Keynesian Long Run Aggregate Supply
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Long run (Recap)
All factors of production are fully flexible
Keynesian Economics
Markets can be imperfect and slow to adjust. Therefore the economy can be below full capacity for a considerable time and there is a rationale for the government to intervene.
Keynesian Long Run Aggregate Supply
The economy can be below full capacity in the long term, when AD is low.
Key Assumption: Unemployment can persist into the LR for several reasons:
Wages are sticky downwards (hard to cut, inflexible) meaning that labour markets don't clear
Negative multiplier effect: Once there is a fall in aggregate demand, this causes others to have less income and reduce their spending. A negative knock-on effect.
A paradox of thrift: In a recession, people lose confidence and therefore save more. By spending less this reduces AD even more.
Key Implication: Keynesians argue greater emphasis on the role of aggregate demand in causing and overcoming a recession.
Governments should act to promote AD growth in recessions.
The growth of AS is not enough to guarantee long term economic growth
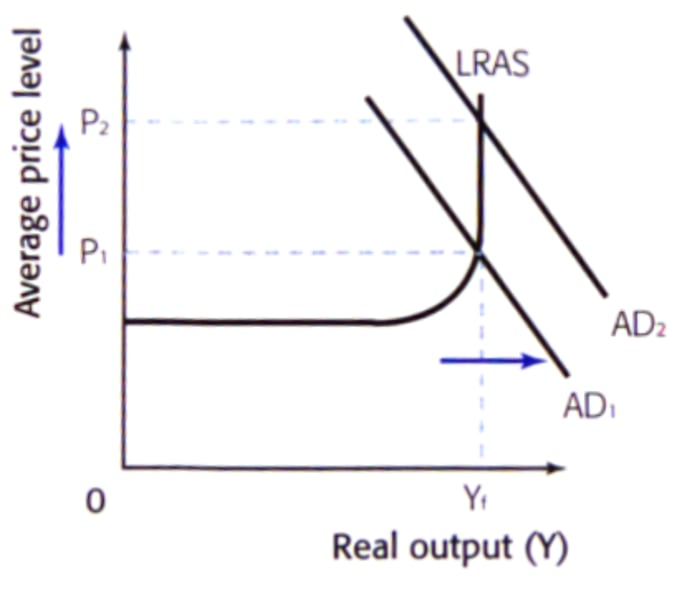
Keynesian LRAS Curve
The Keynesian LRAS curve graphs the relationship between long run real GDP and the price level, whether at potential or below.
Why is the Keynesian LRAS Curve L-shaped?
Part A: The horizontal part of the AS curve is perfectly elastic and occurs when there is spare capacity.
Firms can increase their output without having to pay higher wages
Part B: As the LRAS begins to curve upwards there is falling elasticity, and limited spare capacity.
Firms find it difficult to attract scarce resources and must pay more. Prices begin to rise.
Part C: The vertical part of the AS curve is perfectly inelastic and occurs when there is full employment, all resources are used.
Firms must now be willing to pay more than others to gain resources. Prices increase, but with no change in output.
Shifts of the Keynesian LRAS curve
Correspond to changes to either the quality or quantity of the factors of production (FoP), shifting YFE
Could be caused by improvements in education and skills, changes in relative productivity, changes in government regulations, demographic changes and migration
Keynsian LRAS curve diagram