Software Engineering - Prelims
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/288
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
289 Terms
1
New cards
Capacitor (diagram)
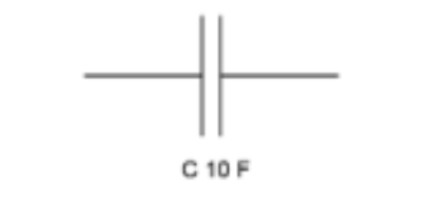
2
New cards
Diode (diagram)
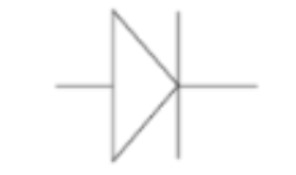
3
New cards
Resistor (diagram)
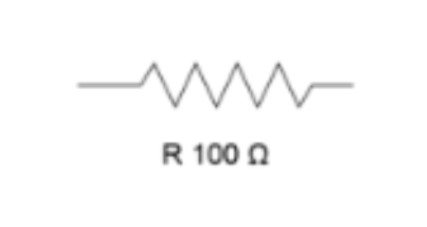
4
New cards
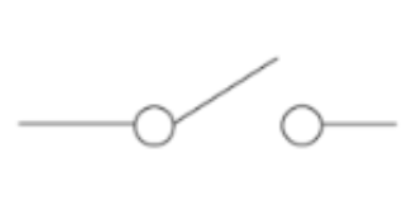
2-way switch (diagram)
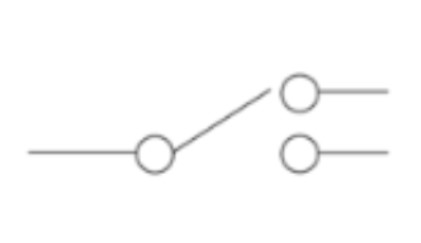
5
New cards
on/off switch (diagram)
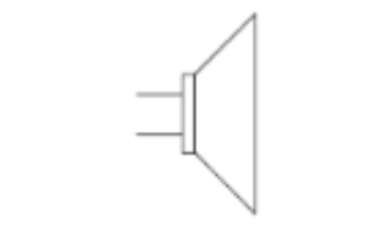
6
New cards
Speaker (diagram)
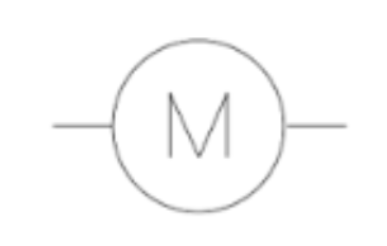
7
New cards
Motor (diagram)
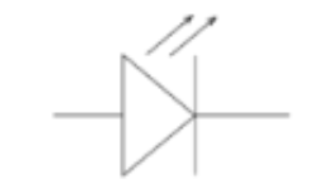
8
New cards
LED (diagram)
9
New cards
Lightbulb (diagram)

10
New cards
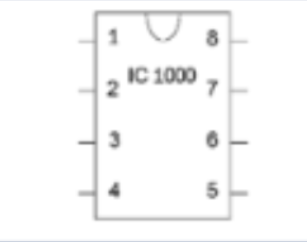
Integrated circuit (diagram)
11
New cards
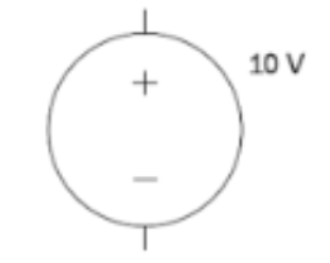
Voltage source (diagram)
12
New cards
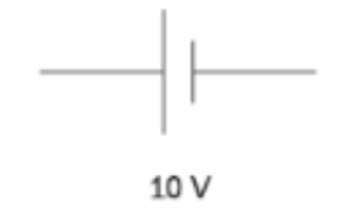
DC Voltage Source (diagram)
13
New cards
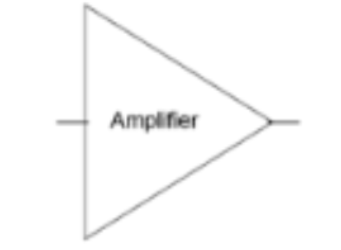
Amplifier (diagram)
14
New cards
Structured/Waterfall Approach
go through each step one at a time in a linear process
15
New cards
Choosing structured approach is influenced by
size and nature of product skills of people involved detail of requirements finances available
16
New cards
What the structured approach is good for
large scale projects with big teams and budgets
17
New cards
Stages of structured approach
Requirements; Determining specifications; Design; Development; Integration; Testing and Debugging; Installation; Maintenance
18
New cards
Remembering Stages
ReStoreDogDoorIdentityTIM
19
New cards
Agile Approach
manage multiple stages at once allowing sudden changes and the ability to work backwards
20
New cards
What the agile approach is good for
small-to-medium organizations; no deadline; requirements aren’t clear; unsure of market need; constant customer involvement
21
New cards
Requirements
general descriptions of services/feature expected from the system from the customer that need to be understood completely
22
New cards
Analysis of requirements
surveys; interviews; time management studies; Business analysis
23
New cards
Determining Specifications
written based off requirements and answering the ‘how’ in design (what the system will do to achieve that requirement)
24
New cards
Functional requirements/specifications
how users interact with the system (e.g. requirement: customers need to be able to search so specification: search bar)
25
New cards
Non-Functional requirements/specifications
performance and quality of the system (e.g need to be compatible with other softwares)
26
New cards
Design
creation of system models and project planning where we identify data types/structure; variable naming convention; algorithms needed
27
New cards
Project planning
use gantt charts or journals or diaries or logbooks or system modeling tools (storyboards and flowchart)
28
New cards
Development
coding the solution with the use of IDEs
29
New cards
IDEs
