aa oxidation & urea cycle
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
eating types and energy
obligate carnivores get over 90% of their energy from protein, omnivores get 10-20%
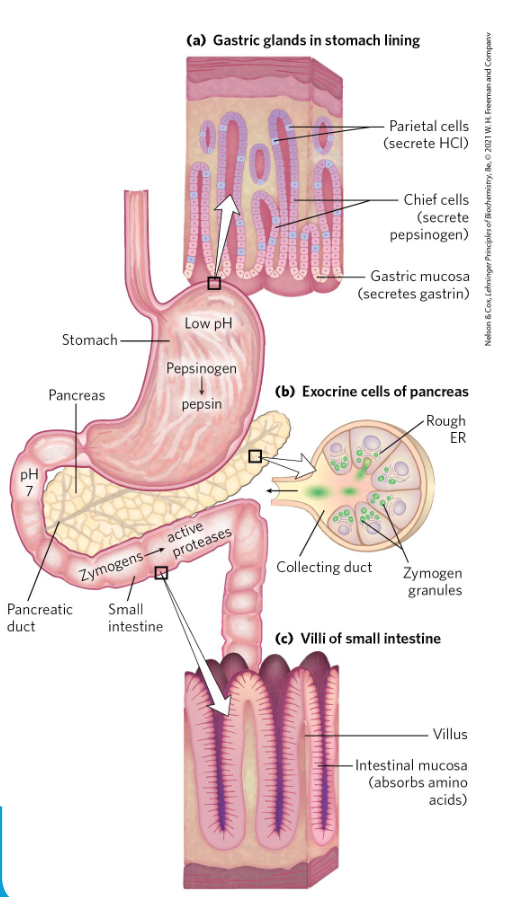
protein digestion
enter stomach, which stimulates release of gastrin
gastrin simulates release of hcl
hcl dec ph, which activates pepsinogen by cleaving it
pepsinogen cleaved yields pepsin, which cleaves long pp’s into smaller fragments
the smeller frag enter intestine and causes pancreas to release bicarbonate (inc ph)
pancreatic proteases released into intestine and activated via proteolytic cleavage
these break pp into aa to be absorbed into intestine cells - any nonabsorbed aa/proteins are excreted as waste
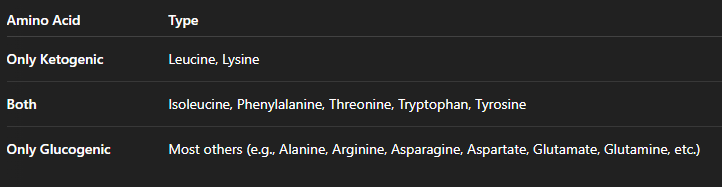
what are 2 classifications of C skeleton in aa
