Muscular Tissue: Structure, Function, and Types in Anatomy & Physiology
1/133
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
134 Terms
What are the three types of muscular tissue?
Skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle.
What is excitability in muscle tissue?
The ability to respond to chemical signals, stretch, and electrical changes across the plasma membrane.
Define contractility in muscle tissue.
The ability of muscle to shorten when stimulated.
What is extensibility in muscle tissue?
The capability of being stretched between contractions.
What does elasticity refer to in muscle tissue?
The ability to return to its original resting length after being stretched.
Describe skeletal muscle.
Voluntary, striated muscle usually attached to bones, subject to conscious control.
What are striations in skeletal muscle?
Alternating light and dark transverse bands resulting from the arrangement of internal contractile proteins.
What is the endomysium?
Connective tissue that surrounds each muscle cell.
What is the perimysium?
Connective tissue that surrounds a muscle fascicle.
What is the epimysium?
Connective tissue that surrounds the entire muscle.
What is the role of tendons?
To attach muscle to bone matrix.
What is the sarcolemma?
The plasma membrane of a muscle fiber.
What is the function of myofibrils?
Long protein cords that occupy most of the sarcoplasm and are essential for muscle contraction.
What is glycogen's role in muscle fibers?
Stored carbohydrate energy for exercise.
What is myoglobin?
A protein that provides some oxygen needed for muscle activity.
What is the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR)?
A smooth endoplasmic reticulum that forms a network around each myofibril and acts as a calcium reservoir.
What are T tubules?
Tubular infoldings of the sarcolemma that penetrate through the muscle fiber.
What constitutes a triad in muscle fibers?
A T tubule and two terminal cisterns associated with it.
What are thick filaments made of?
Several hundred myosin molecules, each shaped like a golf club.
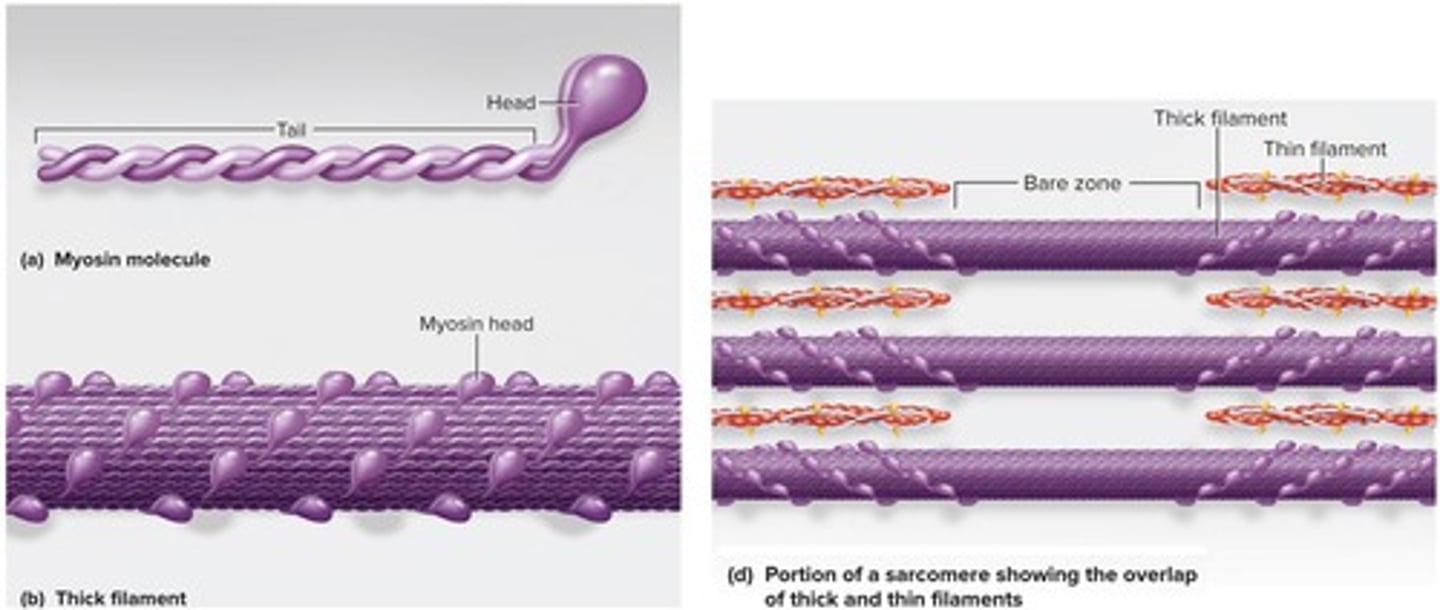
What are thin filaments composed of?
