Ecology 3: Cycles of Matter
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Matter
Anything that has mass and takes up space; "stuff" that stuff is made of
nutrient
substances that organisms need to live, such as food
biogeochemical cycle
Matter is never created or destroyed, so elements travel through living and non-living factors.
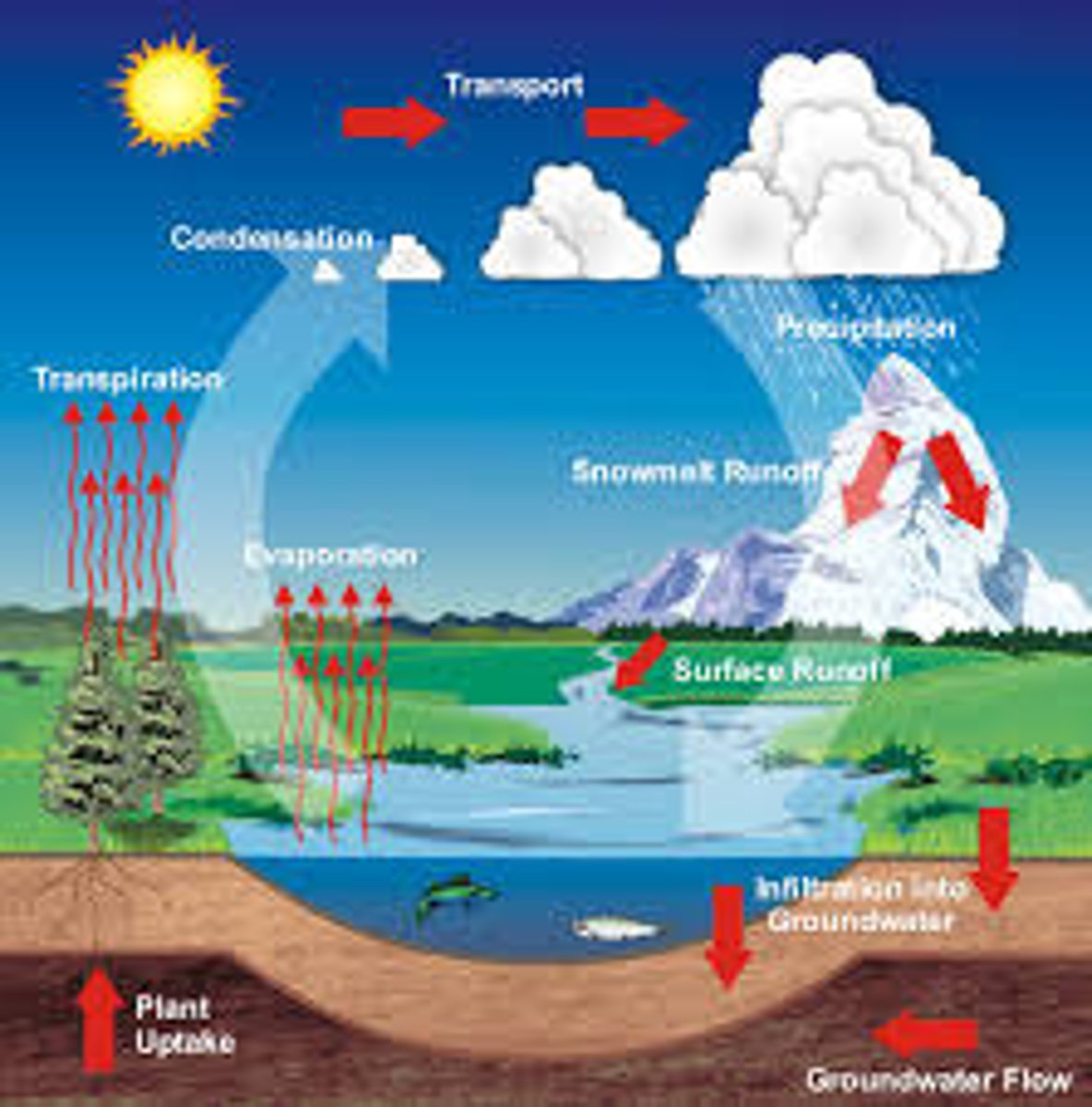
water cycle
water circulates between the atmosphere (air), ground water, oceans, lakes, and rivers, and through living organisms.
