TMOD (Optic Nerve)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
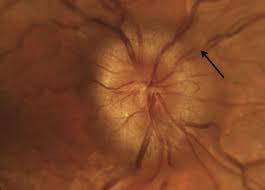
Papilledema
BILATERAL swollen disc due to increased intracranial pressure (from intracranial mass like hemorrhage or edema, pseudotumor cerebri, inhibition of arachnoid villi, malignant HTN, venous sinus thrombosis) posterior to optic chiasm
foster-kennedy syndrome has unilateral papilledema with contralateral optic atrophy
May so present with elevated IOP, abnormal color vision, red cap desaturation, loss of spontaneous venous pulsation, VF defect (enlarged blind spot), paton’s line (retinal folds)
May be asymptomatic or complaints of HA or diplopia (from CN 6 - elevated intracranial pressure that compress CN6 along boney petrous ridge; or CN 7 paresis)
Normal VAs (if poor VA then suspect bilateral disc edema)
Papilledema Treatment/Managaement
MRI and CT to rule out mass
CBC, FBS, ESR, CRP, ANA, ACE
Measure BP
Can tx with acetazolamide
Refer to neurology
Papilledema prognosis
Typically good if early intervention
Pseudotumor Cerebri (Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension)
Usually in women of child bearing age (fat, fertile females)
Can be associated with CATS (contraceptives, accutane, tetracycline (mino or doxy), synthroid (Nalidixic acid)), vit A, or idiopathic
Blur, HA, nausea, color vision abnormalityes, transient vision disturbances
3 Criteria required to dx Pseudotumor Cerebri
1.Papilledema
2.Normal brain MRI/CT