Two intertwined strands of actin proteins with active sites that can bind to myosin.
What are the contractile proteins in muscle?
Myosin and actin.
What are the regulatory proteins in muscle contraction?
Tropomyosin and troponin, which are activated by calcium binding.
What is the role of titin proteins in muscle fibers?
To anchor elastic filaments to the Z-disc and M line, providing stability.
What is a sarcomere?
The segment from Z disc to Z disc, the functional contractile unit of a muscle fiber.
What happens to muscle fibers during contraction?
Individual sarcomeres shorten, pulling Z discs closer together without changing the length of thick or thin filaments.
What is a motor unit?
One nerve fiber and all the muscle fibers it innervates, contracting in unison.
What is the neuromuscular junction (NMJ)?
The synapse where a nerve fiber meets a muscle fiber, containing synaptic vesicles with acetylcholine.
What is required for skeletal muscle contraction?
Skeletal muscle cannot contract unless stimulated by a nerve.
What happens if nerve connections to skeletal muscle are severed?
The muscle becomes paralyzed.
How do muscle fibers of one motor unit behave?
They are dispersed throughout the muscle and contract in unison, producing a weak contraction over a wide area.
What neurotransmitter is released at the neuromuscular junction?
Acetylcholine (ACh) is released from synaptic vesicles.
What is the synaptic cleft?
The synaptic cleft is the gap between the axon terminal and the sarcolemma of the muscle fiber.
What occurs during excitation of a muscle fiber?
Nerve action potentials are converted to muscle action potentials.
What is excitation-contraction coupling?
It is the process where action potentials on the sarcolemma lead to activation of myofilaments.
What happens during the contraction phase of a muscle fiber?
The muscle fiber shortens.
What occurs during the relaxation phase of a muscle fiber?
Stimulation ends, and the muscle fiber relaxes, returning to its resting length.
What is rigor mortis?
Rigor mortis is the hardening of muscles and stiffening of the body that begins 3-4 hours after death.
What causes rigor mortis?
It is caused by the release of Ca2+ from the deteriorating sarcoplasmic reticulum, leading to muscle contraction without relaxation.
What is the threshold in muscle physiology?
The threshold is the minimum voltage necessary to generate an action potential in the muscle fiber and produce a contraction.
What is a twitch in muscle contraction?
A twitch is a quick cycle of contraction and relaxation when the stimulus is at threshold or higher.
What is the latent period in muscle contraction?
The latent period is the brief delay between stimulus and contraction, allowing for excitation and tensing of elastic components.
What happens during the contraction phase of a muscle twitch?
The muscle generates external tension that can overcome the load and cause movement.
What occurs during the relaxation phase of a muscle twitch?
Tension declines to baseline as the sarcoplasmic reticulum reabsorbs Ca2+ and myosin releases actin.
How long can the duration of a muscle twitch vary?
The entire twitch duration can vary between 7 ms and 100 ms.
What happens with subthreshold stimuli?
No contraction occurs.
What occurs at threshold intensity and above?
A twitch is produced.
What factors influence the strength of muscle twitches?
Muscle's starting length, fatigue, temperature, hydration level, and frequency of stimulus delivery.
What is the effect of higher voltages on muscle contractions?
They produce stronger contractions by exciting more nerve fibers and stimulating more motor units.
What is recruitment or multiple motor unit (MMU) summation?
The process of bringing more motor units into play with stronger stimuli.
What principle governs the recruitment of motor units?
The size principle: weak stimuli recruit small units, while strong stimuli recruit both small and large units.
What occurs with low frequency stimuli?
They produce identical twitches.
What is temporal (wave) summation?
Higher frequency stimuli produce higher tension as each new twitch rides on the previous one.
What is incomplete tetanus?
A fluttering contraction due to only partial relaxation between stimuli.
What is complete (fused) tetanus?
A steady contraction caused by unnaturally high stimulus frequencies.
What characterizes isometric muscle contraction?
Muscle produces internal tension but does not change length due to external resistance.
What is isotonic muscle contraction?
Muscle changes in length while maintaining tension.
What is concentric contraction?
Muscle shortens while maintaining tension, such as when lifting a weight.
What is eccentric contraction?
Muscle lengthens while maintaining tension, such as when slowly lowering a weight.
What happens during the isometric phase of contraction?
Muscle tension rises but the muscle does not shorten.
What occurs when tension overcomes the load's resistance?
Muscle begins to shorten and move the load, entering the isotonic phase.
