Biology Honors - Unit 1 - Chemistry of Life
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Hydrophilic
Likes water and can work with it or in it
Hydrophobic
Hates water and has to be separated from it
Macromolecules
A small organic molecule that can be a unit of a large organic molecule
Monomer
The basic building blocks of larger organic molecules called polymer
Polymer
Many smaller molecules that are layered together in a repeating pattern
Monosaccharide
Made up of smaller monomers
Have carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
Are simple sugars that include glucose, fructose, and galactose
Polysaccharide
Long chains made up of smaller carbohydrates
Help the cellular structure and uses it to provide energy for our body
Unicellular
One cell
Multicellular
One or more cells
Organelle
Simple structures that provide the needs of the cells such as nucleus, mitochondria, ribosome, lysosome, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, etc.
Homeostasis
Maintain a stable relatively consistent internal environment
Metabolism
Energy
Virus
NOT considered a living thing
Biological entities
Contain DNA and RNA
Depend on a host cell to survive
Once it infects, its called a bateriophage
Prokaryote
An organism that doesn’t have a nucleus and other organelles
Eukaryote
An organism that does have a nucleus and all of the essential organelles involved
Host
A cell that is invaded by a virus or other microorganism
Cell
The basic unit of life that contains the DNA, cytoplasm, cell membrane, ribosome, etc.
Reproduction
The production organisms that are produced from the same DNA
List the six elements necessary for life and give examples of three molecules that contain those elements.
Elements: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus
Examples: Carbon dioxide, water, glucose
List the monomers and polymers of carbohydrates, lipid, proteins, and nucleic acids.
Monomer
Carbohydrate-monosaccharides
Lipid-glycerol/fatty acids
Protein-amino acids
Nucleic Acid-nucleotides
Polymers
Carbohydrate-polysaccharides
Lipid-triglycerides
Protein-polypeptides
Nucleic Acid-DNA or RNA
Explain the process of polymerization-both the forming of polymers, through dehydration, and the breaking of polymers, through hydrolysis.
Polymerization is the process that includes the formation of polymers through dehydration synthesis and breaking down through hydrolysis.
Dehydration synthesis: releasing water to link monomers
Hydrolysis: adding water to split polymers
Explain the main function of each macromolecule
Carbohydrate-quick energy, structural support
Lipids-long-term energy, insulation to living
Proteins-structure, protection, energy, transportation, etc.
Nucleic Acids-carry the genetic information
List examples of each macromolecule
Carbohydrate-glucose
Lipids-oil
Proteins-eggs
Nucleic Acids-DNA
Sketch a picture of the macromolecule that makes up the majority of the cell membrane and explain why its structure gives the membrane a unique property.
Lipids make up most of the cell membrane since every organelle uses it. It's unique since it contains both hydrophilic and hydrophobic.
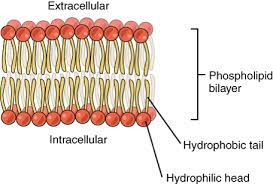
Explain what makes proteins the most diverse macromolecule
They are very diverse because there’s so many different amino acids and they can be placed in any order.
List which macromolecule is not obtained from our food and where do we get it from.
Nucleic acids is the macromolecule that we don’t get from food but from our DNA
List the 3 principles of cell theory
All living organisms are composed of one or more cells
Cells are the basic building blocks of life
All cells are made from pre-existing cells
Create a Venn Diagram comparing prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
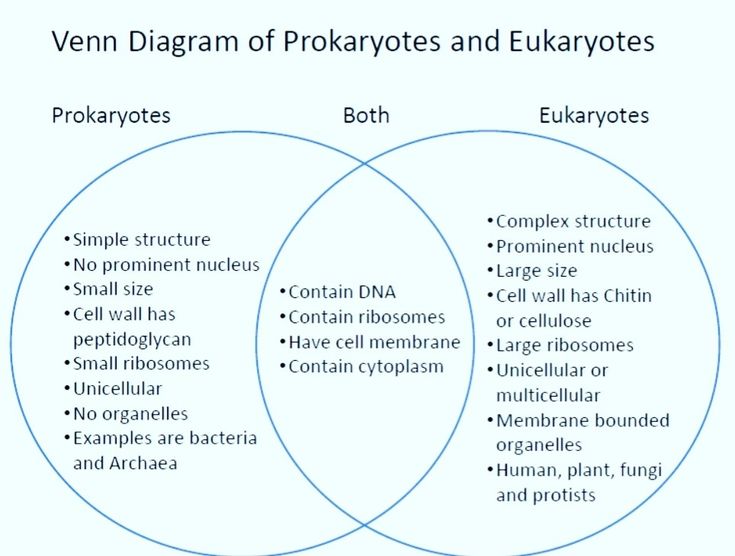
List the structures that distinguish plant cells from animal cells.
Animal-lysosomes and centrioles
Plant-chloroplast, cell wall, central vacuole
Cell Membrane
Controls what goes in and out of the cell
Important for communication and homeostasis
Cytoskeleton
Gives cell it’s shape and provides structural support
Cytoplasm
Holds everything in place and where chemical reaction happens
Nucleus
Protects and stores DNA
Nucleolus
Makes RNA that makes up the nucleus
Ribosome
Makes protein through translation
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Packages protein and sends it to the golgi apparatus
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Makes lipids and stores calcium
Golgi apparatus
Gets vesicles protein from ER
Process, sorts, and ships protein where needed
Vesicle
Mini carts that ships protein around cell
Lysosome
Breaks down dead stuff and programs cell death
Vacuole
Stores water, nutrients, waste, etc.
Centrioles
Appear during cell division
Pulls apart protien
Cilia
Moves fluid throughout the cells surface
Flagella
Moves entire cell through extracellular fluids
Mitochondria
Breaks down chemical energy to release ATP energy
C6H12O6 - cellular respiration
Chloroplast
light energy = chemical energy in sugar
photosynthesis 6CO2 + 6H2O = C6H12O6 + 6O2
Cell Wall
Protects and maintains shape
Central Vacuole
Storage center
Describe the role of proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates in the structure of the phospholipid bilayer. Include how its structure dictates its function.
Lipids form a bilayer that prevents water-soluble (things that dissolve in water) to enter the cell. Proteins provide transport and structural support which carbohydrates attach to them and lipids allow cell recognition and communication.
Defend the statement that viruses are not considered living things with at least three points to support your claim.
Viruses are not living because…
They can’t produce energy to maintain metabolism
They can’t reproduce on their own
They can’t maintain a stable internal/external environment
Summarize the different between the lytic and lysogenic life cycles or viruses.
The lytic cycle happens when you know you are sick immediately. A lysogenic cycle happens after a couple of years and then you get sick.
Lytic- DNA injects and immediately starts translating
Lysogenic- allows the virus to dormant in your body for years