Digestive System
1/167
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
168 Terms
What are the functions of the digestive system?
Prehension
Mastication
Salivation
Swallowing
Digestion/fermentation
Absorpotion
Is waste excretion a function of the digestive system?
No
The digestive system contains components from which embryonic layer?
All three
Which embryonic layer is the gut lining formed from?
Endoderm
Which embryonic layer are the embryonic gut walls and muscles (majority of digestive system) formed from?
Mesoderm
Which embryonic layer is the mouth and anus formed from?
Ectoderm
What is the invagination of the ectoderm in embryos that forms the mouth?
Stomadaeum
What is the invagination of the ectoderm in embryos that forms the anus/cloaca?
Proctodaeum
Describe the primitive gut in embryonic development.
Blind-ended gut tube
Describe the accessory digestive organs in embryonic development.
Outpouchings of primitive gut tube
Describe the intestines in embryonic development.
Herniate into umbilical cord and then retract back into abdominal cavity
Which part of the primitive gut runs from the oropharyngeal membrane to pharynx?
Proximal foregut
Which part of the primitive gut runs from the proximal foregut to liver bud?
Distal foregut
Which part of the primitive gut runs from the distal foregut to transverse colon?
Midgut
Which part of the primitive gut runs from midgut to cloacal membrane?
Hindgut
What composes the digestive tract?
Buccal cavity → pharynx → alimentary canal
What composes the alimentary canal?
Esophagus, stomach, intestines, cloaca, and accessory glands
What type of feeding involves filtering small particles out of the water?
Suspension feeding
What type of feeding involves opening the mouth and sucking in food?
Suction feeding
What type of feeding involves opening the mouth and swimming over food?
Ram feeding
What type of feeding involves using the inertia of food to move it into the oral cavity?
Inertial feeding
What is the term for movement of food within the oral cavity, through water currents or the tongue?
Transport
What is the term for reduction of food size by chewing?
Mastication
What makes up the buccal cavity?
Lips, cheeks, tongue, palate, teeth, and salivary glands
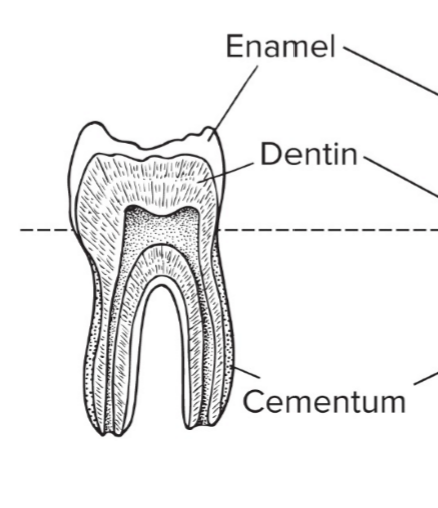
What part of the tooth is located above the gingival line?
Crown
What part of the tooth is located below the gingival line?
Root
What is the outer layer of the crown that is also the hardest substance in the body (unique to vertebrates)?
Enamel
What arrangement does dentin grow in?
Lines of von Ebner
What part of the tooth is located under the enamel and is harder than bone and continues to grow?
Dentin
What part of the tooth contains nerves and blood?
Pulp cavity
What part of the tooth is located outside the dentin in the root?
Cementum
Which embryonic layer does enamel originate from?
Ectoderm
Which cells form enamel?
Ameloblasts
Which embryonic layer does the dental papilla (dentin) originate from?
Mesoderm
Which cells form dentin?
Odontoblasts
Which embryonic cells form odontoblasts?