glucogenic - can enter gng as tca intmd and be converted into glucose
ketogenic - broken down into acetylcoa or acetoacetate, precursors for ketone bodies
some can do both and it just depends on what enzymes get to them first - don’t need to memorize which aa go where
glucogenic aa
inc [oaa] (needed for gng) so C skeleton of aa → oaa, pyruvate, or tca intmd easily, its glucogenic
inc oaa pop w/o directly changing tca
aa → pyruvate, alpha ketogluterate, succinyl coa, fumarate, or oaa
![<p>inc [oaa] (needed for gng) so C skeleton of aa → oaa, pyruvate, or tca intmd easily, its glucogenic</p><p>inc oaa pop w/o directly changing tca</p><p>aa → pyruvate, alpha ketogluterate, succinyl coa, fumarate, or oaa</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/63e3ffb9-6335-4661-a077-1fa563685ffb.png)
ketogenic aa
aa that can form acetyl coa - specifically ile, val, and leu bc they’re branch chains
generate acetyl coa, and acetoacetylcoa to replenish tca but no direct inc in oaa just running cycle more efficiently
aa to pyruvate
don’t need to know mech but common first step: put NH3 from aa onto alpha ketogluterate to make glutamate and cont converting aa from there w/o the NH3
ile and val → succinyl coa, leu → acetyl coa and acetoacetate
what does converting aa do
takes off an NH2 / NH3w
what is done with the NH3 / NH2
enter urea cycle
done bc ammonia is v toxic and can build upw
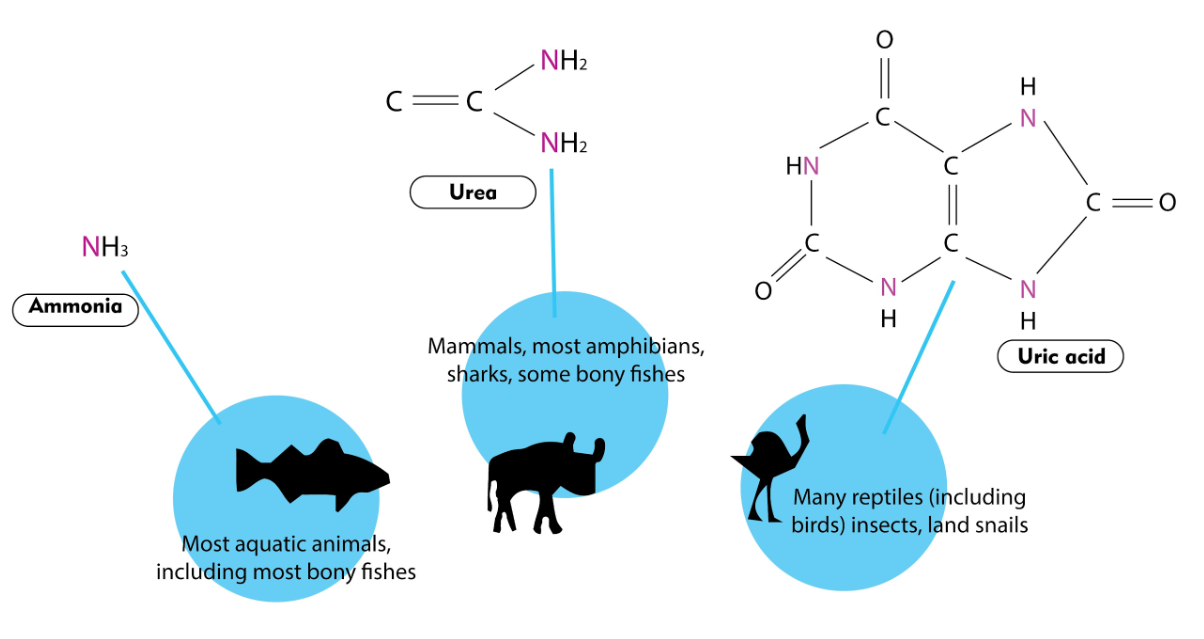
how do diff species deal with ammonia
dept on how aq their environ is
fish - diffuse straight from body, nh3 is directly diluted bc of highly aq environ
mammals - make ammonia bc removes 2N removed in 1 molec and urea isn’t as toxic but still needs to be diluted
