Practical 4 BIO 2
1/1044
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
1045 Terms
What four characteristics are shared by all chordates and what are their function?
Notochord (muscle attachment)Hollow dorsal nerve cord (nerve signal transmission)Pharyngeal slits (various functions)Post -anal tail (movement)
What are the three subphyla included in this phylum?
- Urochordata (sponge-like) 2. Cephalochordata/Lancelet 3. Vertebrata
When did chordates appear in the fossil record?
550 million years ago during the Cambrian period
What are the chordata characteristics found in the adults in this subphylum? (Urochordata)
Pharyngeal slits
What are they considered the closest relative to?
Closest relative to vertebrates
What kind of diet do tunicates have?
Omnivorous diet; filter feeding on planktonic plants and animals
What habitat are tunicates found in?
Benthic Marine
What are the chordate characteristics found in the adults in this subphylum (Cephalochordata)?
Contains all 4 chordate characteristics: Pharyngeal slitPost-anal tailHollow dorsal nerve cordNotochord
What is unique about the way lancelets breath?
Lack a respiratory system; breathe through their skin
What type of diet do lancelets have?
Omnivorous diet; filter feeding on planktonic plants and animals
What are the chordate characteristics found in the adults in this subphylum? (Vertebrata)
All 4 chordate characteristics with some modifications: Pharyngeal slitPost-anal tailHollow dorsal nerve cordNotochord
What type of lifestyle do they demonstrate?
Free-living animals
When did vertebrates diverge from other chordates?
500 million years ago during the Cambrian period
"What is a ""fish""?"
Aquatic chordates with appendages developed as fins (when present)Chief respiratory organs are gillsBody usually covered in scales
What are the four major groups of fish?
- Jawless 2. Cartilaginous 3. Lobe-finned 4. Ray-finned
What are the four types of fish scales, and what groups typically have each kind of scale?
- Jawless fish lack scales 2. Cartilaginous fish have placoid scales 3. Lobe-finned fish have ganoid scales 4. Ray-finned fish have ctenoid and cycloid scales
How do fish scales differ from reptile scales?
Fish scales are made from dermal tissue (vs. reptile scales made from epidermal tissue)
What are the four types of reproductive strategies found in fish? Know the definition of each.
- Ovuliparity: female lays unfertilized eggs, externally fertilized by the male (ex. bony fish) 2. Oviparity: the mother deposits internally fertilized eggs, develop and hatch outside of mother's body (ex. sharks, some bony fish) 3. Ovoviviparity: internally fertilized eggs are retained in oviduct, develop without any nourishment from the mother (ex. few sharks) 4. Viviparity: young develop in mother's uterus, nourished by the mother before being born (live birth) (ex. some sharks, some bony fish)
What do all fish in this superclass lack? (Agnatha - Hagfish)
Lack scales, jaws, and paired appendages
How do hagfish differ from lampreys?
Lack true eyesLack a stomachHave barbels around their mouth
what do hagfish produce?
Produce large quanities of slime/mucus when attacked
What can they do to their bodies and what is the function of this behavior?
Tie themselves in a knot to: secrete slime/mucus or to provide leverage when feeding
Where are hagfish found geographically? How do they find their prey?
Geographically found in temperate ocean waters worldwideBenthic scavengers that find their prey using sense of smell
What are lamprey larvae called? Where are they found and how do they obtain food?
Called ammocoetesFound in burrows in freshwater rivers and streamsObtain food by filter feeding
What happens to the lamprey larvae when going through metamorphosis?
Their entire digestive system must be restructured
Where do they typically live and where do they spawn? What is this term for this type of lifestyle?
Typically live in the oceanMust migrate up freshwater rivers to spawnLifestyle is known as Anadromous
What type of feeding behavior is found in some adult lamprey species? How does this differ from the feeding strategy of the lamprey larvae?
Parasitic/feed by attaching their mouth to fish (secrete anticoagulant into the host --> feed on blood and tissues of the host)Ammocoetes (lamprey larvae) are filter feeders
What characteristics do the organisms within this superclass have? (Gnathostomata)
Jawed vertebrates
What did the jaws likely develop from?
Evolved from the skeletal supports of the pharyngeal slits used for filter feeding
What did the develpoment of jaws allow for? How was this significant to vertebrate evolution?
Allowed for utilization of different food typesSignificant to facilitating the radiation and diversification of vertebrates
What is the chondrichthyan skeleton made of? Is this a primitive characteristic?
Lack true boneSkeleton is made of cartilage (non-primitive characteristic)
What other characteristics are found in chondrichthyans?
Tough skin covered by placoid scalesLarge, bouyant liversSpiral valve intestines
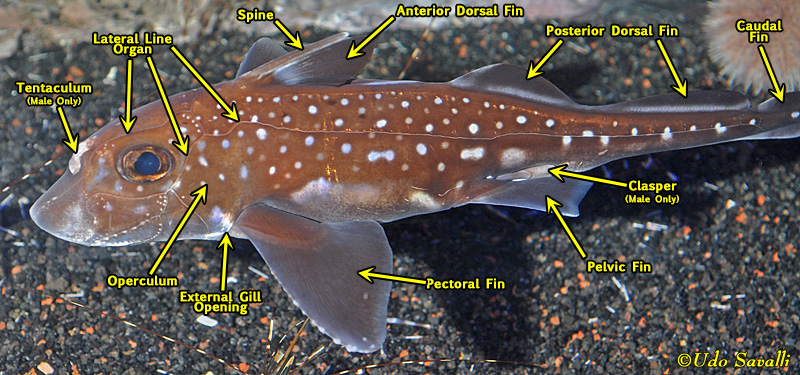
What is the name of the specialized sensory organ found in many chondrichthyans? What does it sense?
Ampullae of Lorenzini: helps sense the electrical fields given off by their prey

