201 - First Three Weeks of Development
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
fertilization
week 1 of embryological development:
implantation
week 2 of embryological development:
gastrulation
week 3 of embryological development:
ampulla
where does fertilization normally occur?
endometrium
where does implantation normally occur?
corpus luteum
identify the structure
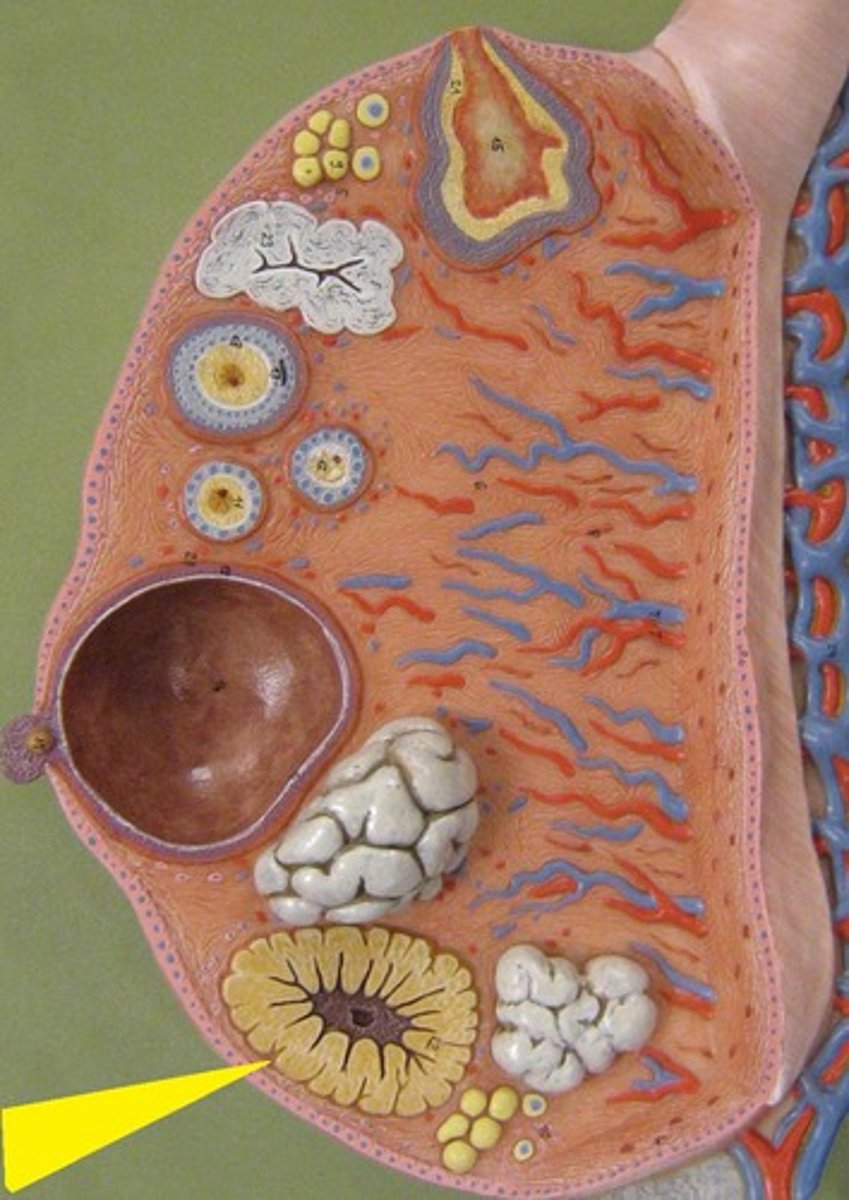
fimbriae
identify the structure
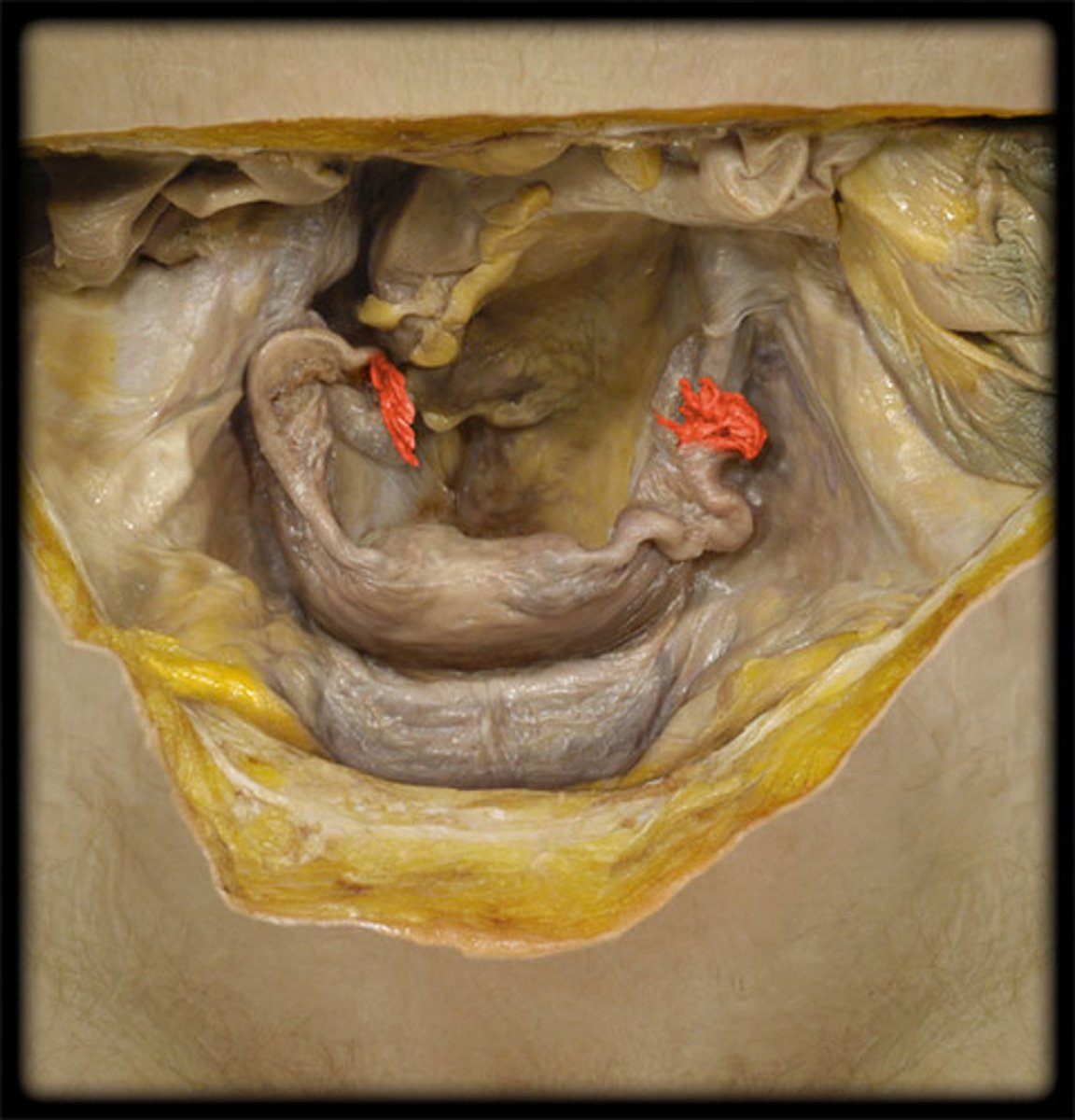
infundibulum
identify the structure
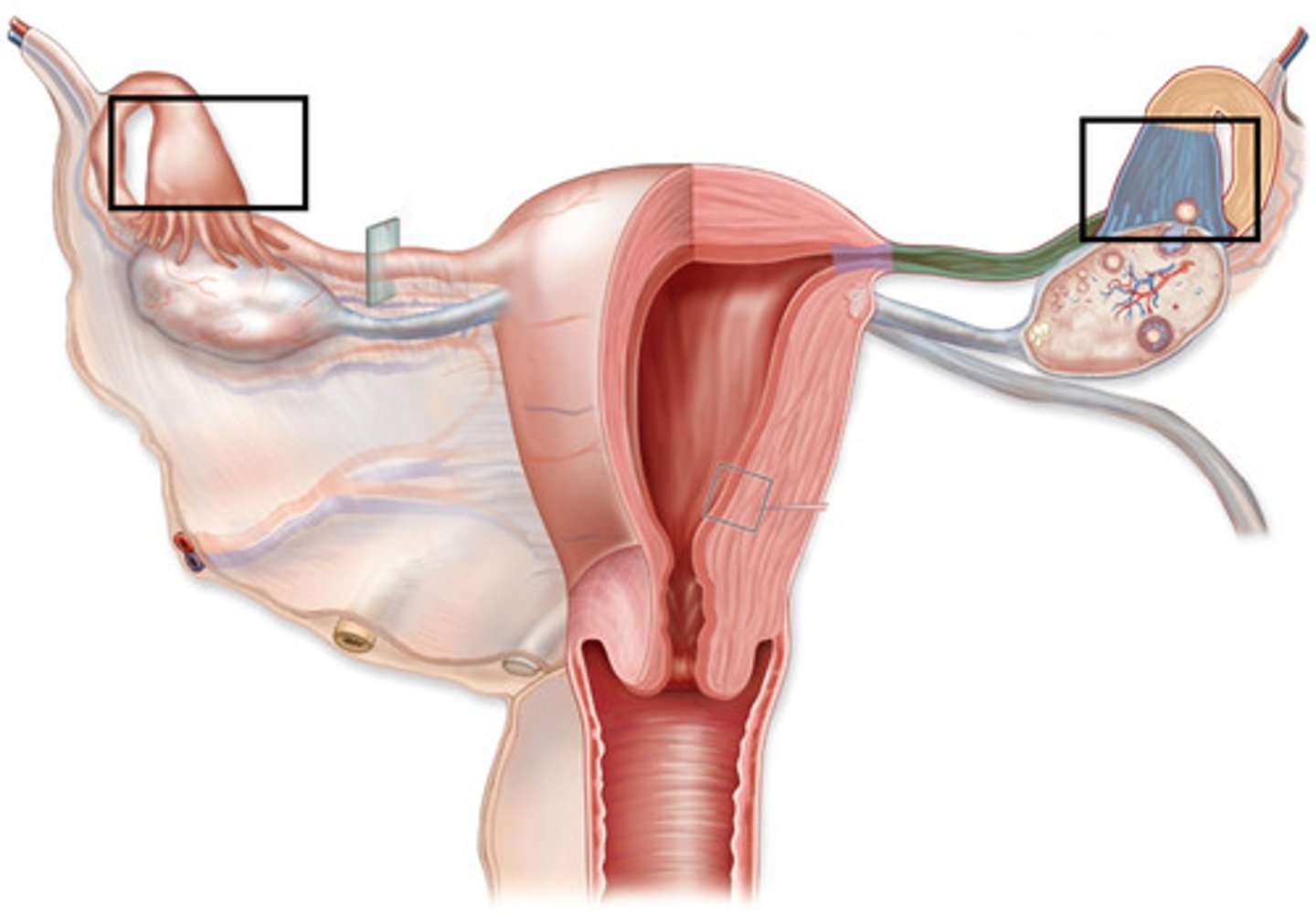