birds / reptiles - make uric acid, requires lses water and results in paste-like waste, gets rid of 4 N groups
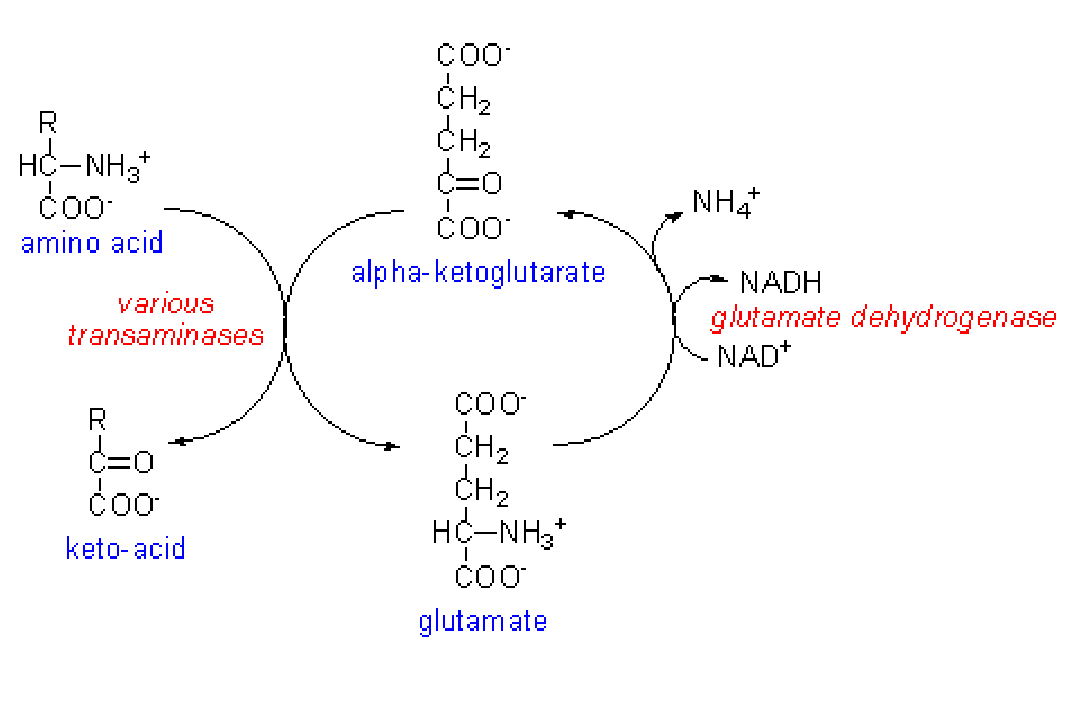
basic removal step of amino groups
in the liver cells, transaminases / amiotransferases remove the NH3 group and put it onto an alpha-ketoglutarate, creating a glutamate (ex-glutamate) and keto acid (ex-aa)
glutamate can be converted back into alpha ketoglutarate by glutamate dehydrogenase, generating NADH and NH4+
requires PLP (vitamin b6) as a cofactor
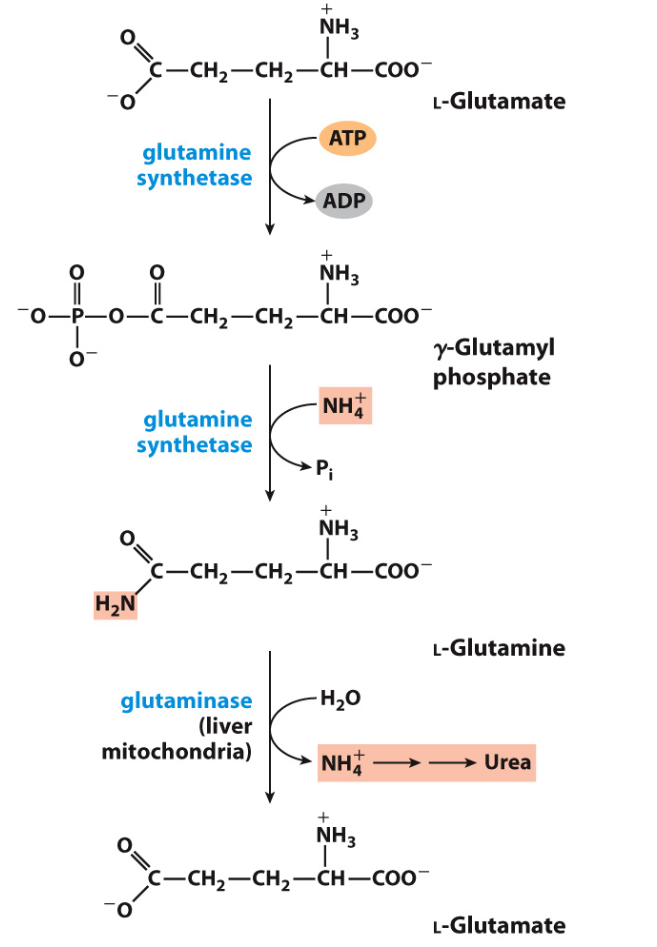
how is the glutamate dealt with
free ammonia (NH4+) is incorporated into the glutamate by glutamine synthetase to make glutamine
gln moves through the bloodstream to the liver - form of transportation of N groups in non-toxic form
