Earth Materials 1 Final
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
Microscopy
the study of the spatial distribution of grains and elements inside of a mineral.
optical/petrographic microscope
A specialized version of a binocular microscope designed for the study of thin sections of rock or cohered soil.
electron microscope
microscope that forms an image by focusing beams of electrons onto a specimen.
Electron beam spectroscopy
electrons gets shot at a sample, which then emits x-rays. the x-rays are then picked up by a detector, which can be used to observe the distribution of elements inside of a sample.
Transition Electron Microscope (TEM)
A form of electron microscopy in which an image is derived from electrons that have passed through the specimen. this creates x-rays that are sensed by a detector. the whole image is formed at once rather than by scanning, and can get up to 100,000x magnification.
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
A microscope that uses an electron beam to scan the surface of a sample, sometimes coated with metal atoms, to study details of its topography. Electrons get bounced off the surface to a detector.
X-ray fluorescence (XRF)
Highly sensitive nondestructive analytical technique that can determine elemental composition of a sample by detecting wavelengths of X-rays emitted after excitation with X-rays emitted from a source.
Miller indices (hlk)
A set of three integers that designate crystallographic planes, as determined from reciprocals of fractional axial intercepts. H = A, K = B, L = C.
Cubic miller indices equation
1/d^2 = (h^2 + k^2 + l^2) / a^2
Hexagonal miller indices equation
1/d^2 = 4/3 ((h^2 + hk + k^2)/a^2) + l^2/c^2
Tetragonal miller indices equation
1/d^2 = (h^2 + l^2)/a^2 + l^2/c^2
Orthorhombic miller indices equation
1/d^2 = (h^2/a^2) + (k^2/b^2) + (l^2/c^2)
Cubic Unit Cell Volume
V = a^3
tetragonal unit cell volume
V = a^2 * c
hexagonal unit cell volume
V = (square root of 3 a^2 c) / 2
Orthorhombic unit cell volume
V = a b c
Monoclinic unit cell volume
V = a b c *sin(beta)
theoretical density formula
density = (# of formula units per cell atomic weight) / (unit cell volume in Angstroms^3 (6.023 * 10^23)). be sure to change angstroms to cm.
XRD limitations
only works on crystalline minerals, doesn't work on partly crystalline or amorphous minerals or glass. mixtures of phases with low symmetry will be difficult to differentiate due to larger numbers of diffraction peaks. cannot work on phases with less than 3 to 5 weight %.
Visible Microscopy Limitations
Opaque minerals like sulfides and oxides do not let visible light through them, which makes them opaque. some silt and clay particles are too small to be clearly seen with visible light.
EDS limitations
Can only detect elements down to 0.1 weight percent or 1000 parts per million.
Polarized Light Microscopy
designed to observe materials internal structured due to their optical characteristics. samples are usually sliced down to 30 micrometers in thickness to let light through them.
Polarized light
light that has been filtered to vibrate in only one direction.
Isotropic
Having identical values of a property in all crystallographic directions. only works in cubic/isometric minerals and produces a gray color.
Anisotropic
Having different values of a property in all crystallographic directions. Found in non-isometric/cubic crystals and causes birefringence and interference colors.
Birefringence
the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light.
interference colors
The iridescent colors that result from the interaction of light rays traveling along the same path.
XRF limitations
Cannot determine how minerals and atoms are put together or distributed within a sample.
electron microscope (EM)
An instrument that focuses an electron beam through, or onto the surface of, a specimen. An electron microscope achieves a hundredfold greater resolution than a light microscope.
Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
uses intermolecular forces between a probe and an object to map the 3D topography of a mineral or other material.
secondary electrons
Electrons that are fired at the surface of a specimen in an electron microscope. produce x-rays that can be used to map the texture and distribution of elements at the sample's surface.
Backscattered electrons
Electrons from the primary beam that produce x-rays when stinking the surface of a specimen in Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM). These electrons penetrate deeper into the sample than secondary electrons do. The higher the density of a material, the more x-rays that are picked up by the detector.
Single Crystal (Laue) Diffraction
a crystal is put in front of a beam of x-rays and a photographic film, resulting in a picture or bright spots where constructive interference occurred.
Powder Diffraction
Samples are crushed into a powder before being fed through an XRD machine. the separated crystal lattice in the powder then refracts x-rays in all directions, which is picked up by a detector. the resulting spectrograph then produces rings depending on which angle the x-rays were diffracted in.
goniometer arm
a swiveling track with an x-ray detector used to sense x-rays refracted during powdered diffraction.
lattice planes
planes connecting equivalent lattice points in unit cells throughout the lattice.
Miller indices H
H = 1/x
Miller indices L
L = 1/y
Miller indices K
K = 1/z
diffraction peaks
associated with planes of atoms. planes with higher densities of electrons tend to produce larger peaks on a spectrograph.
