AP Statistics Unit 2
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
(2.1) How to represent relationship of two categorical variables?
Graphical representation: bar graphs
Numerical representation: two-way tables, conditional relative frequencies
(2.1) How to represent relationship of two quantitative variables?
Graphical reps: scatterplots
Numerical reps: correlation, linear regression, coefficient of determination
(2.2) How to determine if there is association between the two categorical variables?
If distributions are not the same in each group, there is an association between the two variables
(2.2) How to make graphical displays to show relationship of two categorical variables?
Side-by-side graph, segmented bar graph, mosaic plot
(2.3) How to use summary statistics to determine if there is association between two categorical variables?
If distribution of conditional relative frequencies are not the same for all groups, then there is association
(2.4) Explanatory and Response variables
Explanatory (x) variables predict or 'explain' trends in the response (y) variable
(2.4) Form & Unusual Features
Form can be linear or non linear. Unusual features can be clusters or apparent outliers.
(2.4) Strength and Direction
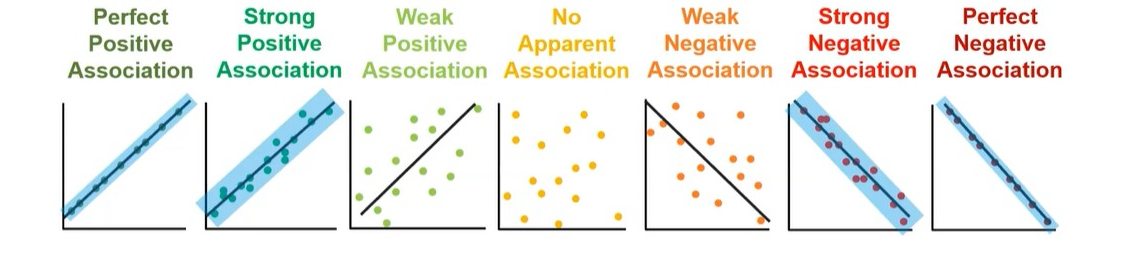
(2.4) When describing relationships between two quantitative variables include what?
Should include direction, form, strength, unusual features, context
(2.5) Is Correlation = Causation?
Correlation ≠ causation
(2.5) Relationship between magnitude of correlation coefficient and strength of linear relationship?
When r is closer to 0 its weaker, when its closer to -1 or 1 it is stronger
(2.5) Sign of correlation coefficient and direction of a linear relationship?
When r is negative, direction is negative. When r is positive, direction is positive.
(2.5) What to watch out for in correlation and causation?
Beware of other variables, as well as coincidental correlations
(2.6) Linear Regression Model Formula?
ŷ= a + bx
ŷ = predicted y-value
a = y-intercept
b = slope
(2.6) Problems of extrapolation?
Extrapolation is dangerous since trends may not continue.
(2.7) Residual formula?
y - ŷ
where y is the actual value and ŷ is the predicted value
(2.7) Residual Values and Linear Model Fit
'Apparent randomness', centering at zero = good sign of model fit
Patterns = bad sign for model fit
(2.7) What do positive and negative residual values indicate?
Positive residual values = Under-prediction
Negative residual values = Over-prediction
(2.9) How do you assess the effectiveness of transformations?
By seeing if patterns in the residual plots were reduced
By seeing if the r2 values increased