EXAM 1 - Arthrology of the Spine
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
amphiarthrosis means ___ movement
slight
bones connected by cartilage are classified as
amphiarthrosis
what is the primary classification of cartilaginous joints
synchondrosis
what is the secondary classification of cartilaginous joints
symphysis
synchondrosis includes ___ cartilage
example?
hyaline
epiphyseal plates
what is a synchondrosis cartilaginous joint that is permanent
costochondral joints
symphysis includes ___ cartilage
example?
fibrocartilage
IVD, pubic symphysis
what plane are symphysis joints always located
median plane
what holds fibrous joints together
fibrous connective tissue
do fibrous joints have a joint cavity
no
example of fibrous joint
sutures
what is the ossification of sutures known as
synostoses
what is the classification of sutures
synarthrosis
what is the classification of a ligament
fibrous amphiarthrosis syndesmosis
what are the types of fibrous joints
suture, syndesmosis, gomphosis, schindylesis
parallel bones united by fibrous connective tissue is classified as
fibrous joint syndesmosis
a conical process into a socket such as roots of teeth in the alveolar processes is classified as
fibrous joint gomphosis
a ridged bone that articulated into a groove on neighboring bone is classified as
fibrous joint schindylesis
what is an example of a fibrous joint schindylesis
vomer articulating with sphenoid
which functional classification allows no movement of joints
synarthrosis
what 4 structures are within a synovial joint
articular capsule, synovial membrane, articular cartilage, synovial fluid within a cavity
what is the classification of synovial joints based on
1. number of bones or articular surfaces
2. types of movement allowed by joint
3. morphological appearance
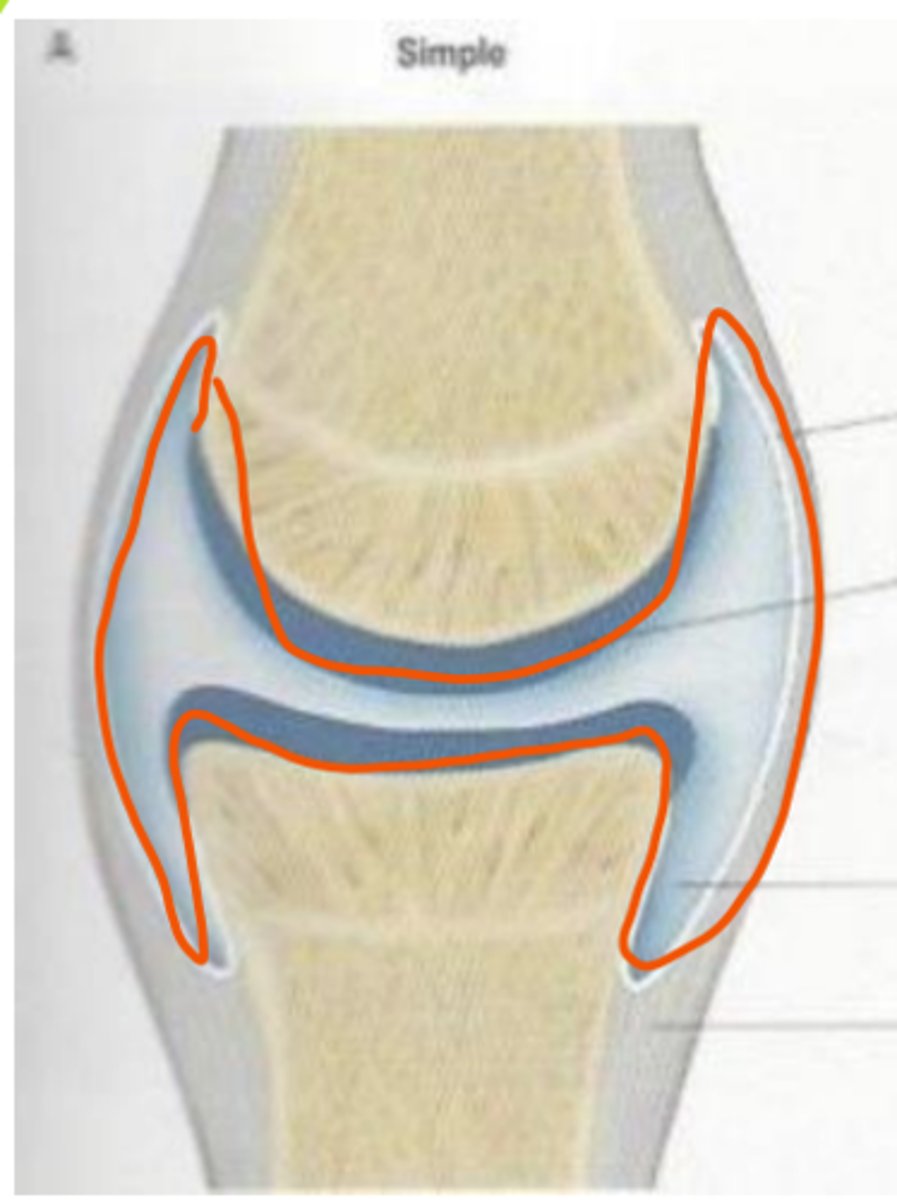
what is a simple synovial joint
opposing bones form a joint
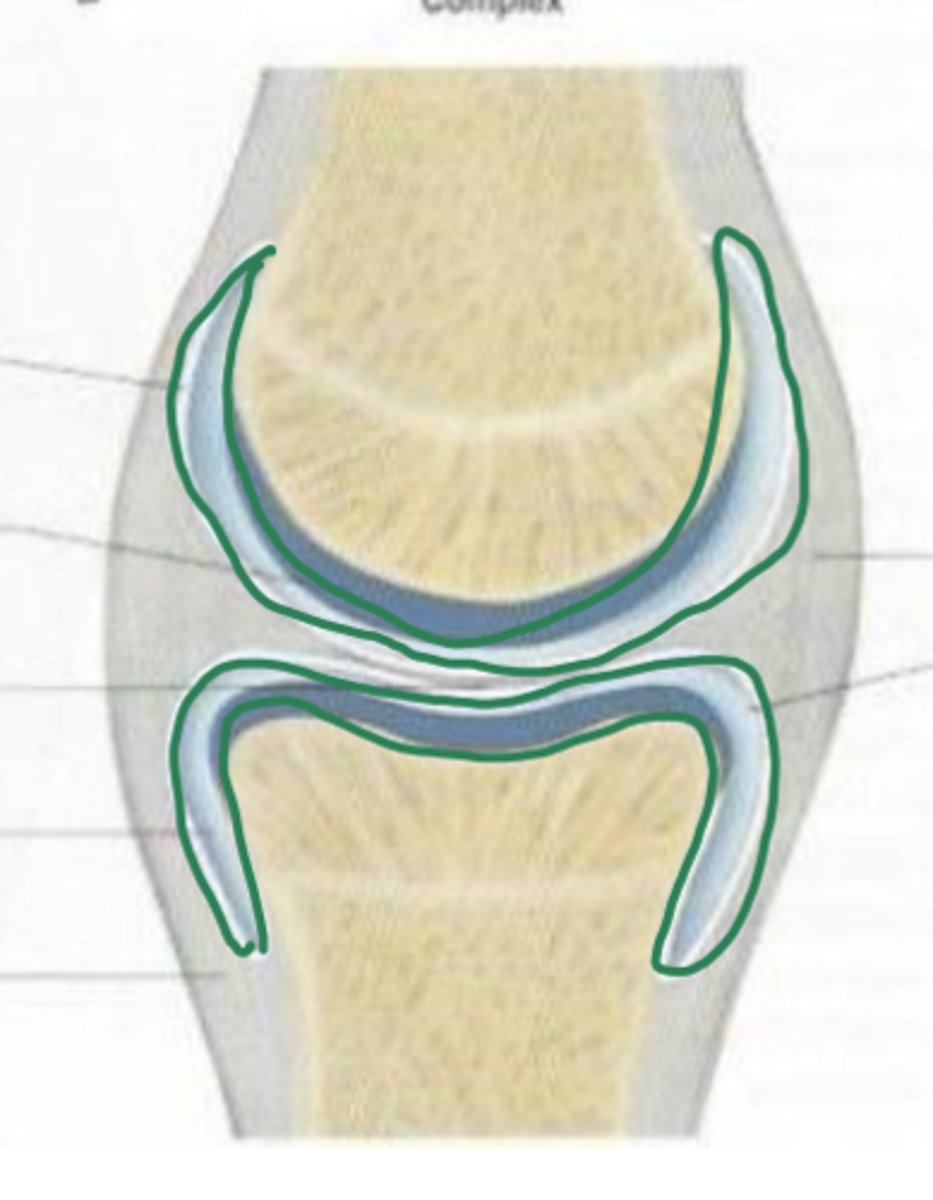
what is a complex synovial joint
joint cavity divided into two compartments
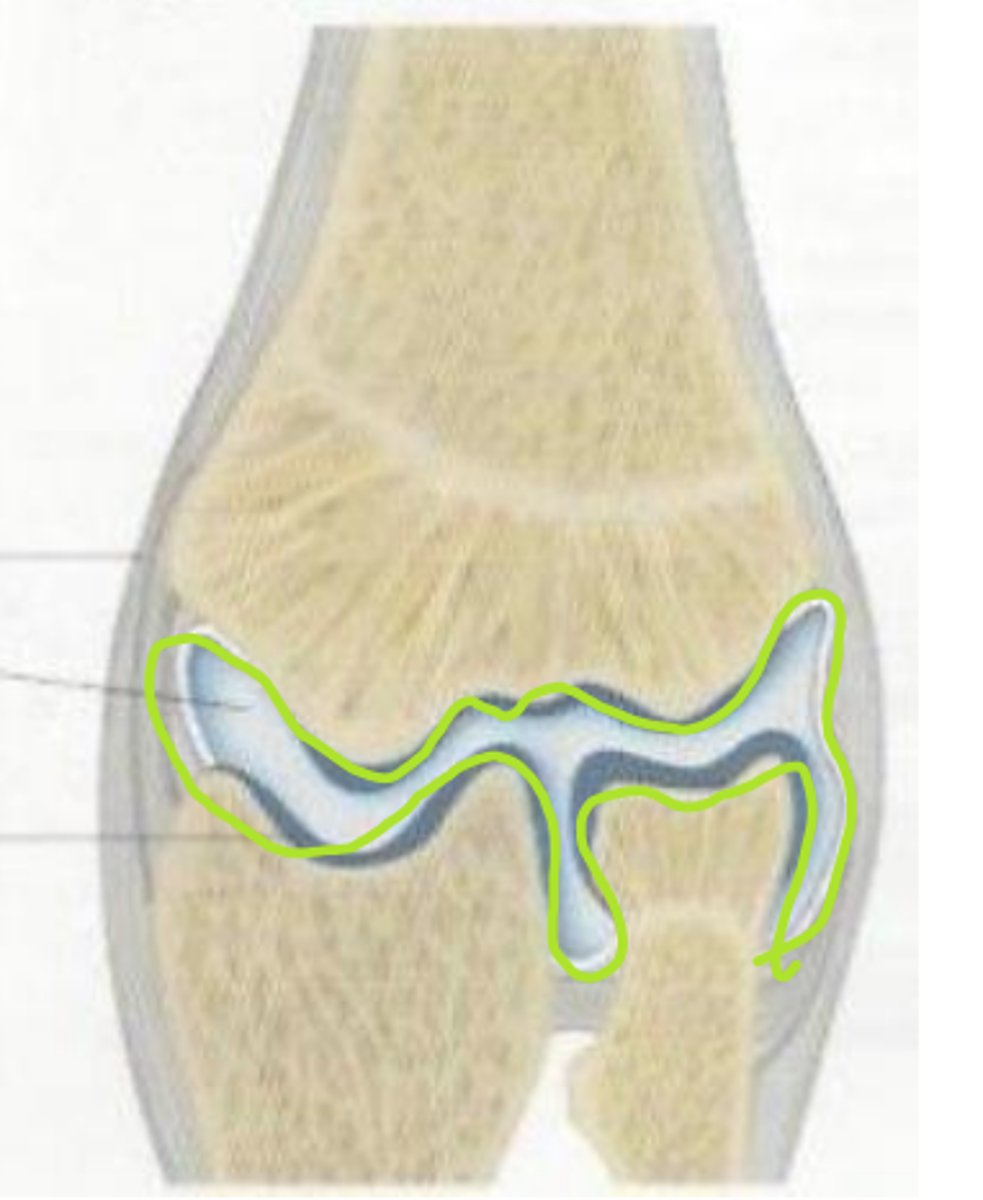
what is a compound synovial joint
more than 2 opposing bones form a joint
what is the primary movement of a synovial plane joint
gliding/translation
a synovial plane joint is also known as a
diarthrosis arthrodial
what is the classification of zygapophyseal joints
