Scientific Method
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Scientific Method
A flexible set of steps that scientists follow to conduct valid experiments and discover new things about the world.
Aristotle
Ancient Greek philosopher & scientific thinker; believed all problems could be solved by simply thinking about them.
Did not test his ideas or conduct science experiments.
Galileo
First true scientist; Actually tested his ideas with experiments and the scientific method
Hypothesis
Second step of the scientific method. An educated guess to a problem or question; stated in the "If, then" format
State the problem/question
The first step of the scientific method
Experiment
Carried out by scientists to test a hypothesis, make a discovery or answer a question
Conclusion
Made after analyzing the experiment's data; states whether the hypothesis was accepted or rejected
Variables
Factors that you are testing and analyzing in an experiment
Independent Variable
Factor that is different between groups, or changed purposely during a scientific experiment.
Dependent Variable
Factor that is measured during a scientific experiment; your results/data
Control Variable
Factor that is kept constant/the same in a scientific experiment
Experimental Group
Group that is being tested; group that receives the independent variable
Control Group
Group that receives normal conditions/treatment during a scientific experiment
Observation
Information we collect about the world using our five senses
Qualitative
Using only words to describe things
Quantitative
Using numbers/exact measurements to describe things
Inference
A conclusion or assumption based on observations
Theory
An explanation to a problem that has been shown to be valid after many repeated experiments
Share & Report Findings
The 6th step of the scientific method that allows others to learn about your results
Refine & Retest
The final step of the scientific method that allows improvement to experiments
Data
A collection of facts, such as numbers, words, measurements, observations or just descriptions of things.
The information we collect from conducting an experiment and analyze to form a conclusion.
Analyze
To examine carefully and in detail as to identify causes, key factors and results.
Scientists must do this to their data.
Reliable
Can be trusted; dependable; accurate
Scientific data must this.
Controlled Experiment
A scientific experiment where everything is held constant/the same, except for one thing, which is the independent variable
X Axis
The horizontal axis found on the bottom of a graph. Typically where the independent variable goes.
Y Axis
The vertical axis found on on the left side of a graph. Typically where the dependent variable goes.
Elements of a Graph
1. Title
2. Axis Titles/Labels
3. Axis Scales
4. Data
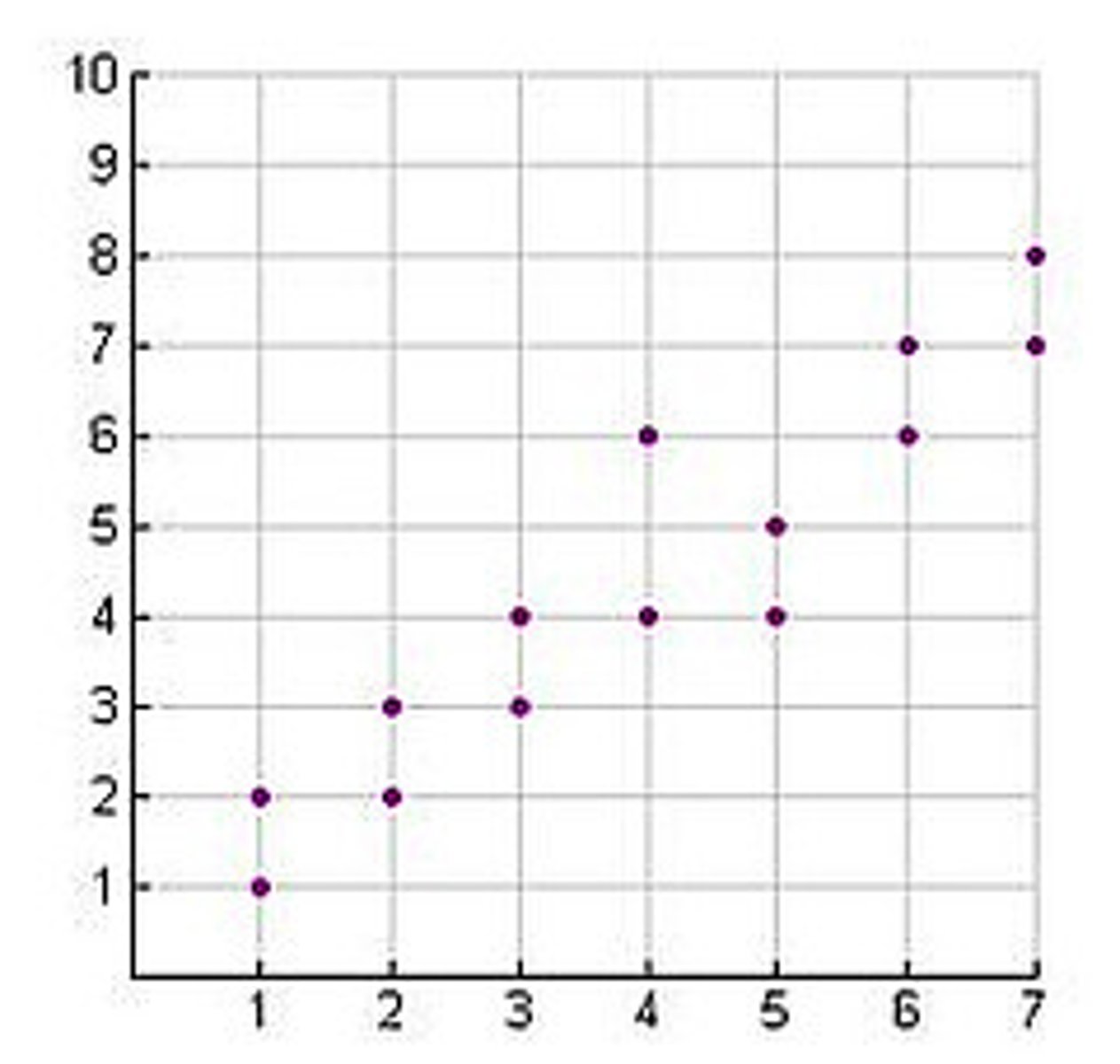
Direct Relationship
A graph that shows an upscaling (positive slope) line/trend; both variables increase at the same time.

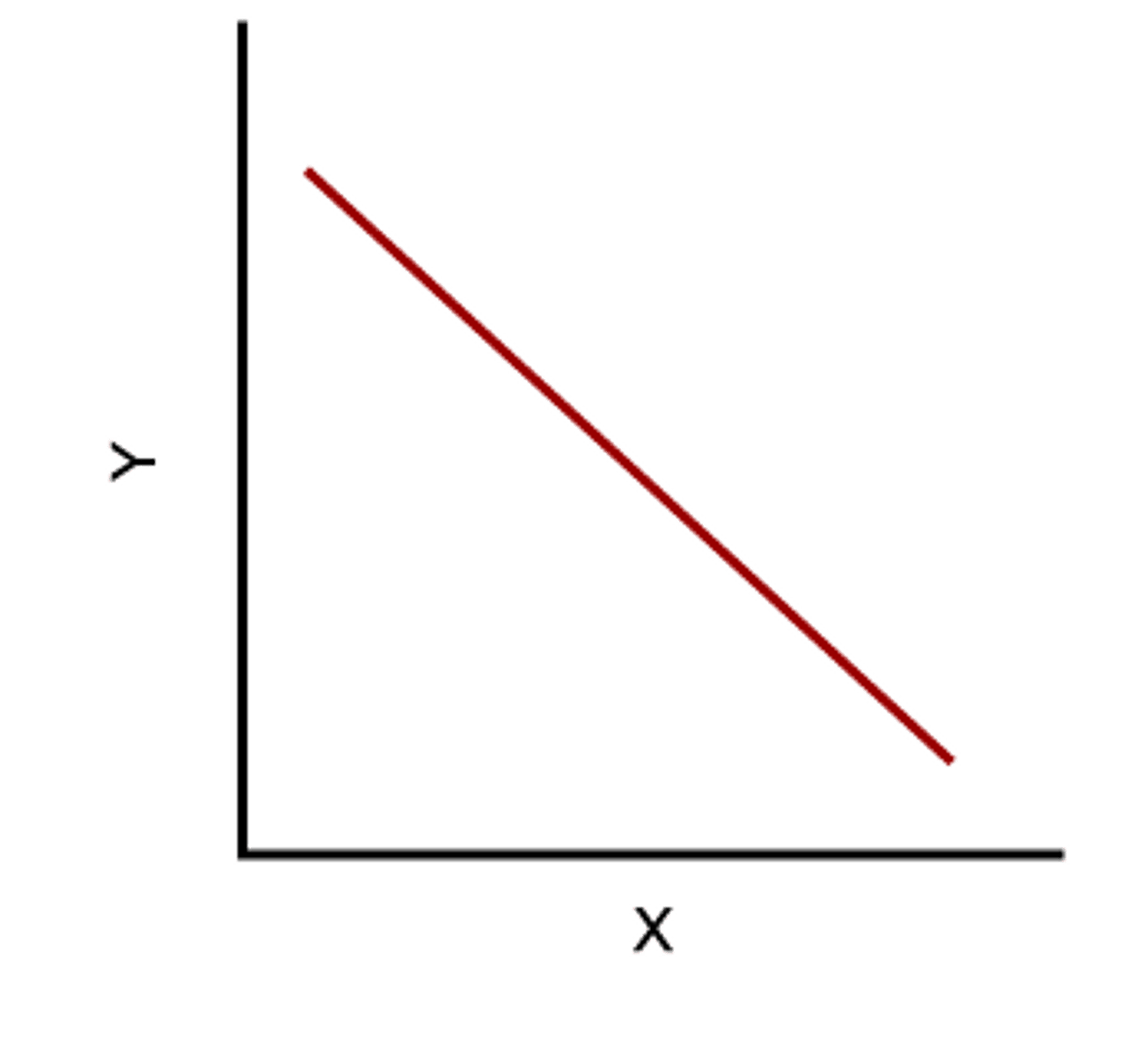
Indirect Relationship
A graph that shows an downscaling (negative slope) line/trend; both variables decrease at the same time.