Neural crest cells
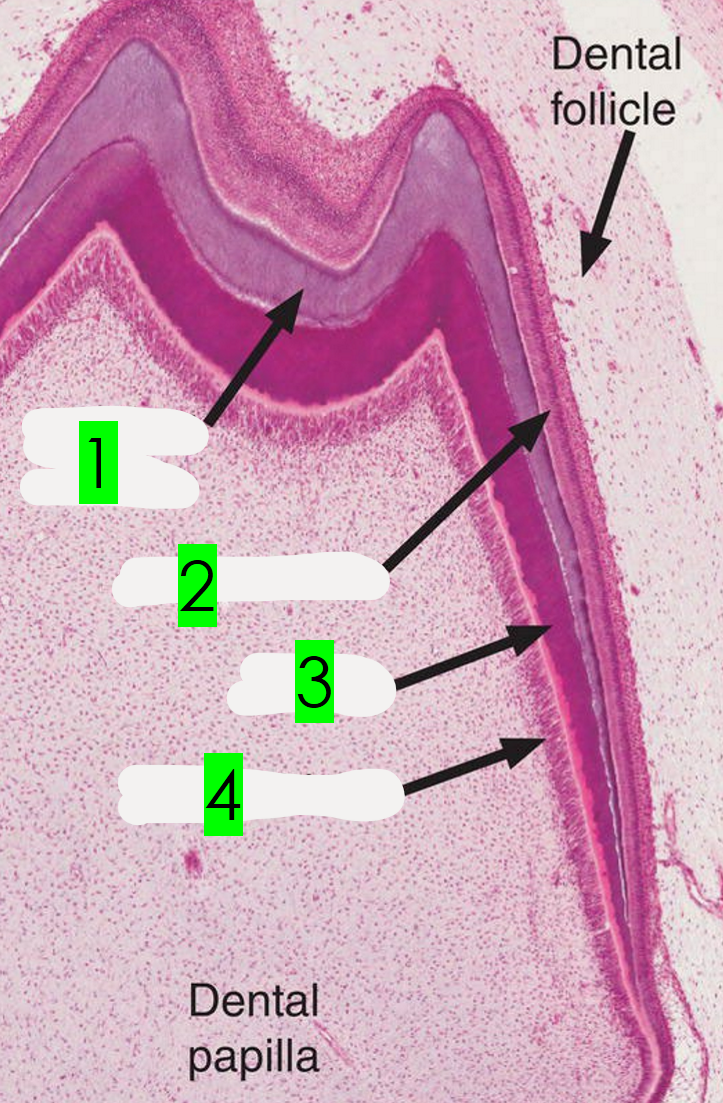
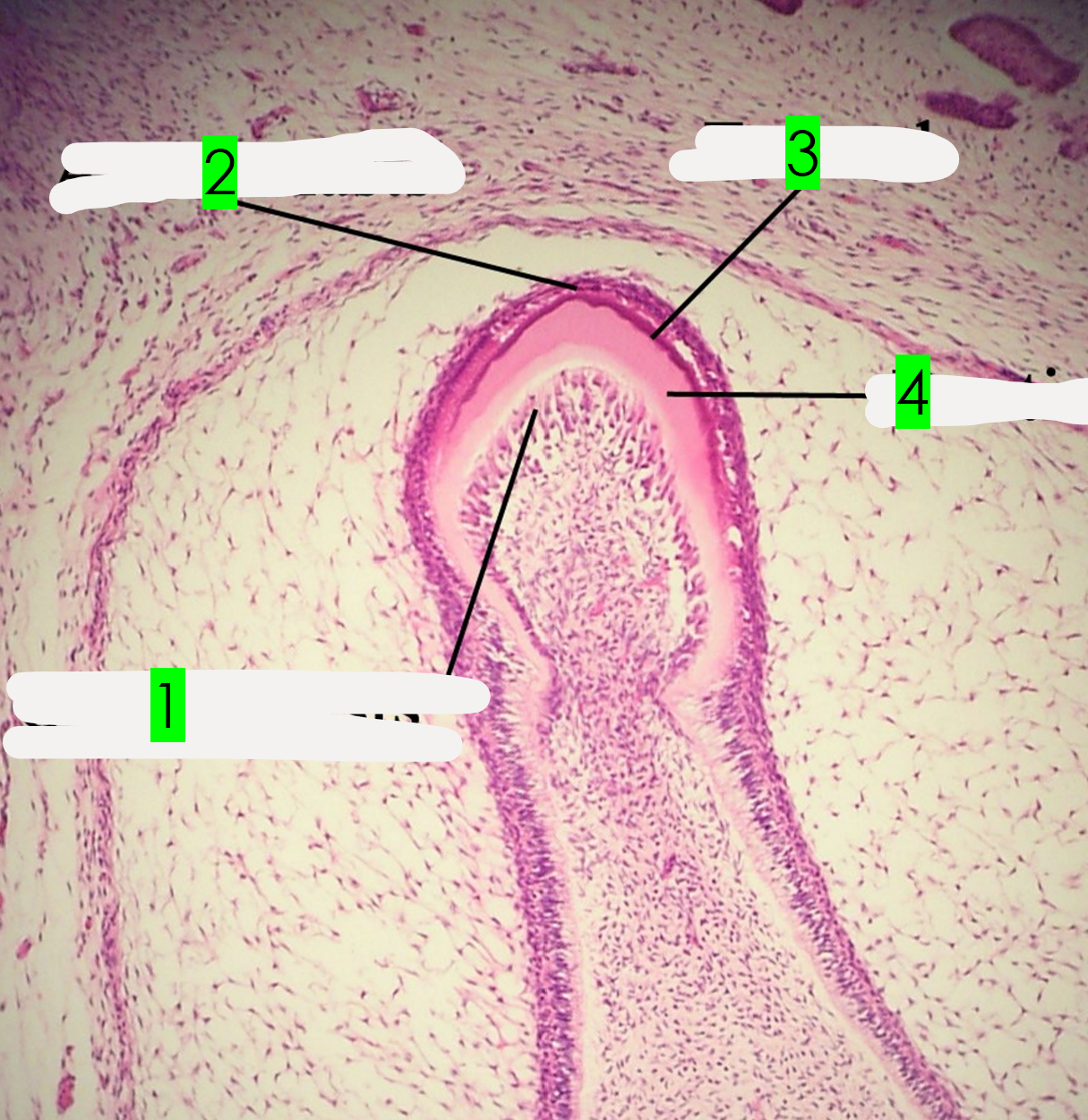
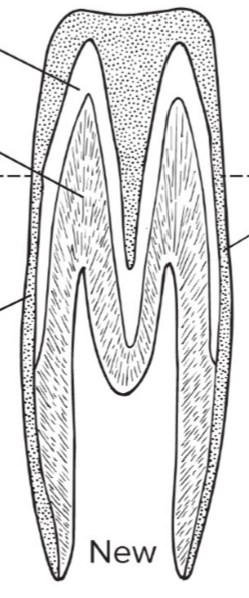
What is arrow 1 pointing to?
