Lecture 14: Minor Ailments & Responding to Symptoms in Community Pharmacy | Travel Health
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
High risk patient groups
Children
Elderly
Pregnant women
Immunocompromised
Health conditions e.g. respiratory, renal/hepatic impairment, diabetics
Travel sickness
Vey common, sickness when travelling due to brains inability to process conflicting sensory information
Can affect anyone in any mode of tranpsort, more common in young children, women and migraine sufferes
Symptoms: nausea, vomiting, dizziness, sweating, drowsiness, headache, pallor
Management of travel sickness
Ideally stop motion causing sickness
Prevent travel sickness by taking medication prior to travel
Choice based on length/duration of action
Sedating antihistamines e.g. Cinnarizine 15mg tablets (P)
Anticholinergic e.g. Hyoscine hydrobromide 300mcg tablets (P)
Acupressure bands - limited evidence
Sun protection
Natural way of getting vitamin D and elevates mood
Sun damages skin by UV radiation - causes skin tanning and skin burns
Skin cells, melanocytes produces melanin on exposure to UV light which causes darkening of skin
UV radiation main cause of skin cancer, damages DNA within skin cells
Avoid excessive skin exposure
Wear sunglasses, long sleeve tops
Sunscreens
SPF 50+ provides highest protection
Apply generously to all areas of skin that are exposed, apply 20-30 mins before sun exposure, reapply if going into water, apply before insect repellants/ moisturiser
Sunburn
Inflammatory response to excessive UV radiation that damages the skin, usually settles within 7 days
Symptoms: red skin, hot to touch, sore, peels away after a few days
Sel-care - get out of sun exposure, cool skin by cold shower/bath/compress, drink plenty of cool fluids
Travellers’ Diarrhoea
Passing unformed stools 3 or more times in 24 hours with wither abdominal pain, nausea/ vomiting, fever
Mainly caused by bacteria usuallu E.coli, Camplyobacter, Salmonella and Shigella, spread by consumptin of contaminated food or water
Increased risk in less developed countries, poor hygiene
Usually occurs in first week of travel
Advise hand hygiene, food hygiene and drinking clean water
Management of travellers’ diarrhoea
Self-limiting, usually lasts 3-5 days
Prevent dehydration - drink plenty of fluids especially young/elderly
Oral rehydration salts
Mild/moderate symptoms: antimotility drug e.g. imodium (GSL/P)
Antibiotic use not routinely recommended
Prophylaxis in high risk patients - Ciprofloxacin (POM)
Self-care - wash hands with soap and water, drink bottled water, cook food thoroughly
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
Long distance travel, increased periods of immobility, slower blood flow increases risk of blood clots in a deep vein
Pulmonary embolism (PE) - blood clot blocks blood vessel in lungs
Risk factors - history of DVT/PE, heart/lung disease, over 60 years old, obesity, pregnancy
Symptoms of DVT - redness, swelling in 1 leg, warm skin, throbbing pain in 1 leg, swollen veins
Symptoms of PE - difficulty breathing, chest pain, coughing up blood
Seek immediate heplp
Preventative meausres for DVT
Move around as much as possible
Do calf excercises
Stay well hydrated
Avoid excessive alcohol
Increased risk - anti embolism stockings/graduated compression stockings/flight socks