3.High cerebral spinal fluid pressure on lumbar puncture (>200 in nonobese, >250 in obese pt)
Pseudotumor Cerebri Treatment/Management
D/C associated medication
Lose weight
Oral acetazolamide to reduce production of cerebral spinal fluid at the choroidal plexus
if sulfa allergy, give furosemide
If tx is unsucessful, consider neurosurgical shunt or optic nerve sheath decompression
FU 3 weeks (if chronic)/month (if acute and no VF defect)
Nonarteritic Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (NAION)
Disc edema due to ischemia from blockage of PCA in pts >55yo
Caused by cardiovascular disorder (HTN, DM, hypercholesterolemia, smoking), amiodarone (for arrhythmia), imitrex (for migraine), vardenafil or viagra
Long term finding is optic nerve pallor
Sudden painless, unilateral vision loss and abnormal color perception
Presents with unilateral swollen optic nerve with APD, VF defect, disc at risk
Nonarteritic Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (NAION) Treatment/Management
Immediate IV steroids
STAT test for CBC and CRP and ESR (abnormal if greater than age/2 in men and age+10/2 for women)
Temporal biopsy (possible false negatives)
If testings rule out AION, discontinue steroids and take daily aspirin as prophylaxis and refer to PCP
Arteritic Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (AION)
Disc edema due to ischemia from blockage of PCA in pts >55yo
Caused by GCA (inflammation of medium AND large arteries)