Enamel
What is arrow 2 pointing to?
Ameloblasts
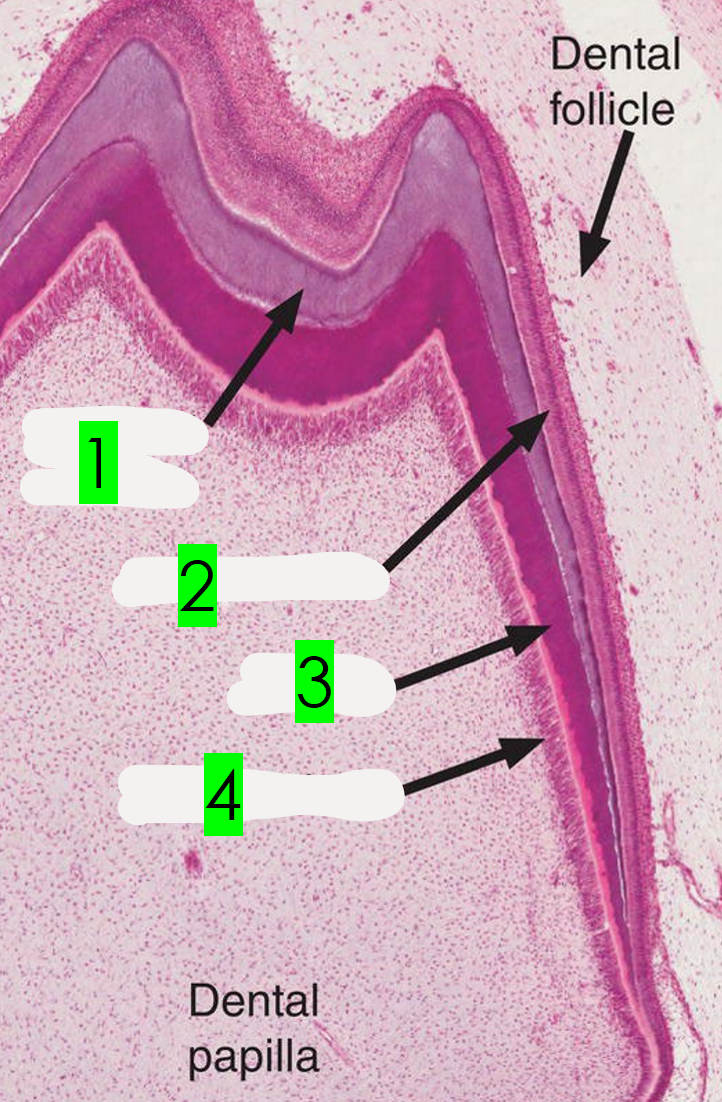
What is arrow 3 pointing to?
Dentin
What is arrow 4 pointing to?
