Urinary System: Renal and Bladder
1/180
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
181 Terms
what does the urinary system consists of?
kidneys
ureter
urinary bladder
urethra
what makes up the upper urinary tract?
kidneys and ureter
what makes up the lower urinary tract?
urinary bladder and urethra
when someone has hypertension, what organ should the sonographer look at?
kidneys because they are closely related to blood pressure
kidneys
aka renals
located in retroperitoneum on each side of spine
bean-shaped
9-12 cm (in adult)
excretory organ
function of the kidneys
maintain body’s chemical equilibrium
maintain composition of blood, blood pressure, and pH balance (through excreting waste products)
which kidney is lower and shorter?
right kidney (because it is pushed down by RLL; closer to bladder)
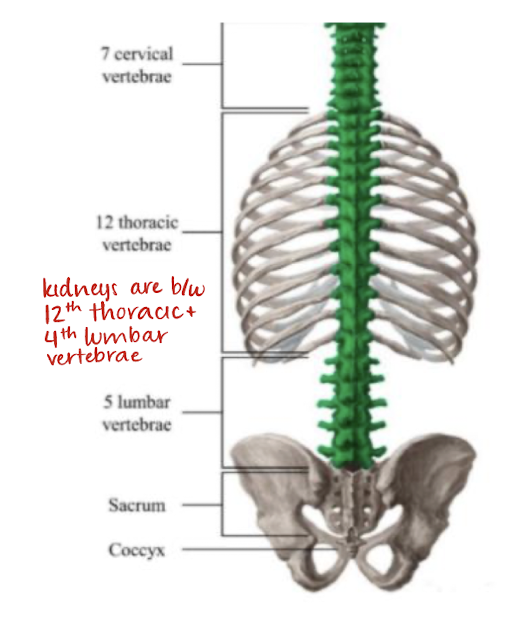
kidneys lie between what vertebrae?
12th thoracic and 4th lumbar vertebrae
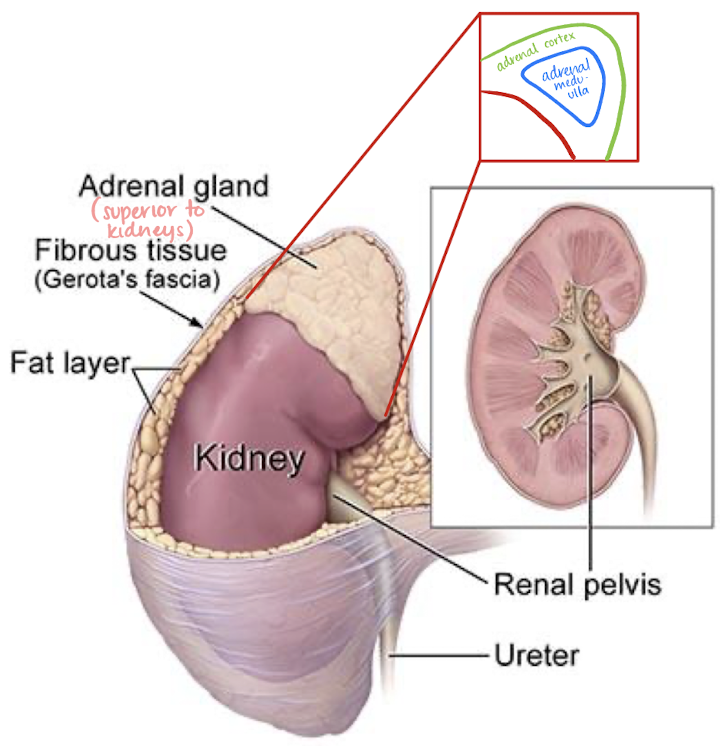
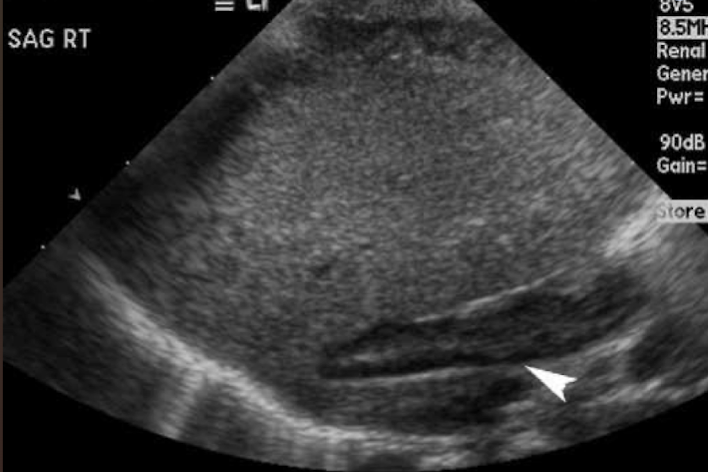
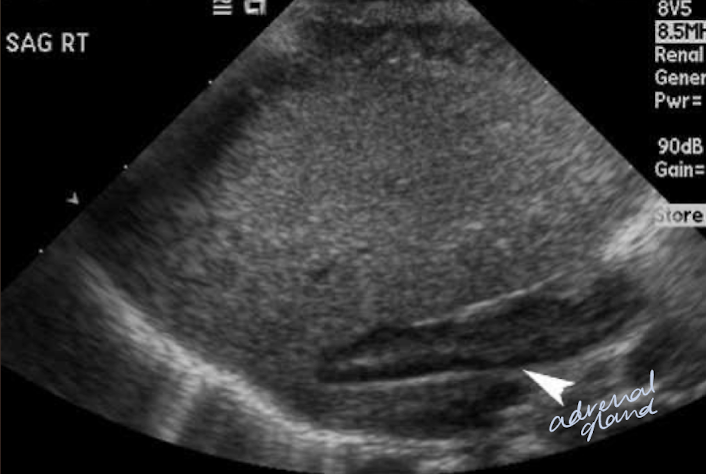
adrenal glands
endocrine organ
could possibly be seen with US in infants and young children
consists of an independently functioning cortex and medulla
supplied by suprarenal arteries
drained by suprarenal vein
adrenal cortex
has 3 zones that produce steroids called corticoids
aldosterone
cortisol
sex hormones
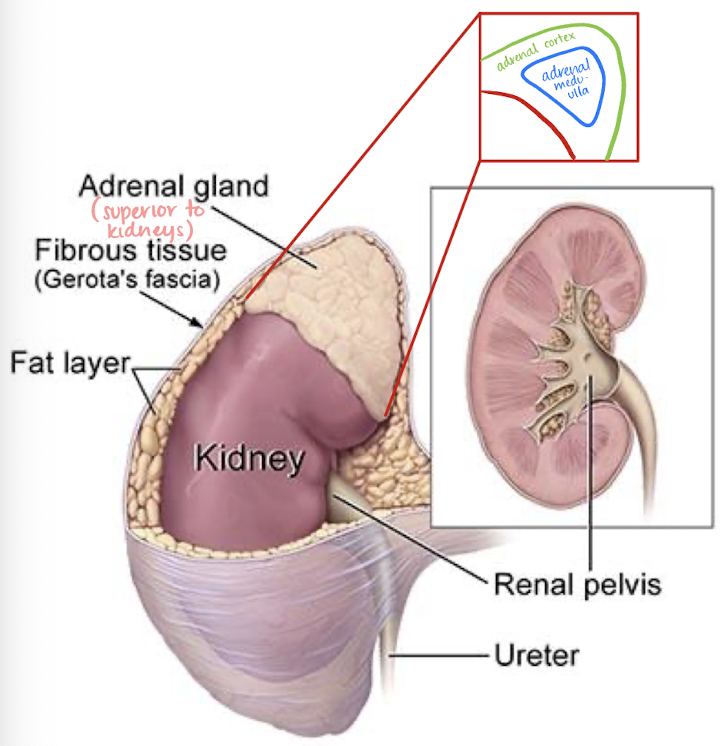
adrenal medulla
secreted epinephrine and norepinephrine
“fight-or-flight response”
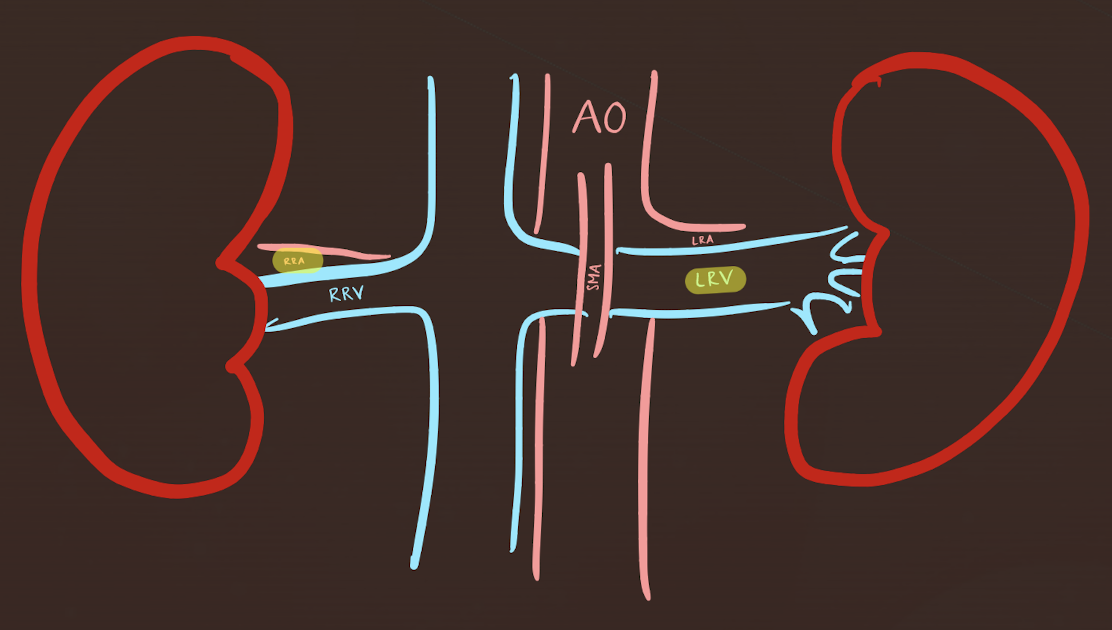
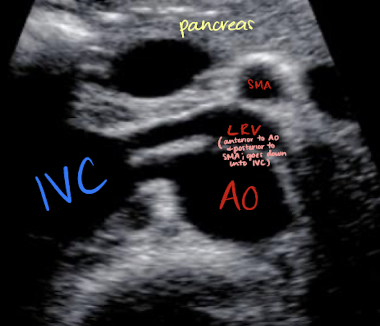
LRV and RRA locations
LRV
anterior to AO; posterior to SMA
runs from left kidney to IVC
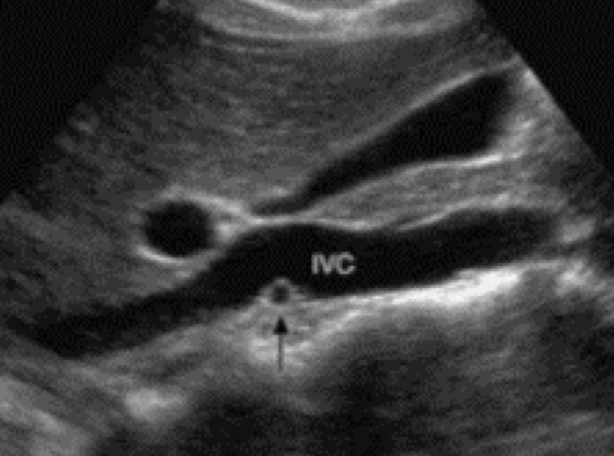
RRA
posterior to IVC (excuse me)
runs from AO to RK
??