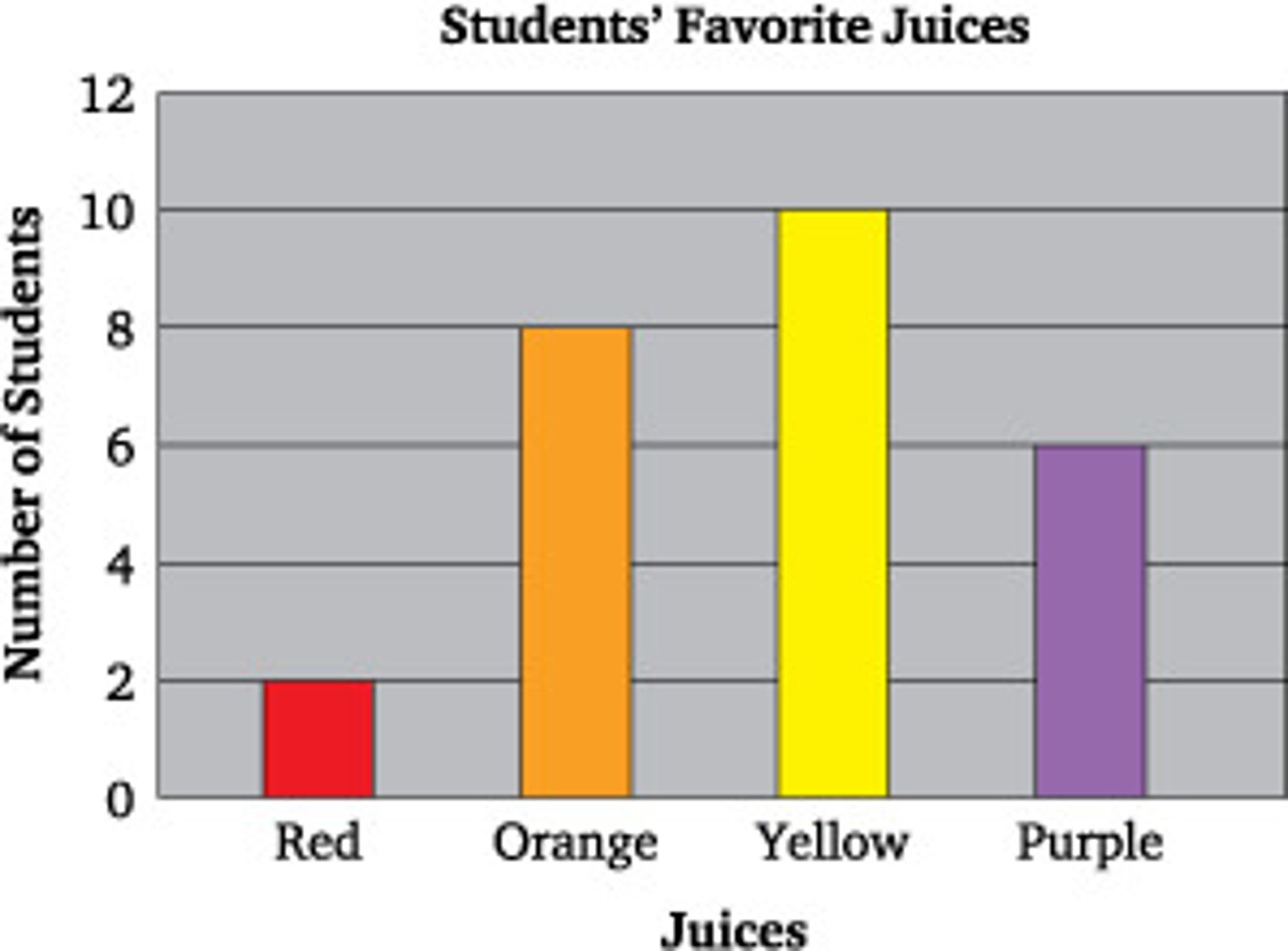
Bar Graph
Used to compare categories of data
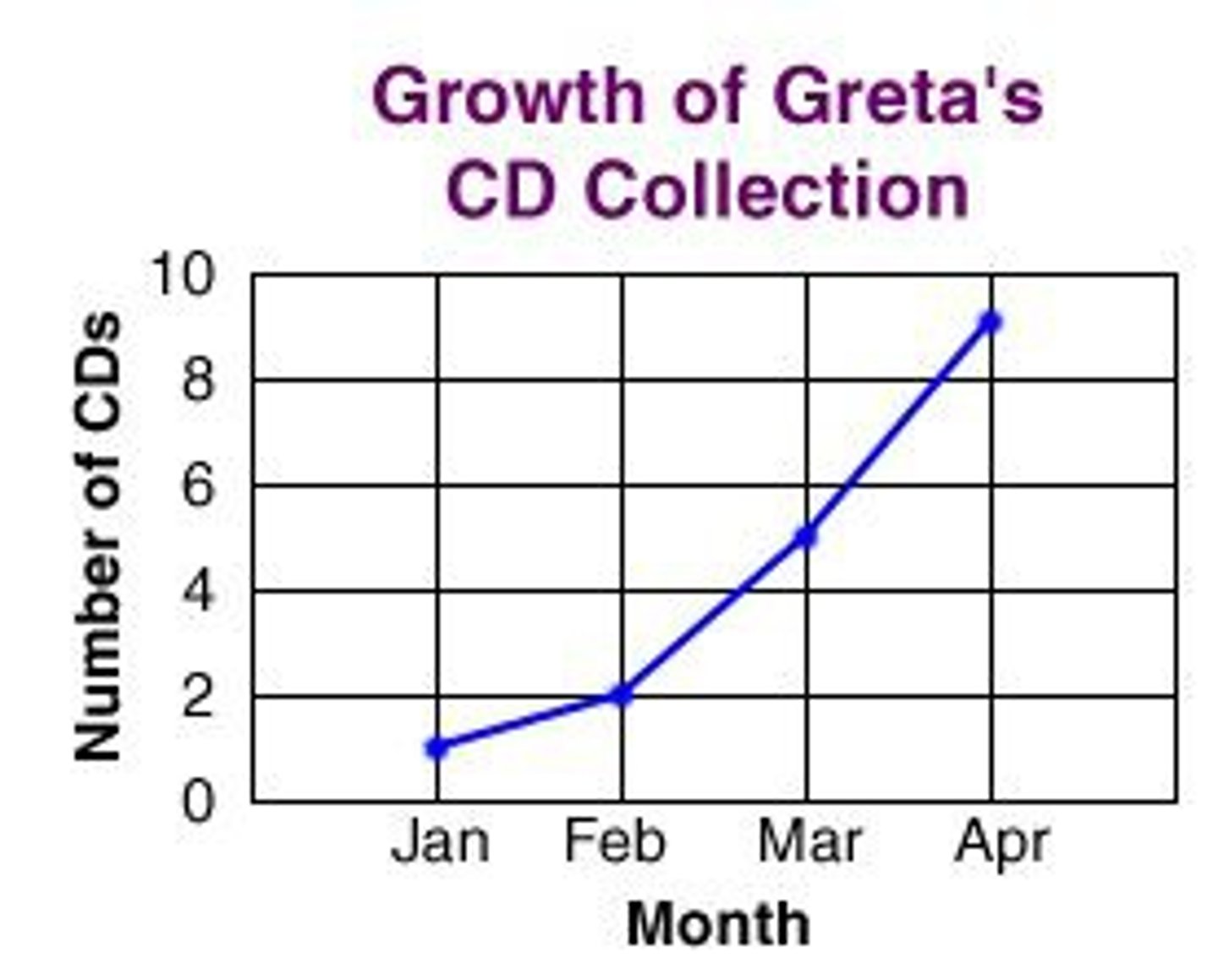
Line Graph
Used to that connect a series of data points with a line to show how something changes over time
Scatter Plot
A graph that uses points to visualize the relationship between two variables