Chemistry Stage 1 Exam Revision
1/208
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
209 Terms
What is the chemical formula of acidified potassium dichromate? What is it?
Cr₂O₇2-/H+
An oxidising agent - a substance that causes another substance to lose electrons (e.g. oxidize) in a chemical reaction
What is a primary alcohol?
Carbon attached to OH (hydroxyl) group only attached to 1 C
Terminal - usually at the end of a carbon chain
What is a secondary alcohol?
Carbon attached to OH (hydroxyl) group attached to 2 C
What is a tertiary alcohol?
Carbon attached to OH (hydroxyl) group attached to 3 C
What reactions occurs with Cr₂O₇2-/H+ for primary alcohol?
2 STEP REACTION
Alcohol changes to aldehyde
Aldehyde changes to carboxylic acid

What reactions occurs with Cr₂O₇2-/H+ for secondary alcohol?
ONLY 1 STEP
Alcohol changes to ketone

What reactions occurs with Cr₂O₇2-/H+ for tertiary alcohol?
NO REACTION
It won’t oxidise without a C-C break which doesn’t typically happen
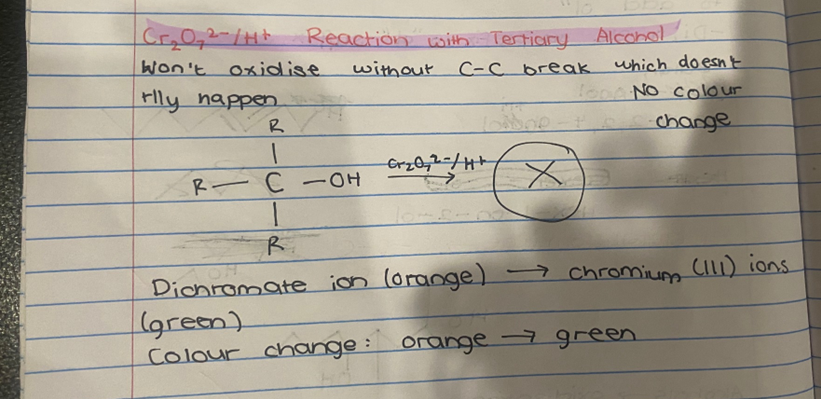
State the colour change of a reaction with Cr₂O₇2-/H+ and primary/secondary alcohols.
Dichromate ions (orange) to chromium (lll) ions (green)
The colour change is orange to green.
Define an isomer?
Same molecular formula diff structure
They can’t be superimposed, placed on top of each other, so that they look the same (e.g. they can’t be rotated/reflected to look the same)
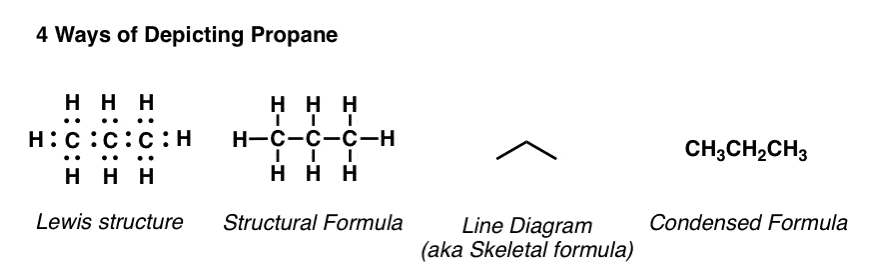
What are ways of depicting molecules?
What are the products for complete combustion?
Enough oxygen to fully oxidize the fuel
→ H2O + CO2
What are the products for partial combustion?
Isn't enough oxygen
→ H2O + CO
What are the products for incomplete combustion?
diff in relative amount of unburnt fuel even though their isn’t enough oxygen still not same as partial
→ H2O + C
What is the main factor determining whether combustion is complete, incomplete, or partial? What is the balancing order for combustion equations?