Integrated Development Environments (programs that have tools like error detection and debugging; Microsoft’s visual studios)
30
New cards
Integration
see how the code works with other softwares and databases (e.g. paypal)
31
New cards
Version control
software that tracks and manages code while multiple people work on it
32
New cards
Version control example
Git that can merge versions and branch versions and snapshot specific points of time when people edit the code
33
New cards
Testing and Debugging
Involves different stages of testing the code/software and the use of correcting any code that doesn’t work
34
New cards
Types of testing
Alpha and Beta testing
35
New cards
Alpha Testing
software/code is tested by the people who know about the software before hand or knows how it works (this is done first before beta)
36
New cards
Beta testing
program is distributed to selected outsiders who test and report back any problems or bugs and also give feedback
37
New cards
Why is testing and debugging important
Ensures the quality assurance and that it meets all requirements and specifications
38
New cards
Quality assurance
represent our goals of ensuring the product meets all requirements set at the start
39
New cards
Levels of testing
Module testing; program testing; system testing
40
New cards
Module testing
test each individual subroutine/module withing a program AS its being created
41
New cards
Program testing
each program tested to ensure modules work together correctly
42
New cards
System testing
testing entire system will all different programs working together correctly
43
New cards
CASE (Computer Assisted Software Engineering)
complete tasks like generating test data or creating test reports
44
New cards
Installation
product needs to be installed and implemented; usually involves conversion from old to a new system
45
New cards
Methods of Installation/Conversion
Direct cut-over; Parallel; Phased; Pilot
46
New cards
Direct cut-over
old system completely dropped and new system completely installed; must make sure new system fully works and that users are fully trained
47
New cards
Parallel
operating the two systems together for a period so that the old system is operational for backup; allows major problems in new system to be corrected without loss of data and users have time to learn how to use
48
New cards
Phased
gradual introduction of the new system while old system is slowly discarded; usually used when new system is still in development and makes conversion more manageable for big businesses
49
New cards
Pilot
new system is just installed for a small number of users where they can evaluate and learn the program and once it is good they install it for everyone; can also be seen as the final testing of the product
50
New cards
Maintenance
final stage that is ongoing process of correction and refinement as to continue to meet requirements from users; includes fixing any bugs or upgrading to enhance functionality or changing requirements
51
New cards
Maintainability
measure of how easily a solution can be maintained
52
New cards
Why change the software?