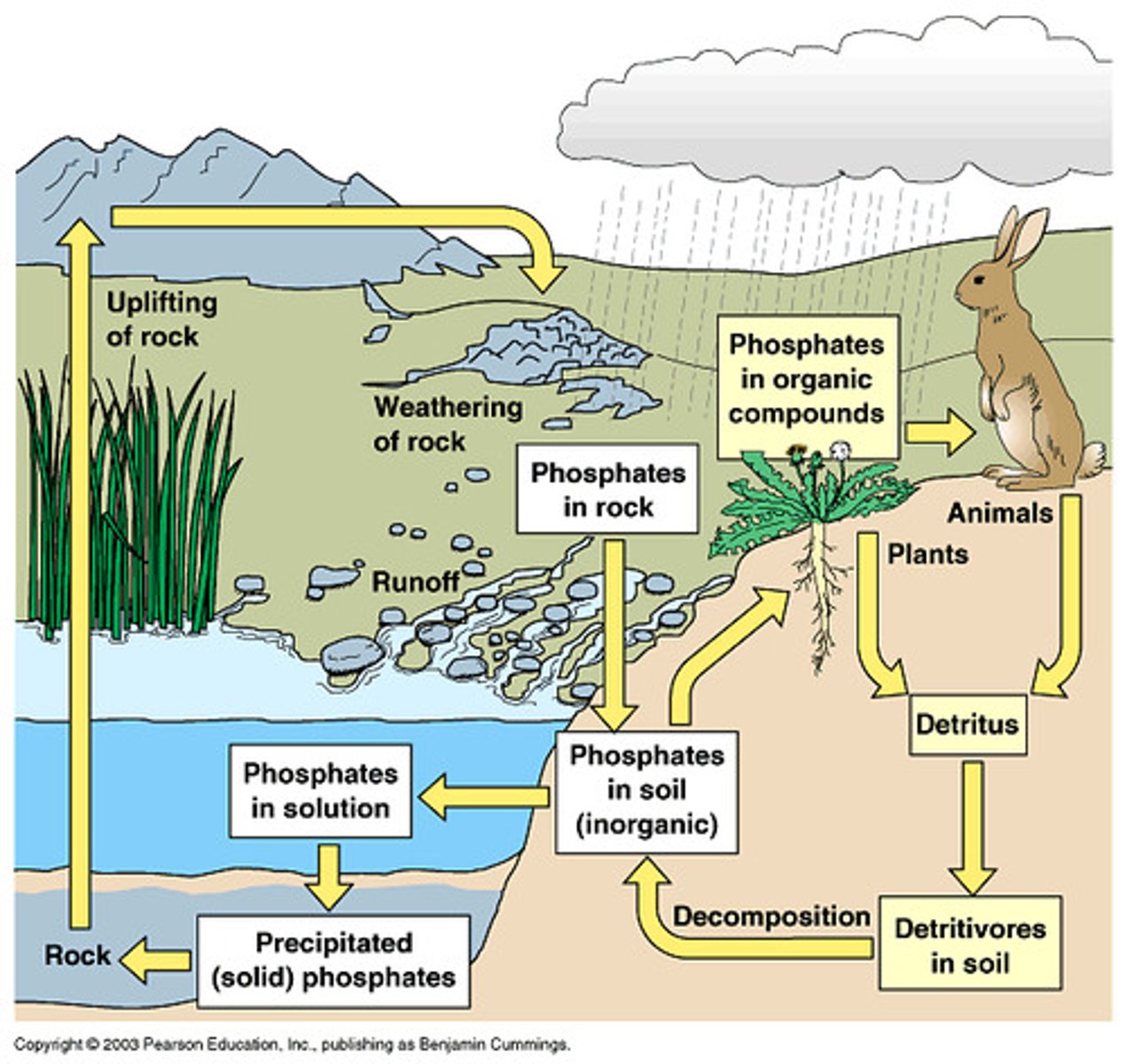
Phosphorus cycle
Phosphorus circulates through rock, into water and soil, and is taken up by living things when they absorb water or eat or drink. When living things die, the phosphorus returns to the soil and may over time become sediment and rock again.
