Multi-store model of memory
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
multi-store model
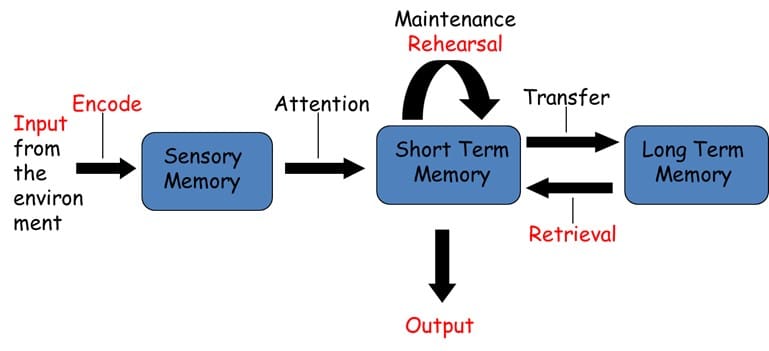
Atkinson and Shiffrin (1968) proposed that memory has more than one store. This is called the multi-store model:
•Memory is made of 3 stores: sensory, STM and LTM.
•For information to get to the stores it must be encoded.
•Each memory store has its own capacity – some stores are bigger than others.
•Each memory store has its own duration – some stores hold information for longer than others
//
•This model attempts to show how information flows from one storage system to another in a linear fashion i.e. one-way, straight line
•
•The model sees sensory memory, STM and LTM as permanent structural components of the memory system.
•Each store has different capacities, duration, encoding and forgetting
•
•Rehearsal is a key control process :
-To transfer information from STM to LTM
sensory register (SR)
•First storage system of the MSM.
•Automatically responds to sensory information being received from the environment.
•There are separate sensory stores for different sensory inputs e.g.
Echoic store (auditory info)
Iconic store (visual info)
Haptic store (tactile info)
Gustatory store (taste info)
Olfactory store (smell info)
•Information is coded in the SR in a raw, unprocessed form
•Duration = less than half a second
•Capacity = high
•Attention to sensory register will allow it to further into the memory system
short term memory (STM)
•Information in the STM store is coded in an auditory/acoustic form.
•The duration of information in the STM store is a maximum of 30 seconds. This can be extended by rehearsal of the information. If rehearsed long enough, this information transfers to the LTM store.
•The capacity of the STM store is 7 (+/-2) items or chunks.
long term memory (LTM)
Information is coded in the LTM in a semantic form.
The duration of information in the LTM potentially unlimited. The stronger or deeper the encoding of LTM the longer the duration of the memory.
The capacity of the LTM is also potentially unlimited. Information may be lost due to displacement, retrieval failure, interference etc. but not because of the limited capacity of the LTM store.
environmental stimuli
Information from the environment that enters the brain via the senses e.g. the teacher talking
attention
Selectively concentrating on a piece of information e.g. you are selectively concentrating on the words on this board.
maintenance rehearsal
Rehearsal or repetition of information to keep information in the STM store.
elaborative rehearsal
Elaborative rehearsal transfers information from the STM to the LTM by processing it as something meaningful.
Issues and debates
nomothetic approach
experimental reductionism