Emergent condition, without tx pt can lose vision in fellow eye within 24 hours
Sudden painless, unilateral vision loss and abnormal color perception, amaurosis fugax, HA, malaise, fever, scalp tenderness, jaw claudication, weight loss
Presents with unilateral swollen optic nerve with APD, VF defect (altitudinal), disc at risk
Arteritic Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (AION) Treatment/Management
Immediate IV steroids
STAT test for CBC and CRP and ESR (abnormal if greater than age/2 in men and age+10/2 for women)
Temporal biopsy (possible false negatives)
Optic Neuritis
Frequently the first sign of MS (if not yet dx, 50% of pts will be dx with MS within 10yrs of optic neuritis)
symptoms associated with MS include uhthoff’s phenomenon (decrease vision with increaded body temp), lhermitte’s phenomenon (electric shock down the back), internuclear ophthalmoplegia (lack of adduction on affected side contralateral nystagmus on abduction
PAIN on eye movement! (compression on EOM)
Vision loss (hours to weeks due to swollen nerve)
Unilateral swollen disc, APD, color vision and VF defect
If disc are not swollen, inflammation may be behind the globe (retrobulbar optic neuritis)
can be confirmed with MRI
Optic Neuritis Treatment/Management
Refer to neurology for MRI (if one or more lesion, risk of MS is 72% in 15 yrs)
IV steroids for inflammation then transition to oral
FU every 1-6 months (depending on severity and response to tx)
Optic Neuritis pronosis