Availability of oxygen (oxidiser) relative to fuel
C,H,O
O can be fractions
What is Tollens’ reagent chemical formula? What are its other names?
Ag+/NH3
aka. ammoniacal silver nitrate or silver mirror test
What does Tollens’ reagent being basic do in a chemical reaction with aldehydes?
Its basic ∴ it accepts the acidic proton (H+)
It forms a carboxylate anion
Which is a carboxylic acid with with the acidic proton (H+) donated since the tollens' reagent is basic
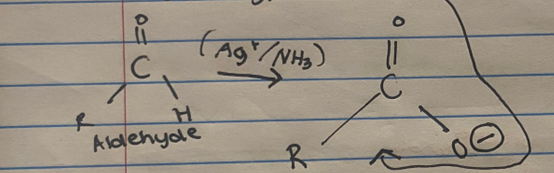
State the colour change of Tollens’ reagent.
Silver mirror finish on the inside of the reaction vessel
Silver ions are reduced to solid silver
What does Tollens’ reagent oxidise?
Only aldehydes 1 STEP REACTION
Aldehyde → Carboxylate anion
State the colour change of alkenes/alkynes in bromine water.
Brown to colourless
Due to the fact they are unsaturated hydrocarbons that undergo addition reactions with bromine
What makes a solute soluble?
Non-polar solvents (e.g. oil/benzene) dissolve non-polar molecules
Polar solvents (e.g. water) dissolve polar molecules
What are amphipathic molecules?
Contain both polar (hydrophilic) and nonpolar (hydrophobic) regions
Meaning that they are at least partially soluble in in both polar and nonpolar solvents
Name and explain the 3 main intermolecular forces from strongest to weakest.
Ion-dipole
Hydrogen bonding
Dipole-dipole interactions
London/Dispersion forces
What is a homologous series?
Groups of organic compounds
Share similar chemical properties
Their physical properties vary gradually as the length of the carbon chain increases.
Common general formula
Each member differs by a repeating unit (e.g. CH2)
What are primary interactions?
Involve the sharing or transfer of electrons between atoms to form stable molecules (e.g. ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds)
Stronger forces than secondary interactions
Explain what secondary interactions are.
Weak interactions between molecules that arise from the distribution of electrons around atoms and molecules
Weaker forces involved than primary interactions
What is the electronegativity trend in the periodic table?
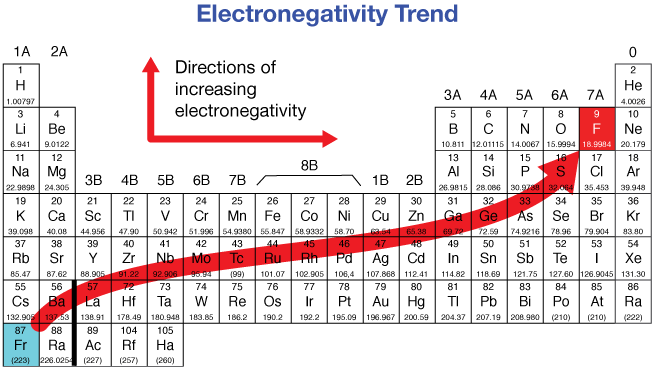
Exceptions:
Noble gases (e.g. hydrogen generally has a partial positive charge)
What are partial charges?
Charges that exist on atoms within a molecule due to uneven electron distribution in chemical bonds
δ±
What makes a molecule polar or non-polar?
A molecule is considered polar if it has a permanent dipole moment—a constant separation of charge.
What is the difference between polar bond and polarity of a molecule?
Polar bond - chemical bond where electrons are shared unequally between two atoms - creates a partial positive charge on one atom and a partial negative charge on the other.
Molecular polarity - the overall polarity of a molecule - depends on the presence of polar bonds and their arrangement in space
(e.g. A molecule can have polar bonds but still be nonpolar overall if the bond polarities cancel each other out due to symmetry)
What are polar bonds?
