Biology Honors Study Guide chordates
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
taxonmy
the ordered and naming of organisms by Carolus Linnaeus
what is the to part scientific name of a species called?
binomial nomenclature
what is the first part of a bionomial nomenclature?
genus
how many groups are in the taxonmic group?
8
what is the first group called?
domain
what is the second group called?
kingdom
what is the third group called?
phylum
what is the 4th group called?
class
what is the 5th group called
order
what is the 6th group called?
family
what is the 8 group called?
species
a taxonomic unit at any level of hierarchy is called what?
a taxon
vetebrates
animals that have a backbone or a spine
invertebrates
animals that don’t have a backbone or spine
amphibians, birds, fishes, reptiles and mammals are all..
vertebrates
Tunicates and Lancelets are ..
invertebrates
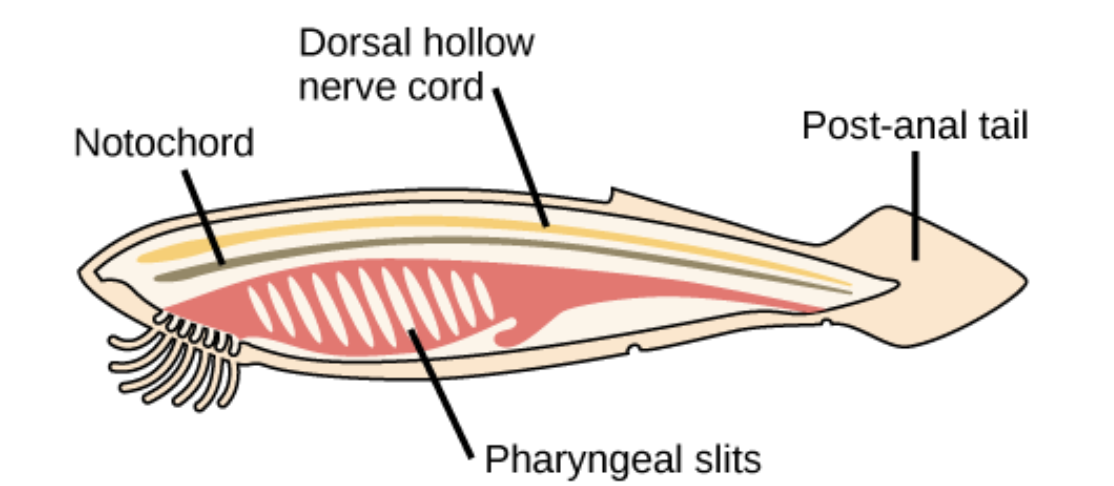
to be a member of the chordate phylum a animal must have what?
a notochord,
a dorsal nerve cord,
pharyngeal slita
postanal tail.
in humans the notochord is reduced to a gelatinous disks between the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disc
true
in vertebrates the dorsal hollow nerve cord is called
a spinal cord
96% of all chordates species are..
vertebrates
pharyngeal slits
openings in the pharynx (the area behind the mouth) that extend to the outside environment,
serving as gill-like structures in aquatic chordates for filter feeding and respiration.
adult tunicates have no notochord, tail, but has..
pharyngeal slits
tunicate tadpoles mature extremely quiclky in..
a few hours
what are tunicates sole job?
to find a suitable place to live out their lives as adults
attacted to docks, rocks or undersides of roads.
Tunicates are..
plankton feeders
why are tunicates plankton feeders?
bc they shoot out a jet of water through the siphon
tunicates are often called what because of this ?
sea squirts
what are small, fishlike creatures that live on sandy floors called?
Lancelets
do lancelets have a true heart?
no
the first vetebrates to envolve were fish called
Ostracoderms
what period did Ostracoderms appear?
Cambrain period
Ostracoderms were les jawless fishes found mainly in fresh water
true
fish went through major changes during what period?
Silurian period
what changes did fish go through during the Silurian period
fish remained jawless
but with less body armor
salps are invertbrates
true
salps are filter feeders and feed on algae
true
do salps go through two phases when they reproduce?
yes
all species construct complicated mucus structures called what?
houses
what do the mucus structures do?
capture plankton which they eat
when the houses becomes clogged what does it do?
its disregared sinking to the bottom
how often do larvacens create “houses”
every 4 hours
what are larvaceans lifepan?