LRV
??
RRA
structures anterior to the RK and LK
anterior to RK
right adrenal gland
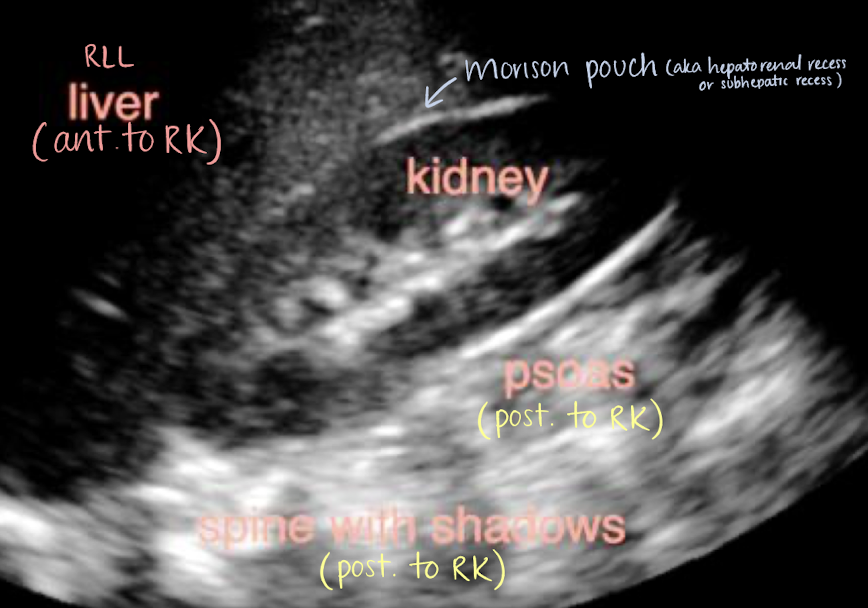
RLL
Morison’s pouch
2nd part of duodenum
hepatic flexure of colon
anterior to LK
left adrenal gland
splenic flexure of colon
coils of jejunum
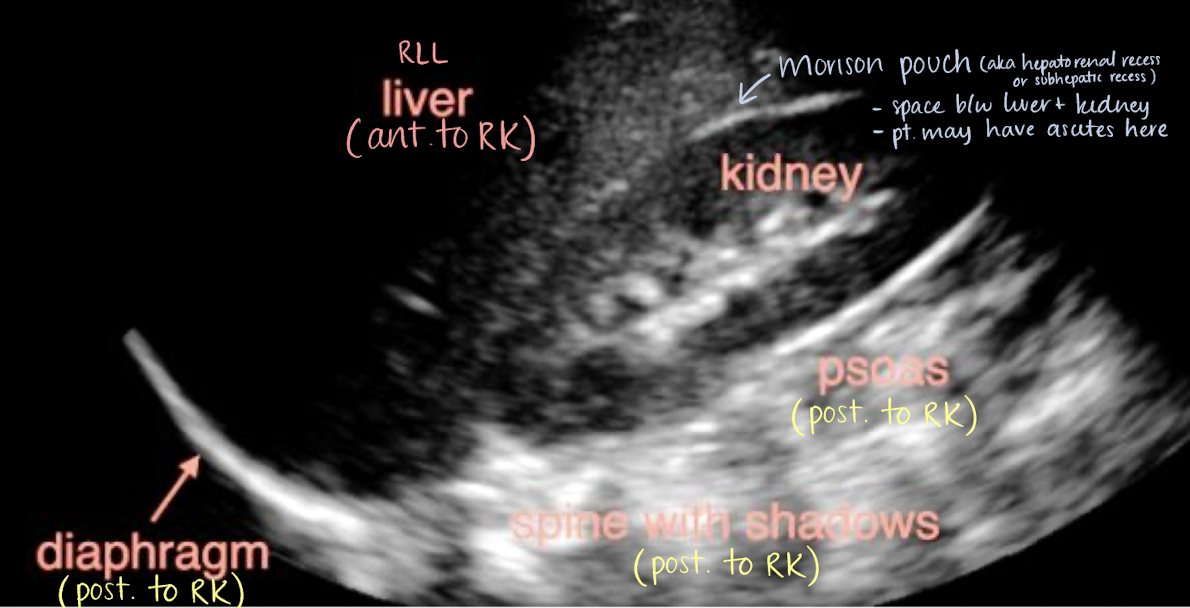
Morison’s pouch
aka hepatorenal recess or subhepatic recess
space between liver and RK
patients may have ascites here
right posterior subhepatic space located anterior to kidneys and inferior to liver where fluid may collect
anatomy of the kidneys
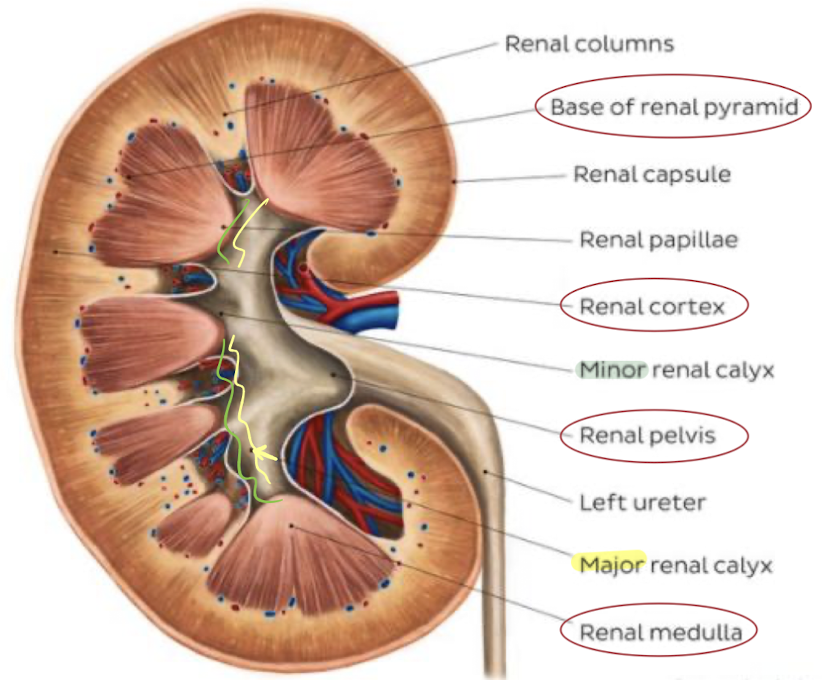
composed of 2 distinct areas:
peripheral parenchyma (cortex and medulla)
central sinus
renal parenchyma
homogeneous
consists of cortex (outer) and medulla (inner)
renal cortex
outer parenchyma of kidney
contains renal corpuscle and proximal and distal convoluted tubules
renal medulla
inner portion of renal parenchyma
consists of 8-18 pyramids
pyramids are triangular
apex is located in minor calyx
base is located in renal cortex
pyramids contains the loop of Henle
SONO: anechoic; located just at the hyperechoic/echogenic sinus
what is the loop of Henle responsible for?