How do you tell the difference between males from female chondrichthyans?
Only males have claspers (extensions of the pelvic fins used to transfer sperm during internal fertlization)
What are the two subclasses found in this class? What are their characteristics?
Elasmobranchii (sharks, skates, & rays): have 5-7 gill openings, ridged dorsal fin, and upper jaw detached from skull 2. Holocephali (chimeras): have a gill cover over a single gill opening, a spine in front of so
ft dorsal fin, and an upper jaw fused to their skull

How big do great whites get?
20 ftCan weigh up to 4200 lbs
What type of reproduction do great white sharks have?
Female great whites are ovoviviparous
In the last 100 years, more people have been killed in the U.S. by what animal over this shark?
Dogs
Where are they geographically found? What is the name of the zone where enough light penetrates to sustain photosynthesis? (Great White Sharks)
Found worldwide in coastal and offhsore waters (54-75 degrees F)Epipelagic Zone
What type of diet do they have? (Great White Sharks)
Carnivorous diet
How big do hammerhead sharks get?
18ftCan weigh up to 1000 lbs
What type of reproduction do hammer head sharks have?
Female hammerheads are viviparous
What does the hammer head do for the animal and how many more times effective is it than other sharks?
Spread receptors across larger area making them 10x more likely to detect prey
What type of diet do they have? (Hammerhead Shark)
Carniverous diet
How big do leopard sharks get?
6.5 ftCan weigh up to 40 lbs
How do they differ from their close relatives? How might this benefit leopard sharks?
More red blood cells than close relativesAllow them to process more oxygen in oxygen-poor estuarine environments
What type of diet do they have? (Leopard Shark)
Carniverous diet
How big do whale sharks get?
40 ftCan weigh up to 47,000 lbs
What type of reproductive strategy do whale sharks have?
Ovoviviparous and been found with more than 300 pups
How much water can they filter in an hour?
600 cubic meters (160,000 gallons) of water an hour
What type of diet do they have? (Whale Shark)
Omnivorous diet
What does the caudal fin look like in skates?
Tiny caudal fin with no stinging spines
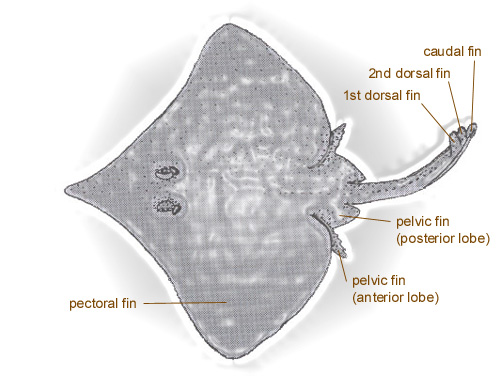
What do stinging spines look like in skates?
Does not have stinging spines
What do pelvic fins look like in skates?
Bilobular pelvic fins
Each pelvic fin divided into two lobes
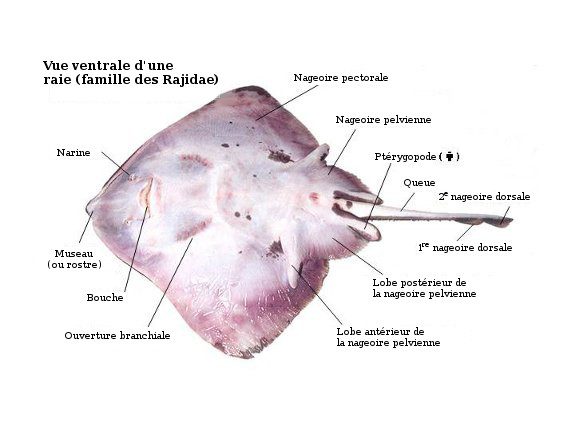
How do skates reproduce?
Oviparous or ovoviviparous
What does the caudal fin look like in rays?
No caudal fin, slender whip-like tail
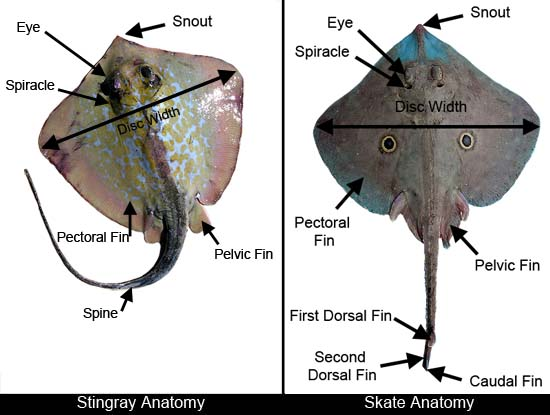
What do stinging spines look like in rays?
Stinging spine near the end of the tail
What do pelvic fins look like in rays?
Single-lobed pelvic fin
How do rays reproduce?
Ovoviviparous
How big do skates get?
2.4 meters in length (about eight feet)
What type of reproduction do skates have, and what are their eggs often called?
Oviparous, hard-shelled eggs called mermaid's purse

