Biological Molecules
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
What is starch made up of?
Amylose (1,4 glycosidic linked with 1,4 a-glucose)
Amylopectin (1,4 glycosidic linked with 1,6 a-glucose)
Polysaccharide storage characteristics:
Convenient, can be made quickly available
Compact, can store a lot
Insoluble and inert
Starch for animals, glycogen for humans
Cellulose formation:
1) B-glucose monomer makes up structure to form
2) 1,4 glycosidic bonds with each other
3) When subsequently linked, rotates 180*
4) causes many -OH groups to branch out with a linear structure
5) in turn, forms weak hydrogen bond between parallel chains of B-glucose molecules
6) 60-70 cellulose bonds later, cellulose microfibrils form
7) Many cellulose microfibrils form cellulose fibres
8) these fibres layer alternatively between layers–criss-crossing with gaps in between them
9) This allows for the cell wall formed by cellulose to be permeable
10) Hydrogen bonds are strengthened when multiplied which prevents the cell from bursting, providing high tensile strength
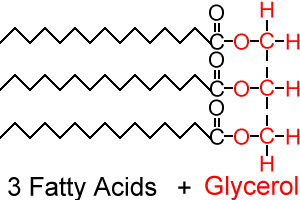
Name this biological molecule
Triglyceride
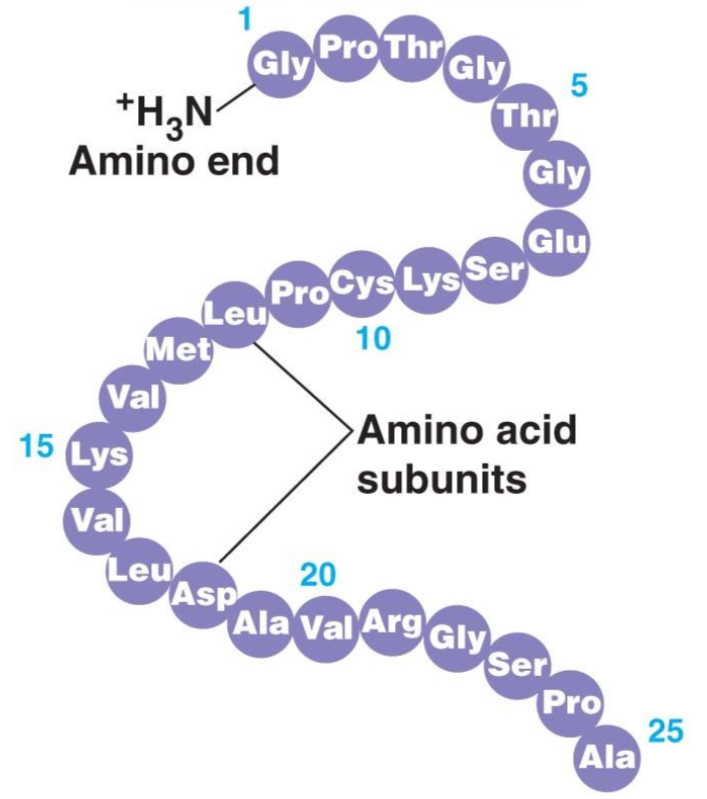
What is the primary structure of protein?