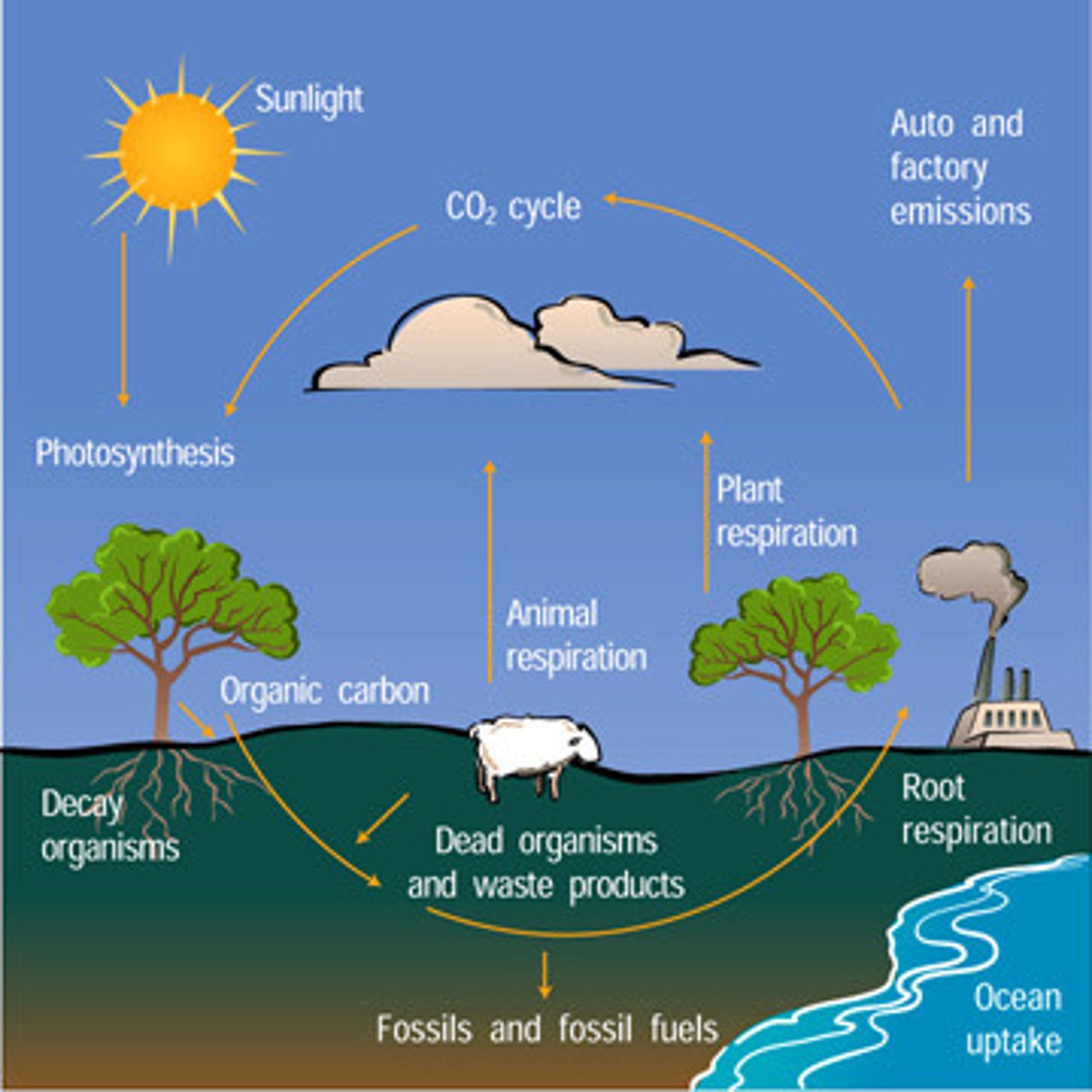
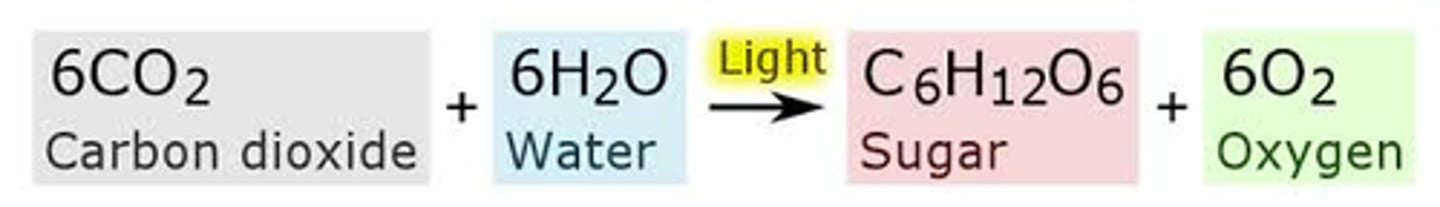
carbon-oxygen cycle
Carbon and oxygen cycle through respiration and photosynthesis: plants use carbon dioxide and water, and create glucose sugar and oxygen as a waste product; other organisms (including animals) use the oxygen and glucose to create energy and produce carbon dioxide as a waste product. Carbon in organisms may also return to the ground when they die and decompose.