Odontoblasts
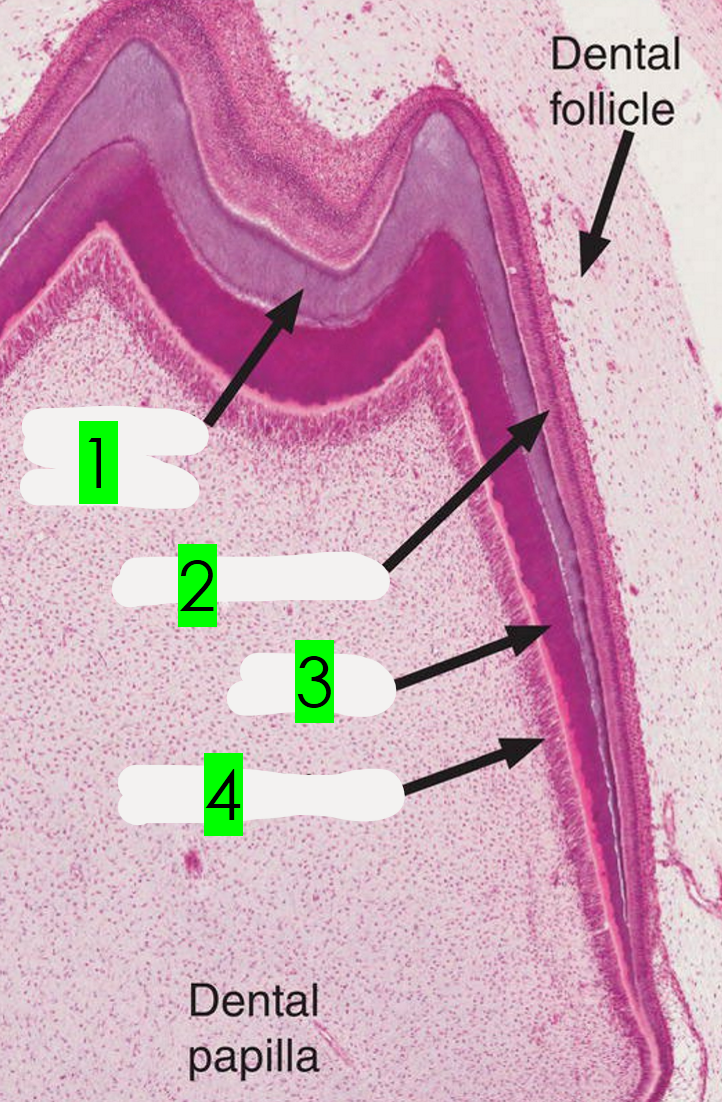
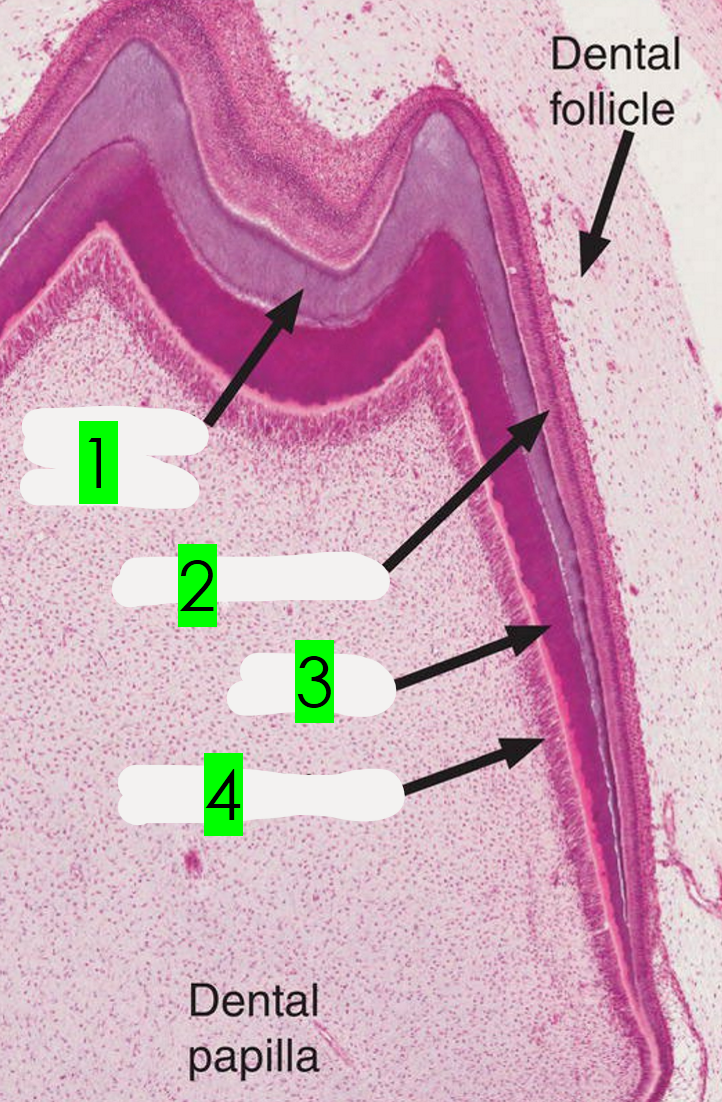
What is arrow 1 pointing to?