The sequence of specific amino acids in a polypeptide chain
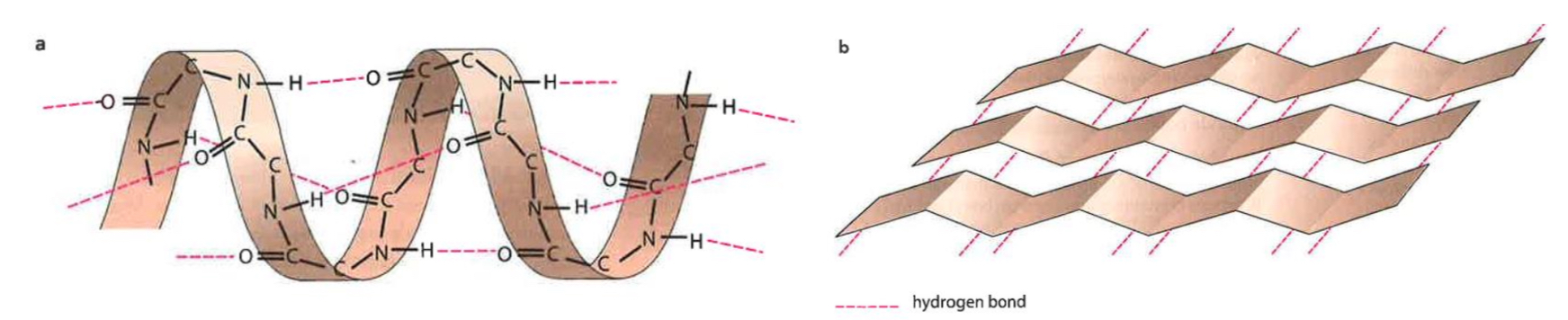
What is the secondary structure of protein?
A-helix is a coiling structure due to hydrogen bond with -NH group
B-pleated sheet is a folded structure due to hydrogen bond with -NH group
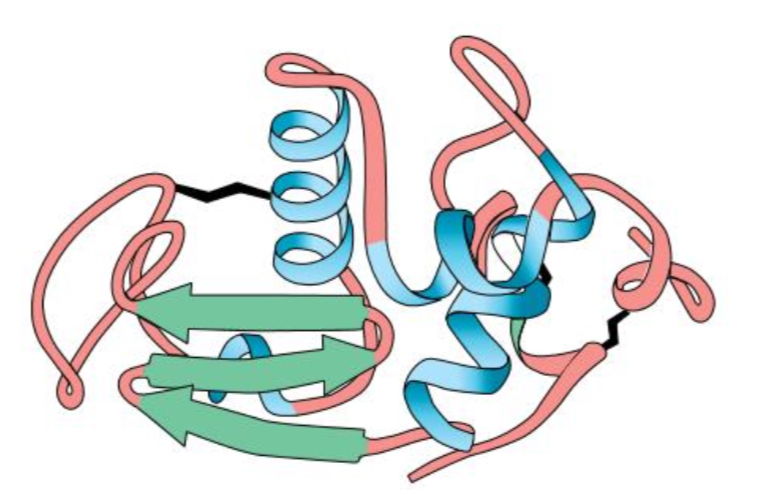
What is the tertiary structure of protein?
The proteins of the secondary coil and fold more with bonds between side groups (R-groups). NOT from -OH, -NH, or central C.
What are the R-groups that can bond with the proteins in the secondary structure?
Hydrogen bonds: Forms between many R-groups, weak in isolation but many together form a strong structure
Disulfide bonds: Forms between S-S groups with a covalent bond
Ionic bonds: Forms between R-groups containing amino and carboxyl groups
Hydrophobic interaction: Forms between R-groups that are non-polar (attracting to one another) which leads to them repelling against the water around them
Characteristics of haemoglobin, a globular protein
Contains 4-polypeptide chain to form 1 haemoglobin (quartenary structure)
There are 4 haem groups in 1 haemoglobin
Consists of a-globin and b-globin
Hydrophobic R-group points towards the centre of the molecule to sustain its three-dimensional shape
Hydrophilic R-group points outwards to sustain solubility
Each globin has a haem group which contains an iron atom (site of oxygen)
Characteristics of collagen, a fibrous protein
Acts as a structural protein, insoluble in water
Needs three polypeptides to form and is held together by -OH -H covalent bonds
Every ⅓ in the amino acids is glycine (-H R-group)
Has high tensile strength
Water as a solvent
Due to uneven charge distribution, it is able to attract ions and polar molecules–allowing it to act as a solvent
Structural differences between sucrose and fructose
Fructose has no glycosidic bonds and is a monosaccharide
Sucrose has glycosidic bonds and is a disaccharide
Functions of glycoproteins in cell surface membranes
Cell signalling, cell recognition, act as enzymes, and cell adhesion