ampulla
identify the structure
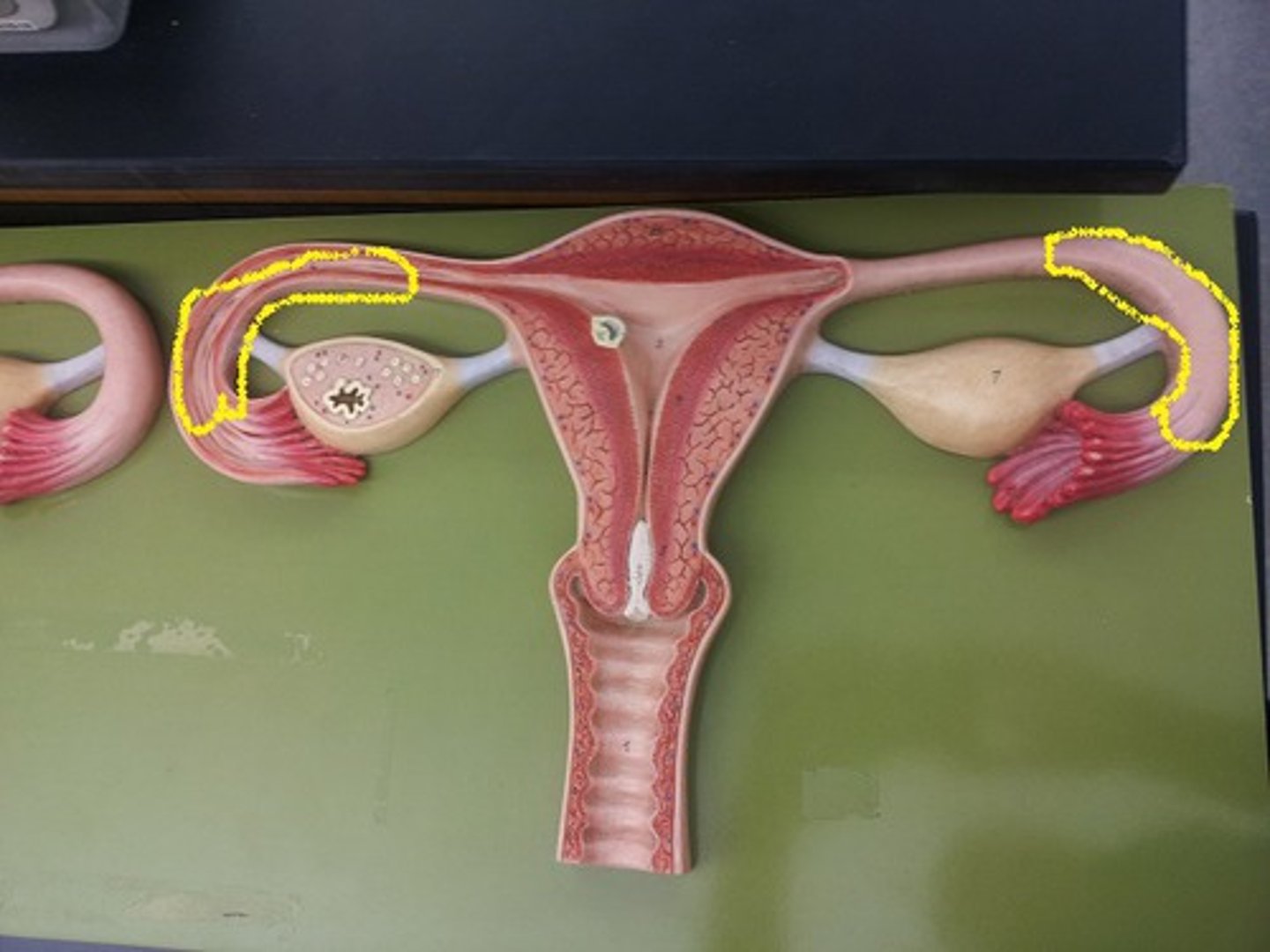
endometrium
identify the structure
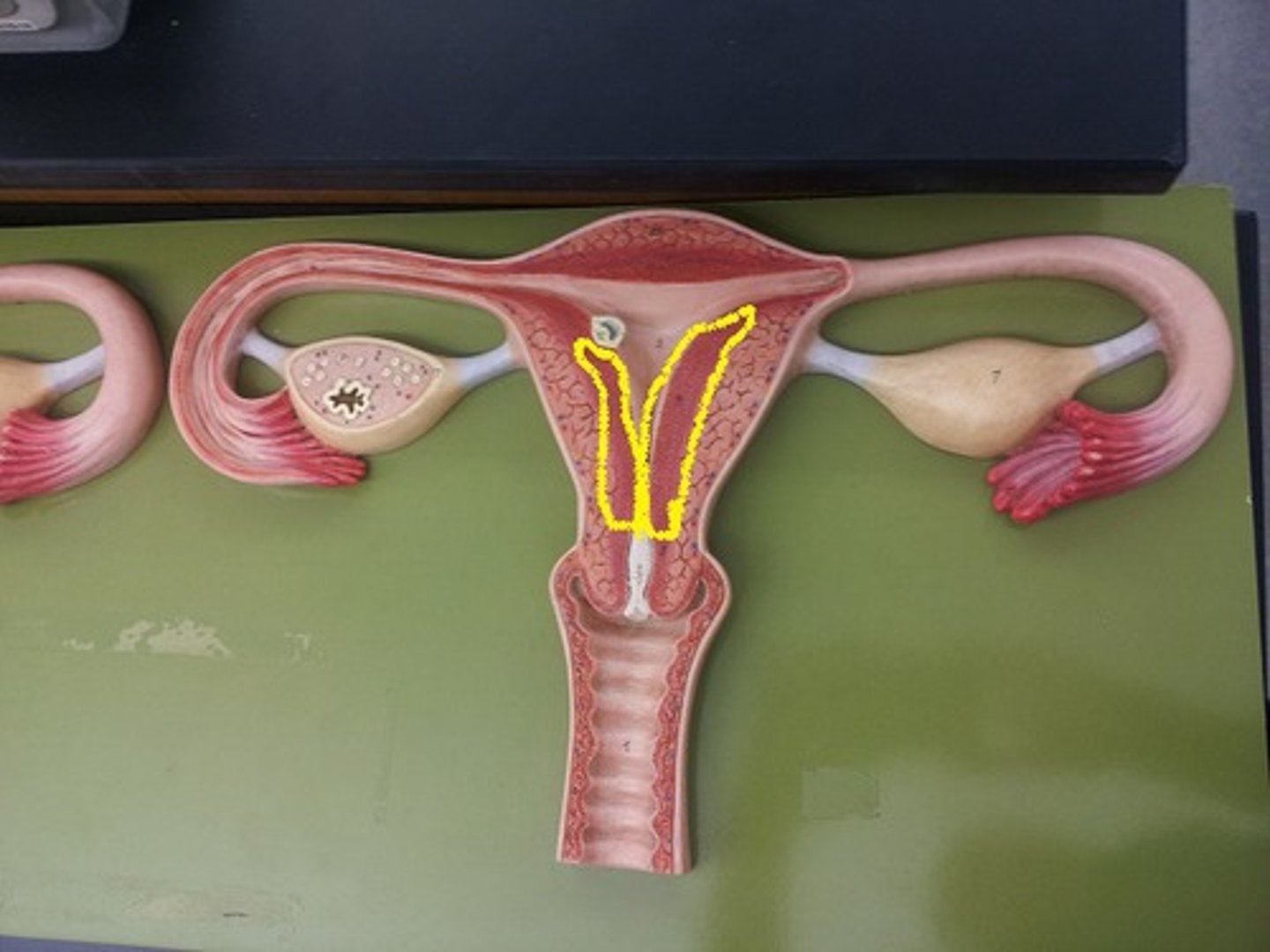
corpus luteum
Remnants from the ruptured follicle form the:
HCG
what hormone keeps the corpus luteum alive?