in mt of liver cells, glutaminase converts the glutamine into glutamate and releases the NH$+
COSTS 1 ATP
in general, what’s the rule about glu vs gln
in cells, its glu but while moving, its gln
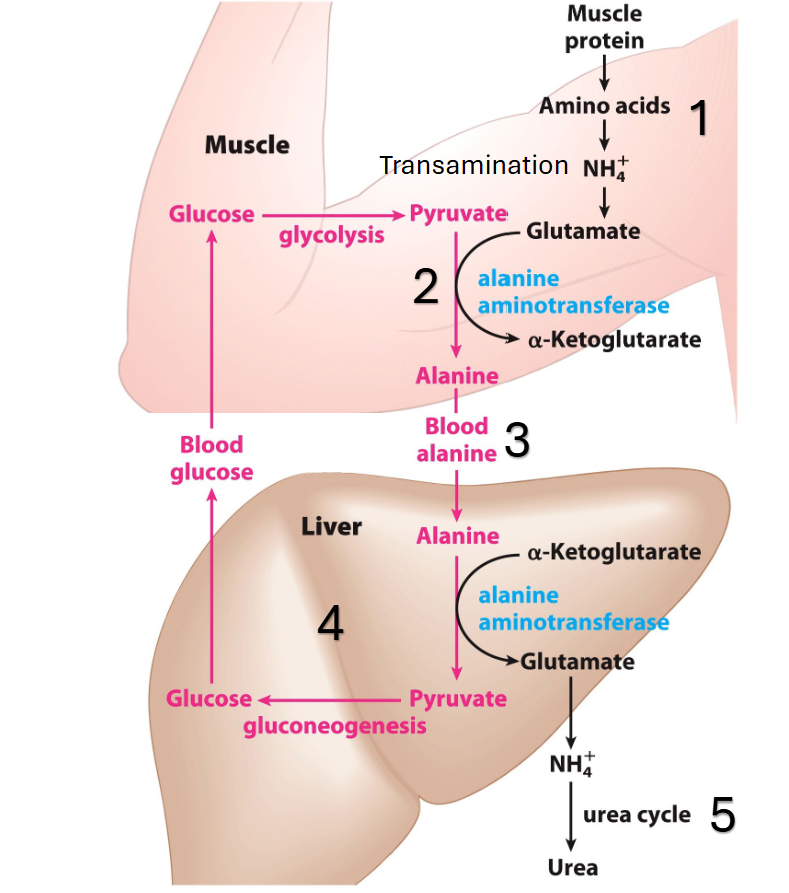
what’s different for muscle cells
muscles cells do the previously mentioned method as well but when used vigorously, they max glycolysis, resulting excess pyruvate that can’t be oxidized bc of lack of O2 - only some pyruvate goes to lactic acid
also short on ATP so they break down aa, generating N waste
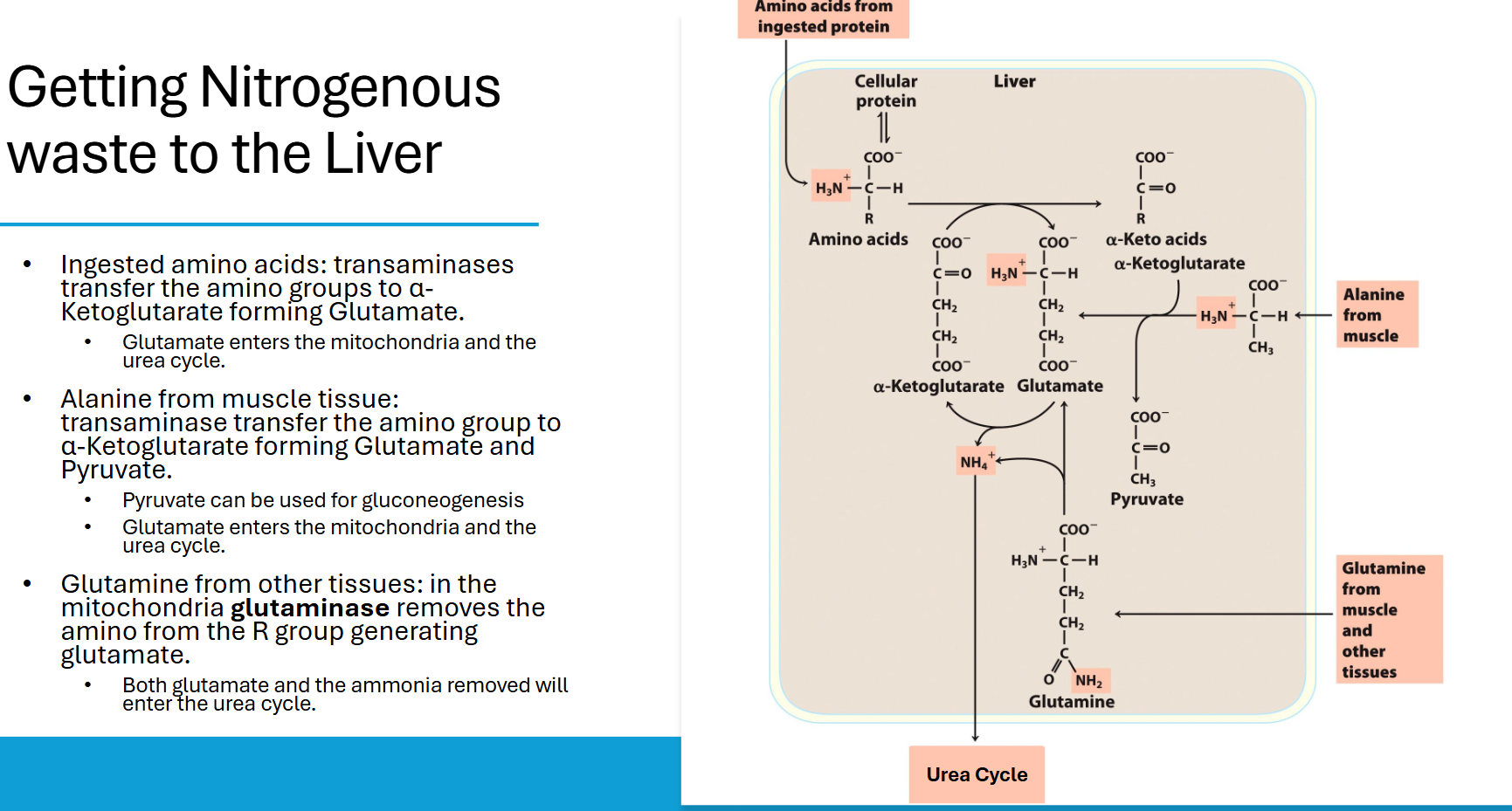
how do muscle cells dispose of amino groups in aa and recycle pyruvate
free NH4+ all gets put onto aa to make glutamate (previous pathway)
put NH4+ onto pyruvate → ala
both glutamate and ala go to liver safely