synovial plane joint (diarthrosis arthrodia)
what is a pivot synovial joint also known as
diarthrosis trochoid
what is the movement of a synovial pivot joint
axial rotation
what movements are limited with a synovial pivot joint
flexion, extension, lateral flexion
what is the classification of the median atlantoaxial joint (dens and osteoligamentous ring of atlas)
synovial pivot joint
what is another name for a synovial saddle joint
diarthrosis sellar
what are the movements of a synovial saddle joint
flexion-extension, abduction-adduction
circumduction
is a synovial saddle joint uniaxial or biaxial
biaxial
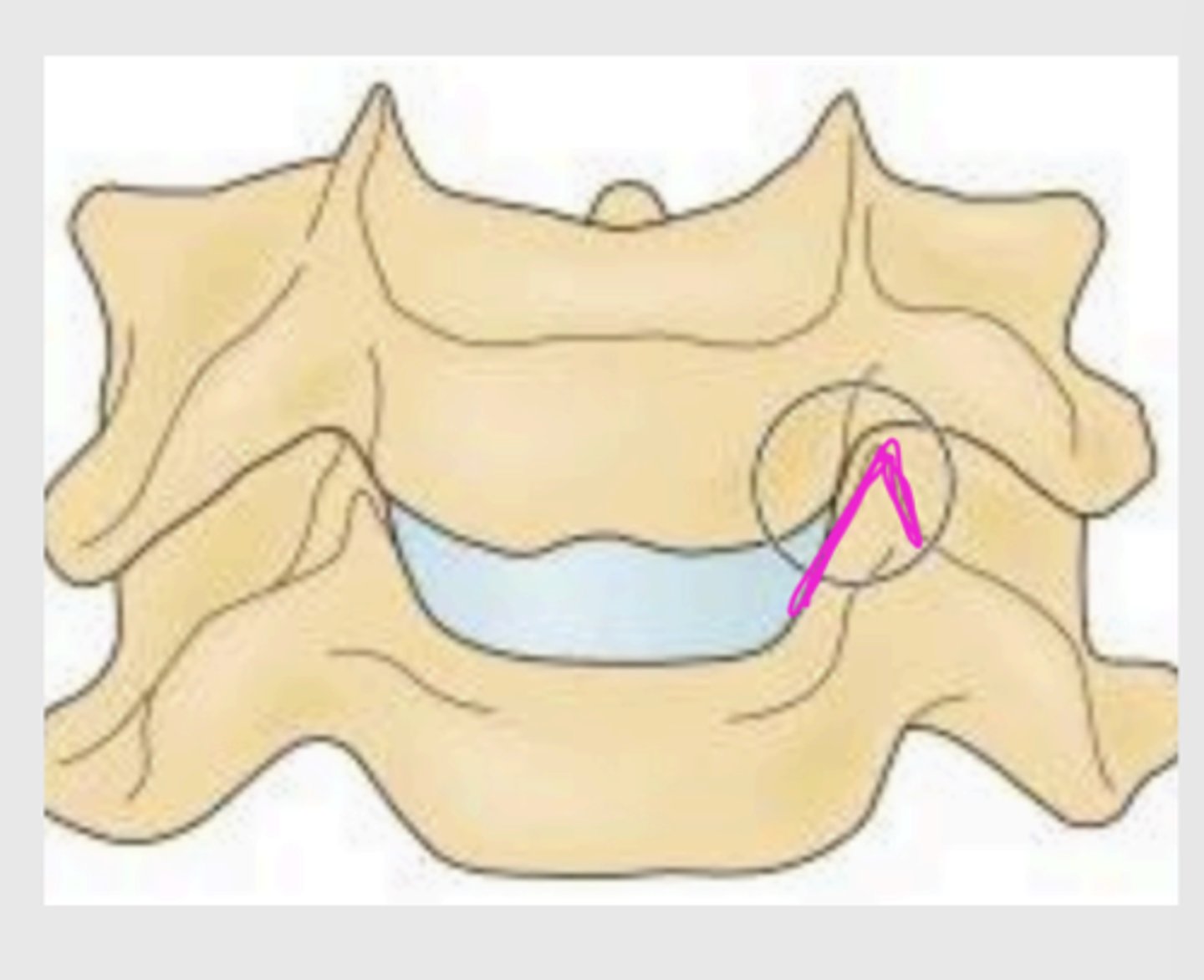
what is the classification of the joint of luschka (uncinate process with lateral groove)
synovial saddle joint
what is another name for ellipsoidal synovial joint
diarthrosis condylar
what movement do ellipsoidal synovial joints have
lateral bending
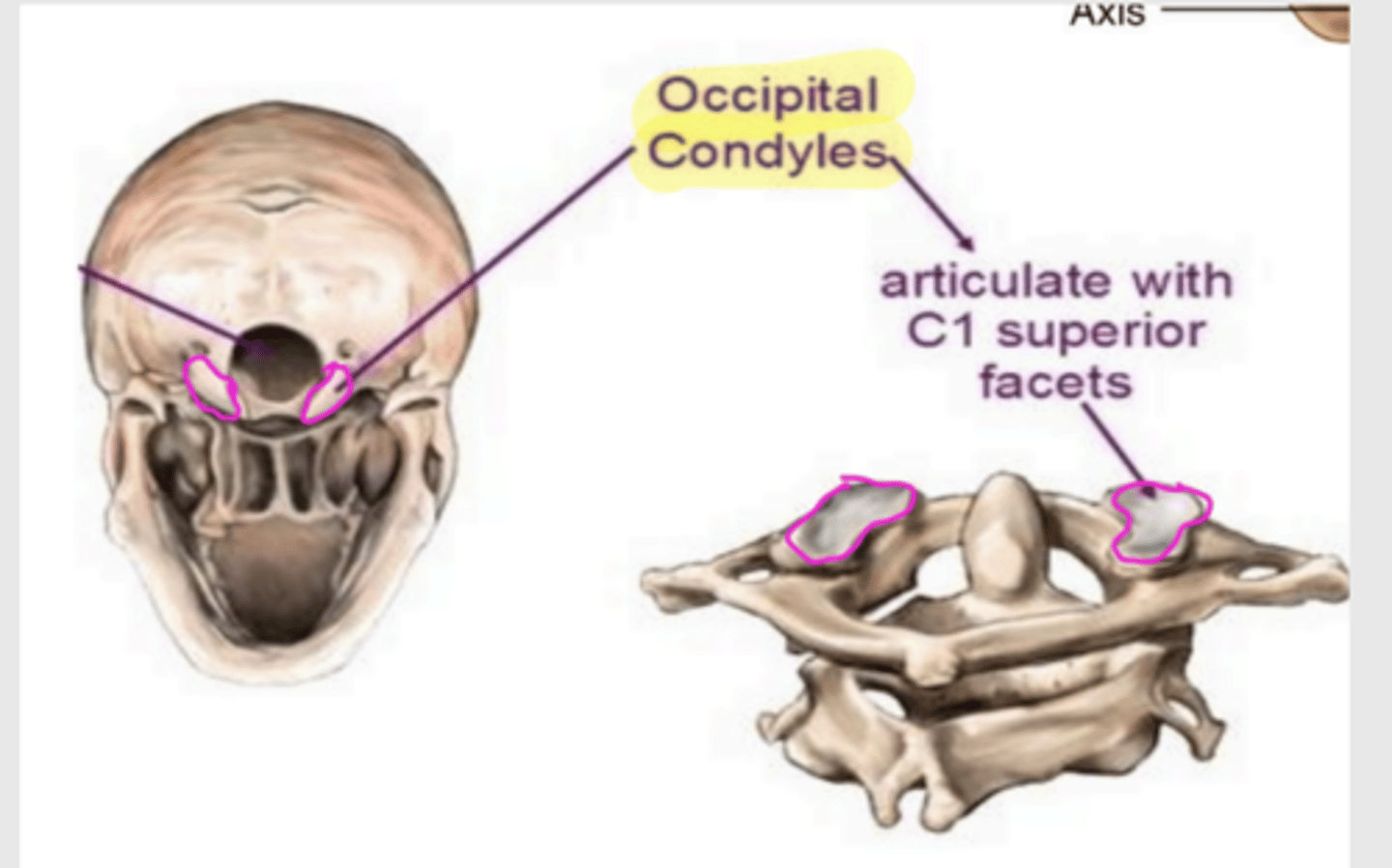
what is the classification of the atlanto-occipital joint
synovial ellipsoidal
what is a shared morphological characteristic of diarthrosis trochoid joints
osseous pivot and osteo-ligamentous ring
