vs hyena)
27
New cards
predator-prey relationship
the interaction between 2 different species where one hunts and feeds on the other
-predator stops the prey from overpopulating
(hunted is prey, hunter is predator)
-predator stops the prey from overpopulating
(hunted is prey, hunter is predator)
28
New cards
predation and herbivory
an interaction in which one organism kills another for food
-good for predator, bad for prey
(shark/seal, cat/mouse, panda/bamboo)
-good for predator, bad for prey
(shark/seal, cat/mouse, panda/bamboo)
29
New cards
symbiosis
species living closely together (interactive relationship)
30
New cards
commenalism
-symbiotic relationship
-good for one species, neutral for the other
(whale/barnacle, bird nesting in a tree)
-good for one species, neutral for the other
(whale/barnacle, bird nesting in a tree)
31
New cards
mutualism
-symbiotic relationship
-good for both species
(bee/flower)
-good for both species
(bee/flower)
32
New cards
parasitism
-symbiotic relationship
-good for one species, bad for the other
(dog/flea)
-good for one species, bad for the other
(dog/flea)
33
New cards
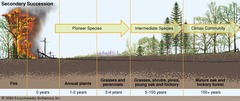
succession
a series of predictable events that occur overtime
-an ecosystem is destroyed but comes back
-an ecosystem is destroyed but comes back
34
New cards
primary succession
ecological succession that begins in an area where no community previously existed
-total destruction
-total destruction
35
New cards
examples of succession not occuring as it normally should
-deforestation
-animal endangerment (hunting)
-maintaining a lawn
-climate change
-animal endangerment (hunting)
-maintaining a lawn
-climate change
36
New cards
pioneer species
first species to populate an area during primary succession
37
New cards
secondary succession
type of succession that occurs in an area that was only partially destroyed
-partial destruction
-partial destruction
38
New cards
climax community
final stage of succession, in which the community is stable
-collection of most stable organisms (resembling goal of succession)
-collection of most stable organisms (resembling goal of succession)
39
New cards
biodiversity
the variety of life in the world or in a particular habitat or ecosystem
-ecosystem diversity, species diversity, and genetic diversity
-ecosystem diversity, species diversity, and genetic diversity
40
New cards
why is biodiversity important?
-maintains healthy biosphere
-provides natural resources (food, water, etc.)
-natural services (water purification, pest control, etc.)
-ecosystem resilience (ability to recover after a disturbance
-provides natural resources (food, water, etc.)
-natural services (water purification, pest control, etc.)
-ecosystem resilience (ability to recover after a disturbance
41
New cards
mechanical digestion
physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces of food
42
New cards
chemical digestion
breaking of chemical bonds in food by enzymes
43
New cards
accessory organs
food never passes through these organs
-gall bladder
-salivary glands
-liver
-pancreas
-gall bladder
-salivary glands
-liver
-pancreas
44
New cards
oral cavity
(mouth)
-begins mechanical digestion, begins chemical digestion, swallowing
-major secretion is saliva (salivary amylase)
-source of secretion: salivary glands
saliva: acts on all food
salivary amylase: acts on startches
-begins mechanical digestion, begins chemical digestion, swallowing
-major secretion is saliva (salivary amylase)
-source of secretion: salivary glands
saliva: acts on all food
salivary amylase: acts on startches
45
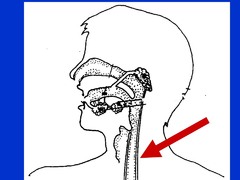
New cards
espohagus
assists in moving food from mouth to stomach (peristalsis)
46
New cards
stomach
-mechanical digestion (chyme) & chemical digestion (proteins)
-major secretion is hydrochloric acid, pepsin, & mucus
-source of secretion: stomach
pepsin: enzyme that breaks down proteins
HCl: activates pepsin
mucus: protection
-major secretion is hydrochloric acid, pepsin, & mucus
-source of secretion: stomach
pepsin: enzyme that breaks down proteins
HCl: activates pepsin
mucus: protection
47
New cards
liver
-produces bile (fat digestion) & detoxification
-major secretion is bile
-source of secretion: liver
bile: emulsifies fats (breaks large fat droplets into small ones)
-major secretion is bile
-source of secretion: liver
bile: emulsifies fats (breaks large fat droplets into small ones)
48
New cards
gall bladder
-stores and releases bile
-major secretion is bile
-source of secretion: liver
bile: emulsifies fats (breaks large fat droplets into small ones)
-major secretion is bile
-source of secretion: liver
bile: emulsifies fats (breaks large fat droplets into small ones)
49
New cards
pancreas
-produces enzymes & sodium bicarbonate
-regulates blood sugar
-major secretion is enzymes & sodium bicarbonate
-source of secretion: pancreas
enzymes: carbs, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acid
-regulates blood sugar
-major secretion is enzymes & sodium bicarbonate
-source of secretion: pancreas
enzymes: carbs, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acid
50
New cards
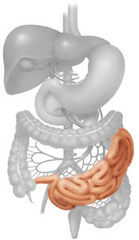
small intestine
-chemical digestion
-absorbs into blood (villi & microvilli)
-major secretion is bile (liver), enzymes (pancreas & small intestine) & sodium bicarbonate (pancreas)
-source of secretion: liver, pancreas, and small intestine
acts on all food types
-absorbs into blood (villi & microvilli)
-major secretion is bile (liver), enzymes (pancreas & small intestine) & sodium bicarbonate (pancreas)
-source of secretion: liver, pancreas, and small intestine
acts on all food types
51
New cards
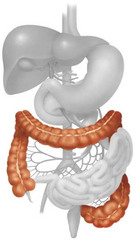
large intestine (colon)
-regulates H2O content of waste
-bacteria home
-bacteria home
52
New cards
rectum and anus
store, compact, and remove waste
53
New cards
autotroph
organisms that make their own food/glucose
-such as plants
-such as plants
54
New cards
heterotroph
organism that consumes others for food/glucose
-humans, etc.