Covalent bond - unequally shared electrons
Greater electronegativity diff = greater polar nature of the bond
What are characteristics of non-polar molecules?
Low melting/boiling points - due to weak secondary interactions (disperson forces holding the molecule tgt) - which require little energy to overcome
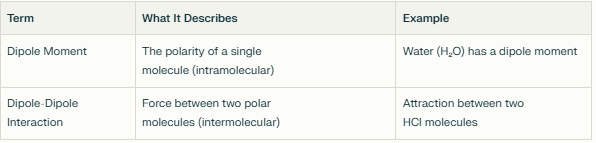
What is a dipole-dipole moment? How is it different from dipole-dipole interactions?
Dipole- two poles of charge
Moments - Measure of the separation of positive and negative charges within a molecule, indicating its overall polarity
Interactions - attraction between δ+ end of one polar molecule and the δ− end of another.
This attraction is electrostatic in nature
Arises because polar molecules have permanent dipoles due to differences in electronegativity between atoms within the molecule
What type of molecule do dipole-dipole interactions and H bonding primarily occur with? Explain why.
Polar molecules
Both hydrogen bonding and dipole-dipole interactions require polar molecules because polarity provides the partial positive and negative charges necessary for these intermolecular attractions.
Hydrogen bonding is a particularly strong and specific case of dipole-dipole interaction, occurring only when hydrogen is bonded to N, O, or F.
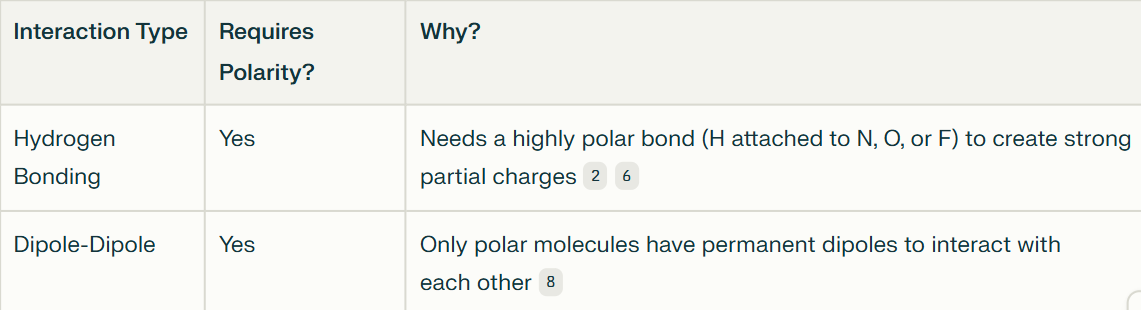
Explain hydrogen bonding?
H - N, O, F - highly electronegative
Between 2 separate molecules
The partially positive hydrogen and a partially negative N, O, or F atom
Explain dispersion forces
Present in all polar/non-polar molecules
Instantaneous dipoles - temporary fluctuations in electron distribution, creating instantaneous dipoles that induce dipoles in neighbouring molecules
When one molecule develops this temporary dipole, the positive side attracts the electrons in a nearby molecule, causing a shift in its electron distribution. This creates a second, induced dipole in the neighbouring molecule
The temporary dipoles caused by electron fluctuations result in only brief, weak attractions (London dispersion forces), not a permanent charge separation. Since these fluctuations average out over time, the molecule as a whole remains non-polar
Weakest intermolecular force
Are C-H bonds polar or non-polar? Why is it that the longer the carbon chain the less soluble it is?
NP
Larger NP region due to larger area is that hydrophobic - there are fewer favourable interactions between the solute and solvent
Decreased solubility - water molecules cannot surround and stabilize the nonpolar parts effectively
If a molecule has the same amount/type of atoms but a diff structure, which 1 has a higher boiling point?
Straight chained alkanes - higher boiling point due to larger SA
Branched - Lower boiling point due to smaller SA
If the intermolecular forces are the same, what concludes which molecule has the higher boiling point?