filtration and reabsorption
what separates the medullary pyramids?
columns of Bertin—area between pyramids
renal pelvis/sinus
aka renal sinus
area in midportion of kidney that collects urine before entering the ureter
central area of kidney that includes calyces, renal vessels, fats, nerves, and lymphatics
composed of collecting system and renal hilum (includes the artery and vein)
SONO: central, hyperechoic area of kidneys
collecting system
consists of an infundibulum that has a minor and major calyces that receive urine
minor calyces: forms periphery of sinus
major calyces: receives urine from minor calyces
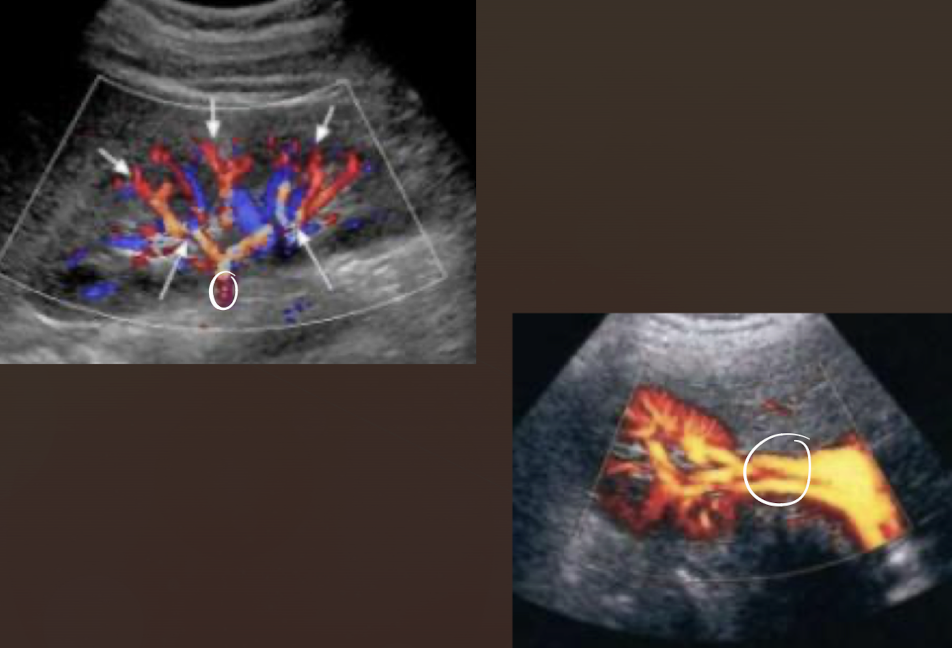
renal hilum (hilus)
medial portion of sinus where artery enters and vein and ureter exits
area in midportion of kidneys where renal vessels, ureter, and lymphatics enter and exit
ureters
retroperitoneal structures that exit the kidneys to carry urine to the urinary bladder
begins as expanded upper area of renal pelvis
urine enters bladder via the ureters every several seconds or minutes
SONO: not seen unless obstruction present
SONO: “jets” in bladder
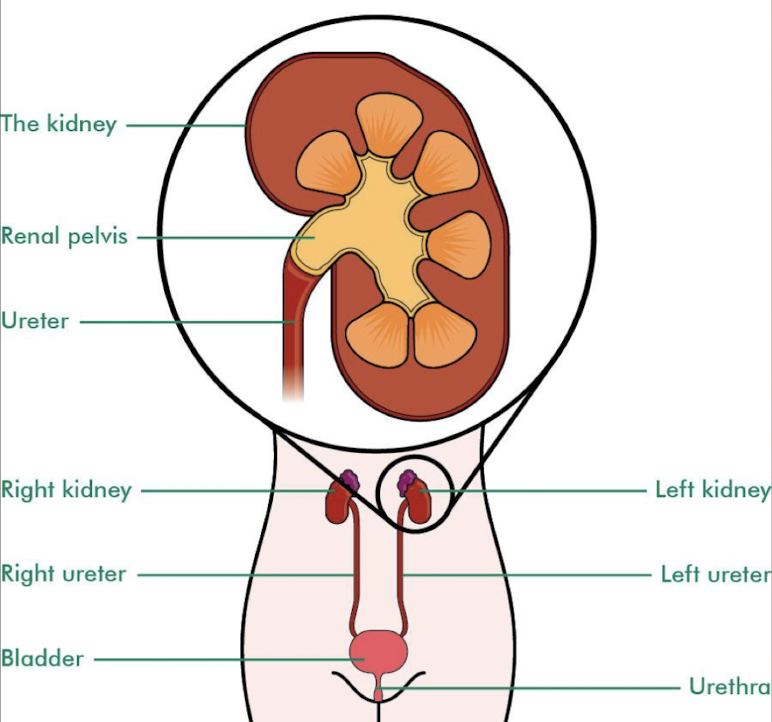
what process allows for urine to be transported from the kidneys to the bladder?
peristalsis
UPJ
short for ureteropelvic junction
near kidneys
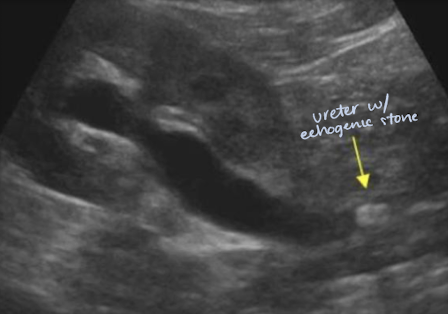
UVJ
short for ureterovesical junction
near bladder
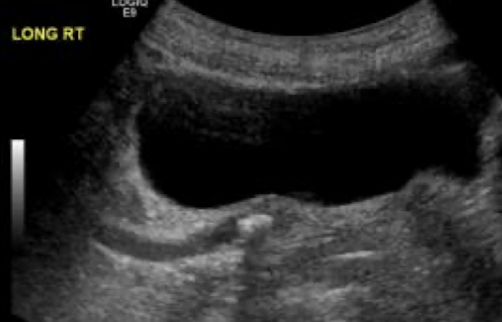
urinary bladder
muscular retroperitoneal organ that serves as a reservoir for urine
midline muscular elastic sac anchored to pelvis by pubovesical or puboprostatic ligaments (in females and males respectively)
bladder wall is primarily composed of the detrusor muscle (smooth muscle)
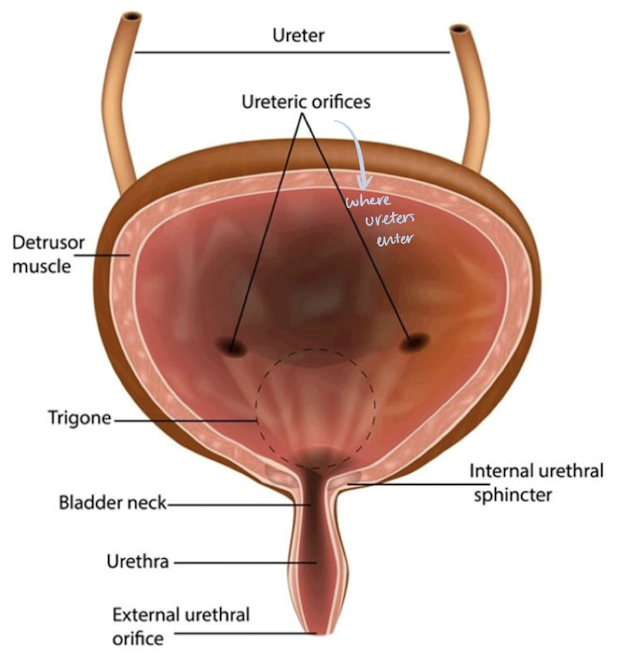
openings:
posterior, lateral openings for the ureters
anterior opening for the urethra
inferior portion of bladder is the base (trigone area) and neck
located between the two ureteral openings and the internal urethral orifice
SONO: bladder wall should be smooth, thin, and hyperechoic (3-6 mm); lumen should be anechoic, urine-filled
detrusor muscles _____ to expel urine
contract (needs to squeeze and expel urine)
urethra
small, membranous canal that excretes urine from urinary bladder
contains internal and external sphincters
male urethra: ~20 cm long
male has 3 parts: prostatic, membranous, and penile urethra
female urethra: ~3.5 cm long
SONO: not routinely visualized (but image shows where it would be)
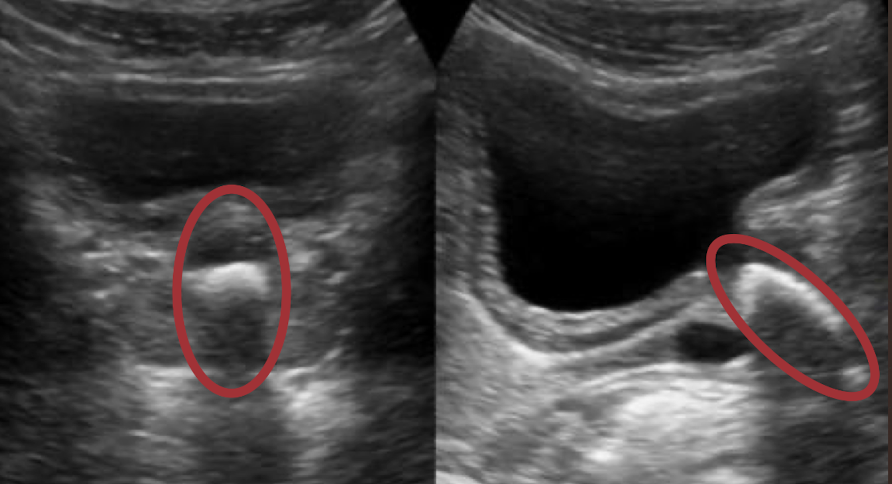
indications for imaging renals
low urine output (low UOP)
flank pain
blood or debris in urine
elevated labs
known renal disease
HTN or diabetes
nephrectomy
surgical removal of kidney(s)
scanning techniques for imaging renals
curvilinear probe; linear probe for peds
pt. supine, decubitus, or oblique
use liver/spleen as acoustic window
have patients take in deep breaths to move diaphragm and kidneys downward
must have 3 kidney measurements (L x H x W)
TCG adjustments
compare renal cortex to liver parenchyma
renal detail may be obscured if patient has hepatocellular disease, gallstones, rib interference, or other abnormal conditions
renal vasculature
M.S.I.A.I.