(“Fancy Cats Bake Mini Cookies Before Breakfast”)
fertilization
cleavage
blastomere
morula
compaction
blastocyte
name the 6 steps of development that occur in week 1: fertilization (in order):
fertilization stage
stage where capacitation and fertilization occur
cleavage stage
identify the stage of fertilization:
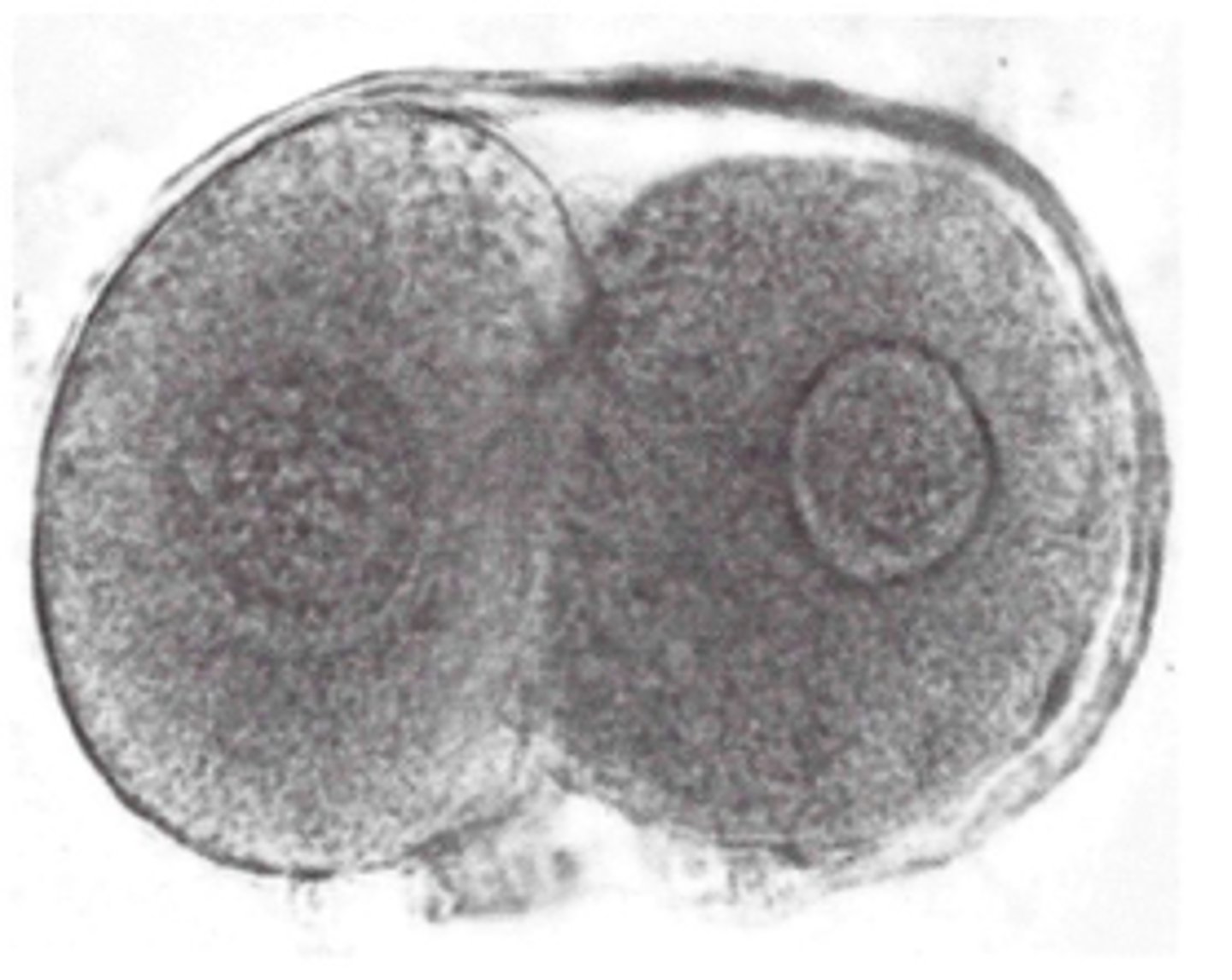
blastomere stage
identify the stage of fertilization:
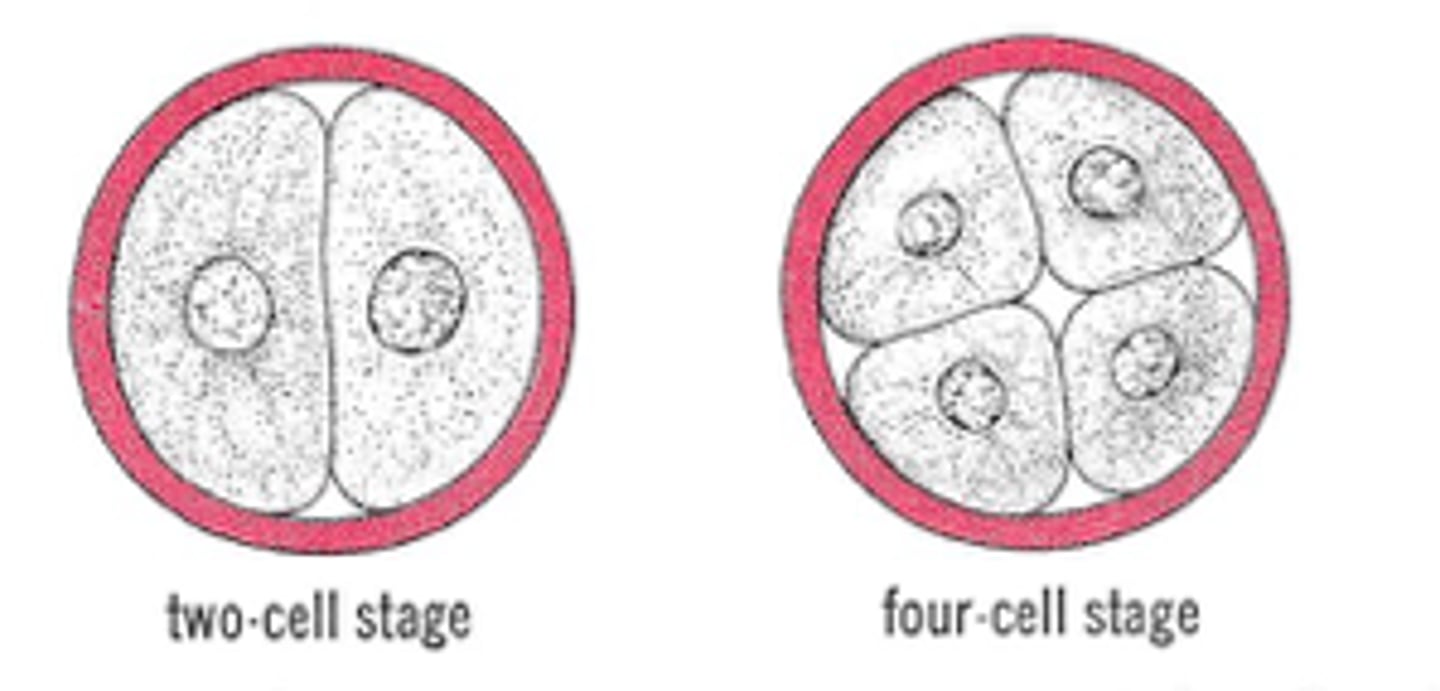
morula stage
identify the stage of fertilization:
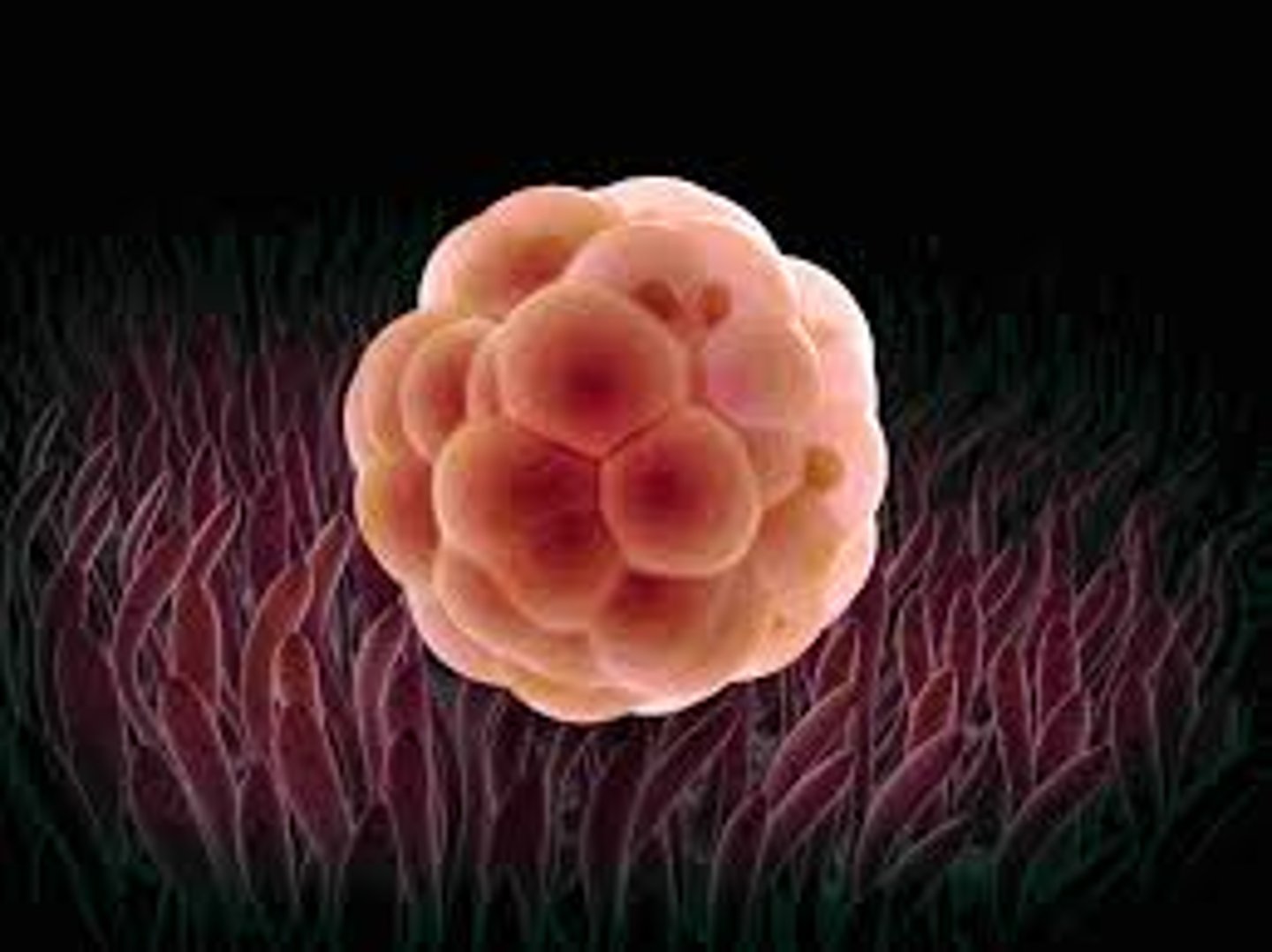
compaction
identify the stage of fertilization:
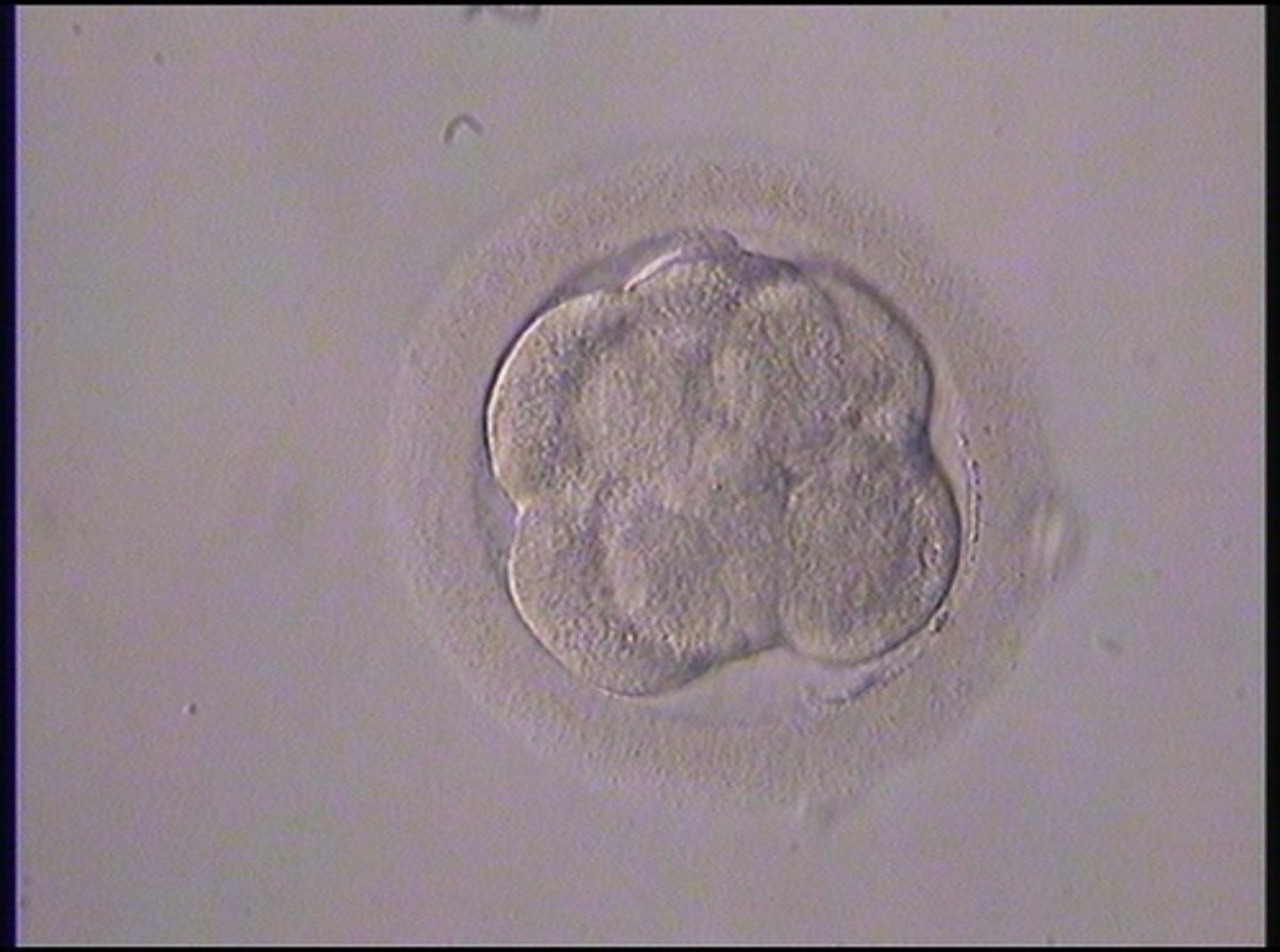
blastocyst stage
identify the stage of fertilization:
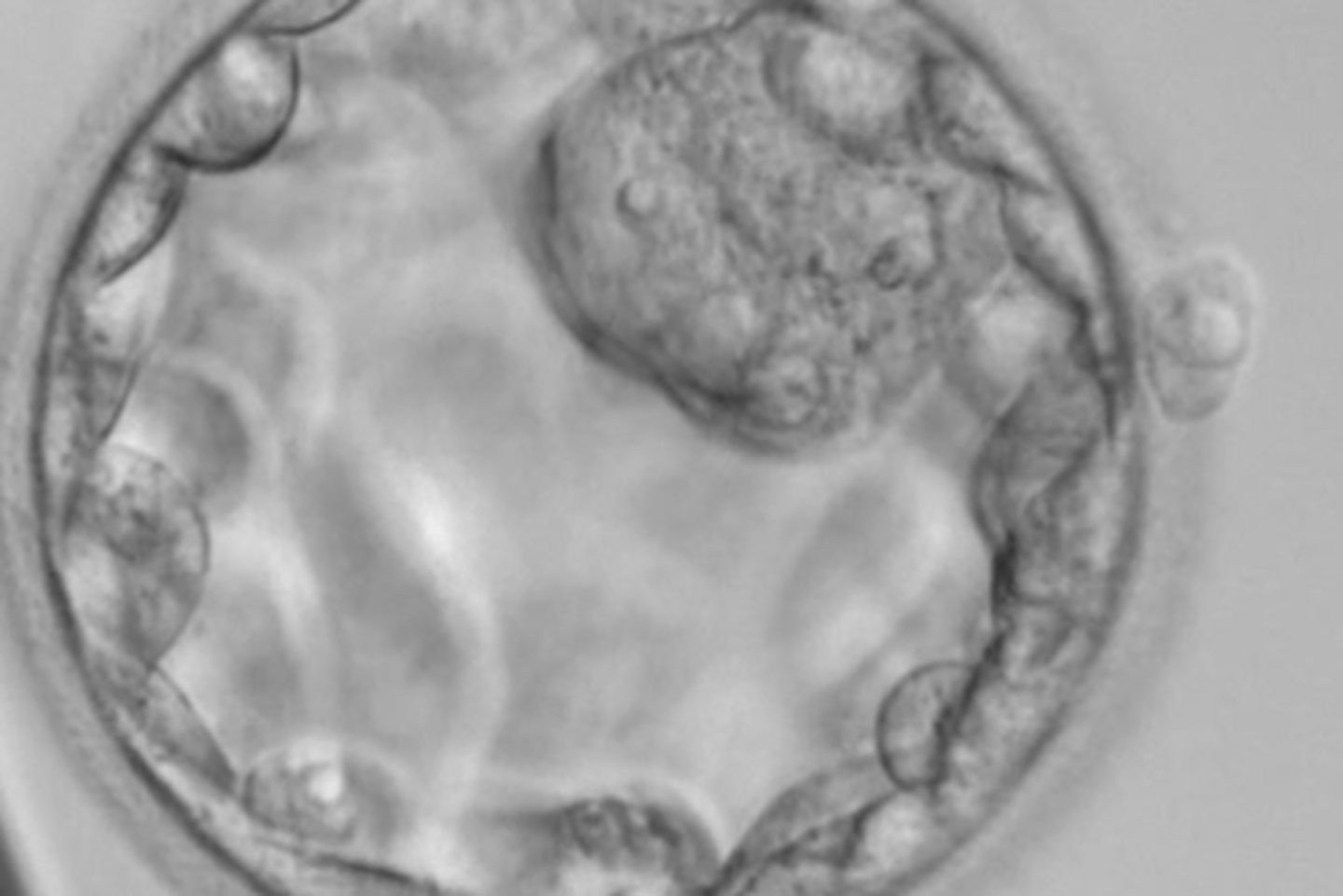
capacitation
maturation step for sperm
acrosomal reaction
final maturation step that allows sperm to penetrate egg
uterus
where does blastocyte formation take place?
cleavage stage