Odontoblasts
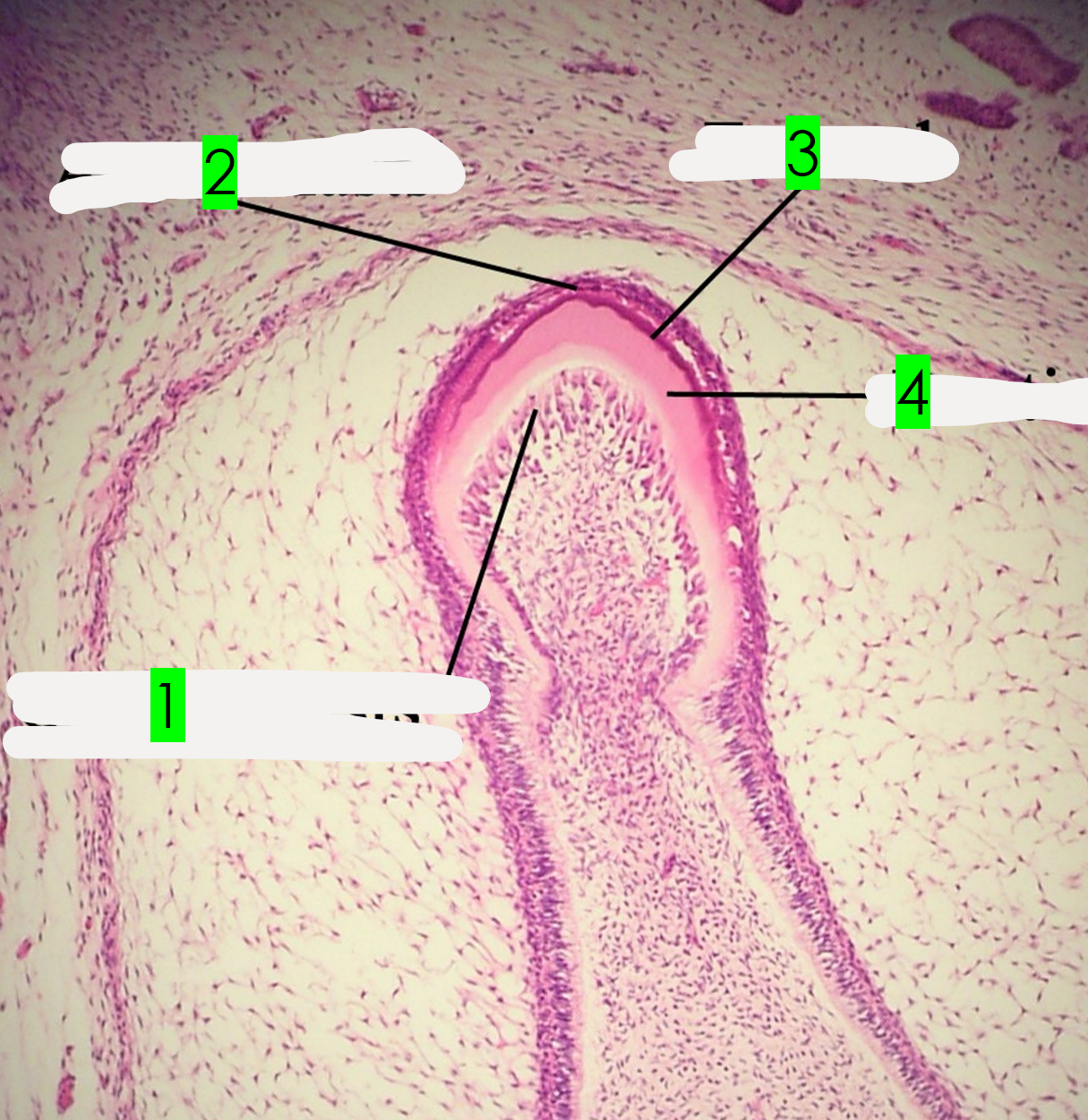
What is arrow 2 pointing to?