main renal artery
segmental renal artery
at hilum
interlobar arteries
between/along pyramids
arcuate arteries
at base of pyramids
interlobular arteries
near edge of cortex
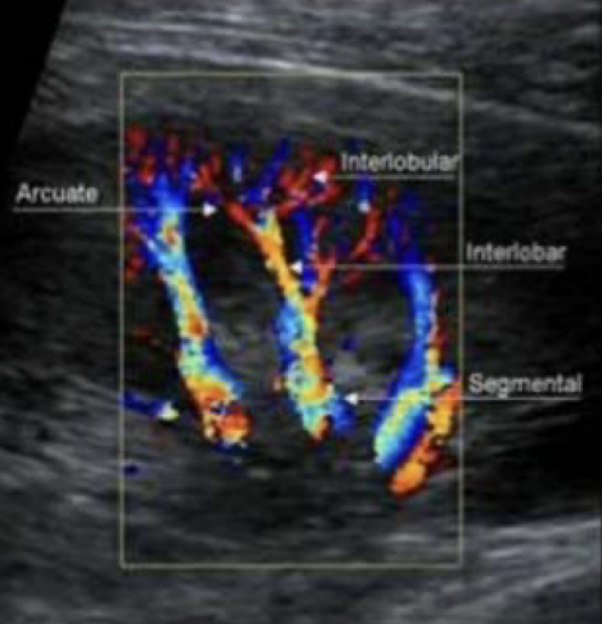
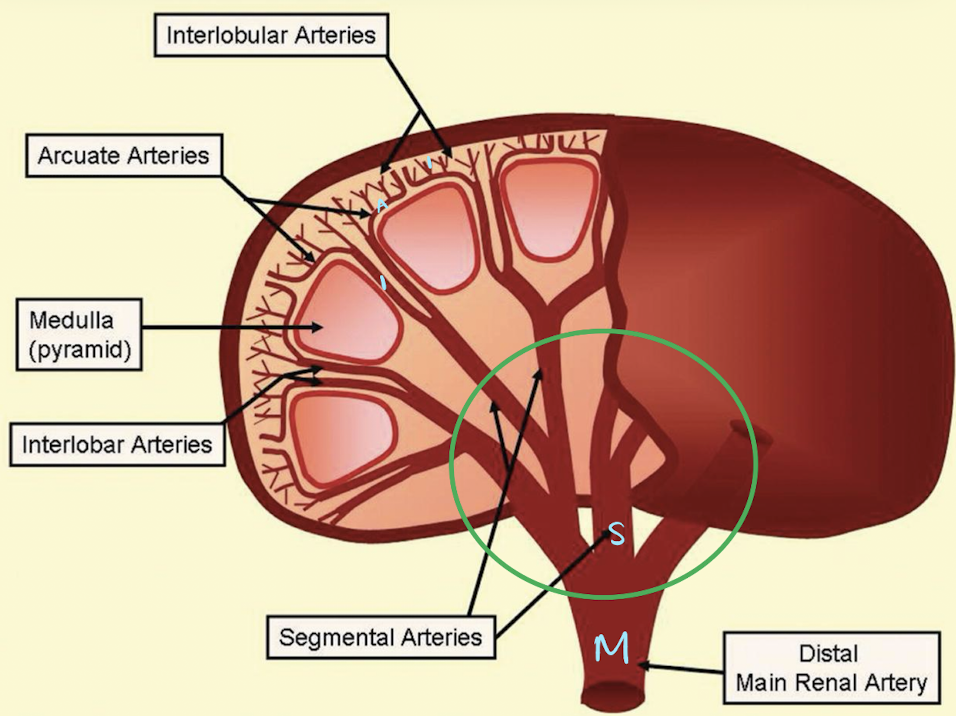
M.S.I.A.I.
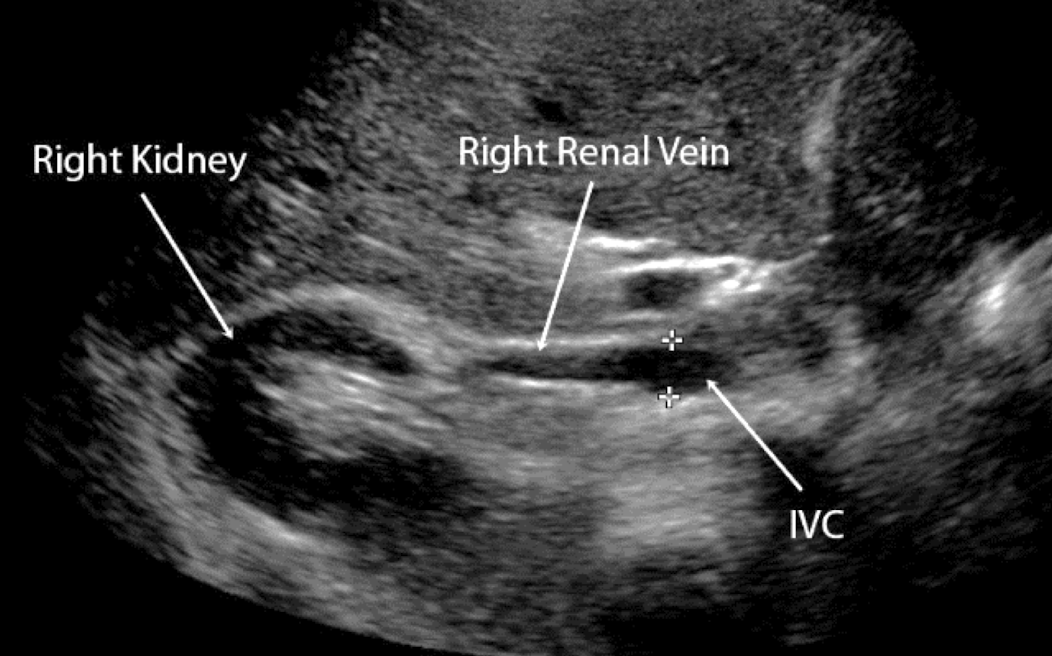
what is the course of the RRV?
RRV extends from central renal sinus directly into IVC
renal physiology
primary function is urine production and homeostasis
excrete waste and maintain blood volume
filter ~1600 mL of blood per minute
produce ~150 mL of urine daily
nephron=functioning unit of the kidneys
cortical nephron (outer; closer to cortex)
juxtamedullary nephron (inner; closer to medulla)
urine is composed of what?