Visual prognosis is typically good
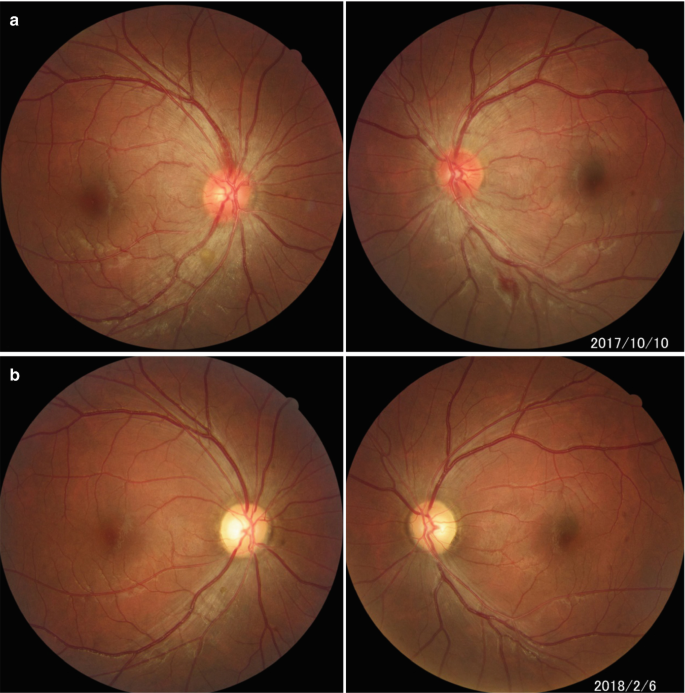
Toxic Optic Neuropathy
Most commonly caused by ethambutol (TB drug)
other causes are chloramphenical (50s), digitalis, isoniazid (TB), streptomycin, lead, malnutrition, alcohol, deficiency of B1 or B12 or folate
May cause centrocecal VF defect
Acute onset of permanent reduced vision (as poor as 20/400) and dyschromatopsia
Bilateral optic nerve pallor with swelling, NFL defect, reduced contrast sensitivity, may have APD (if asymmetric damage)
Toxic Optic Neuropathy Treatment/Management
D/C offending agent
Spontaneously improve within 1 yr (but permanent visual changes may occur)
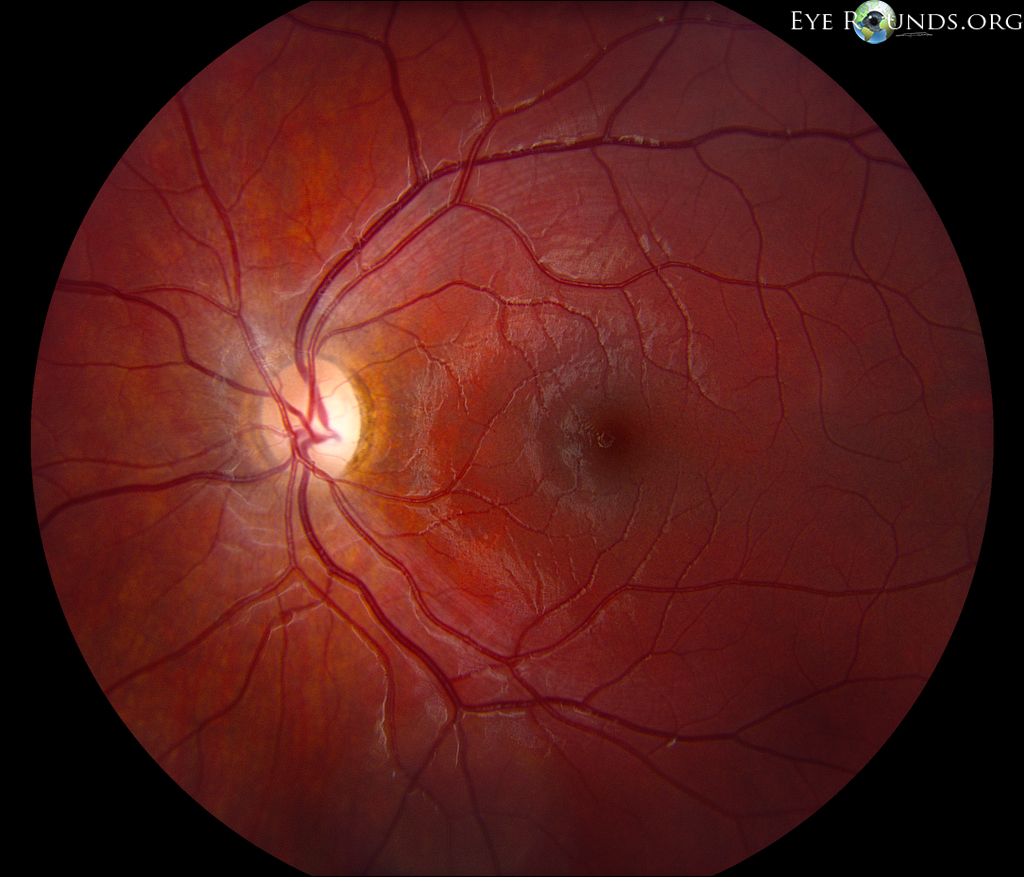
Dominant Optic Atrophy (Kjer or Juvenile Optic Atrophy)
Hereditary optic neuropathy
Most common hereditary optic neuropathy
AD around the age of 5
Slow progressive loss of vision (as poor as 20/800)
Wedge of temporal pallor
Dominant Optic Atrophy (Kjer or Juvenile Optic Atrophy) Treatment/Management
Refer for genetic counseling and low vision specialist
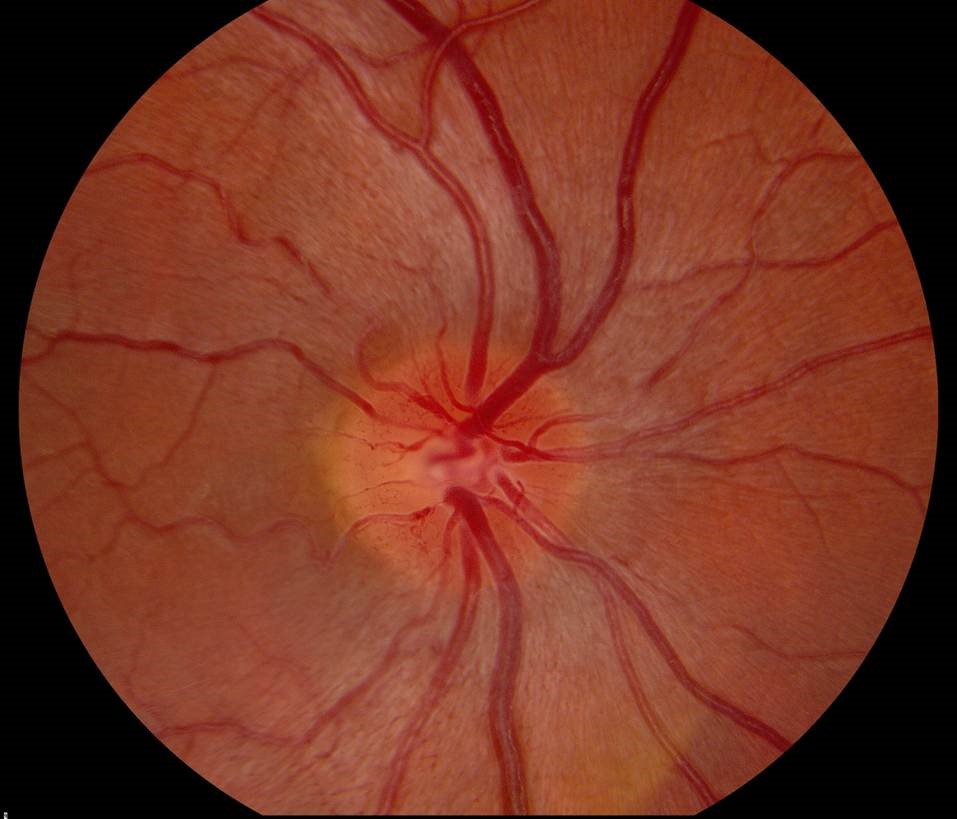
Leber’s Hereditary Optic Neuropathy
(dont confuse with Leber’s Congential Amaurosis)
Hereditary optic neuropathy
Pseudo optic disc edema
From mother to son via mitochondria
Onset age 10-30
Severe, acute, painless, loss of central vision in one eye and progress to fellow eye within days to months
Presents with abnormal blood vessels, optic nerve hyperemia (cause blurring of disc margin), dilated capillaries with telangiectasia, optic atrophy