bug fixes; existence of new hardware; integrating new software (e.g. AI); requests from users on changes
53
New cards
Computational thinking
understanding how to break down a task (decision making process; identifying problems and breaking them down to smaller parts)
54
New cards
Variables
named containers that store data in your programs (can hold different data types)
55
New cards
Control structures
Sequence and Selection and Repetition
56
New cards
Sequence
plays code line by line following a process
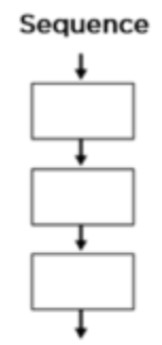
57
New cards
Selection
Ask a question that has two options and then plays the code due to the chosen option
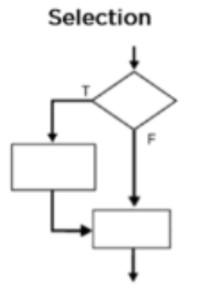
58
New cards
Repetition
repeating an action over and over (loops)
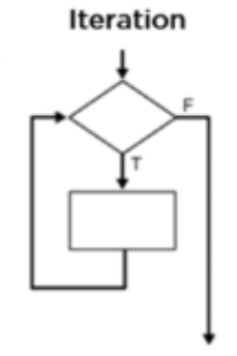
59
New cards
Snake case
name_name
60
New cards
Pascal case
NameName
61
New cards
Camel case
nameName
62
New cards
Integer
whole negative and positive numbers
63
New cards
Floating point
positive and negative decimal points
64
New cards
String
word or phrase
65
New cards
Boolean
yes; no; true; false
66
New cards
Data dictionaries
ensures all members of development team are aware of what has been used; their data types; storage size; display size and format; scope of usage and other details
67
New cards
What's included in data dictionaries
Variable name; data type; format; number of bytes; size of display; description; example; validation
68
New cards
Format (data dictionary)
e.g XXNNN = MS255
69
New cards
Number of bytes (data dictionary)
mostly all 1 byte each
70
New cards
Size of display (data dictionary)
characters that appear on screen
71
New cards
Description (data dictionary)
purpose of the variable
72
New cards
Example (data dictionary)
what might be stored at given time
73
New cards
Validation (data dictionary)
the range of allowed variables
74
New cards
Types of errors in code
Syntax; Logic and Runtime
75
New cards
Syntax errors
involves misspelling words or forgetting to indent or add symbols to code
76
New cards
Logic errors
code works but doesn’t give correct results
77
New cards
Runtime errors
program works but then crashes while running it
78
New cards
Mathematical operators
Add (+) Minus (-) Multiply (x) Divide (/)
79
New cards
Logical operators
ADD (x && y)(only true when both are true) OR (x || y)(true when either or both are true) XOR (x ^^ y)(Only true when one of them are true) NOT (!x)
80
New cards
Decision trees
acts as a flowchart that shows how a series of decisions can lead to different outcomes
81
New cards
Pseudocode rules
keywords in capitals; every structural element has and end pair; indenting like normal; a subroutine can be referred to in an algorithm by its name
82
New cards
Flowchart symbols
subprogram; input or output; terminator; process; decision
83
New cards
Subprogram flowchart
rectangle with two lines on the sides
84
New cards
Input/output flowchart
slanted square
85
New cards
Terminator flowchart
bean shaped
86
New cards
process flowchart
rectangle
87
New cards
Decision flowchart
diamond on its side
88
New cards
Arrays
example of a data structure that allows us to store multiple values in one single variable
89
New cards
Index of an Array
identifiable position of values (e.g. position 0 or 1)
90
New cards
Desk check
manual process used to test and algorithm or code by working through it step by step with sample inputs
91
New cards
Why use a desk check
ensures the logic of the program works as expected before running on a computer and helps you understand the flow of your code
92
New cards
Writing a desk check
create a table with a column for each variable used and then follow the code line by line entering any changes in variables into the table
93
New cards
Subprograms or subroutines
when a function is called inside our main function
94
New cards
Functions in pseudocode
underline the name
95
New cards
Why we use functions
Avoid repeating code; break up complex programs into smaller pieces
96
New cards
Local variables
when we create a variable inside a function
97
New cards
Arguments
values passed during a function call
98
New cards
Parameters
mentioned in the function definition
99
New cards
Modular design
approach used in software development involving the use of decomposition to break down complex problems into smaller parts like modules or objects; classes; subroutines
100
New cards
Benefits of modular design
code reusability; ease of maintenance; enhanced collaboration; scalability; improved testing code readability