Spectroscopy
the study of how matter interacts with or emits electromagnetic radiation.
infrared light
electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths about 10 µm (micrometers) in size. usually felt as heat.
visible light
Electromagnetic radiation that can be seen with the unaided eye, has a wavelength between 700 to 400 nanometers
ultraviolet light
part of the electromagnetic spectrum that consists of waves with frequencies higher than those of visible light (around 100 nanometers). marks the beginning of ionizing radiation.
gamma rays
Electromagnetic waves with the shortest wavelengths and highest frequencies. are ionizing and can be carcinogenic.
microwaves
Electromagnetic waves that have shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies than radio waves. have a wavelength of roughly 100 cm.
radio waves
Electromagnetic waves with the longest wavelengths and lowest frequencies. have a wavelength of 1 km or greater.
"Major" XRF element
element with more than 1 weight % in XRF Data, comprises a major portion of a sample. reported as oxides and use weight % for value.
"Minor" XRF element
element with a value between 1 to 0.1 weight %. reported as an element and uses atomic % as value.
"Trace" XRF element
element with less than 0.1 weight % in a sample. reported as an element and uses atomic % as value.
Interior rings in powdered diffraction
sample is reflecting x-rays at a low angle.
Exterior rings in powdered diffraction
sample is reflecting x-rays at a high angle.
EDS microscope
A kind of scanning electron microscope that fires electrons at a sample in a vacuum and records the x-rays it emits from bombardment. used to determine average atomic number.
1 mole
6.022 x 10^23 atoms
K electron shell
shell valence electrons jump down to when replacing missing core electrons. results in the emittance of x-rays.
M electron shell
usually written as the Greek letter β (beta). has a higher energy level and is further out than the K or L shells, and thus gives off more energy when loosing electrons.
L electron shell
usually written as the Greek letter α (alpha). has a lower energy level and is closer to the K shell than the M shell is.
frequency equation
f=1/Time period
ionic radius
Distance from the center of an ion's nucleus to its outermost electron
ionic bond
Formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another.
covalent bond
A chemical bond that involves sharing a pair of electrons between atoms in a molecule. very strong.
metallic bond
a bond formed by the attraction between positively charged metal ions and the electrons around them. forms a "sea" of electrons that can flow when influenced by a magnetic field.
Van der Walls forces
a slight attraction that develops between the oppositely charged regions of nearby molecules.
hydrogen bond
A type of weak chemical bond formed when the slightly positive hydrogen atom of a polar covalent bond in one molecule is attracted to the slightly negative atom of a polar covalent bond in another molecule. Typically occurs in water.
electron sheilding effect
Electrons between the nucleus and the valence electrons repel each other making the atom larger.
cation trends
The size of a cation decreases as compared to that of its neutral atom as you progress down the periodic table.
anion trends
The size of a anion increases as compared to that of its neutral atom as you progress down the periodic table.
Mineral Criteria
1. Inorganic
2. formed in nature
3. solid in form
4. their atoms form a crystalline pattern
5. its chemical composition is fixed within narrow limits
crystalline
a qualitative statement about the order/arrangement of the 3D order of ions in a solid.
crystal
a substance in which the particles are arranged in an orderly, geometric, repeating pattern
most common elements in earth's crust (in order of highest to lowest)
oxygen, silicon, aluminum, iron, calcium, sodium, potassium, magnesium.
crystalline minerals
Naturally occurring inorganic compounds composed of atoms arranged in a 3D and repeating (periodically) pattern.
Amorphous minerals
Naturally occurring inorganic compounds that have no periodic 3D arrangement of atoms.
Monocrystalline
Composed of a single crystal.
Polycrystaline
Isotropic, this solid is a collection of many small crystals or grains.
Ahedral Crystals
Mineral with no crystal faces
Subhedral Crystals
imperfect but have enough crystal faces that their forms are recognizable.
Euhedral Crystals
Occurs as well-formed crystals showing good external form.
Angstrom
A unit of length equal to one ten-thousandth 10-10 of a meter or 100 picometers.
Ionic bond length
the sums of the cation and anion's radii.
chromophore
a transitional metal in a mineral whose electrons absorb certain wavelengths of light to enter a higher energy level. This blocks out certain wavelengths of light, causing the mineral to appear a certain color.
fluorescence
occurs when chromophores in a mineral absorb ultraviolet light and then re-emits it as visible light in dark conditions. Stops glowing as soon as ultraviolet light source is removed.
molecular orbital transitions
Occur in minerals when valence electrons transfer back and forth between ions and adjacent sites. Electrons can go back and forth between atoms, and the atoms' charge state will be changing.