Ameloblasts
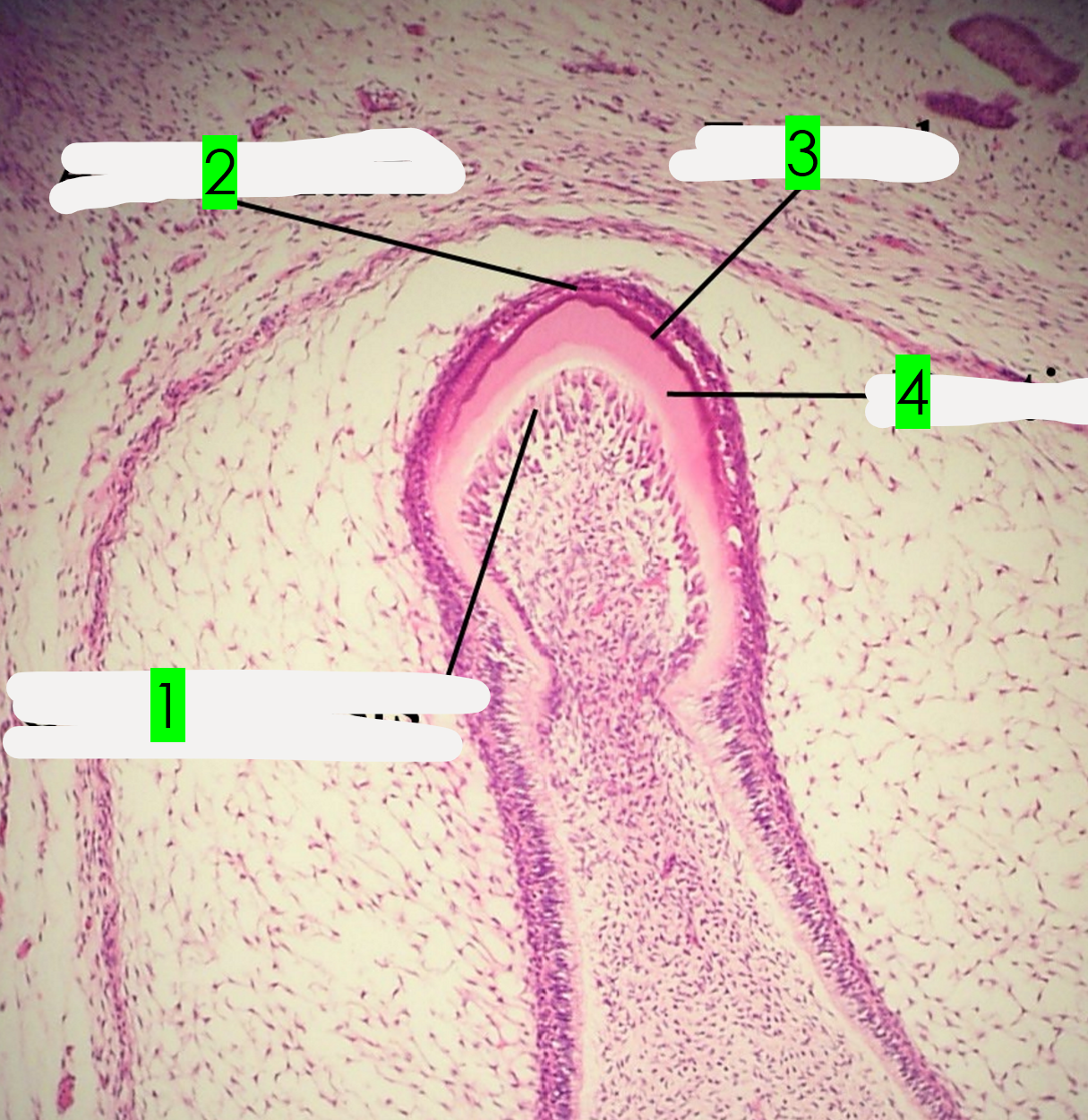
What is arrow 3 pointing to?