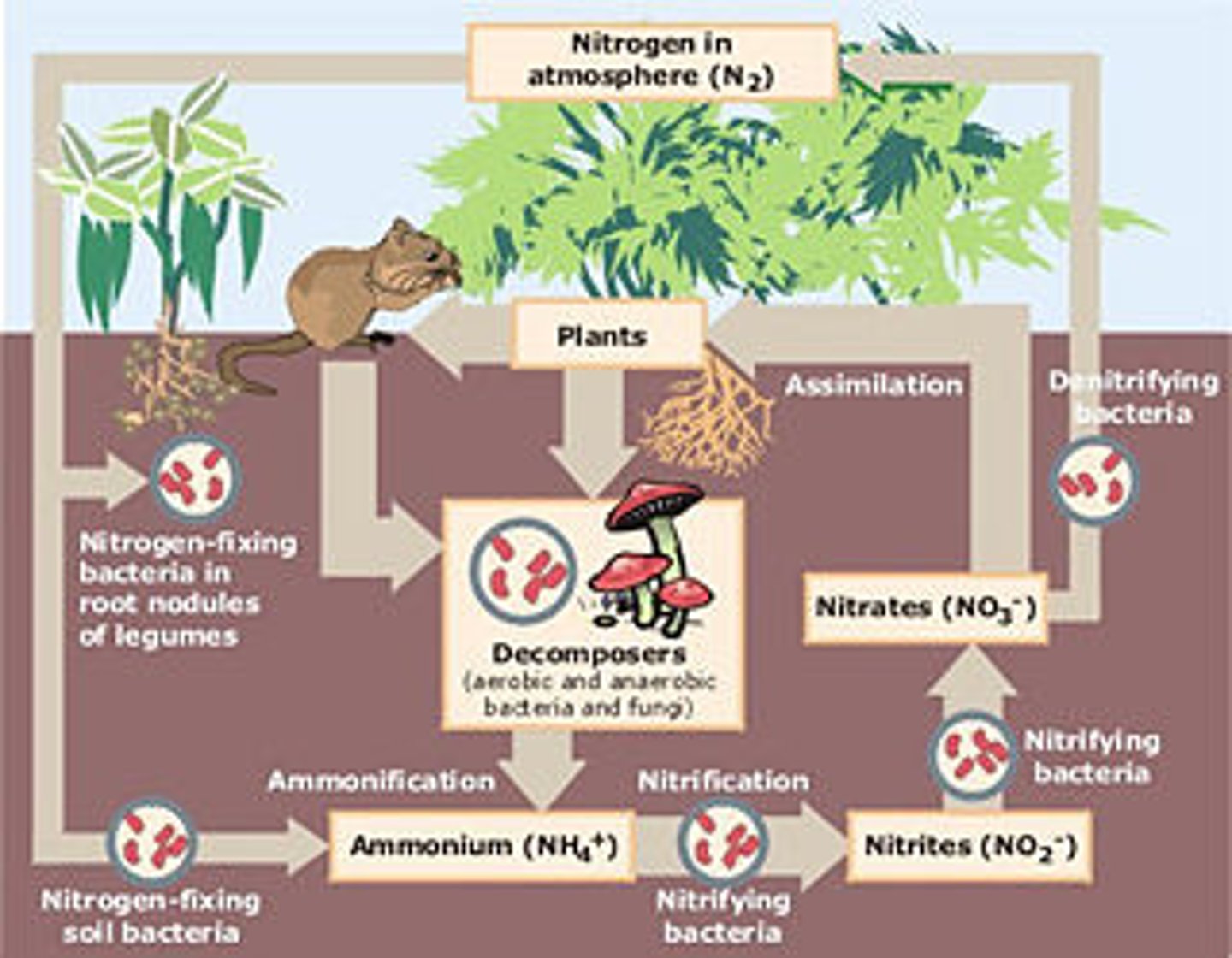
Nitrogen cycle
The atmosphere is 78% nitrogen, but most living things cannot use it in that form. Bacteria change the nitrogen gas into a form usable by plants. Consumers get nitrogen by eating other organisms. When organisms die, nitrogen in their bodies returns to the soil through decomposition (this process also relies on bacteria). Other bacteria return some nitrogen to the atmosphere.
nitrogen fixation
Bacteria take nitrogen gas from the atmosphere and turn it into a usable form for plants
respiration
oxygen gas + sugar (glucose, which includes carbon) to produce energy in the form of ATP; carbon dioxide and water are byproducts

photosynthesis
plants and other photosynthetic organisms use energy from the sun, water, and carbon dioxide gas to produce sugars (glucose, which includes carbon); oxygen gas is a byproduct
decomposition
Decomposers (some free-living bacteria and fungi) break down animal and plant material from dead organisms and nitrogenous waste products to release energy. During this process, nitrogen is released into the soil.
combustion
burning anything (especially fossil fuels) puts carbon dioxide into the atmosphere