Electrons move back and forth between crystal sites (localization)
Color center
A small defect in the atomic structure of a material that can absorb light and give rise to a color.
luminescence
light emitted by means other than burning, such as chemical or biochemical action or radiation.
Refraction of light
occurs when wave of light passes from one medium to another and the light wave is bent or refracted.
Crystal Field Transitions
Electronic transitions between partially filled 3d orbitals of transition elements.
band gap
The energy gap between an occupied valence band and a vacant band called the conduction band.
phosphorescence
Object absorbs ultraviolet light before re-emitting it as visible light. Electrons in the solid loose energy over a long span of time, causing the solid to glow for longer than fluorescent materials.
rotoinversion axis
Symmetry operator that combines rotation about the center and inversion through the center
Designated by a number with a bar, or a symbol with a circle inside
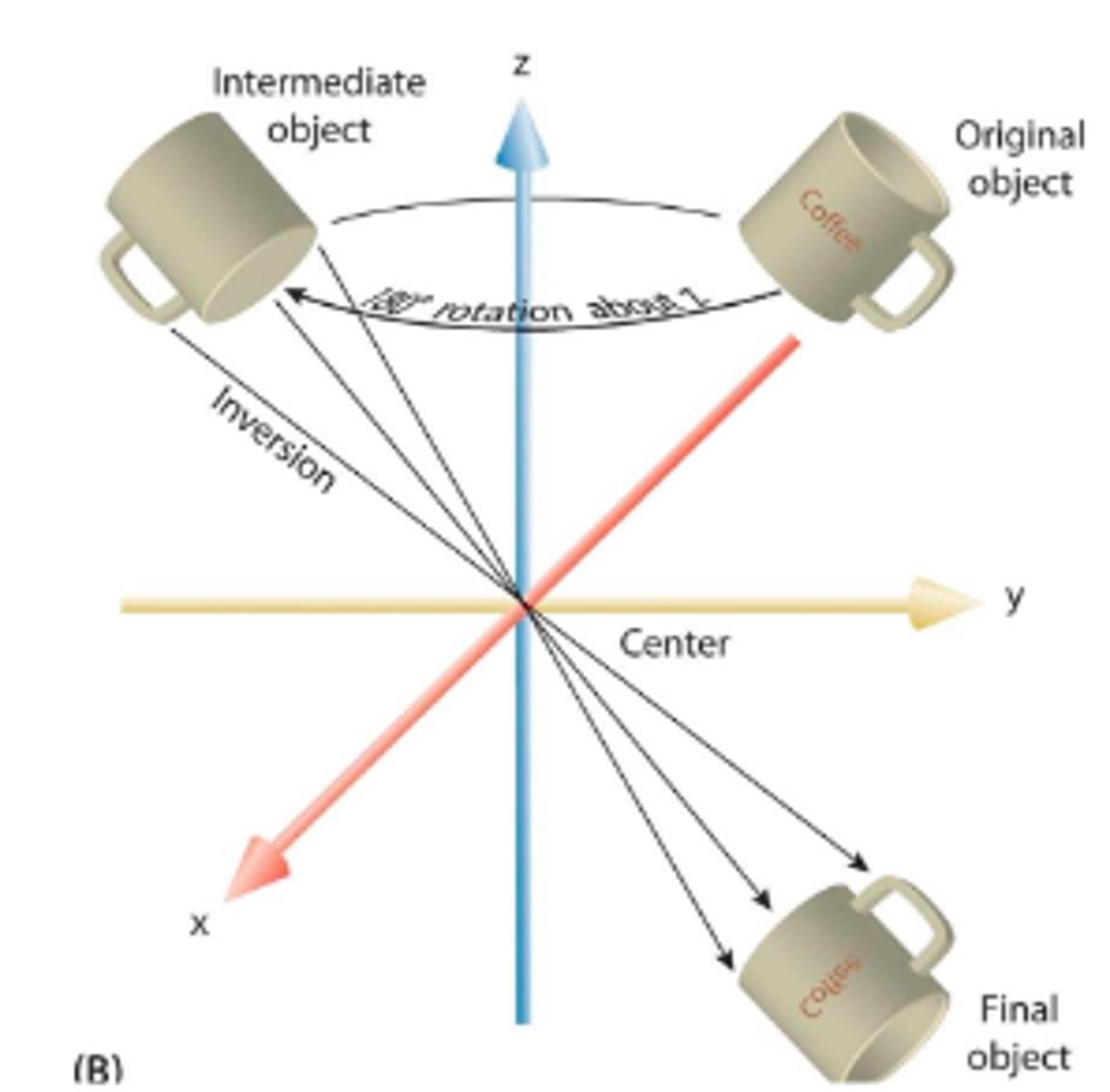
Mirror Plane Symmetry
determination if a crystal looks the same after it is cut in half with a single plane
rotation axis
Point on which an object can be rotated and it would still look the same. Rotation axes can be 2, 3, 4, or 6 fold.