95% water
5% nitrogenous waste and inorganic salts
BUN (blood, urea, nitrogen)
Cr (creatinine)
nephron and urine production (steps)
filtration
1st step in urine formation
tubular reabsorption
takes place in proximal convoluted tubule (65%) AND
ascending and descending loop of Henle
tubular secretion
urine exits distal convoluted tubule and flows through collecting ducts —> renal pyramids that lie in minor calyx —> major calyx —> renal pelvis —> ureter —> bladder —> urethra
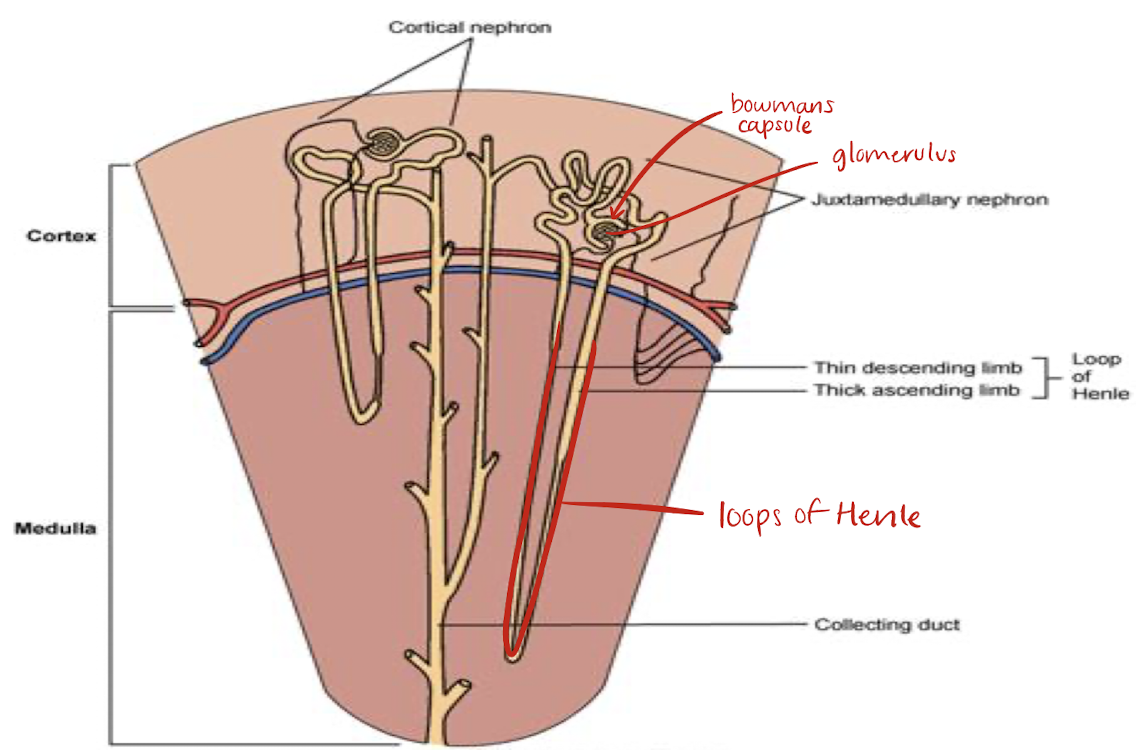
Bowmans capsule
site of filtration in kidneys
contains water, salts, glucose, urea, and amino acids
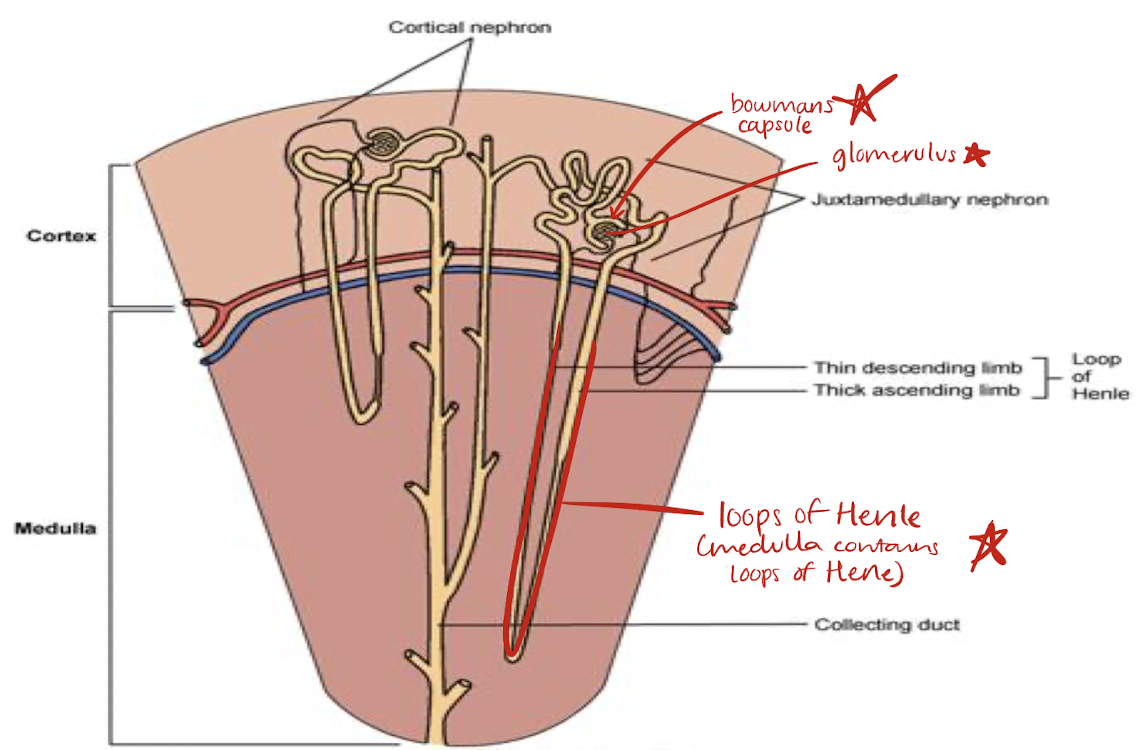
glomerulus
network of capillaries that are part of filtration process in kidneys
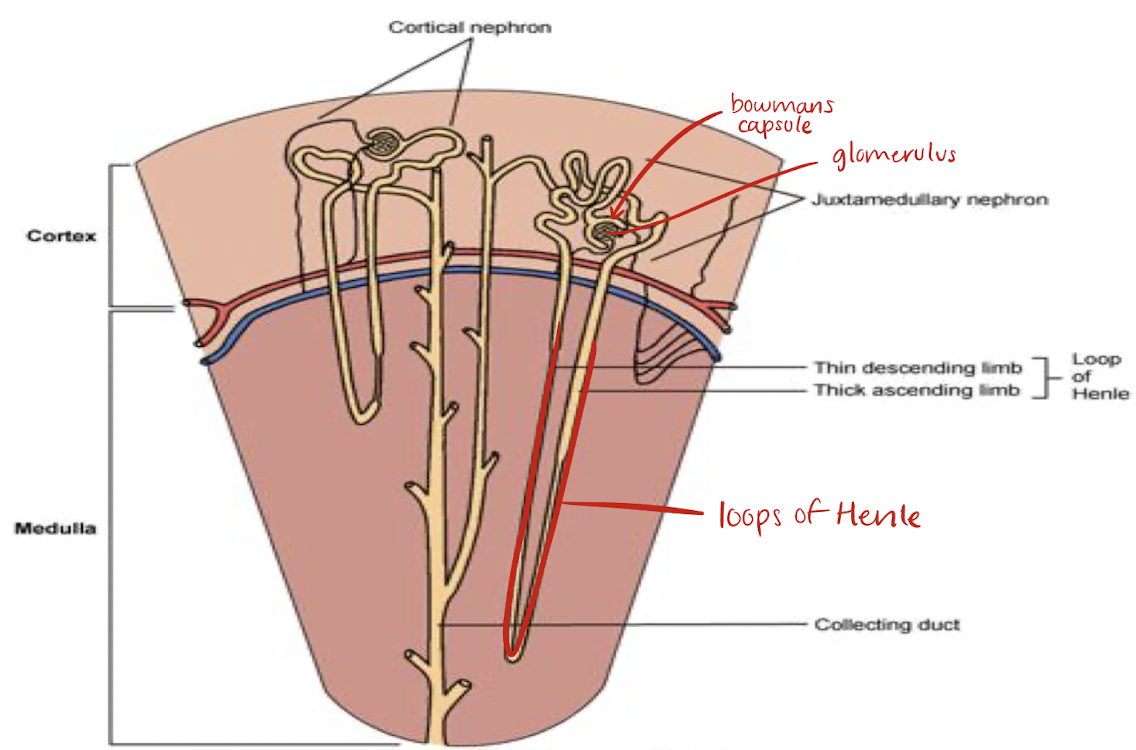
loop of Henle
located in medulla
portion of renal tubule lying between proximal and distal convoluted portion
reabsorption of fluid, sodium, chloride occurs here and in proximal convoluted tubule
lab values associated with kidneys
urinalysis
urine pH
specific gravity
blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
hematocrit
hemoglobin
protein
creatinine clearance
glomerular filtration rate
renal variants and anomalies
prominent columns of Bertin
dromedary hump
extrarenal pelvis
junctional parenchymal defect
fetal lobulation
renal agenesis
horseshoe kidney
ectopic kidney
double collecting system
prominent columns of Bertin
invagination of cortex into medulla; indent of renal sinus (between pyramids)
??
prominent columns of Bertin
dromedary hump
bulge in cortex; pyramids go up with the buldge
??
dromedary hump
extrarenal pelvis
central cystic pelvis that extends outside the pelvis; best seen in TRANS
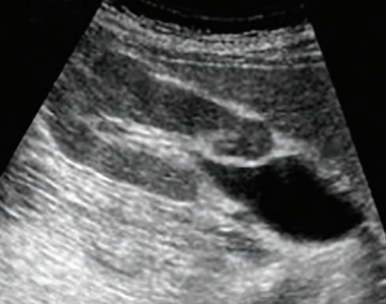
??
extrarenal pelvis
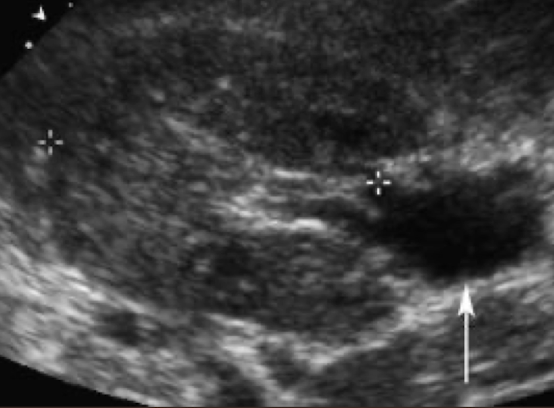
junctional parenchymal defect
echogenic triangle located anteriorly and superiorly—congenital; best seen in SAG
??