What habitats are skates found in?
Coastal bays, estuaries, along continental shelves
What type of diet do skates have?
Polychaetes, mollusks, crustaceans, and small fish
What adaptation do Shovel-nosed Guitarfish (Skates) have that allows them to breathe while buried in the sand?
Spiracles

How are guitarfish different from other rays?
Swim with shark-like tail

Which habitats are guitarfish found in?
Coastal soft bottoms
What type of diet do guitarfish have?
Bottom feeding carnivores
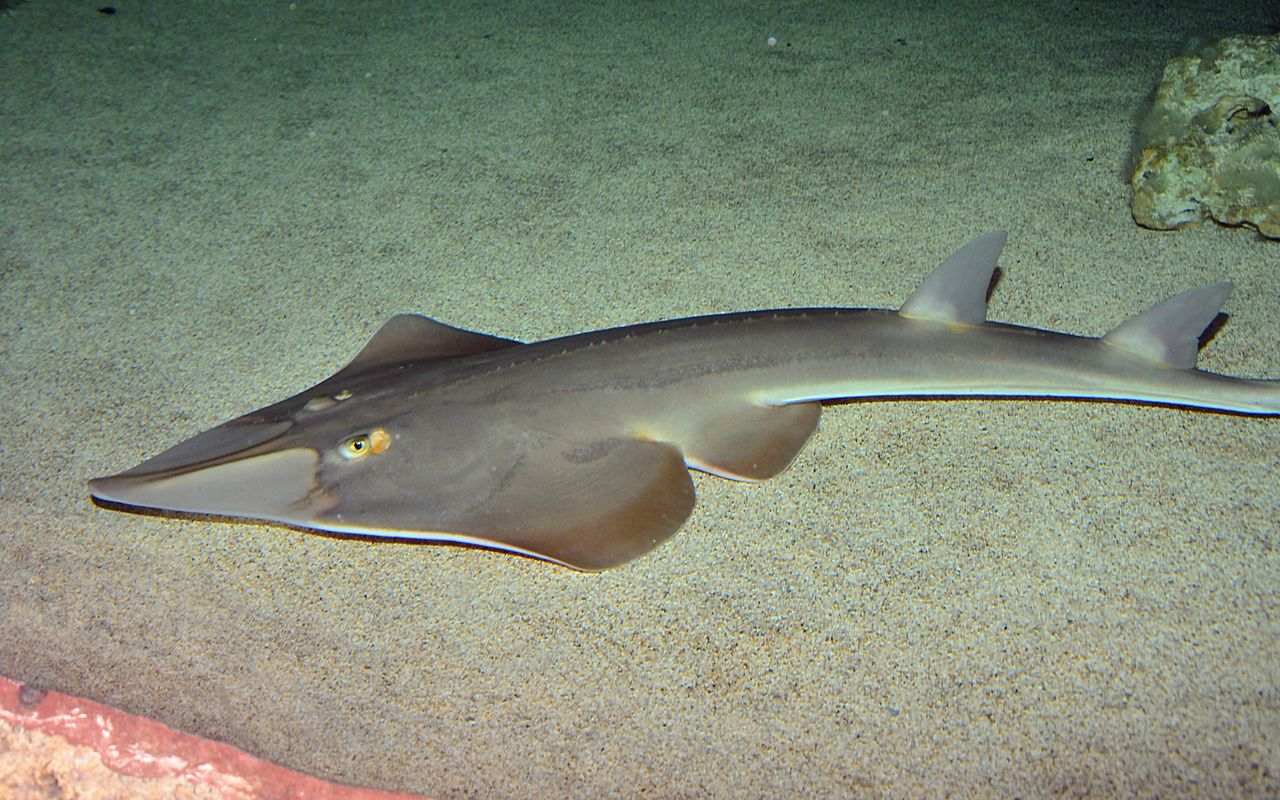
What do sawfish use their rostrum for?
Elongated rostrum with teeth used for hunting and protection.
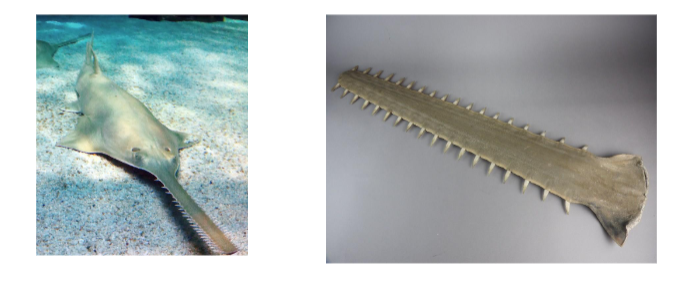
What organ do they have similar to sharks? What does this organ do?
Like sharks, the head and rostrum contain thousands of sensory organs, the ampullae of Lorenzini, that allow the sawfish to detect and monitor the movements of other organisms by measuring the electric fields they emit.
Where are sawfish geographically found? What type of habitat are they found in?
Worldwide in tropical and subtropical waters; Sawfish are primarily found in coastal marine and estuarine brackish waters
What type of diet do sawfish have?
Carnivorous diet; fish crustaceans and molluscs
What adaptation do Round Rays have to protect themselves from predators?
Venomous stinging tail with rear-facing barbs