Which molecule is heavier
Increasing molecular weight leads to stronger dispersion forces due to more electrons and a larger SA, making it harder for the molecules to separate and enter the gas phase
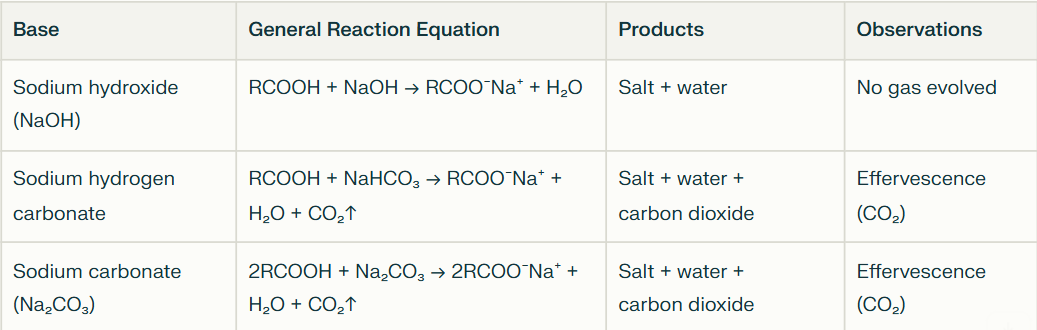
What common bases does carboxylic acid react with? What type of reactions are they?
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
Sodium hydrogen carbonate/Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3)
Sodium carbonate (Na2CO3)
Acid-base neutralisation reactions
What products form from carboxylic acid reacting with NaOH?
Carboxylate Salt + Water
No gas evolved
What products form from carboxylic acid reacting with NaHCO3?
Carboxylate Salt + Water + Carbon dioxide