What is the primary energy source for muscle contraction?
ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
What are the two main pathways of ATP synthesis?
Anaerobic fermentation and aerobic respiration.
What is the result of anaerobic fermentation?
It produces little ATP and lactate in the absence of oxygen.
What is the advantage of aerobic respiration?
It produces far more ATP and does not generate lactate.
What is the phosphagen system?
A combination of ATP and creatine phosphate that provides energy for short bursts of activity.
How do muscles meet ATP demand during short, intense exercise?
By borrowing phosphate groups from other molecules and transferring them to ADP.
What are the two enzyme systems that control phosphate transfers?
Myokinase and creatine kinase.
How long can the phosphagen system provide energy for sprinting?
Approximately 6 seconds.
What happens to muscles as the phosphagen system is exhausted?
Muscles shift to anaerobic fermentation.
How much ATP does glycolysis generate from one glucose molecule?
A net gain of 2 ATP.
What is the anaerobic threshold?
The point at which lactate becomes detectable in the blood.
What is the glycogen-lactate system?
The pathway from glycogen to lactate that produces enough ATP for 30-40 seconds of maximum activity.
What occurs after about 40 seconds of exercise?
The respiratory and cardiovascular systems deliver oxygen fast enough for aerobic respiration to meet most of the muscle's ATP demand.
How much ATP does aerobic respiration produce per glucose compared to glycolysis?
Aerobic respiration produces an additional 30 ATP per glucose.
What is VO2 max?
The maximum oxygen uptake, a major determinant of one's ability to maintain high-intensity exercise for more than 4-5 minutes.
What is Excess Postexercise Oxygen Consumption (EPOC)?
The difference between the elevated rate of oxygen consumption following exercise and the usual resting rate.
What are the characteristics of slow-twitch muscle fibers?
Well adapted for endurance, resist fatigue, contain abundant mitochondria, capillaries, and myoglobin.
What are fast-twitch muscle fibers adapted for?
Quick responses and powerful movements, utilizing glycolysis and anaerobic fermentation for energy.
What is the difference between fast-twitch and slow-twitch fibers?
Fast-twitch fibers are thicker and stronger, while slow-twitch fibers are thinner and more fatigue-resistant.
What is the role of resistance training?
To stimulate muscle growth through contraction against a load that resists movement.
What adaptations occur in muscles due to endurance training?
Increased mitochondria, glycogen, blood capillary density, and improved skeletal strength.
What are the properties of cardiac muscle?
Contracts with a regular rhythm, highly resistant to fatigue, and can contract without nervous stimulation.
What are intercalated discs in cardiac muscle cells?
Structures that join cardiomyocytes, allowing for electrical and mechanical connections.
How does smooth muscle differ from skeletal muscle?
Smooth muscle lacks striations, is slower, and can contract for long periods without fatigue.
What is the significance of myoglobin in cardiac muscle?
It aids in aerobic respiration and contributes to the muscle's resistance to fatigue.
What is the length-tension relationship in muscle contraction?
A muscle resting at optimal length can contract more forcefully than one that is excessively contracted or stretched.
What is the effect of fatigue on muscle contraction?
Fatigued muscles contract more weakly than rested muscles.
What is the role of the autonomic nervous system in cardiac muscle function?
It can increase or decrease heart rate and contraction strength.
What is the primary energy source for cardiac muscle?
Aerobic respiration, using myoglobin and glycogen.
What is the average lifespan of a muscle fiber?
Muscle fibers can regenerate well, particularly smooth muscle.
What adaptations occur in fast-twitch fibers during training?
They become thicker and stronger, synthesizing more myofilaments and myofibrils.
What is the significance of the plateau in VO2 max?
It indicates the point at which the rate of oxygen consumption does not increase further with added workload.
What is the effect of muscle size on strength?
Thicker muscles can form more cross-bridges, allowing for greater tension generation.
What is anaerobic fermentation?
A process that enables cells to produce ATP in the absence of oxygen, yielding little ATP and lactate.
What is aerobic respiration?
A process that produces far more ATP than anaerobic fermentation and requires a continual supply of oxygen.
What energy system is primarily used during short, intense exercise?
The phosphagen system.
How does the phosphagen system provide energy?
By borrowing phosphate groups from other molecules and transferring them to ADP to form ATP.
What are the two enzyme systems involved in the phosphagen system?
Myokinase and creatine kinase.
What happens to ATP production after 40 seconds of exercise?
Aerobic respiration begins to meet most of the muscle's ATP demand.
What are slow-twitch muscle fibers also known as?
Slow oxidative (SO) fibers or type I fibers.