nonaxial means
no range of movement
uniaxial means, example
one plane of movement
hinge joint
biaxial means
example
two planes of movement
saddle joint
multiaxial means
example
multiple planes of movement
ball and socket
Type I-III mechanoreceptors are ____ with ___ function
encapsulated, proprioceptive
Type IV mechanoreceptors in a joint capsule are ___ and unmyelinated _____
non-encapsulated, free nerve endings
Type I mechanoreceptors monitor _____
joints at rest
type II mechanoreceptors monitor ____
normal movement
type III mechanoreceptors monitor _____
tendons during movement
type IV mechanoreceptors mediate ___ and are normally silent
nociception
what covers all non-articular surfaces lining the synovial joint cavity
synovial membrane
what are the 3 modifications of the synovial membrane that aid in spreading synovial fluid
synovial villi, articular fat pads, synovial menisci/intra-articular disc
finger like projections that increase surface area and increase with age are known as
synovial villi
fibrous layer of synovial membrane that fills the gaps between joint tissue is known as
articular fat pads
fibrocartilaginous projections from a synovial membrane are known as
synovial menisci/intraarticular discs
what is the term for the intra-articular disc that separates from joint articular surfaces
meniscoids
what is the outer fibrous layer of the articular synovial membrane made of
connective tissue, blood vessels, lymphatics, nerve endings
what is the function of the inner cellular (luminal) layer of a articular synovial membrane
synovial fluid secretion
which layer of the articular synovial membrane is continuous with the articular capsule
outer fibrous layer
the inner cellular layer is also known as the
synovial lamina intima
what cell type within the cellular layer of a synovial membrane is phagocytic
Type A synovial cells/synoviocytes
what cell type within the cellular layer of a synovial membrane produces protein and hyaluronic acid (synovial fluid)
Type B synovial cells
TQ:
Where is synovial fluid created and what cells create it
inner cellular layer of the synovial membrane via Type B synoviocytes
what are articulating surfaces covered in hyaline cartilage called
articular cartilage
what causes articular cartilage to lose potential for growth and repair
avascular, lacks lymphatics and innervation
nutrition/waste elimination of articular cartilage is provided by
synovial fluid, blood vessels, sinuses of bone marrow
what provides network for water retention in articular cartilage
arrangement of GAGs
water accounts for ____% of volume of articular cartilage
what makes up the rest
60-80
Type II collagen
proteoglycan gel
T/F
there is a high volume of synovial fluid observed in human joints
FALSE
modified tissue consisting of fats, salts, albumins, hyaluronate is known as
synovial fluid
what is responsible for the viscosity and lubrication of joints
hyaluronate and/or lubricin
what do synovial lamina intima cells secrete to add to the final consistency of synovial fluid
wandering blood cells and connective tissue cells
what are the functions of synovial fluid
nutrition, lubricant, increase joint efficiency, reduce erosion
All are modifications of articular synovial membrane EXCEPT:
A. Synovial villi
B. Articular fat pads
C. Synovial menisci
D. Intra-articular folds
E. Perichondrium
E
Which role does aging have on the abundancy of synovial villi?
A. Increase
B. Decrease
C. Consistent throughout life
A