-humans, etc.
55
New cards
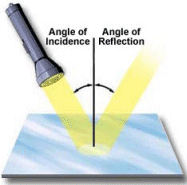
reflect
to bounce off without absorbing
-color is reflected
-what we see
-color is reflected
-what we see
56
New cards
chlorophyll
a pigment that reflects green
57
New cards
pigments
a substance/molecule that absorbs and reflects light
58
New cards
ATP
the energy cells use
59
New cards
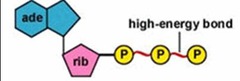
how energy is stored in ATP
in high energy phosphate bonds
60
New cards
how energy is released from ATP
energy is released from ATP by breaking the bonds between the phosphate groups by hydrolysis. when the bond is broken, ATP loses a phosphate group and becomes ADP.
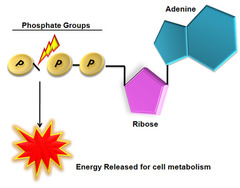
61
New cards
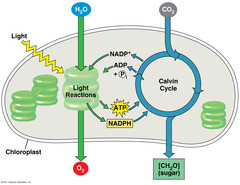
photosynthesis
makes glucose (food) using sun energy
62
New cards
reactants and products of photosynthesis
reactants: carbon dioxide and water
products: glucose and oxygen
products: glucose and oxygen
63
New cards
photosynthesis equation
CO2 + H2O --> light energy --> C6H12O6 + O2
64
New cards
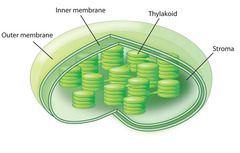
chloroplast
an organelle found in plant and algae cells where photosynthesis occurs
outer & inner membrane: two membranes
stroma: fluid inside chloroplast
granum (grana): stack of disks
thylakoid: individual disk
thylakoid membrane
thylakoid space: space inside thylakoid
outer & inner membrane: two membranes
stroma: fluid inside chloroplast
granum (grana): stack of disks
thylakoid: individual disk
thylakoid membrane
thylakoid space: space inside thylakoid
65
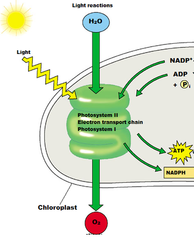
New cards
light dependent reactions
converts light energy into more useable energy in a cell (ATP, NADPH)
-location: thylakoids
-location: thylakoids
66
New cards
electron transport chain (photosynthesis)
series of electron carrier proteins that shuttle high-energy electrons during ATP-generating reactions
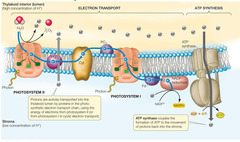
67
New cards
light independent reactions (calvin cycle)
makes glucose as a food source
-location: stroma
-location: stroma
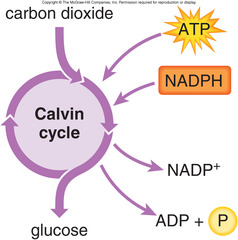
68
New cards
factors affecting the rate of photosynthesis
light intensity, light wavelength, concentration of carbon dioxide, temperature
69
New cards
cellular respiration
breaks down glucose for energy
70
New cards
reactants and products of cellular respiration
reactants: glucose and oxygen
products: carbon dioxide, water, and ATP
products: carbon dioxide, water, and ATP
71
New cards
cellular respiration equation
C6H12O6 + O2 --> CO2 + H2O + ATP
72
New cards
mitochondria
powerhouse of the cell, organelle that is the site of ATP (energy) production
matrix: fluid filled
inner & outer membrane
intermembrane space
matrix: fluid filled
inner & outer membrane
intermembrane space
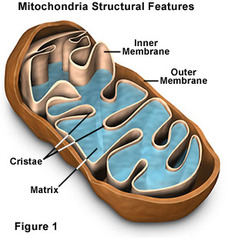
73
New cards
connection step
continuing the breakdown of glucose (prepares for krebs cycle)
-aerobic