Aspirin not recommended for prophylaxis of travel DVT/PE
Malaria
Parasitic infection transmitted to humans by bite of an infected femal anopheles mosquito
Mainly occurs in tropcial regions, most cases in Africa
Preventable and curable if diagnosed and treated promptly
Potentially life-treatening disease
Risk of severe disease for pregnant women, children, elderly, immunocompromised
ABCD of malaria prevention
A - awareness of risk
B - bite prevention
C - chemoprophylaxis: use of appropriate malaria prevention tablets
D - diagnosis: prompt diagnosis and treatment
Bite prevention
Guaranteed way to avoid contracting malaria
Insect repellent’s - stop mosquitoes landing on skin
Clothing - prevents mosquitoes reaching skin, wear loose fitting clothes with long sleeves, high neckline
Accomodation - keep dopors/windows closed in the evening/night
Insect repellents
Repels mosquitoes from landing on skin
DEET - most effective and commonly used insect repellent
Concentration of 50% recommended for malaria areas
Above 50%, not to be applied directly to skin as causes skin irritation
Less than 50%, apply more frequently
Mosquito nets
Create barrier betwen mosquito/insects and skin, especially when sleeping
More effective if impreganated with insecticide
Nets can be retreated with insecticide
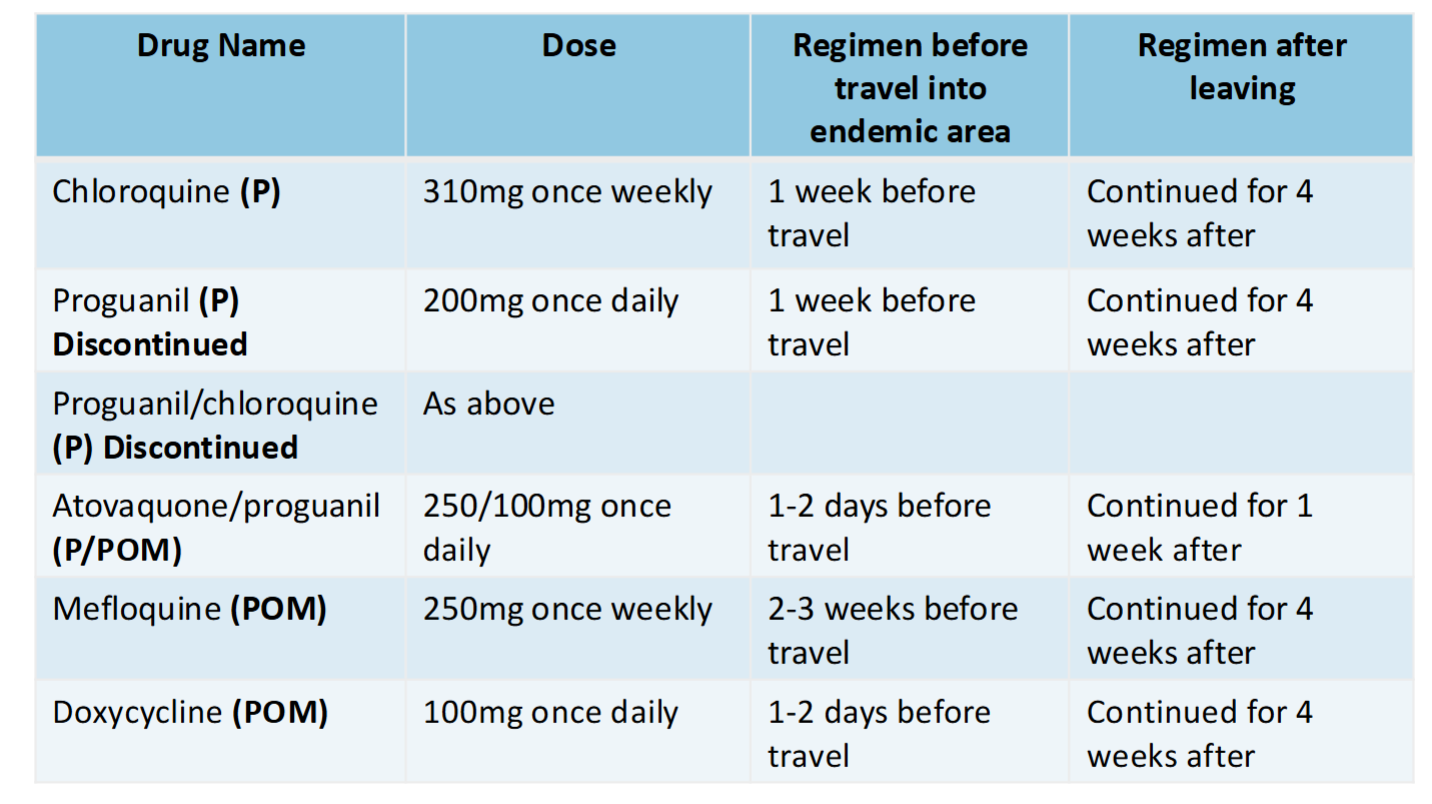
Chemoprophylaxis
Antimalarial tablets don’t prevent mosquito bites but help to stop spread of infection and symptoms
No regemin is 100% effective but antimalarial medication with bite prevention measures provides significant protection
Ensure appropriate for destination according to guidelines, tailored to individual
Full clinical history - medical conditions, current medication, allergies
Antimalarial tablets taken before, during and after visiting the malaria area
Differ in dosage, side effects, regimen
Malaria diagnosis
Any illness especially fever, cold, flu like symptoms that occur within 1 year and especially within the first 3 months of return may be malaria
Advise patients seeks immediate help and specifically mention risk of exposure to malaria
Even if recommended precautions against malaria were taken
Symptoms of malaria
Headache
Dry cough
Vomiting, nausea
Fever, shivering, jaundice
Pain, fatigue, convulsions
Travel vaccinations
Reduce risk of contracting certain diseases from other countries by being vaccinated
Vaccinations are available to protect against: Hepatitis A, Meningococcal meningitis, Poliomyelitis, Tetanus, Typhoid fever, Yellow fever
Available form GP, private travel clinics
First Aid Kit
Tailored to specific individual, destination
Wound care - bandages, dressings, plasters, blister plasters, steri strips, gauze, sterile saline solution, antiseptic wipes, sling, tweezers safety pins, scissors, disposable gloves, setrile eye wash
Thermometer
Pain killers e.g. paracetamol, ibuprofen
Antihistamines e.g. loratadine
Antihistamine/corticosteroid creams e.g. mepyramine
Other considerations
When taking medication abroad, check rules of the country you’re travelling to, contact embassy
Carry medication in hand luggage, keep in original packaging, ensure sufficient supplies
Carry a list of prescribed medication
Controlled drugs - letter from GP
Copy of vaccine records
Proof of travel health insurance
Contact card - details of next of kin