What habitats are stingrays found in?
Coastal soft bottoms
What type of diet do stingrays have?
Carnivores, eat crabs, mollusks, and polychaetes
How big do Bat Rays get?
6 feet and over 200 pounds
What are bat rays considered?
Euryhaline: able to withstand a wide range of salinities

What habitat are Bat Rays found in?
Coastal sandy bottoms in bays and estuaries
What type of diet do Bat Rays have?
Carnivores, eat mullusks and crustaceans
What type of adaptation do Bat Rays have to better consume their prey?
Rows of flat teeth to grind down the shells of mollsuks and crustaceans
How big do Manta Rays get?
7.6 m (about 25 ft)

What did Manta Rays likely evolve from?
Bottom-feeding rays
How do Manta Rays feed?
Filter-feeders
What habitats are Manta Rays found in?
Open ocean
What type of diet do Manta Rays have?
Omnivores, eat planktonic algae and animals
What are the common names for Chimaeras?
Ratfish or rabbit fish

How do Chimaeras differ from sharks, skates, and rays?
Upper jaws are fused with their skulls Separate anal and urogenital openings Few large permanent grinding tooth plates

What type of diet do Chimaeras have?
Carnivores, feed on benthic invertebrates
What are the skeletons of Osteichthyes made of? (Bony fish)
True bone

What type of scales do Osteichthyes have?
Ganoid, cycloid, or ctenoid scales

What two other adaptations do Osteichthyes have?
Operculum (hard covering over gills) allows them to breathe without actively swimming, and a swim bladder to create a neutral balance between sinking and floating

What two classes have Osteichthyes been divided into?
Sarcopterygii: lobe-finned fish Actinopterygii: ray-finned fish
What is unique about the coelacanth fins?
Lobe-finned, with pectoral and anal fins made up of fleshy stalks supported by bones
tail divided into three lobes

What specialized adaptation do Coelacanths have that helps them detect prey?
Electro-receptive device called rostral organ
What habitats are Coelacanths found in?
Rocky bottom at depths of 100-300 meters
What type of diet do Coelacanths have?
Carnivores, eat fish, cephalopods, and small sharks
What type of fins do Lungfish have?
Lobe-finned

What are Lungfish best known for?
Their ability to breathe air using a lung that is homologous to tetrapods
What adaptation do Lungfish have that allows them to survive desiccation?
Burrows into the mud and estivating through the dry season
What habitats are Lungfish found in?
Freshwater
What type of diet do Lungfish have?
Omnivores with an extremely diverse diet. Fish, insects, mollusks, worms, crustaceans, and plants