Visible effervescence due to CO₂ release which is a common test for the presence of carboxylic acids
What products form from carboxylic acid reacting with Na2CO3?
Carboxylate Salt + Water + Carbon dioxide
Visible effervescence due to CO₂ release which is a common test for the presence of carboxylic acids
Which molecules are more soluble in polar substances?
Hydrocarbons are generally more soluble in polar solvents
more soluble in non-polar solvents as their hydrocarbon chain increases
Why are carbon chains non polar?
Similar electronegativities of C and H, resulting in weak or negligible polarity in C-H bonds
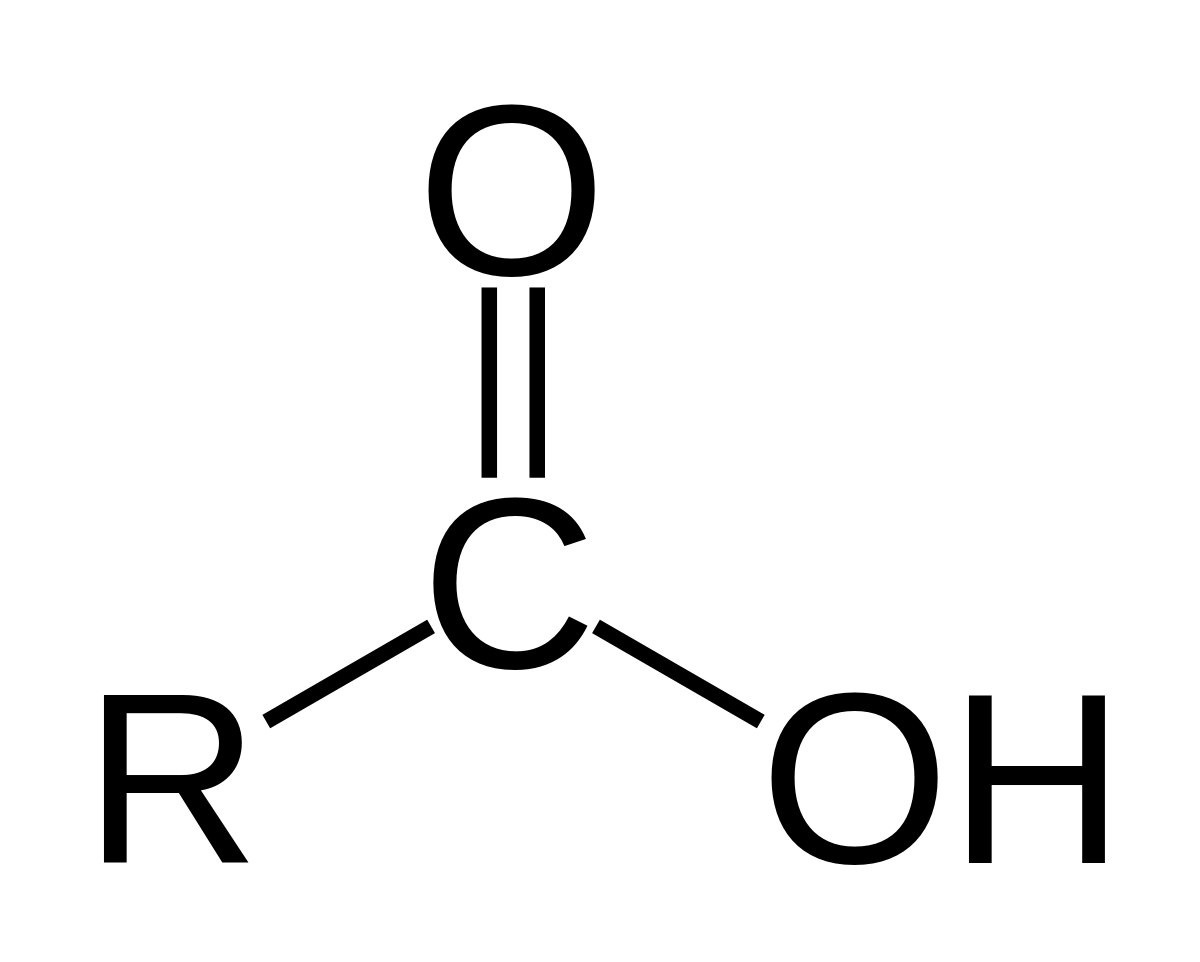
How to recognise carboxylic acids?
Carboxyl functional group
C double bonded O and OH
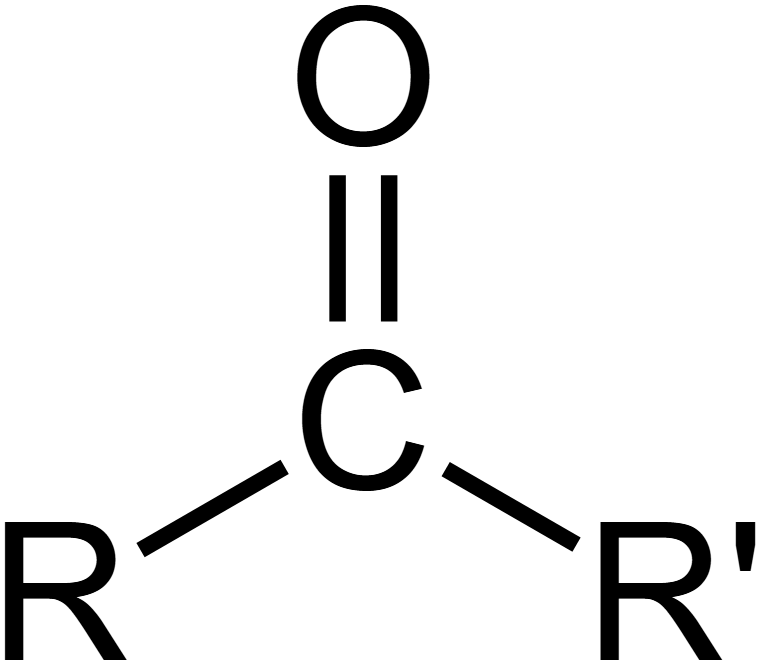
What is a carbonyl?