stage: At about 30 hours post-fertilization the zygote undergoes the first cell division also known as cleavage into 2 cells.
blastomere stage
stage: cells produced as the result of cleavage
morula stage
stage: Between 3 and 4 days there are about 12 to 16 blastomeres adhered together that appear under a microscope to look somewhat like a mulberry
compaction
stage: Blastomeres change how they attach to each other
blastocyst stage
stage: Embryo begins to absorb fluid forming a cyst,
embryoblast
in the blastocyte stage of development, inside the cyst a compact inner cell mass forms at one side of this cavity
embryo
the embryoblast will eventually become the:
trophoblast
The cells on the outside the blastocyte organize into a thin, single-layered epithelium called the:
placenta
the trophoblast will eventually become the:
trophoblast
which cells proliferate and begin to invade into the uterine epithelium during implantation?
syncytiotrophoblast
cytotrophoblast
Trophoblast differentiates into 2 distinct cell types:
syncytiotrophoblast
which cells initiate uteroplacental circulation?
syncytiotrophoblast
what part of the embryoblast produces HCG?
syncytiotrophoblast
produces human chorionic gonadotropin, erodes the endometrium, isolated cavities called lacunae, form an interconnected lacunar network
epiblast
embryoblast layer of columnar shaped cells closer to the uterus:
hypoblast
embryoblast layer of cuboidal cells adjacent to the blastocyst cavity:
epiblast
hypoblast
what two cells form the bilaminar disc?
epiblast
cytotrophoblast
the amniotic cavity forms from fluid filling in between what two sets of developing cells?
epiblast
the amniotic cavity differentiates from what group of cells?
amniotic cavity
Layer of epiblast cells migrates and differentiates into a thin membrane separating the new cavity from the cytotrophoblasts and forms the:
yolk sac
Hypoblast cells proliferate and migrate along the cytotrophoblast, extending from hypoblast around the blastocyst cavity and forms the:
hypoblast
the yolk sac differentiates from what group of cells?
trophoblast
the outer layer of the chorion is made of what cells:
inner extraembryonic mesoderm
the inner layer of the chorion is made of what cells:
chorionic cavity
Extraembryonic mesoderm splits into two layers forming the:
inner extraembryonic mesoderm
the bilaminar disc along with the amnion and definitive yolk sac, is suspended within the chorionic cavity by a thickened portion of__________ called the connecting stalk.
gastrulation
the primitive streak appears in what stage of development?
primitive streak
day 15 a thickening containing a midline groove forms along the midsagittal plane of the embryonic disc:
primitive streak
defines the embryo's craniocaudal axis, dorsal and ventral surfaces, and right and left sides?
