Enthalpy and Thermodynamics: Key Concepts and Calculations
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What does the First Law of Thermodynamics state?
Energy is neither created nor destroyed in any process.
What is the mathematical expression for the First Law of Thermodynamics?
ΔEsystem = -ΔEsurroundings; ΔE = q + w, where q is heat and w is work.
Why are constant pressure conditions relevant in heat transfer?
They represent normal laboratory conditions due to relatively constant atmospheric pressure during a reaction.
What does qp represent in thermodynamics?
qp represents enthalpy (ΔH).
What is the sign of ΔHrxn for an exothermic reaction?
ΔHrxn is negative, indicating heat is released.
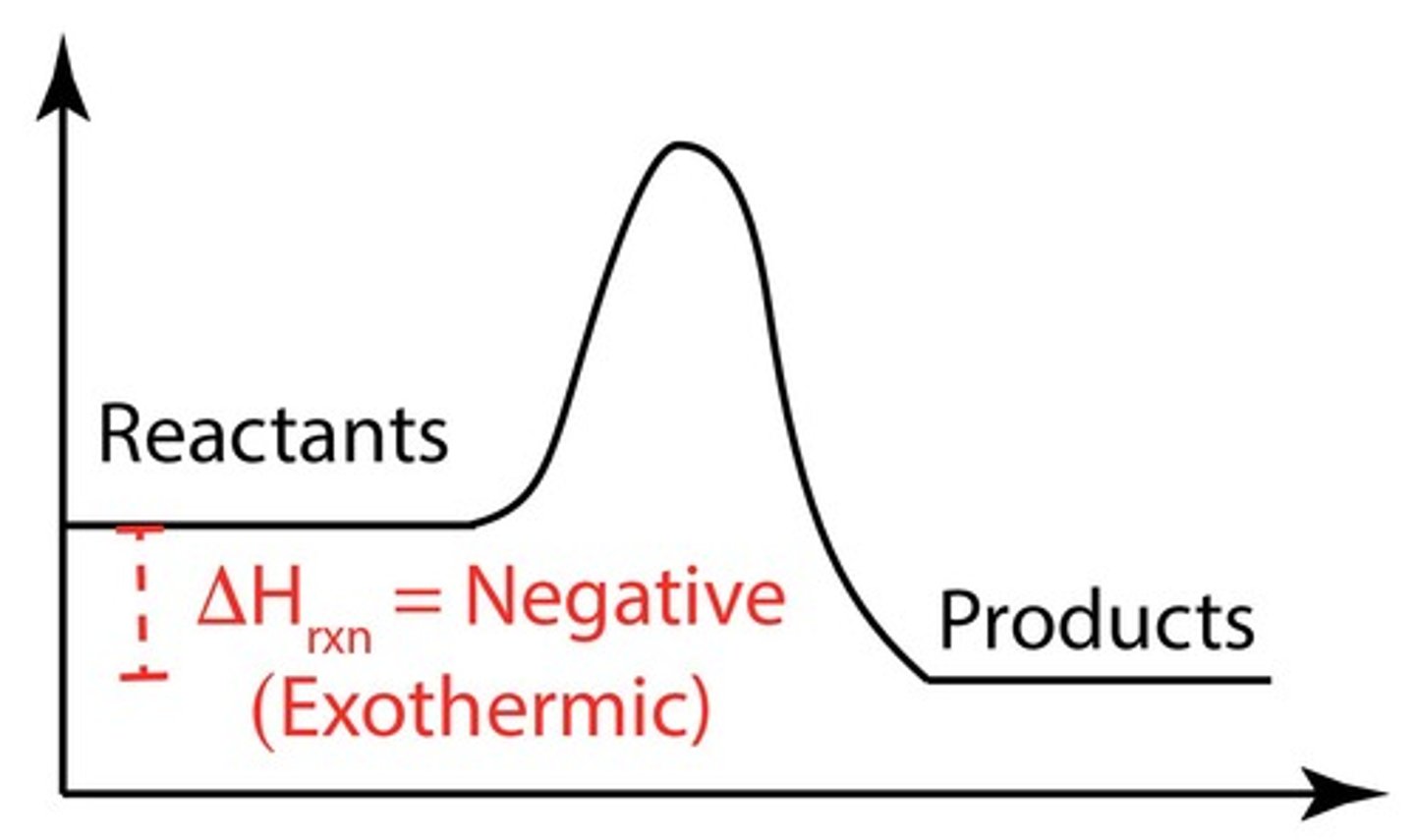
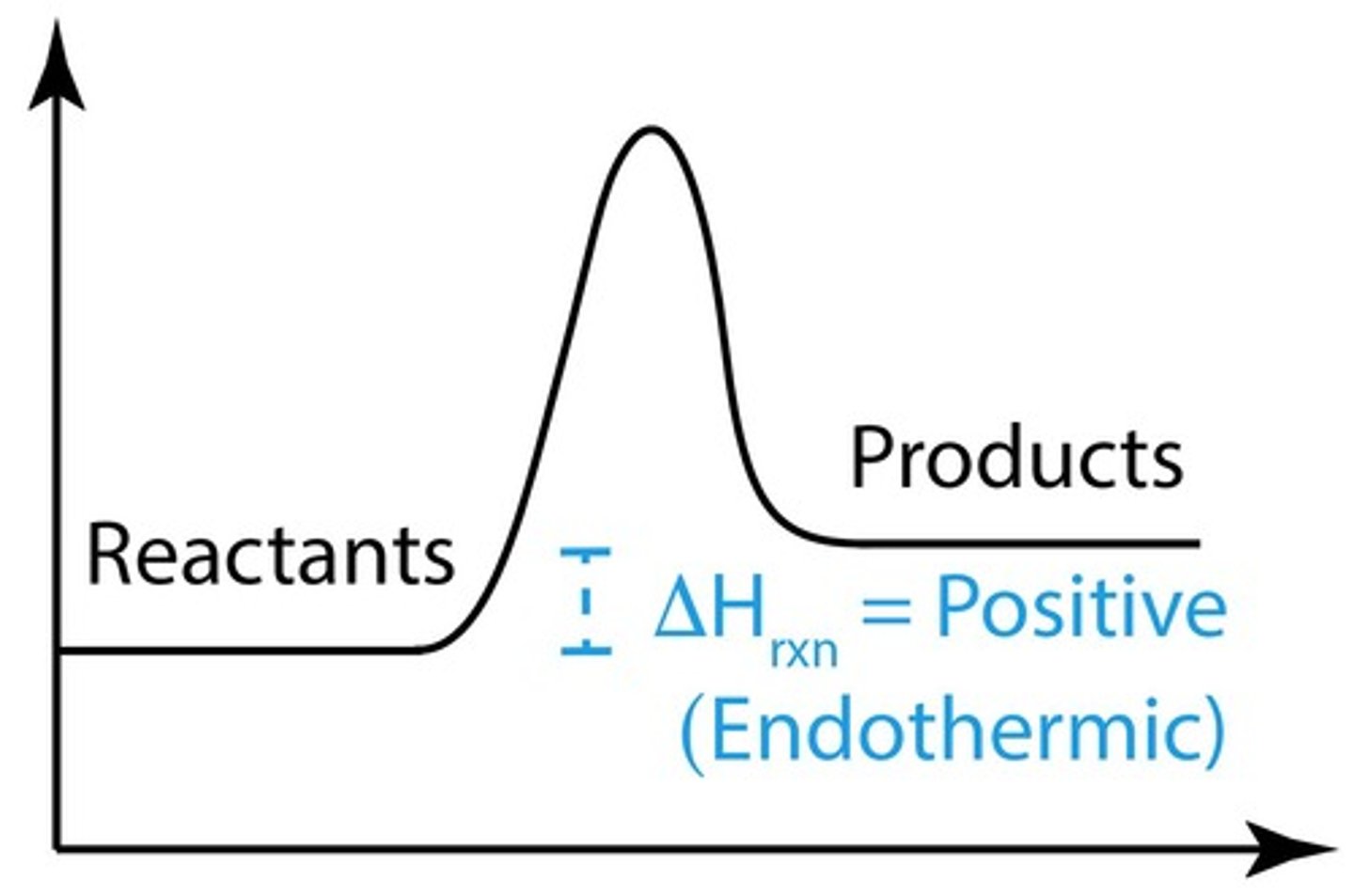
What is the sign of ΔHrxn for an endothermic reaction?
ΔHrxn is positive, indicating heat is absorbed.
Where does the energy released by an exothermic reaction come from?
It comes from the products having lower chemical potential energy than the reactants.
What type of reaction is more thermodynamically favored?
Exothermic reactions are favored because they result in more stable products with lower potential energy.
What is the formula to calculate ΔHrxn from bond energies?
ΔHrxn = Σ(ΔH bonds broken) + Σ(ΔH bonds formed).
What does bond breaking require in terms of energy?
Bond breaking requires energy, making it endothermic.
What does bond forming release in terms of energy?
Bond forming releases energy, making it exothermic.
What is the typical unit of energy in thermodynamics?
Joule (J) is a common unit of energy.
How is a calorie defined in terms of Joules?
1 calorie = 4.184 Joules.
What is the relationship between calories and kilocalories?
1000 calories = 1 kilocalorie (kcal).
In the context of thermodynamics, what is kinetic energy?
Kinetic energy is the energy of motion, proportional to temperature.
What is potential energy in thermodynamics?
Potential energy is stored energy, such as bonding and nuclear energy.
What happens to the energy in a system when sweat evaporates?
The system (sweat) absorbs heat from the surroundings, resulting in a cooling sensation.
In a combustion reaction in a car engine, what is the system and surroundings?
System: combustion reaction; Surroundings: car and everything else.
If a reaction does 75.4 J of work and absorbs 25.70 cal of heat, how do you calculate ΔErxn?
ΔE = q + w; convert calories to Joules and then apply the values.
What is the energy change (ΔErxn) for a reaction that absorbs 107.5 J of heat and does 75.4 J of work?
ΔErxn = 107.5 J - 75.4 J = 32.1 J.