Predation
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
predator- prey interactions (+/-)
predators often focus on prey that is the better competitior because there is more of them. Their pops are higher and this predation often results in increased diversity- grazing of large herbivores, starfish, etc.
Lotka voltera
dNh/dt= rhNh-aNhNp. Nh= prey population, Np= predator population r- reproduction, a= capture efficiency (rate of predation) dNp/dt= baNhNp- mpNp, b =conversion of prey into pred offspring, m=predator deaths. Growing rate of prey pop=0. When Np=rh/a, grows when Np< rh/a, decreases if Np>rh/a. Growth rate of predator population = 0. When Nh=mp/ba increase if Nh> mp/ba, decrease if Nh< mp/ba
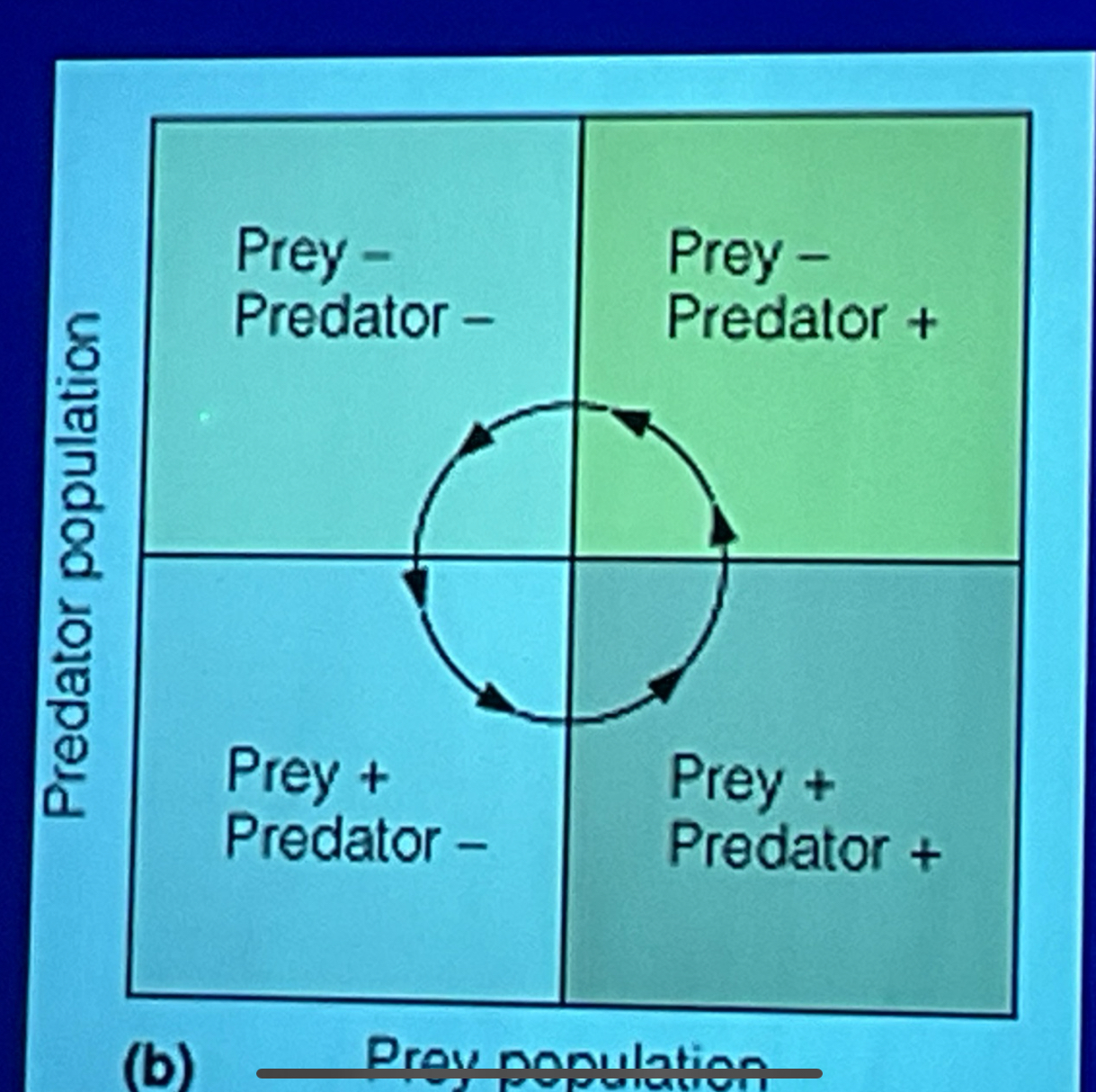
models of predator prey interactions
predator and prey populations cycle (sometimes), predator population lags slightly. Eventually stability because of interactions between the populations.
factors that cause cycles
habitat complexity, other species, genetics, hormones, evolution. but we dont know for sure what causes it.
reproductive response to prey
is the change in predator reproductive rates in relation to the abundance of prey populations. When prey is abundant, predators may have higher reproductive success, influencing population dynamics.
agressive response to prey
is the behavior exhibited by predators that increases with the availability of prey, leading to enhanced hunting efficiency and higher predation rates.
developmental response to prey
have plenty of food to develop faster and and reproduce sooner
functional response to prey
refers to the change in the rate of predation as prey density changes. It describes how predators adjust their feeding rate based on the availability of prey, impacting predation pressure.