prechordal plate
epiblast and hypoblast cells fuse to become site of future mouth:
mouth
the prechordal plate will eventually be the:
ingression
As cells of the epiblast reach the primitive streak, they change shape and pass through it on their way to forming new layers beneath (ventral to) the epiblast:
epiblast
which cells of the bilaminar disc participate in ingression?
definitive endoderm
which 'derm' layer develops first?
intraembryonic mesoderm
which 'derm' layer develops 2nd?
definitive endoderm
First ingressing epiblast cells invade the hypoblast and displace its cells, so that the hypoblast eventually is completely replaced by a new layer called the:
definitive endoderm
gives rise to the lining of the future gut and gut derivatives
intraembryonic mesoderm
epiblast cells migrating through the primitive streak into the space between epiblast and the newly formed endoderm to form 2nd germ layer:
cardiogenic
paraxial
intermediate
lateral plate
4 fates from migrating mesoderm:
notochordal process
A fifth population of epiblast cells migrates cranially from the primitive node in the midline to form a thick-walled midline cord called the:
sacrococcygeal teratoma
Remnants of the primitive streak that persist after birth, contains tissues derived from all three germ layers in incomplete stages of differentiation:
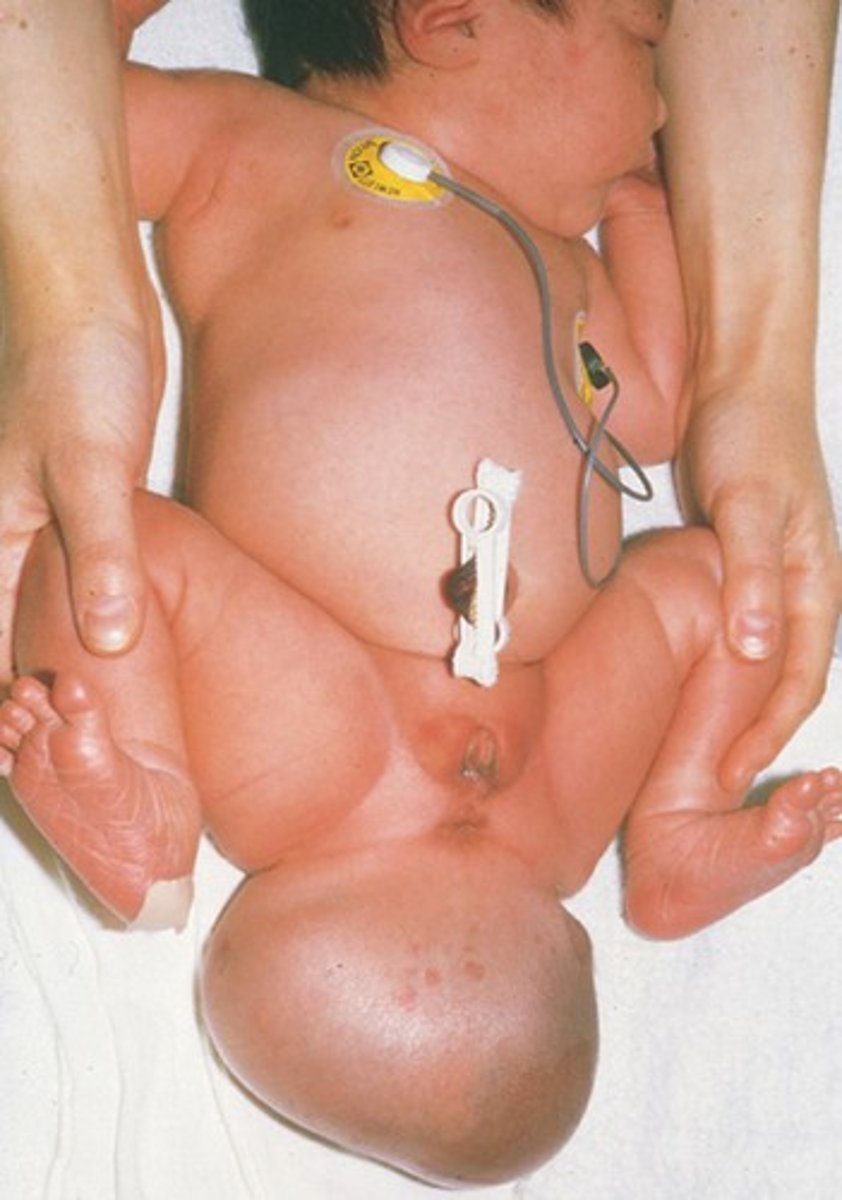
primitive streak
sacrococcygeal teratomas are remnants of what developmental structure?
cranio-caudal
what direction does the notochord form?
notochord
this structure serves as the basis for the development of the axial skeleton
notochord
the vertebral discs are remnants of what embryological structure?
paraxial mesoderm
this section of the mesoderm will develop into cartilage, tendons, muscles and bones:
lateral plate mesoderm
this section of the mesoderm will develop into
-body wall
-circulatory system, gut wall:
intermediate mesoderm
this section of the mesoderm will develop into urogenital and reproductive systems:
embryonic ectoderm
this derm layer is the epiblast after the migration through the primitive streak that formed the definitive endoderm, mesoderm and notochord is complete:
embryonic ectoderm
this derm layer will develop into neural crest, neural tube
neural tube
what embryologic structure does the CNS derive from?
neural crest
what embryologic structure does the PNS derive from?
neural crest
dorsal root ganglia are derived from what embryonic tissue?
neural tube
the spinal cord is derived from what embryonic tissue?
PNS
the neural crest will give rise to what nervous system?
CNS
the neural tube will give rise to what nervous system?
intermediate mesoderm
the kidneys are derived from what embryonic tissue?
intermediate mesoderm
the bladder is derived from what embryonic tissue?
definitive endoderm
the stomach is derived from what embryonic tissue?