L48: Anti Cancer drugs
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What is chemotherapy
Treatment of cancer with drugs
Many of the drugs are cytotoxic
Interfere with cell growth/division
action is not specific to cancer cells- destroy rapidly dividing cells
what is the difference between veterinary and human chemotherapy
same drugs but smaller doses
less intense schedules
QOL over curative intent
prolonging life over curative intent
define induction chemotherapy
induce a remission
define consolidation chemotherapy
sustain a remission
define adjuvant chemotherapy
administered in the microscopic setting
define neo-adjuvant chemotherapy
Administered in the macroscopic setting
define maintenance therapy
maintain remission
controversial benefitde
define reinduction chemotherapy
re introduce the induction protocol
define rescue chemotherapy
administered if patient out of remission and presumed resistance against induction chemotherapy
what are the indications for chemotherapy
treatment of disseminated disease
lymphoma
multiple myeloma
leukemia
mast cell tumour
histiocytic disease
adjuvant following surgical resection
incase of incomplete excision, metastasis, high malignancy
neo-adjuvant to reduce tumour size prior to surgery or RT
transmissible venereal tumour
What are the routes of administration of chemotherapy
oral
IV
intracavitary
intralesional
subcutaneous
What is the MOA of chemotherapy
Interfere with cell growth and division
some cell cycle specific, others not
most drugs work best on actively dividing cells
tumours with high mitotic index are more likely to be sensitive
Cells in G0 (resting) are relatively resistant
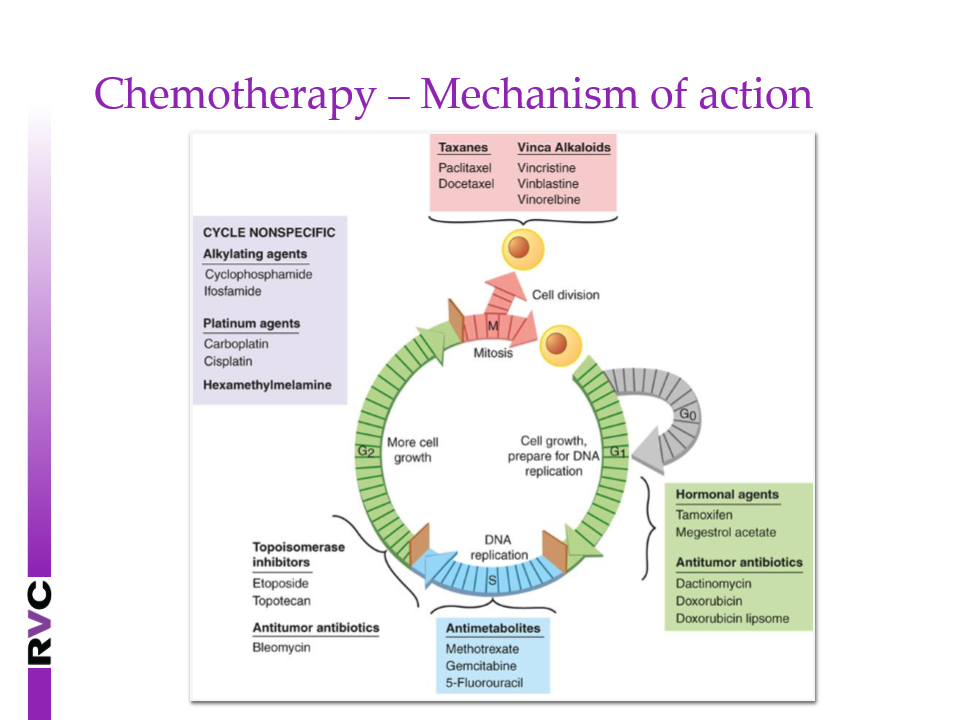
How do you time chemotherapy
time as early as possible
unlikely effective in macroscopic and end stage disease
as early as possible post surgery (10-14 days)
define maximum tolerated dose
a fixed dose kills off a fixed % of cells rather than number of cells
cannot kill tumour with on dose
what do you aim for when chemotherapy dosing
multiple doses
pulse dose at intervals
Normal tissue recovery
prevent tumour regrowth
How do you dose chemotherapy
dosing for body surface area (mg/m2)
conversion charts available
dogs <10kg are often overdosed
dose for mg/kg
doxorubicin, carboplatin
What is combination chemotherapy
combination protocols often more effective
drugs that are
effective as single agents
different MOA and dont interfere
avoid overlapping toxicities
What are some examples of combination therapy
CHOP-based protocols (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin/epirubicin, vincristine, prednisolone)
COP-based protocols
LOP/LOPP based protocols (lomustine, vincristine, +/-procarbazine, prednisolone)
define metronomic chemotherapy
administration of regular low, daily dose of cytotoxic agents
targets blood vessels
whats an example drug of metronomic chemotherapy
cyclophosphamide
What does metronomic chemotherapy act on
tumour microenvironment
anti-angigenic
induction of tumour dormancy
What is tumour dormancy
where tumour doesnt grow or change
what is targeted therapy
not to do with interrupting cell cycle
but growth factors on cell surface- this avoids cell proliferation, metastasis and angiogenesis
what are some examples of targeted drugs
toceranib phosphate
masitinib
What determines the success of chemotherapy
Tumour cell type (e. g. Lymphoma vs. Melanoma)
Drug distribution
Blood supply
Blood-brain barrier
Development of resistance
Tumours are genetically unstable
Drug exposure →selects resistant cells
MDR1 gene up regulation
What are some classes of chemotherapy drugs
Alkylating agents: cyclophosphamide, lomustine, chlorambucil, melphalan.