junctional parenchymal defect
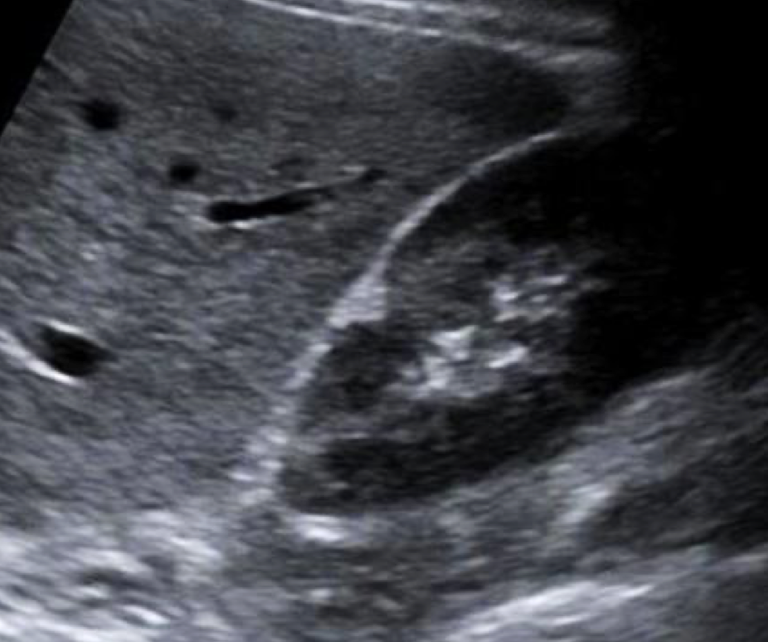
fetal lobulation
lumpy kidney—not smooth
??
fetal lobulation
renal agenesis
absence of kidney
leads to enlarged kidney and enlarged adrenal gland in peds
sonographer should still image kidney area (“right renal fossa”) and take cine in SAG and TRANS to ensure there is no mass
??
renal agenesis
horseshoe kidney
fusion of lower poles, connected via isthmus (anterior to spine and AO)
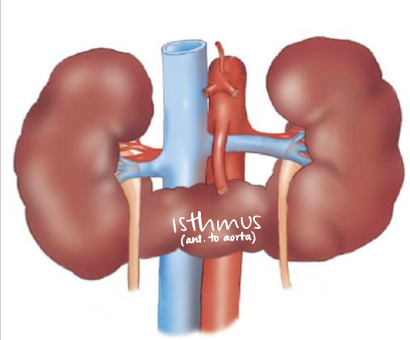
??
horseshoe kidney
ectopic kidney
aka sacral kidney; adjacent to pelvis
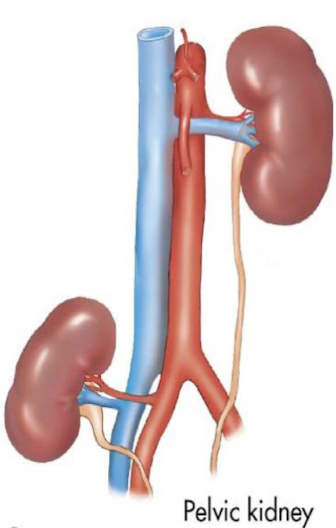
??
ectopic (or sacral) kidney
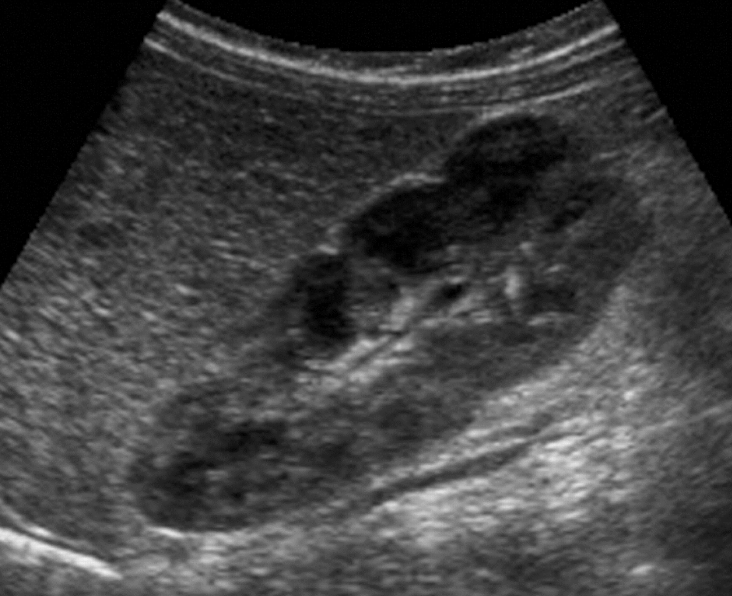
double collecting system
duplex system—2 ureters and 2 renal sinuses
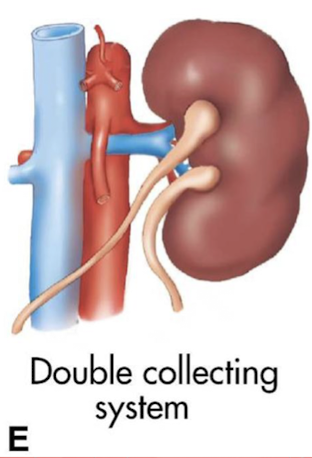
??
double collecting system
what method is used to determine the appropriate work-up for a cystic mass?
Bosniak classification system
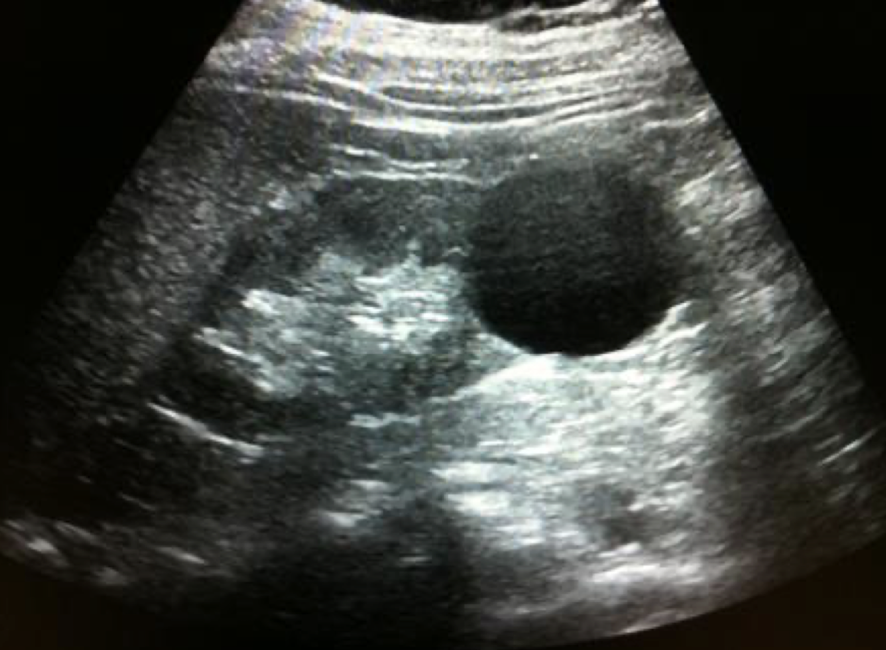
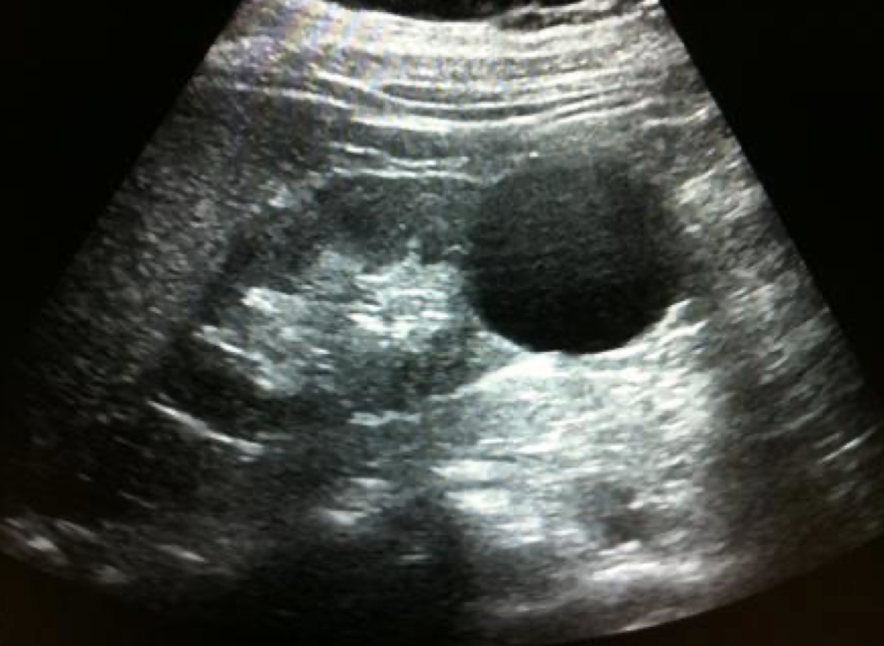
cystic mass
anechoic
smooth, thin, well-defined
round or oval shape
sharpe interference between cyst and renal parenchyma
increased posterior acoustic enhancement
describe
“cystic structure with posterior enhancement measuring 3 cm x 3 cm x 3 cm noted in LP or RK”
simple renal cyst
MC renal mass lesion
occur in 50% of population
solitary or multiple
s/s: asymptomatic—often incidental finding
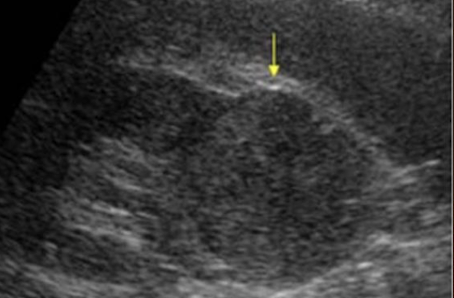
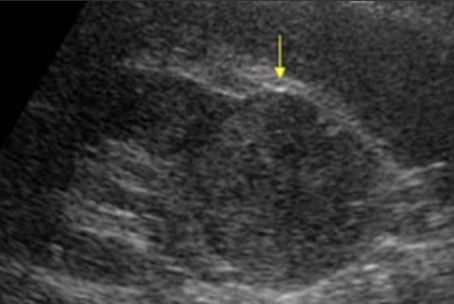
solid mass
echogenic shades of gray representing tissue (low-level internal echoes)
? irregular borders
? weak posterior borders
poorly defined interface between mass and kidney
poor through-transmission
describe
“solid structure measuring 3 cm x 3 cm x 3 cm noted in LP of RK. no vascularity noted within”
complex mass
shows characteristics of both cystic and solid lesions
may contain septations, thick walls > 1 mm, nodularity, calcifications, internal echoes from areas of necrosis, hemorrhage, or abscess/infection
** if there is septation in cyst, put color box on it, especially if its thick
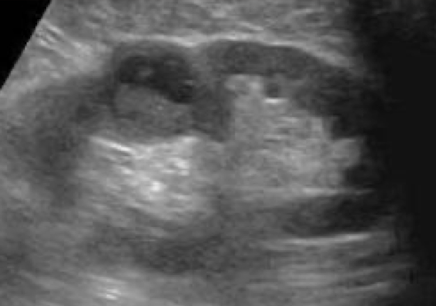
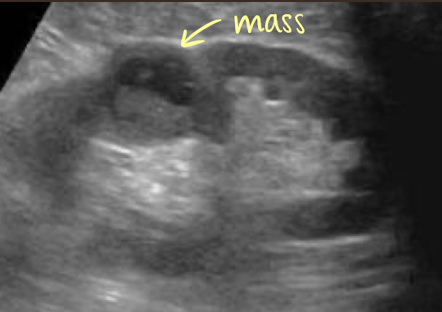
describe
“complex structure measuring 3 cm x 3 cm x 3 cm noted in UP/MP LK. vascularity noted within”
complex cyst
may contain septations, thick walls, calcifications, internal echoes, and mural nodularity
considered malignant until proven benign, especially if septa >1 mm thick with vascular flow on color or Power Doppler
any irregularity at the base of the cyst should be considered a malignant growth
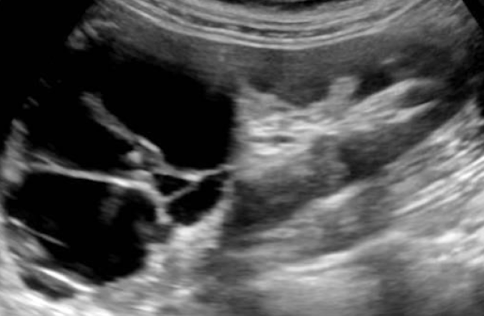
??
complex cyst
has septations and solid components
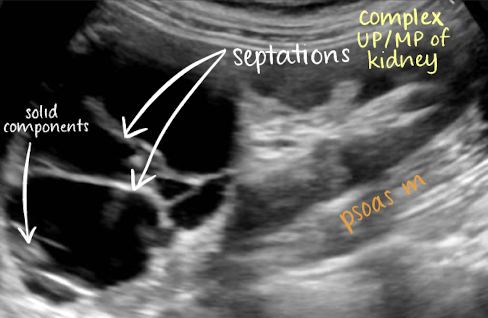
renal cysts associations
von Hippel-Lindau
tuberous sclerosis
acquired cystic kidney disease or acquired cystic disease of dialysis