C double bonded O
What is a polymer?
Long chain molecule formed by many repeating units of monomers
What is a monomer?
A small molecule that combines with many other monomers to form a polymer.
Double bond present
What is the correct notation to draw a polymer from a monomer?
Replace the double bond in the monomer with a single bond
Draw brackets around the repeating unit.
“n” outside the brackets - repeating unit
What kind of of hydrocarbon can undergo addition polymerisation?
Only alkenes
Reaction conditions: High temp/pressure
What are esters formed by?
Esterification - condensation reaction - where 2 molecules react to form a larger molecule while releasing a smaller molecule (e.g. water)
Reactants: Alcohol + carboxylic acid
Reaction conditions: Heat and Acid catalyst
How many bonds does carbon form?
4!!!!!
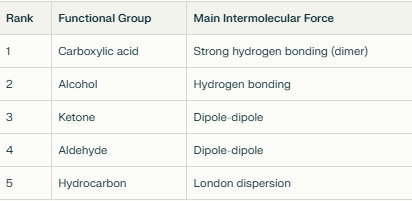
Rank the functional groups and their boiling points from highest to lowest.
What is a thermosetting polymer?
Hardens instead of melting
Has covalent cross links between polymer chains
Not recyclable
What is a thermoplastic polymer?
Can be melted and reshaped
Secondary interactions only - small energy amount is required to break the attractive forces
Recyclable
What is the difference between thermosetting and thermoplastic polymers?
Thermosetting polymers have covalent cross links between polymer chains, allowing them to harden instead of melting.
Whereas thermoplastics do not have cross links, meaning they can be melted and reshaped.
Why would a halogenated product be more soluble than its non-halogenated original?
Halogenation Increases Polarity - highly polarizable, which increases the overall polarity of the molecule compared to a simple alkene. This increased polarity enhances the molecule's ability to interact with polar solvents like water or alcohols through dipole-induced dipole interactions
.
Comparison to Alkene: The double bond in 7-methyloct-5-en-1-ol does not significantly increase the molecule's polarity compared to the effect of two large, polarizable iodine atoms. Thus, it remains more hydrophobic overall.
Hydrophobic Effect: Both molecules have a similar alkyl chain length and a terminal alcohol group, but the hydrophobic effect is slightly mitigated in the diiodo compound due to the increased polarity from the iodine atoms.
Hydrogen Bonding: Both molecules can hydrogen bond via their -OH group, but the overall solubility is also dictated by the rest of the molecule. The diiodo derivative, being more polar, will be less hydrophobic and thus more soluble in polar solvents than the alkene6.
Why would a halogenated product have a higher boiling point than its non-halogenated original?
Halogenation allows for dipole-dipole interactions where there weren’t any before
These interactions are stronger than the dispersion forces they replaced
Stronger forces require more energy to overcome
Overall, increasing the boiling point of the halogenated product.
NOT THE ONLY ASNWER OBVI ITS JS IF U GET STUCK
What is the solubility of nitrates?
ALWAYS SOLUBLE
What is the solubility of Na+/sodium salts
ALWAYS SOLUBLE
What is the solubility of NH4 + /ammonium salts
ALWAYS SOLUBLE
What is the solubility of K+ /potassium salts
ALWAYS SOLUBLE
What is the solubility of CH3 COO- /acetate salts?
ALWAYS SOLUBLE
What is general solubility rule for sulfates?
Most are SOLUBLE
Exceptions: Ba2+, Sr2+, Pb2+, Ca2+ (Barium, Strontium, Lead, Calcium)
What is the general solubility rule for iodides?
Most are SOLUBLE
Exceptions: Ag+, Pb2+
What is the general solubility rule for chlorides?