when ala arrives, it dets deaminated and the NH4+ is put on glu and goes into urea - turns ex-ala into pyruvate which gets put into gng and sent into bloodstream
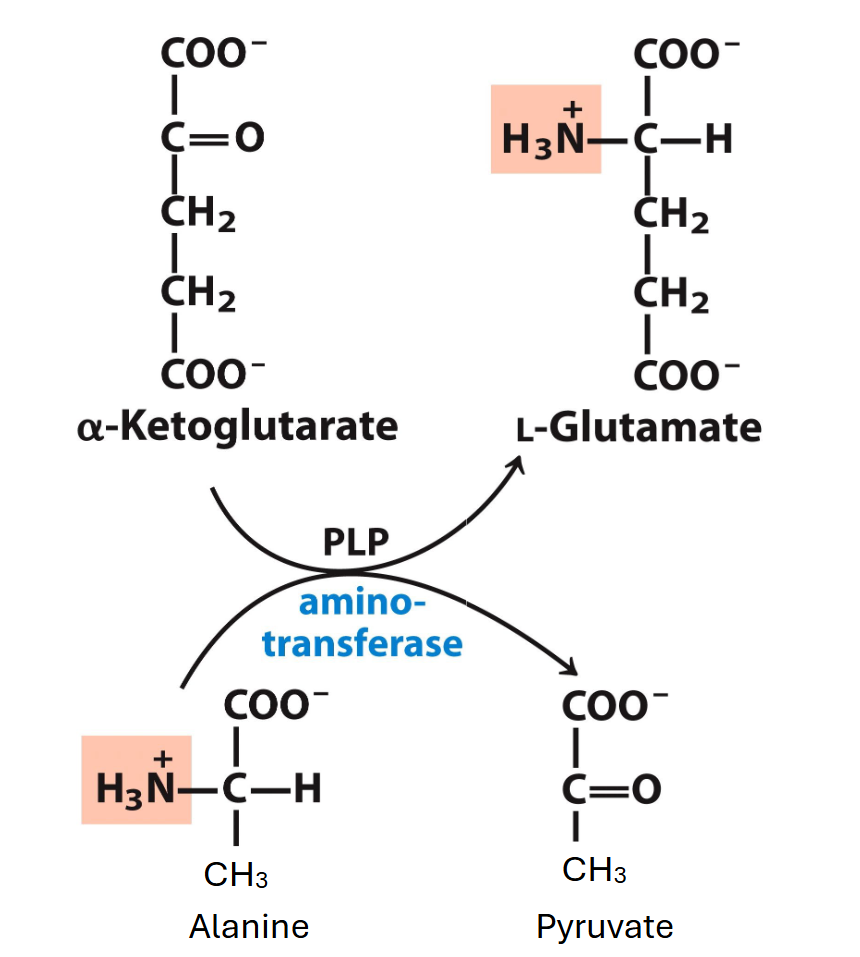
ala to pyruvate
done via an aminotransferase with PLP as cofactor
also converts alpha ketoglutarate into glutamate
urea cycle
takes place in liver mt mostly
urea cycle prep
gln (glutamine) imported into the mt and → glu via glutaminase, releasing NH4+ (NH4+ and glu/gln from flashcard 11)
OR it enters as glutamate from ala or aa oxidation
glutamate → alpha-ketoglutarate via glutamate dehydr, produces NH4+ and NAD(P)H
OR asp aminotransferase takes the NH3+ and turns oaa → asp
2 ATP + bicarbonate + NH4+ → carbamoyl phosphate
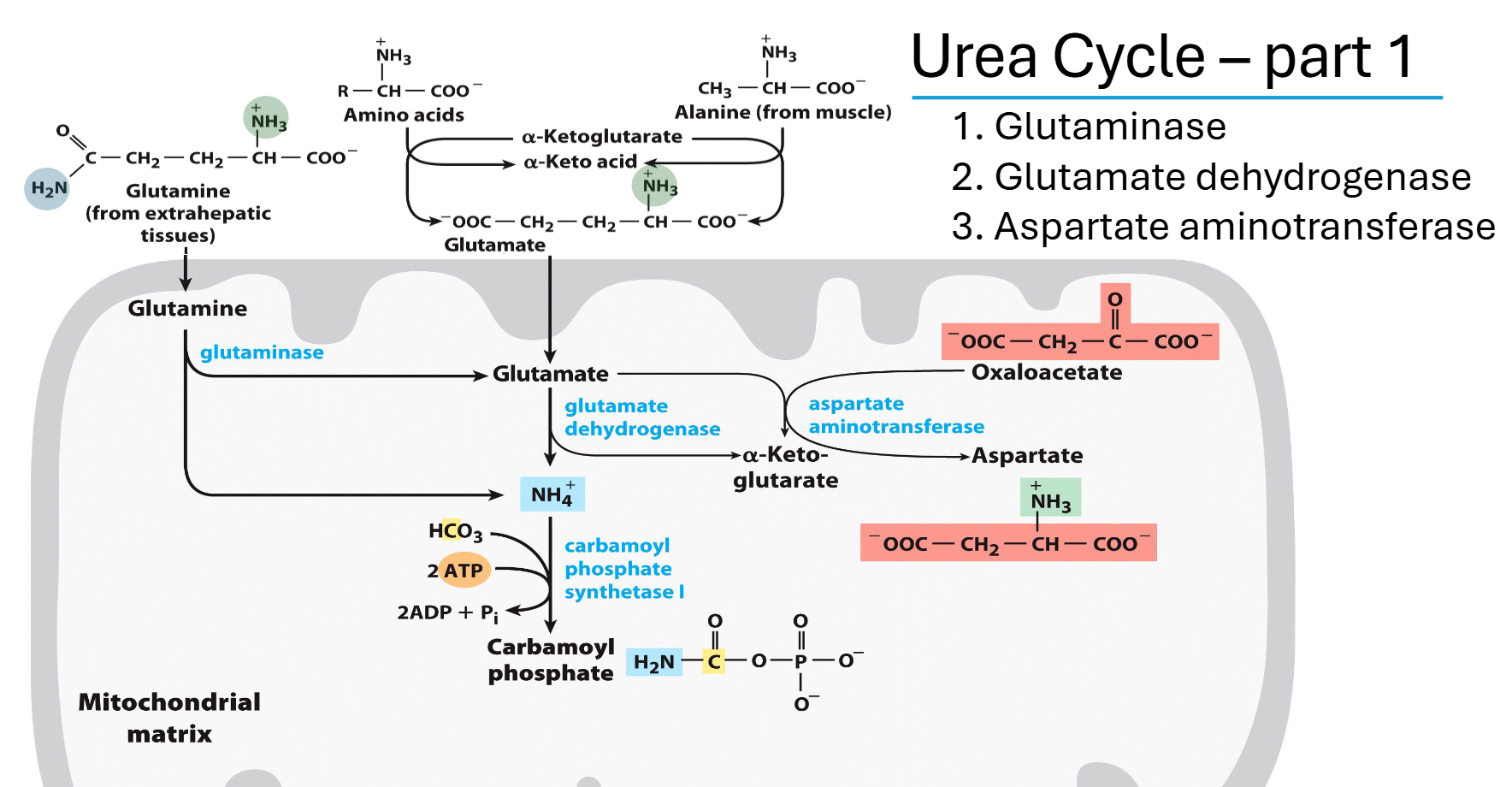
after prep pjase of urea, where does everything end up