von Hippel-Lindau
autosomal dominant genetic disorder involving many body systems
abnormal growth of blood vessels called angiomas develop (retinal)
SONO:
multiple cortical cysts
abdominal cysts
tuberous sclerosis
autosomal dominant genetic disorder
characterized by mental retardation and seizure
SONO:
angiomyolipomas
multiple renal cysts
differential dx: adult polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) or angiomyolipoma
acquired cystic kidney disease or acquired cystic disease of dialysis
found in native kidneys of patients in renal failure
require dialysis
increased risk of adenomas and renal carcinoma
SONO:
small echogenic native kidneys
small cysts in cortex
autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD)
aka infantile polycystic disease
rare disorder caused by gene located on chromosome 6
4 forms based on age of patient when clinical signs present:
Perinatal, neonatal, infantile, and juvenile
dilation of renal collecting tubules → renal failure and later liver involvement
what is another name for autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD)?
infantile polycystic disease
SONO: autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD)
enlarged echogenic (cortex and medulla) kidneys with microscopic or small cysts
lack corticomedullary differentiation (can’t tell difference between cortex and medulla)
autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)
ADPKD1 is MC and found on the short arm of 16th chromosome (affects kidney more severely)
severity varies depending upon the genotype
manifest around 40-50 y/o
s/s: pain; HTN; hematuria; headache; UTI; palpable mass; renal insufficiency
family history and tissue sampling is required for dx confirmation
high incidence of urolithiasis and RCC in dialysis patients
what is another name for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)?
adult polycystic renal disease
SONO (neonates vs. adults): autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)
neonates:
enlarged kidneys
adults:
enlarged kidneys with asymmetrical cysts in cortex and medulla
loss of reniform shape (kidney shape)
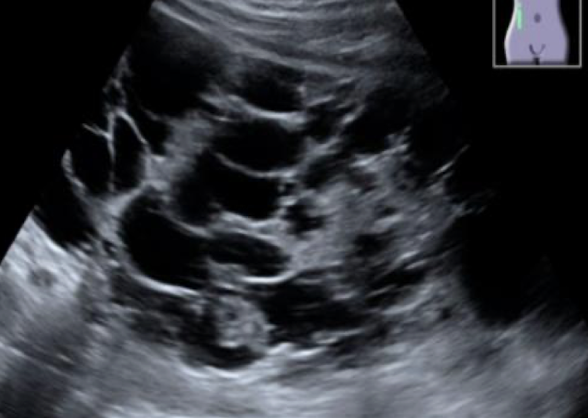
?? describe
autosomal dominant polycystic kidney
“multiple cystic structures noted throughout RK. ?polycystic kidney dz”
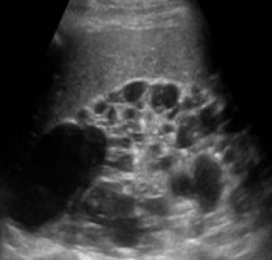
??
autosomal dominant polycystic kidney (ADPKD)
multicystic dysplastic kidney (MCDK)
MC form of cystic disease in neonates
unilateral non-functioning kidney
bilateral MCDK is incompatible with life
s/s: hematuria; infection; flank pain
increased risk of malignancy of kidney is not removed
SONO (neonates/children vs. adults): multicystic dysplastic kidney (MCDK)
neonates/children:
kidneys are multicystic and enlarged
renal artery atresia
adults:
atrophic kidneys
calcified
echogenic
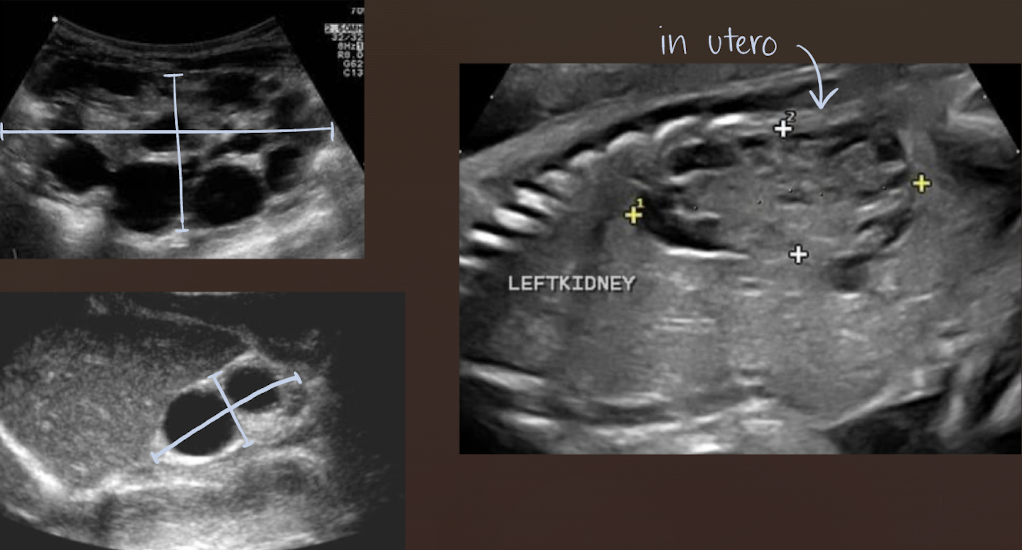
??