-location: matrix of mitochondria
-aerobic
-location: matrix of mitochondria
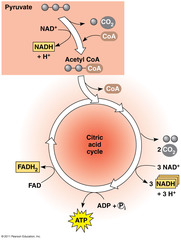
74
New cards
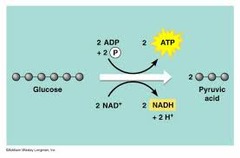
glycolysis
gain ATP, begins the breakdown of glucose
-anaerobic
-location: cytoplasm
-anaerobic
-location: cytoplasm
75
New cards
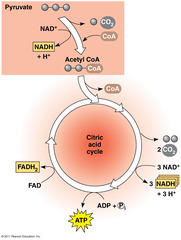
krebs/citric acid cycle
completes the breakdown of glucose into CO2
-aerobic
-location: matrix of mitochondria
-aerobic
-location: matrix of mitochondria
76
New cards
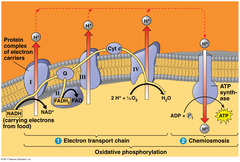
electron transport chain (cellular respiration)
use the energy of the e- from glucose to make ATP
-aerobic
-location: inner membrane of mitochondria
-aerobic
-location: inner membrane of mitochondria
77
New cards
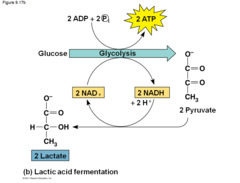
lactic acid fermentation
keep glycolysis going when there is no oxygen (2 ATP)
-anaerobic
-location: cytoplasm
-anaerobic
-location: cytoplasm
78
New cards
alcoholic fermentation
keep glycolysis going when there is no oxygen (2 ATP)
-anaerobic
-location: cytoplasm
-anaerobic
-location: cytoplasm
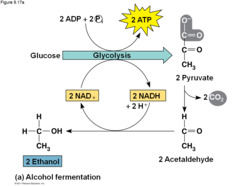
79
New cards
anaerobic respiration
does not require oxygen
80
New cards
aerobic respiration
requires oxygen
produces a lot more ATP
produces a lot more ATP
81
New cards
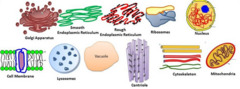
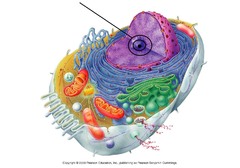
organelle
specialized structure that performs important functions within a eukaryotic cell
82
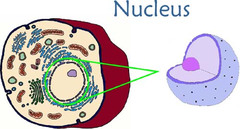
New cards
nucleus
eukaryotic
in animal & plant cells
contains DNA (instructions go make proteins)
control center
in animal & plant cells
contains DNA (instructions go make proteins)
control center
83
New cards
nucleolus
eukaryotic
in animal & plant cells
produces ribosomes
in animal & plant cells
produces ribosomes
84
New cards
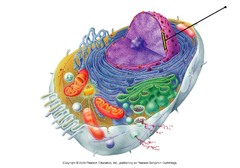
nuclear membrane
eukaryotic
in animal & plant cells
controls what goes in and out of the nucleus
in animal & plant cells
controls what goes in and out of the nucleus
85
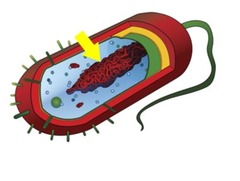
New cards
nucleoid
prokaryotic
a dense region of free-floating DNA
a dense region of free-floating DNA
86
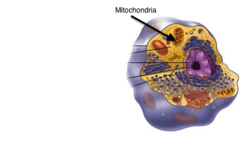
New cards
mitochondria
eukaryotic
animal & plant cells
2 membranes (inner is bigger), has own DNA
cell respiration (food to energy)
capture & release energy
animal & plant cells
2 membranes (inner is bigger), has own DNA
cell respiration (food to energy)
capture & release energy
87
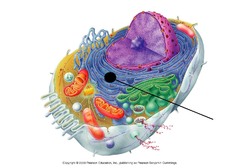
New cards
rough endoplasmic reticulum
eukaryotic
animal & plant cells
internal membranes (covered w/ ribosomes)
makes proteins for export
animal & plant cells
internal membranes (covered w/ ribosomes)
makes proteins for export
88
New cards
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
eukaryotic
animal & plant cells
internal membranes