all N from food / tissues converted into NH4+ or onto asp, all glu made into alpha-ketoglutarate
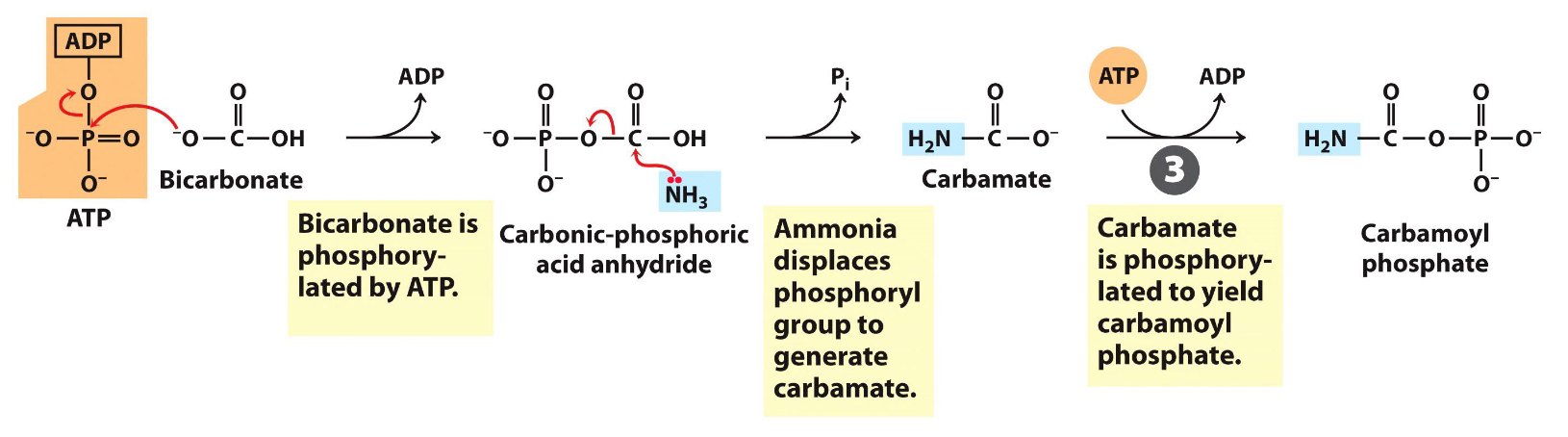
NH4+ to carbamoyl-P
done via carbamoyl phosphate synthetase i
N capturing reaction
uses 2ATP
need to know mech
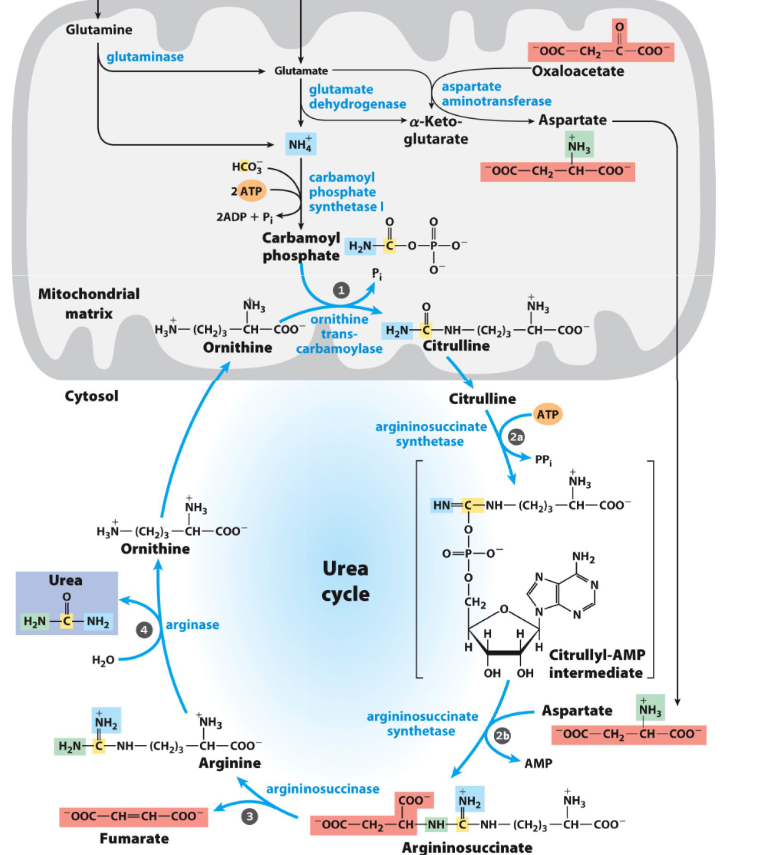
urea cycle summary
carbamoyl phosphate → citrulline (mt → cytosol)
citrulline → argininosuccinate
argininosuccinate → arg and fumarate
arg → ornithine + urea (cytosol → mt)
fumarate → tca
urea water soluble, non-toxic, moves to kidneys for removal
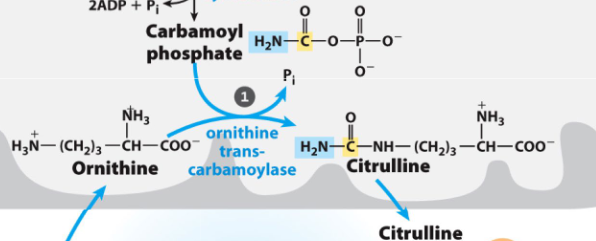
rxn 1 of urea cycle
carbamoyl phosphate + ornithine to citrulline via ornithine transcarbamoylase
citrulline leaves mt to go to the cytosol
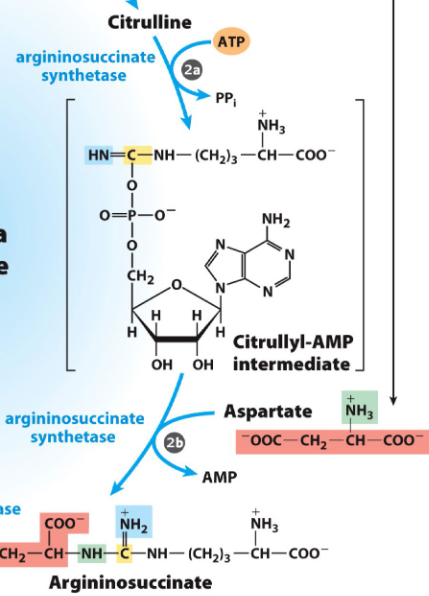
rxn 2 of urea cycle
citrulline + AMP + asp from prep phase → argininosuccinate + amp via argininosuccinate synthetase
