biotech unit 2
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
C.H.O.P.N.S
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, Nitrogen, and Sulfur
Carbon
can form up to four bonds, and can participate in covalent and ionic bonding
Covalent bonding
electrons are shared between atoms
Ionic bonding
one atom takes away valence electron(s) from another atom
Structure = Function
structure of a molecule determines its function
Variation in carbon skeletons
arrangements of carbon atoms in organic molecules, including differences in length, branching, double bonds, and rings
Isomers
Compounds with the same formula but different structure
Hydrolysis
breaking down large molecules into smaller ones by adding water
Dehydration synthesis
building larger molecules by removing water
Functional groups
Groups of atoms within a molecule that behave the same way regardless of the molecule they are attached to, and can affect the function of the molecule
Monomers
Single building blocks that make up larger molecules
Monosaccharides
Simple sugars with a CH2O, which serve as nutrients for cells and are involved photosynthesis
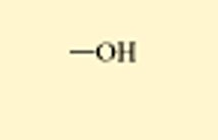
what is this
hydroxl, alcohol
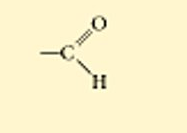
?
carbonyl, aldehyde
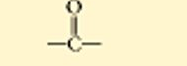
??
carbonyl, ketone
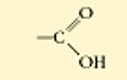
?
non ionized carboxylic acid
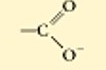
??
ionized carboxylic acid
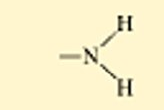
??
non ionized amine
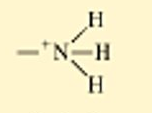
??
ionized amine
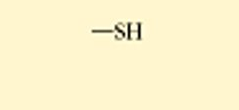
1) —— and a 2) ——
sulfhydryl and thiol
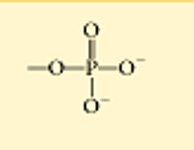
??
organic phosphate