Chase it down
predator must be faster than prey, have good endurance and can handle prey on your own.
Sit and wait: ambush
deceit (camouflage, angler fish, mimicry). Strategy may depend on body condition (cool lizards vs warm ones). Ambush techniques vary (spiders specializes on harvestor ants (traop door))
Use tools
Use an aspect of the enviornment to help in foraging, prode for termites, under bark for grubs, etc, sea otter use rock to carry around, egyptian vulture, ant lion, archer fish.
Cooperate with others
common in carnivors (especially cats, dogs, and hyenas), can overwhelm otherwise unmanageable prey (pack hunters, social foragers, white pelicans, bubblenetting)
Benefits for cooperation
more efficient, protection (viglance)- more time to eat. can handle prey otherwise impossible.
Costs of cooperates
have to share, increased conspicouousness, have to obtain more food.
preys compensatory responses
are behavioral or physiological adjustments by prey species in response to predation pressure, aiding in survival and resource acquisition. constitutive vs inducible
preys defensive responses
include a range of behaviors and adaptations that prey species employ to avoid detection and capture by predators, such as camouflage, fleeing, and forming groups.
mechanical defenses
such as shells, spines, or armor that physically protect prey from predators.
chemical defenses
are toxic substances or deterrents produced by prey species to fend off predators, making them unpalatable or harmful. like poison ivy
social defenses
are strategies prey use to enhance survival through social behaviors, like flocking or herding, which confuse predators and decrease individual risk.
behavioral defense
involves actions taken by prey to avoid predation, such as hiding, fleeing, or displaying warning signals to deter predators. alarm calling
camouflage
crypsis that allows prey to avoid detection by blending into their environment. form of mimicry
Aposematic coloration
is a warning coloration strategy used by prey to signal to predators that they are toxic or unpalatable, enhancing survival by deterring attacks.
Batesian
mimicry is a survival strategy where a harmless species evolves to resemble a harmful or unpalatable species, thus deceiving predators. model is unplatable, mimic is platable
Müllerian
mimicry is a form of mutualistic mimicry where two or more unpalatable or harmful species evolve similar warning signals. This reinforces the avoidance behavior of predators. Both model and mimic are unpalatable
parasitism
consume only part of host item- usually dont kill it outright, attack relatively few hosts in lifetime
Cannibalism
form of predation, reduce population density, reduce stress, weed out runts, help your own offspring
“True” predators
kill prey more or less immediately =, consume several or many prey in lifetime
Grazers
consume only part of each prey item-usually dont kill it. consume several or many in lifetime. liek cows and horses that are herbivorss
predation vs parasitism
both : one player benefits other is harmed, effect population of exploited. Prey is killed outright and used for sustenance. Host is not killed outright. Parasites usually need host for more tan sustenance. (place to live, transportation (to next host)).
parasites have more than one host
transmission from one host to another may require a vector (carrier).
Micro parasites
bacteria, viruses, protozoans.
Macro parasites
fleas, ticks, worms, plants
ecto-external parasites
lampreys, ticks, mosquitos.
Endo- internal
tapeworms
Holo
obligate parasite that completes its life cycle only with a host. (must have it)
Hemi
facultative parasites (doesn’t have to).
problem for parasites
is how to find and exploit a suitable host without being eliminated. Infect other hosts, intermediate hosts (carrier)
Definitive host
parasite becomes adult and reaches maturity to reproduce
Direct contact (transmission)
spend basically whole life cycle w one host
indirect transmission
different parts of life cycle are spent with different hosts. may change behavior of intermediate host at a particular time in order to “get itself transferred” to the next host.
Facultative or obligate
describes whether a parasite can or must rely on a host for its entire life cycle. Facultative parasites can survive outside a host, while obligate ones cannot.
temporary or permanant
describes the dependence of a parasite on a host, indicating whether it uses the host only for part of its life cycle (temporary) or must be associated with it for its entire life cycle (permanent).
interspacific or intraspecific
refers to relationships or interactions that occur either between different species (interspecific) or within the same species (intraspecific). These terms help to categorize competition, predation, and other ecological interactions.
kleptoparasitism
is a form of parasitism where one animal steals food or resources from another, rather than obtaining it through direct predation. This behavior often occurs in species that are able to exploit the foraging efforts of others.
Temporary facultative intraspecific
Brad parasites, common in waterfowl, can lay more eggs, also effectively “spreading around” your kids- safer. describes a parasitic relationship where the parasite only uses its host temporarily and can also parasitize other species, or even members of its own species
Temporary obligate interspecific
Brown- headed cowbird, specialized behaviors of young. a situation where a parasite, while obligately dependent on a host for a portion of its life cycle, is not permanently parasitic
effects of parasitism
can change outcome of competition, can regulate populations of host species, can affect male choices (feather colors), can lead to co-evolution (red queen hypothesis), eventually perhaps to mutualistic relationship
Mutualisms
interactions are positive for both participants. Reationship may depend on enviornmental conditions. Again may be facultative or obligate, symbiotic or not.