Enamel
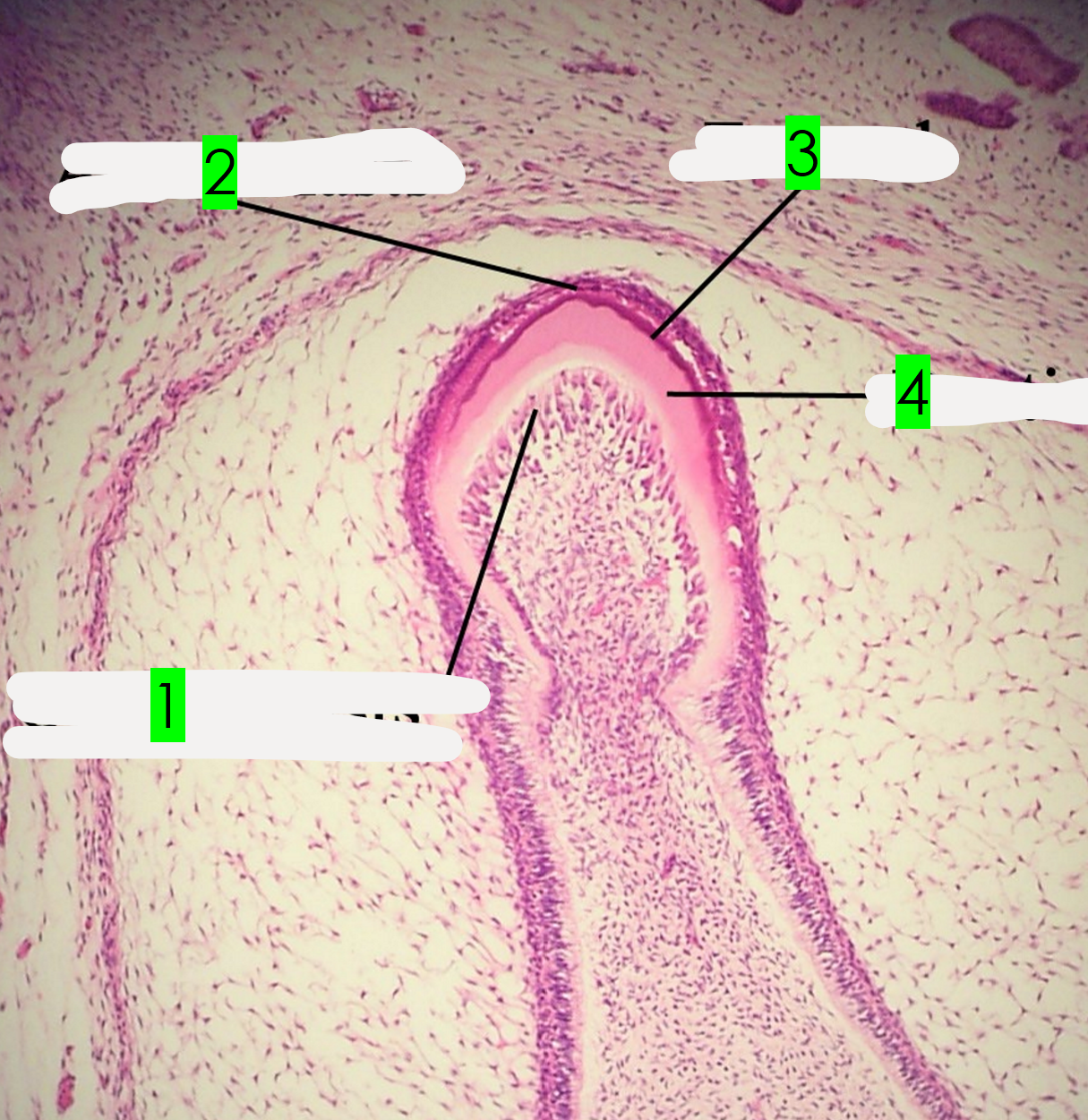
What is arrow 4 pointing to?
Dentin
What is the term for animals with a single set of teeth?
Monophyodont
What is the term for animals with two sets of teeth?
Diphyodont
What is the term for animals with continuous tooth replacement?
Polyphyodont
Which animals are monophyodont?
Rodents
Which animals are diphyodont?
Mammals
Which animals are polyphyodont?
Vertebrates except mammals
Which tooth arrangement structure involves having teeth of similar shape along the jaw?
Homodont
Which tooth arrangement structure involves having teeth of different shapes along the jaw?
Heterodont
What is special about lungfish teeth?
Tooth plate → teeth are fused together
What term describes molar teeth with low crowns?
Brachydont
What term describes molar teeth with high crowns?
Hypsodont
What term describes molar teeth with rounded peaks for crushing?
Bunodont
What term describes molar teeth with cusps in ridges for grinding?
Lophodont
What term describes molar teeth that are crescent-shaped for lateral chewing?
Selenodont
What type of tooth is this?
Brachydont
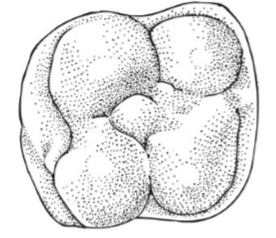
What type of tooth is this?
Hypsodont
What type of tooth is this?
Bunodont
What type of tooth is this?
Lophodont
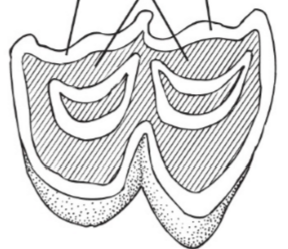
What type of tooth is this?