oral
Vinka alkaloids: vincristine, vinblastine, vinorelbin
lymphoma
Antimetabolites: cytarabine, gemcitabine, methotrexate, 5-FU
interefere with metabolism
Platinum agents: carboplatin
osteosarcoma
Anti-tumourantibiotics: doxorubicin, epirubicin, mitoxantrone
lymphoma
L-asparaginase (enzyme)
What are some examples of commonly used chemotherapy drugs and what do they treat
Cyclophosphamide(lymphoma, softtissuesarcoma)
Lomustine(lymphoma, mast cell tumour, histiocyticsarcoma)
Chlorambucil(lymphoma, chroniclymphocyticleukaemia)
Melphalan(multiplemyeloma)
Vincristine(lymphoma, transmissible venereal tumour)
Vinblastine(mast cell tumour)
Doxorubicin(lymphoma, carcinomas, sarcomas)
Epirubicin(lymphoma, carcinomas, sarcomas)
Mitoxantrone(lymphoma, carcinomas)
What is the role of prednisolone
Apoptosis of lymphoid cells
lymphoma
leukaemia
apoptosis of mast cells
mast cell tumour
Adverse events Pu/PD, panting, muscle wastage
What are some NSAIDS that can be used as chemotherapy
COX inhibition
plays role in cancer progression
inflammation and angiogenesis
Anti-angiogenic
promote apoptosis
anti-inflammatory
analgesic
indications
transitional cell carcinoma, other carcinomas and sarcomas
What are some adverse effects of chemotherapy
mild and self limiting
prevention medicine
increase with organ dysfunction (hepatic or renal)
metabolism of drug
activation through liver
cyclophosphamide
What areas/ cells are more susceptible to toxicity
bone marrow
myelosuppression
gastrointestinal
What is seen in myelosuppression
neutropenia
nadir down around 7 days post chemotherapy
platelets can also drop
mild to moderate thrombocytopenia
What are some adverse effects of myelosuppression and how can it be avoided
Monitor CBC prior to each treatment
Neutrophil nadir may be recommended (e. g. Doxorubicin, carboplatin)
Delay + retest if neutropenic in 3-7 days dependent on severity
Antibiotics if:
Neutrophil count <0.75 x109/l -DO NOT hospitalise
Neutropenia + febrile -HOSPITALIZE for IV
Consider dose reduction
What are the adverse effects of GI toxicity
Effects of gut epithelium
risk of bacterial translocation
acting via CRTZ
consider preventative medicine- antiemetics
antibiotics if
haemorrhagic diarrhoea
Persistent diarrhoea (other causes excluded)
How can you prevent/treat the adverse effects from GI toxicity
Antiemetics
Maropitant
Ondansetron
Metoclopramide
Gut protectants
Omeprazole
Ranitidine
Anti-diarrhoeal medication
Bland diet
Pro-kolin
Metronidazole
What drugs are more susceptible to hair loss
alopecia is a breed disposition in
old english sheepdog
maltese
WHW terrier
etc
loss of whiskers
How do you prevent drug extravasation
clean placed catheter
firmly taped in
flush with saline
How do you treat drug extravasation
Try aspiration of drug
incristine
hot compresses
hyalauronidas
doxorubicin: ice, dexrazoxane
What are some cardiotoxicity adverse effects
dysrhythmmia
cardiomyopathy
monitor
cardiac murmur
predisposed breed: Great Dane, Cocker spaniel, doberman
Cats-nephrotoxicity
how do you prevent sterile haemorrhagic cystitis
monitor
access to water
furosemide
what does sterile haemorrhagic cystitis cause
haematuria and stranguria but cultures negative
how do you treat sterile haemorrhagic cystitis
stop medication
analgesia
instillation of DMSO, glycoaminoglycans
What are some other adverse effects
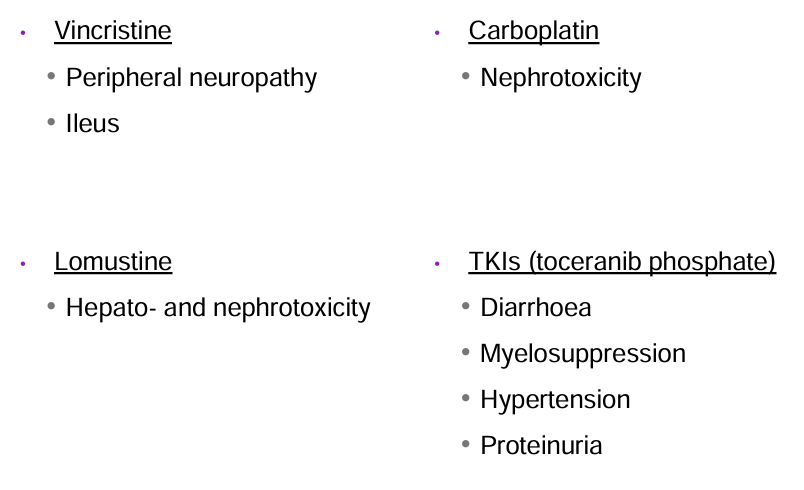
what chemotherapy drugs do you not give to cats
cisplatin (pulmonary oedema)
5-fluorouracil (neurotoxicity)
What is the MDR1 mutation
Breed predisposition
shepherds
Defective drug excretion and uptake across blood brain barrier
Vincristine, doxorubicin
MDR1 metabolised
PCR test