multicystic dysplastic kidney (MCDK)
medullary sponge kidney (MSK)
developmental anomaly occurring in pyramids —> stasis of urine and stone formation
cystic/fusiform dilation of distal collecting ducts —> stasis and stone
s/s: asymptomatic; hematuria; infection; renal stones
may be associated with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome, polycystic kidney disease, Caroli’s disease (Type 5) and congenital hepatic fibrosis
medullary cystic kidney disease (MCKD)
MCKDs include: medullary nephrocalcinosis and cortical nephrocalcinosis
both are inherited disorders that eventually lead to ESRD
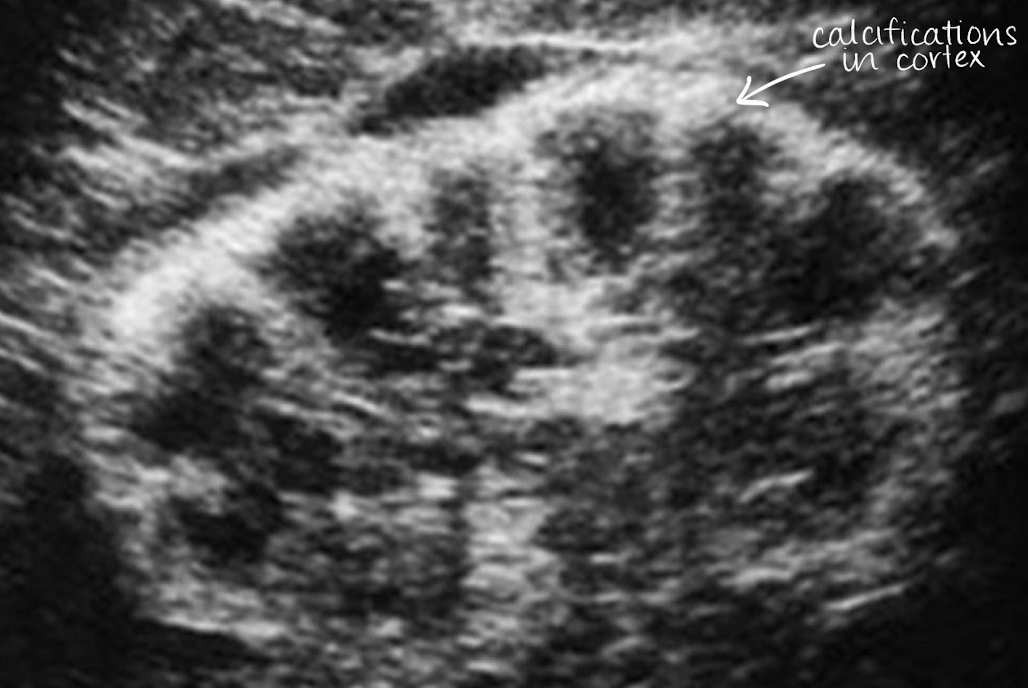
SONO: medullary cystic kidney disease (MCKD)
hyperechoic calyces with or without stones
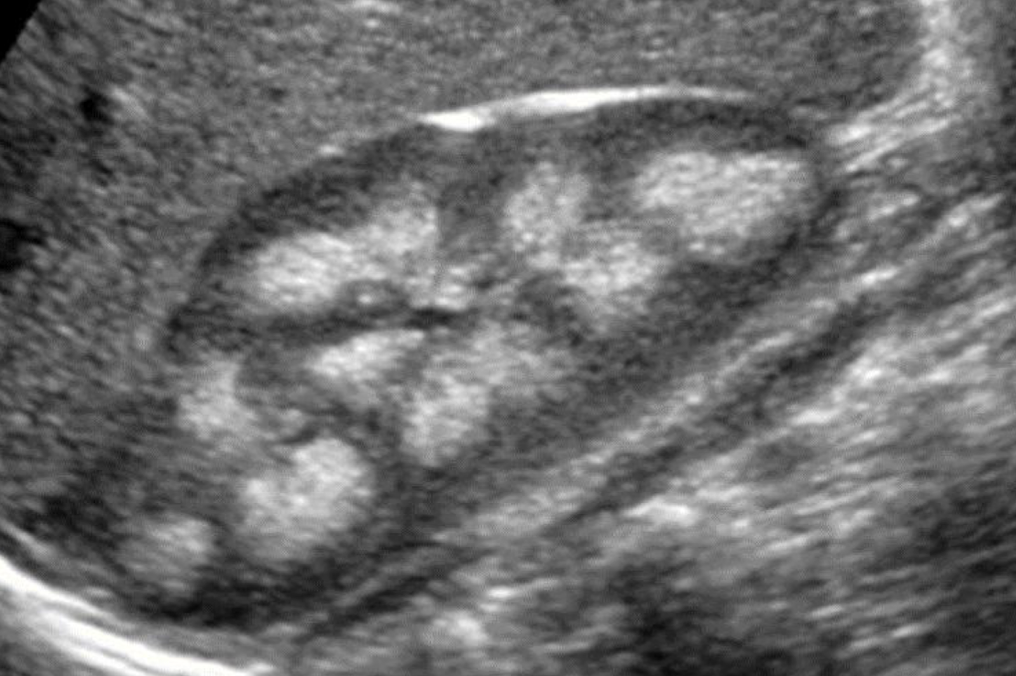
??
medullary cystic kidney disease
calcium deposits in calyces
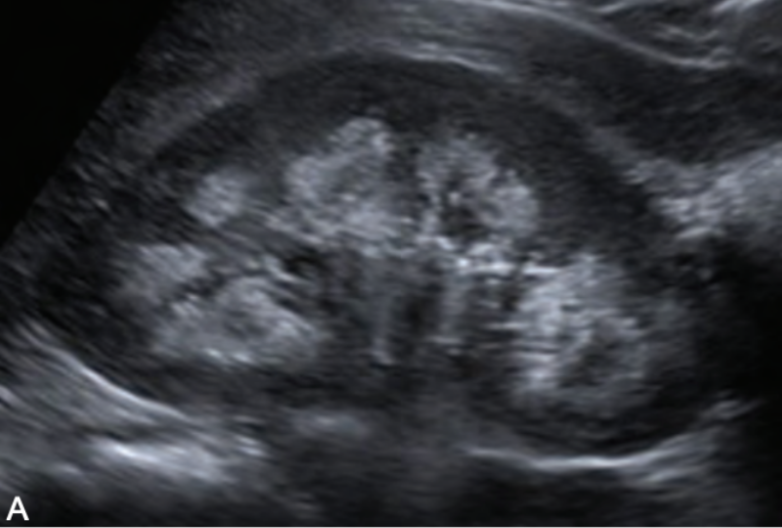
??
medullary nephrocalcinosis (medullary cystic kidney disease)
calcium deposits in medulla (heart-shaped ♥)
??
cortical nephrocalcinosis (medullary cystic kidney disease)
calcium deposits in cortex
renal cell carcinoma (RCC)
MC renal malignant
higher incidence in men ~60-70 years old
s/s: hematuria, flank pain, and palpable mass
associated with von Hippel Lindau disease, acquired cystic disease in dialysis patients, and tuberous sclerosis
metastasis to lungs, mediastinum, liver, bone, ipsilateral kidney
what are other names for RCC?
hypernephroma and Grawitz Tumor
SONO: renal cell carcinoma (RCC)
isoechoic or hyperechoic
solid or cystic
intratumoral calcification
hypoechoic rim (represents vascular pseudocapsule on color Doppler)
MC vascular patterns is “basket sign” and/or “vessels within tumor”
?invasion of the renal vein and IVC
RCC can invade what vessels?
renal vein and IVC
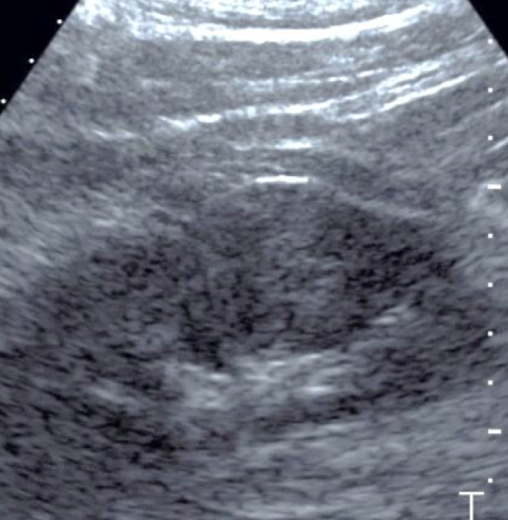
?? describe
RCC
“isoechoic solid circumscribed structure noted in MP/LP of RK measuring 3 cm x 3 cm x 3 cm. difficult to determine border”