Selenodont
Which two terms describe human teeth?
Brachydont and bunodont
What is a unique adaptation of beaver and rabbit teeth?
Continual growth
What is a unique adaptation of elephant molars?
Fused together → sequential eruption
What somite muscles does the tongue originate from?
Hypobranchial muscles
What are the three functions of the tongue?
Lingual feeding
Taste
Transport of bolus
What is the difference between fish and tetrapod tongues?
Fish: limited structure to allow suction feeding
Tetrapods: mobile, muscular tongue
What type of cell are taste buds?
Chemoreceptor cells
Which type of papilla is square-shaped?
Fungiform papillae
Which type of papilla has a sharp point and moves food around?
Filiform papillae
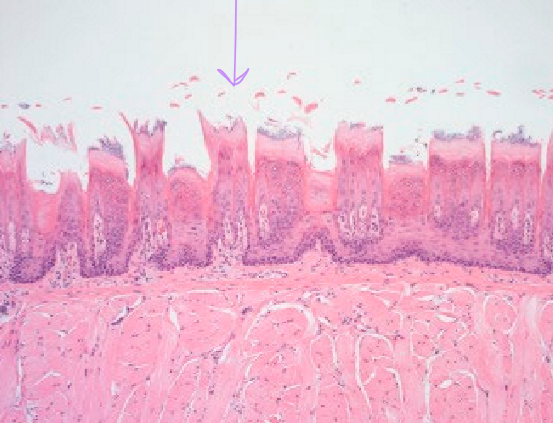
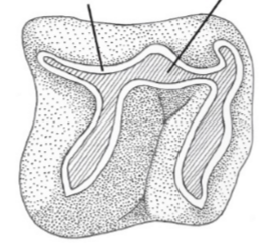
What type of papilla is this?
Fungiform
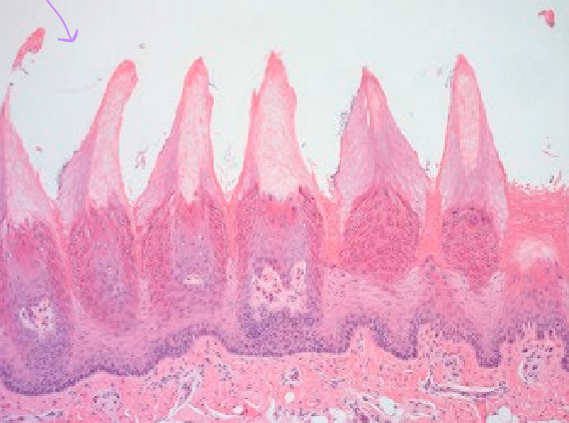
What type of papilla is this?
Filiform
What do oral glands secrete?
Mucus and serum
Do fish have oral glands?
Rarely
What is the most common type of oral gland?
Salivary
What type of oral gland do reptiles have?
Supra- and -infralabial
What type of oral gland do poisonous snakes have?
Venom
What type of gland is associated with the snout?
Premaxillary/nasal
What type of gland is associated with the eye?
Lacrimal
What are the three functions of salivary gland secretions?
Lubrication
Buffers
Digestive enzymes
What condition results from a buildup of fluid from the sublingual gland?
Salivary mucocele
What are the three salivary glands?
Parotid, mandibular, and sublingual
Which part of the digestive tract is the passageway to the esophagus?
Pharynx
Which specific part of the pharynx transports food from the oral cavity to the rest of the digestive system?
Oropharynx
What are the layers of the alimentary canal, from innermost to outermost?
Mucosa → submucosa → muscularis externa → serosa
Which embryonic layer is the mucosa derived from?
Endoderm
Which embryonic layer is the submucosa derived from?
Mesoderm
Which embryonic layer is the muscularis externa derived from?
Mesoderm
What is the function of the esophagus?
Transport food from the oropharynx to the stomach
What two structures keep food within the esophagus?
Upper and lower esophageal sphincter
What muscular action of the esophagus moves food to the stomach?
Peristalsis
What glands produce mucus that lubricates the esophagus?
Luminal glands
What are the three functions of the stomach?
Store food → carnivores
Mix/churn food
Digestion
What types of epithelium make up the stomach?
Glandular and nonglandular
Which area of the glandular stomach comes out of the esophagus and contains mucus glands?
Cardia
What is the function of mucus secreted in the stomach?
Lubricate/soften bolus
Which area of the glandular stomach contains parietal and chief cells?
Fundus
What do parietal cells in the fundus secrete? What type of digestion is this?
HCl → acid digestion