AMP comes from ATP and releases 2(Pi)
asp comes from the glu to alpha ketoglutarate via asp aminotransferase
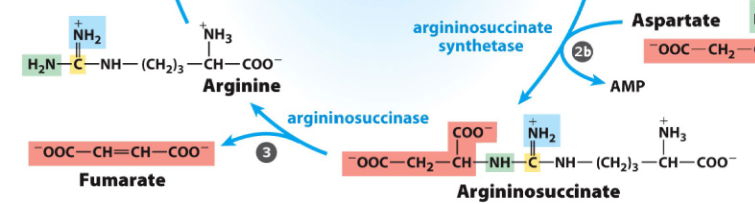
rxn 3 of urea cycle
arginosuccinate → arginine + fumarate via argininosuccinase
fumarate goes into tca and arg cont
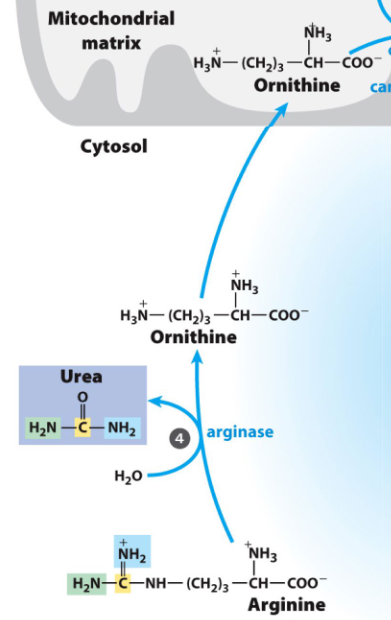
rxn 4 of urea cycle
arg + h2o → ornithine + urea via arginase
urea moves to kidneys
ornithine omves back into mt
what are the 4 aa that play key roles in N metabolism
glu, gln, ala, asp
all 4 can easily be converted into tca intmd
glu/gln → alpha ketoglutarate
ala → pyruvate
asp → oaa
energetics of urea cycle
cost is high - 2ATP to activate carbamoyl-P and 2 to gen arginosuccinate (bc AMP used, means lost 2P)
fumarate goes into tca → oaa, making NADH
NADH → etc → 2.5ATP
basically covers the cycle but not by much