3-5 days
Larvaceans produce both egg and sperm
true
Fertilization and development take place in the open water
true
Durkleasteus
don’t have teeth
instead exposed bone
Devonian period is also known as the
“ Age of fish”
bc fish were the most abundant creatures
mudskipper
a fish out of water
eats plants
builds a house by digging a hole, putting mud in his mouth, and spitting it back up
males travel back and forth carrying oxygen for the eggs by removing water/mud
what is a subgroup of bony fish called?
lobe-finned fish
herbivores
eats plants, no meat
carnivores
eats other fish, and meat
what do parasitic fish do?
suck all the juice of of prey
example of a parasitic fish?
lamphreys
detritus
eat decaying organic matter from dead plants or animals.
Pyloric Ceca
Fingerlike pouches that aid in digestion and nutrient absorption.
Liver –
Produces bile, which helps digest fats.
Gallbladder –
Stores bile for digestion.
Pancreas –
Produces digestive enzymes.
Swim Bladder
Helps control buoyancy.
what is the absorption of lipids and fats called?
emulsification
what liquid helps digestive food
hydrochloric acid
Gills –
Organs that extract oxygen from water.
Countercurrent Exchange
Process that maximizes oxygen absorption in fish gills.
Lungfish –
Can survive in oxygen-poor environments by burrowing into the mud and forming a protective mucus cocoon.
what circulatory system do fishes have?
closed circulatory system
how many chambers does a fish heart have?
4
what is the first chamber?
Sinus Venosus
what does the Sinus Venosus do?
Collects oxygen-poor blood.
what is the 2nd chamber?
Atrium
what does the Atrium do?
A chamber that pumps blood into the ventricle.
what is the third chamber?
Ventricle
what does the Ventricle do?
Main pumping chamber.
what is the 4th chamber?
Bulbus Arteriosus
what does the Bulbus Arteriosus do?
– Maintains blood flow into the gill arteries.
Closed Circulatory System
Blood is contained within vessels.
Single-Loop Circulation
Blood flows from the heart to the gills, then to the body, and back to the heart.
Parasitic Fish
Feed on other living organisms.
Filter Feeders
Strain food particles from the water.
Operculum –
– Bony gill cover protecting the gills.
Lateral Line
A sensory system that detects water movement.
Paired Fins
Fins found on both sides of a fish (pectoral, pelvic).
Dorsal & Anal Fin
Fins used for stability.
Caudal Fin –
The tail fin used for propulsion.
Pyloric Ceca
Fingerlike pouches that aid in digestion and nutrient absorption.
Liver –
Produces bile, which helps digest fats.
Gallbladder –
Stores bile for digestion.
Pancreas
Produces digestive enzymes.
Swim Bladder
Helps control buoyancy.
Cartilaginous Fish
– Fish with skeletons made of cartilage (e.g., sharks and rays).
Bony Fish –
Fish with skeletons made of bone.
Lobe-Finned Fish
A subgroup of bony fish with fleshy fins that led to the evolution of chordate limbs.
Excretion:
The Process of removing waste and excess water.
Kidney:
Filters waste from the blood.
Parts of kidney:
Main unit: Nephron’’
Parts: Glomerulus & Renal tubule (within Bowman's capsule)
Freshwater fish:
Constantly gain water and excrete large amounts of dilute urine.
Actively absorb salt from food & gills.
Saltwater fish:
Constantly lose water; drink seawater & excrete excess salt via chloride cells in gills.
Produce very concentrated urine
The breakdown of proteins releases nitrogenous waste.
true
Ammonia (toxic) is expelled through the gills, diluted by surrounding water.
true
Olfactory lobes
Detects smells, especially large in sharks & catfish.
Cerebrum:
Processes smell (unlike in mammals, where it controls voluntary movement).
Optic lobes:
Allow color vision; some fish prefer certain colors.