lattice points
points in a crystal all of which have identical environments
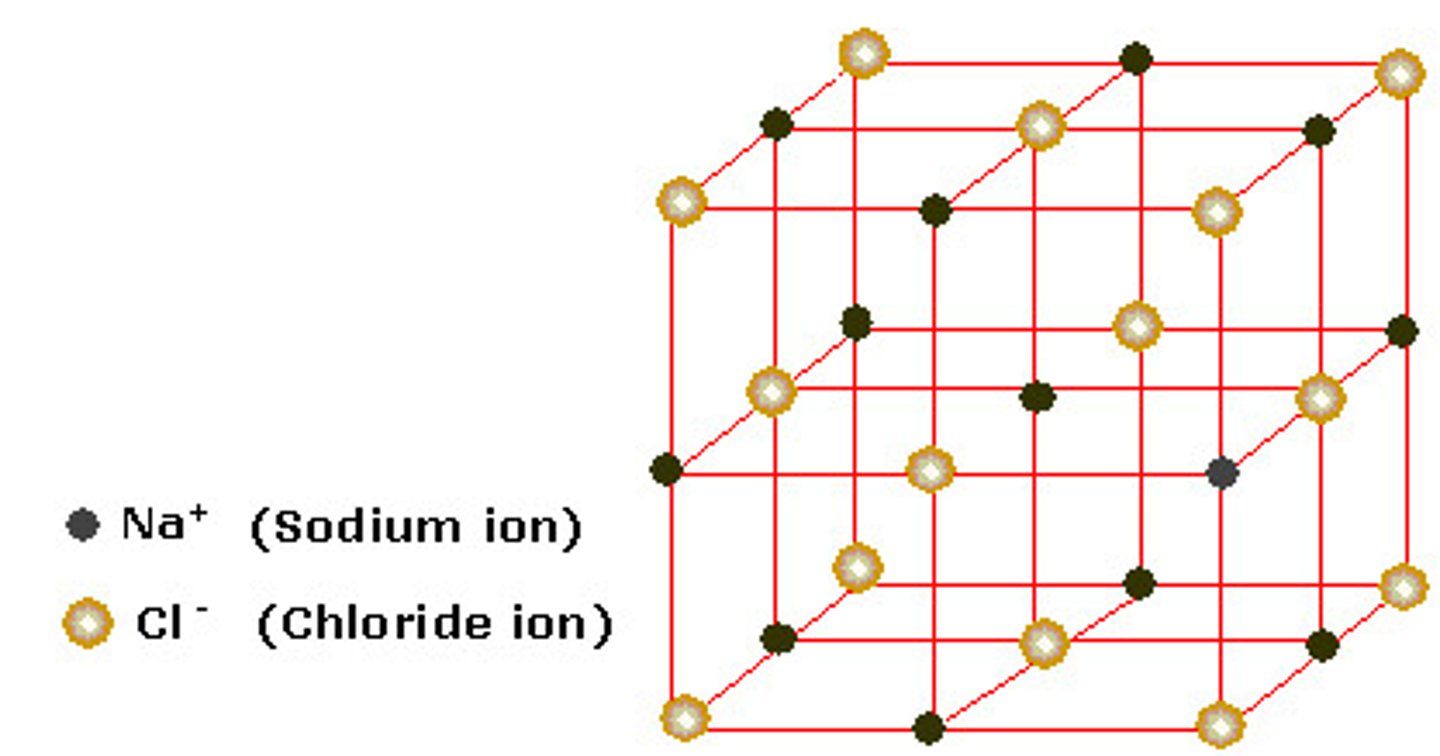
unit cell
the smallest group of particles within a crystal that retains the geometric shape of the crystal.
Primitive Arrangement
Unit cells share up to 4 lattice points, resulting in a total of 1 total lattice point per unit cell.
Non-Primitive Arrangement
Unit cell has an additional lattice point inside of it, along with the 4 lattice points it shares with its neighbors. the total number of lattice points in the unit cell is 2.
Oblique Unit Cell
lengths a and b (side lengths) are not equal and the corners are not 90 degrees.
Rectangular Unit Cell
Sides a and b aren't equal length, but all the corners are 90 degrees.
Centered Rectangular Unit Cell
Sides a and b aren't equal, but the corners are 90 degrees. There is a lattice point inside of the unit cell in the exact middle. Only kind of unit cell with non-primitive arrangement.
Hexagonal Unit Cell
Sides a and b are equal, but the corners are 120 or 60 degrees. The unit cell still has 4 sides, but they can tesselate to form hexagons.