Leber’s Hereditary Optic Neuropathy Treatment/Management
Spontaneous vision recovery
Refer for genetic counseling and low vision specialist
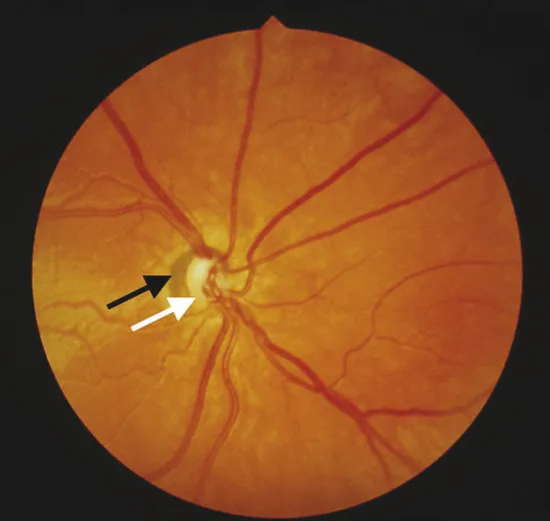
Optic Nerve Hypoplasia (Midline Dysgenesis - De Morsier Syndrome)
Congenital optic neuropathy
Reduced number of optic nerve fibers
Unilateral or bilateral (more common)
Seen in infants whose mothers with endocrine disorder (DM) or abused drugs (quinine, alcohol, LDS) while pregnant
Vision loss (mild to NLP), small disc (“double ring sign”), APD, roving eye and min pupillary rxn to light (sever cases)
Optic Nerve Hypoplasia (Midline Dysgenesis - De Morsier Syndrome) Treatment/Management
No effect tx
Refer to low vision consult
If young, MRI and endo workup
If older, no work up needed
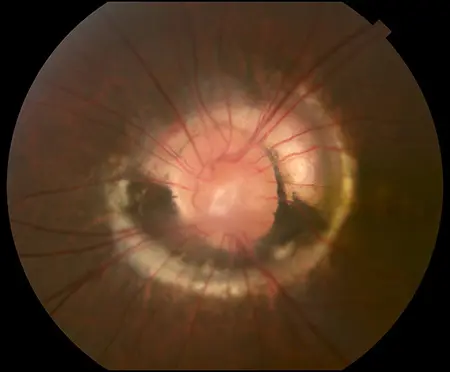
Morning Glory Syndrome
Congenital optic neuropathy
Rare, unilateral, usually females with midline facial defects and forebrain anomalies
Severe vision loss
Enlarged funnel shaped optic nerve with overlying glial tissue, blood vessels leave the nerve in spoke-like pattern, nerve. is surrounded by pigment
May develop secondary serous retinal detachment
Morning Glory Syndrome Treatment/Management
No effective tx
Refer to low vision
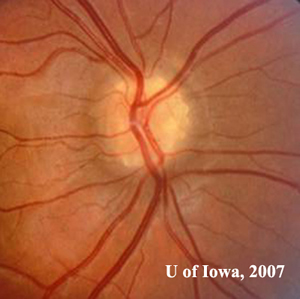
Optic Nerve Drusen
Congenital optic neuropathy
Hyaline-like material (may look like refractile clumps) buried in the NFL around optic nerve