makes lipids & detox
animal & plant cells
internal membranes
makes lipids & detox
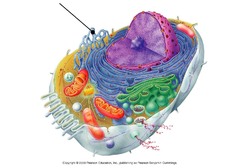
89
New cards
ribosome
eukaryotic & prokaryotic
animal & plant cells
makes protiens
animal & plant cells
makes protiens

90
New cards
cell membrane
eukaryotic & prokaryotic
animal & plant cells
phospholipid bilayer
regulate materials entering/exiting the cell,protection/support
animal & plant cells
phospholipid bilayer
regulate materials entering/exiting the cell,protection/support
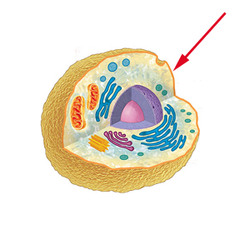
91
New cards
cell wall
eukaryotic & prokaryotic
plant cells only
shape, support, & protection
not selectively permeable
plant cells only
shape, support, & protection
not selectively permeable
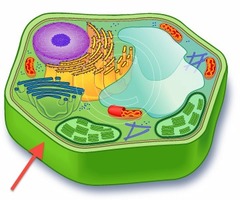
92
New cards
vacuole (animal cell)
eukaryotic
-found in animal cells
-used for storage
-found in animal cells
-used for storage
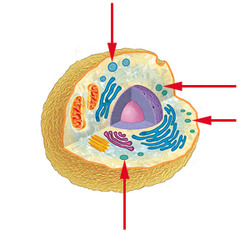
93
New cards
vacuole (plant cell)
eukaryotic
-found in plant cells, large & central
-used for storage
-found in plant cells, large & central
-used for storage
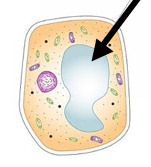
94
New cards
vesicle
eukaryotic
plant & animal cells
-used for storage
-membrane-bound sac w/ transport materials
-moving
plant & animal cells
-used for storage
-membrane-bound sac w/ transport materials
-moving
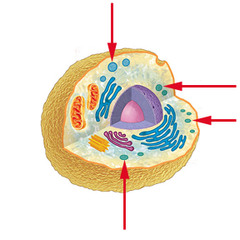
95
New cards
chloroplast
eukaryotic
plant cells only
2 membranes, chlorophyll (green) has own DNA
photosynthesis (sun energy to food)
capture & release energy
plant cells only
2 membranes, chlorophyll (green) has own DNA
photosynthesis (sun energy to food)
capture & release energy
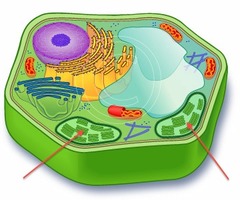
96
New cards
centrioles
eukaryotic
animal cells only
pair of microtubule that organize cell division
animal cells only
pair of microtubule that organize cell division
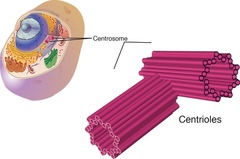
97
New cards
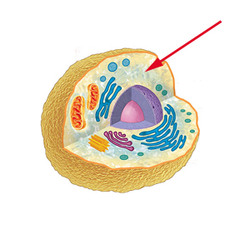
cytoplasm
eukaryotic & prokaryotic
animal & plant cells
water-based
support organelles, perform reactions
animal & plant cells
water-based
support organelles, perform reactions
98
New cards
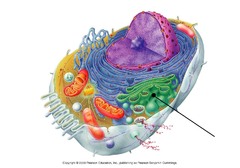
golgi apparatus
eukaryotic
animal & plant cells
stack of pancakes (vesicles merging)
ships out proteins (modifies, sorts, & packs)
animal & plant cells
stack of pancakes (vesicles merging)
ships out proteins (modifies, sorts, & packs)
99
New cards
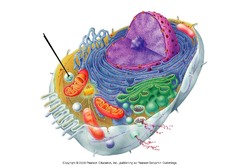
lysosome
eukaryotic
mostly in animal cells
membrane-bound sac w/ hydrolytic enzymes
used to break down materials/digestion
mostly in animal cells
membrane-bound sac w/ hydrolytic enzymes
used to break down materials/digestion
100
New cards
cytoskeleton
eukaryotic
animal & plant cells
microfilaments, microtubules (long proteins)
framework, movement
animal & plant cells
microfilaments, microtubules (long proteins)
framework, movement