Most are SOLUBLE
Exceptions: Ag+, Pb2+
What is the general solubility rule of carbonates?
Most are INSOLUBLE
Exceptions: Na+, K+, NH4+
What is the general solubility rule of hydroxides?
Most are INSOLUBLE
Exceptions: Na+, K+, NH4+
What is the polyatomic carbonate ion?
CO32-
What is the polyatomic sulfate ion?
SO42-
What is the polyatomic nitrate ion?
NO3-
What is the polyatomic hydroxide ion?
OH-
What is the polyatomic iodide ion?
I-
What is the general charge of silver?
Ag+
What is the general charge of iron?
Fe2+
What is the general charge of copper?
Cu2+
What is the general charge of lead?
Pb2+
What is the general charge of barium?
Ba2+
RMBR THE STATES OF MATTER? What are they?
(aq) - aqueous
(s) - solid
(g) - gas
(l) - liquid
What is the general charge of magnesium?
Mg2+
What is an electrolyte?
Ionic compounds dissolved in water
Electrolytes can conduct electricity
What is a double displacement reaction?
AB + CD → AD + CB, where A and C are typically cations and B and D are anions
NO ELECTRONS TRANSFERRED
What is a precipitate?
2 water soluble solutions can react to form an insoluble solid product - the precipitate
Step by step explain how to do a net ionic equation
Write the products
Balance
Write a dissociated equation {leave (s) as one molecule}
Remove spectator ions
Rewrite the equation with only those molecules left
RMBR CHARGES AND STATES OF MATTER
What is a spectator ion? How do I identify them?
An ion that appears unchanged on both the reactant and product sides of a chemical equation. DOES NOT PARTICIPATE IN THE CHEMICAL REACTION!
Write complete ionic equation
Identify the ions that are the same on both sides of the chemical equation
How to write a complete ionic equation?
Write the dissolved ionic compounds as dissociated ions
Leave (s) as the same molecule
RMBR CHARGES AND STATES OF MATTER
Explain all the unit conversions
Rmbr gL-1 to %w/v is ÷ 10
Rmbr %w/v to gL-1 is × 10

What are the criteria for a reaction to occur?
-Sufficient activation energy
-Correct orientation
What factors affect the rate of reaction?
-Temperature
-Concentration
-Surface Area
-Catalysts
How does temperature affect the rate of a reaction?
Temperature - affects how fast the atoms move
Higher temp leads to more collisions which means a higher chance of productive collisions, that have sufficient activation energy for the reaction to occur.
How does surface area affect the rate of a reaction?
SA
More SA means more area that is able to react which enhances the rate of reaction.
How does concentration affect the rate of reaction?
Concentration - not necessarily (aq)
More particles increase the chance of collisions which leads to a higher chance of productive collisions
How do catalysts affect the rate of reaction?
Catalysts - remain unchanged (aren’t consumed in the reaction)
They provide an alternative pathway with lower activation energy making it easier for the reactant molecules to transform into products.
By lowering the energy barrier, catalysts help more collisions result in a successful reaction, effectively speeding up the reaction.
What is the Brønsted-Lowry acid-base theory?
Defines acids as proton donators (H+) and
bases as proton acceptors
What are conjugate acids and bases?
Conjugate base - acid that has donated its proton
Conjugate acid - base that has accepted a proton
State the products of a reaction between an acid and a hydroxide?
Acid + base → salt + water (H2O)
State the products of a reaction between an acid and a carbonate?
Acid + carbonate → carbon dioxide (CO2) + water (H2O) + salt
State the products of a reaction between an acid and a metal?
Metal + acid → hydrogen gas (H2) + salt
What is a polyprotic acid?
An acid with more than 1 acidic proton (H+)
Monoprotic - 1 proton to be donated
Diprotic - type of polyprotic acid - 2 protons to be donated
What is an amphiprotic substance?
Can act as a base, accepts a proton (H+), or an acid, donates a proton (H+), in a chemical reaction