asymptomatic or enlarged blind spot
Hyperr-reflective on Bscan
May cause CNVM if there is a break in Bruch’s within an area of peripapillary atrophy
Optic Nerve Drusen Treatment/Management
MRI to differenctiate drusen vs opitic neuritis
No tx necessary if optic neuritis is rule out
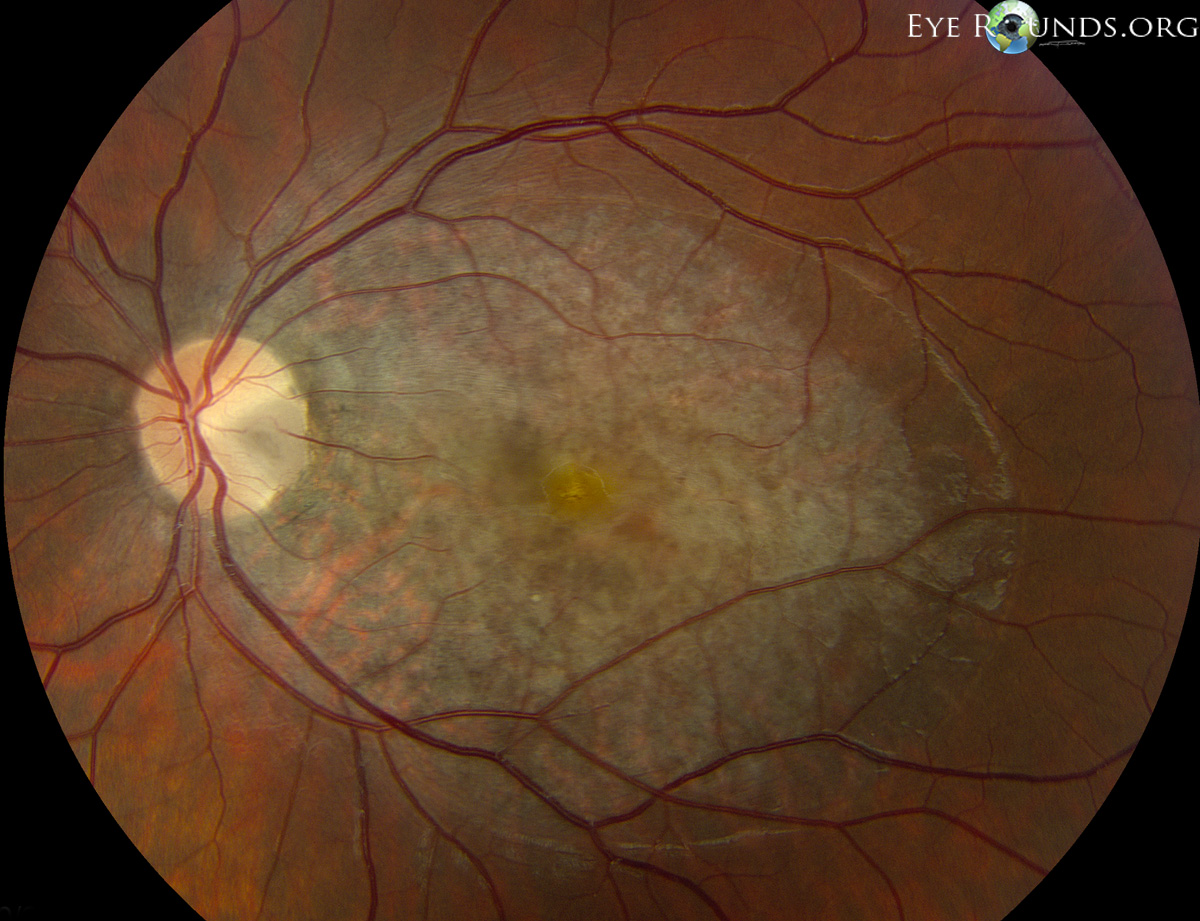
Optic Nerve Pit
Congenital optic neuropathy
Asymptomatic unless serous macular detachment forms
Temporal grey-white depression of the optic nerve (0.1-0.7DD)
Optic Nerve Pit Treatment/Management
If asymptomatic, monitor annually
If serous retinal detachment, monitor
If serous macular detachment, tx with laser photocoagulation and monitor monthly
Optic Nerve Glioma
Progressive unilateral vision loss with painless proptosis
Presents with proptosis, APD, disc edema, enlargement of the optic nerve on CT scan
2 Types of Optic Nerve Glioma
1.Glioblastoma Multiforme
rare malignant form found in adults
leads to blindness within months and death within a year
2.Juvenile Pilocytic Astrocytoma
most common intrinsic neoplasm of optic nerve
dx at age 6 (benign if found in childhood, malignant if found in adults)
associated with neurofibromatosis type 1
Optic Nerve Glioma Treatment/Management
If stable with no vision changes and no cosmetic disturbance, monitor
Otherwise, surgical excision or radiotherapy combined with chemo
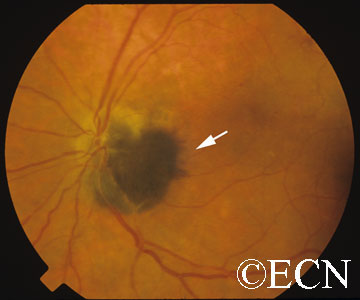
Optic Disc Melanocytoma
Rare tumor seen in darkly pigmented 50yo that rarely metastasize
Usually asymptomatic
Jet-black tumor with fuzzy edges adjacent to optic nerve, can be flat or slightly elevated
Optic Disc Melanocytom Treatment/Management
If metastasis, refer to oncologist
Otherwise monitor yearly
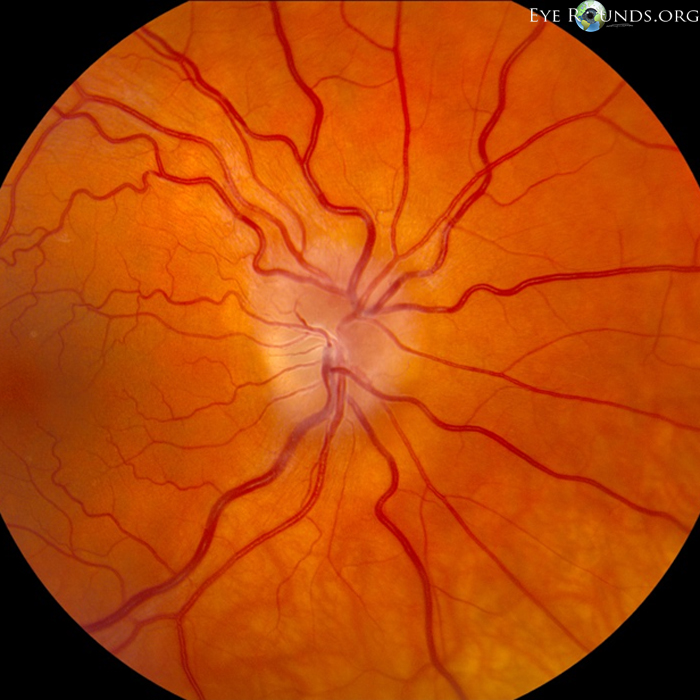
Meningioma
Usually seen in middle aged women
Usually benign but can be malignant
Complaints of progressive unilateral vision loss with painless proptosis and color vision defects
Presents with APD, optic nerve edema then atrophy, optociliary shunt vessels, and angiomas
Tumor may compress the globe and cause EOM restriction, increased IOP, metamorphopsia
Meningioma Treatment/Management
If increased IOP, tx with hypotensives
If angiomas, tx with laser photocoagulation
Malignant tumors tx with radiation, chemo, or surgical excision
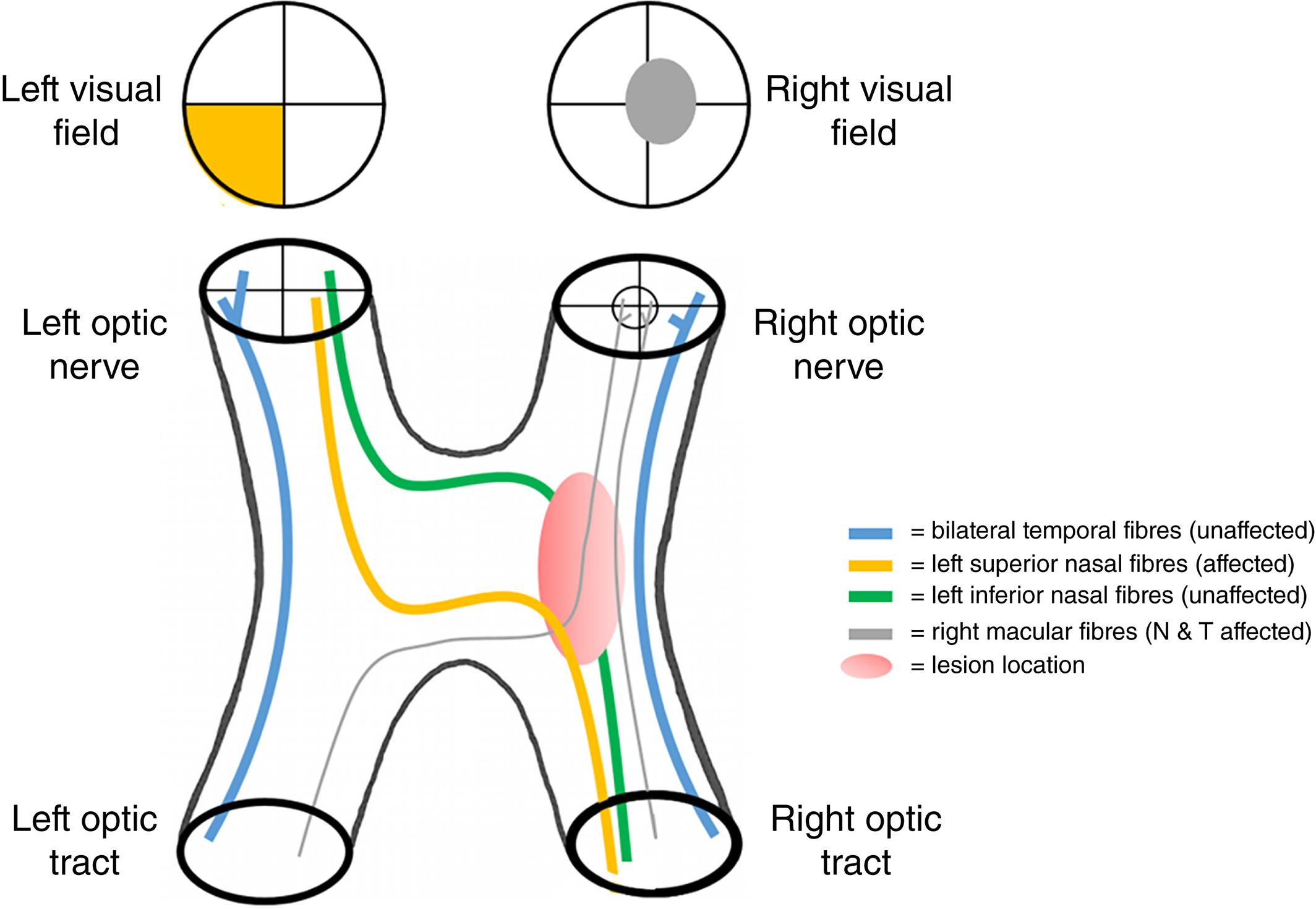
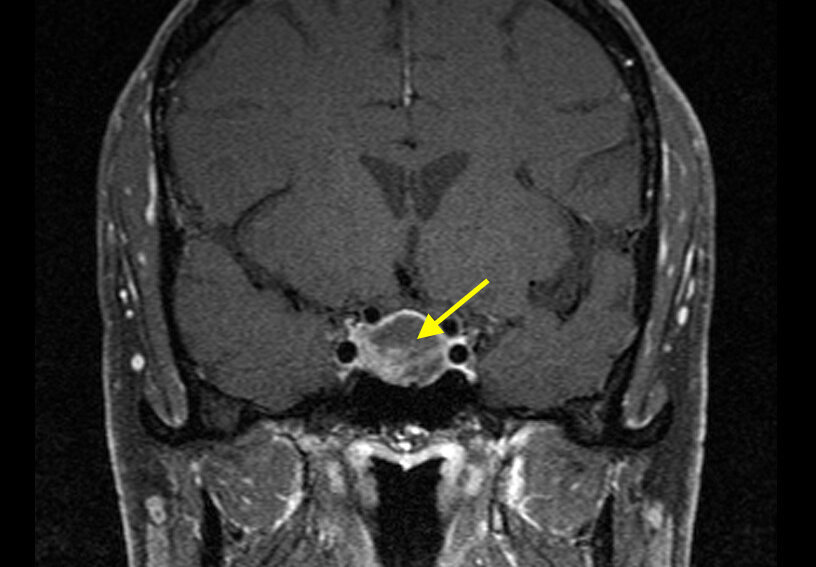
Pituitary Gland Tumor
Located in the sella turcica inferior to optic chiasm
No complaints or have reduced vision, HA, color vision/VF defect
Possible optic atrophy and APD
May have reduced libido, malaise, infertility
Bitemporal hemianopia or junctional scotoma
Bow-tie atrophy (horizontal band of pallor across ONH)
Pituitary Gland Tumor Treatment/Management
Refer to neurosurgeon for MRI, surgery, bromocriptine, radiation, or hormone replacement therapy
Pituitary apoplexy (loss of blood flow) tx with systemic steroids and surgical decompression
Pituitary Gland Tumor prognosis
Good