Biochemistry I Lesson 11: Metabolism
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
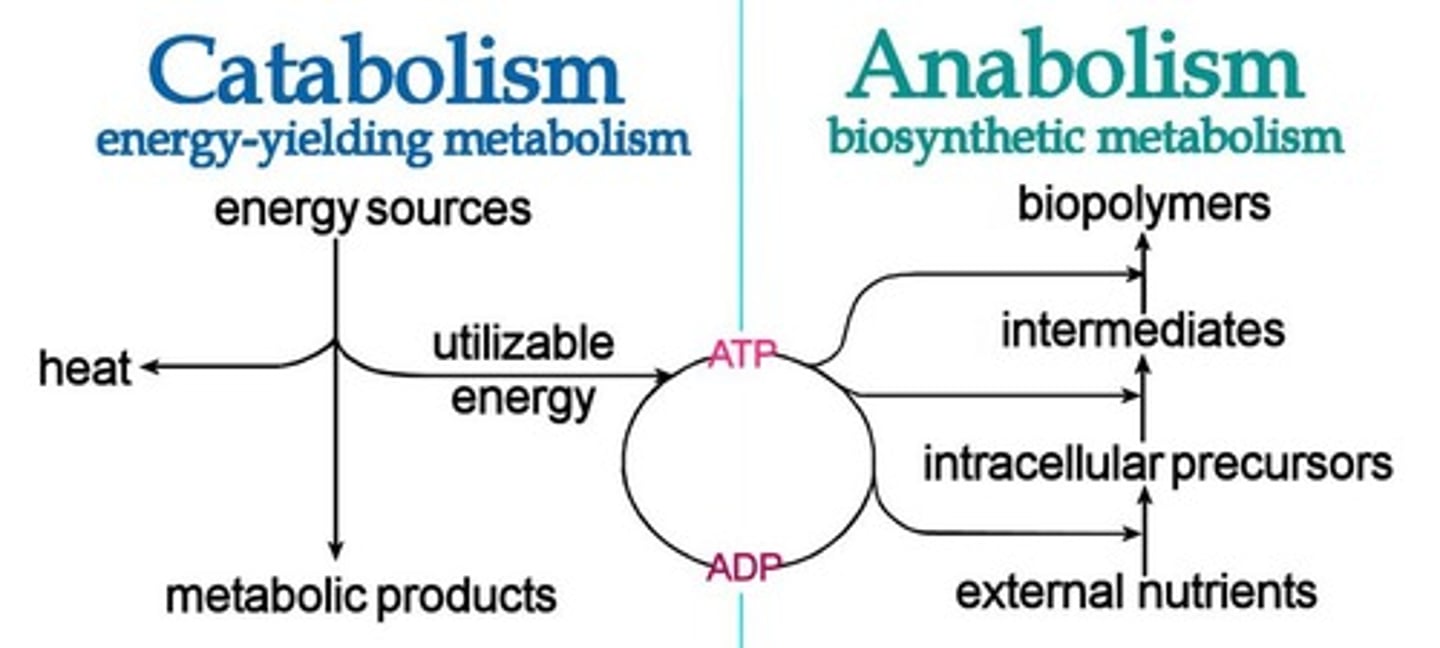
What is the difference between catabolism and anabolism?
Both catabolism and anabolism are important steps in metabolism. Catabolism is the breaking down/digestion of macromolecules, whereas anabolism is the building of macromolecules in the correct configuration for the body to use.
_________ is the process of breaking down fuels to provide cellular energy in the form of ATP.
(A) Digestion
(B) Catabolism
(C) Cellular Respiration
(D) Anabolism
(C) Cellular Respiration
Cellular Respiration is the process of breaking down fuels to provide cellular energy in the form of ATP.
CRB Between Fats and Carbohydrates, which would store more energy per gram, and by how much?
(A) Fats store twice as much energy per gram as carbohydrates do.
(B) Fats store 1.25 times as much energy per gram as carbohydrates do.
(C) Carbohydrates store twice as much energy per gram as fats do.
(D) Carbohydrates store five times as much energy per gram as fats do.
(A) Fats store twice as much energy per gram as carbohydrates do.
CRB Why are fats able to store so much more energy per gram than carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates are hydrophilic and will have a shell of solvation around them, increasing the effective mass of the carbohydrates. Fats are also more reduced, storing more potential for energy from oxidation!
CRB Both Fats and Carbohydrates are not readily used in reactions as energy sources. What molecule is their energy converted to in order to be easily accessed in other reactions?
ATP (Adenosine TriPhosphate).
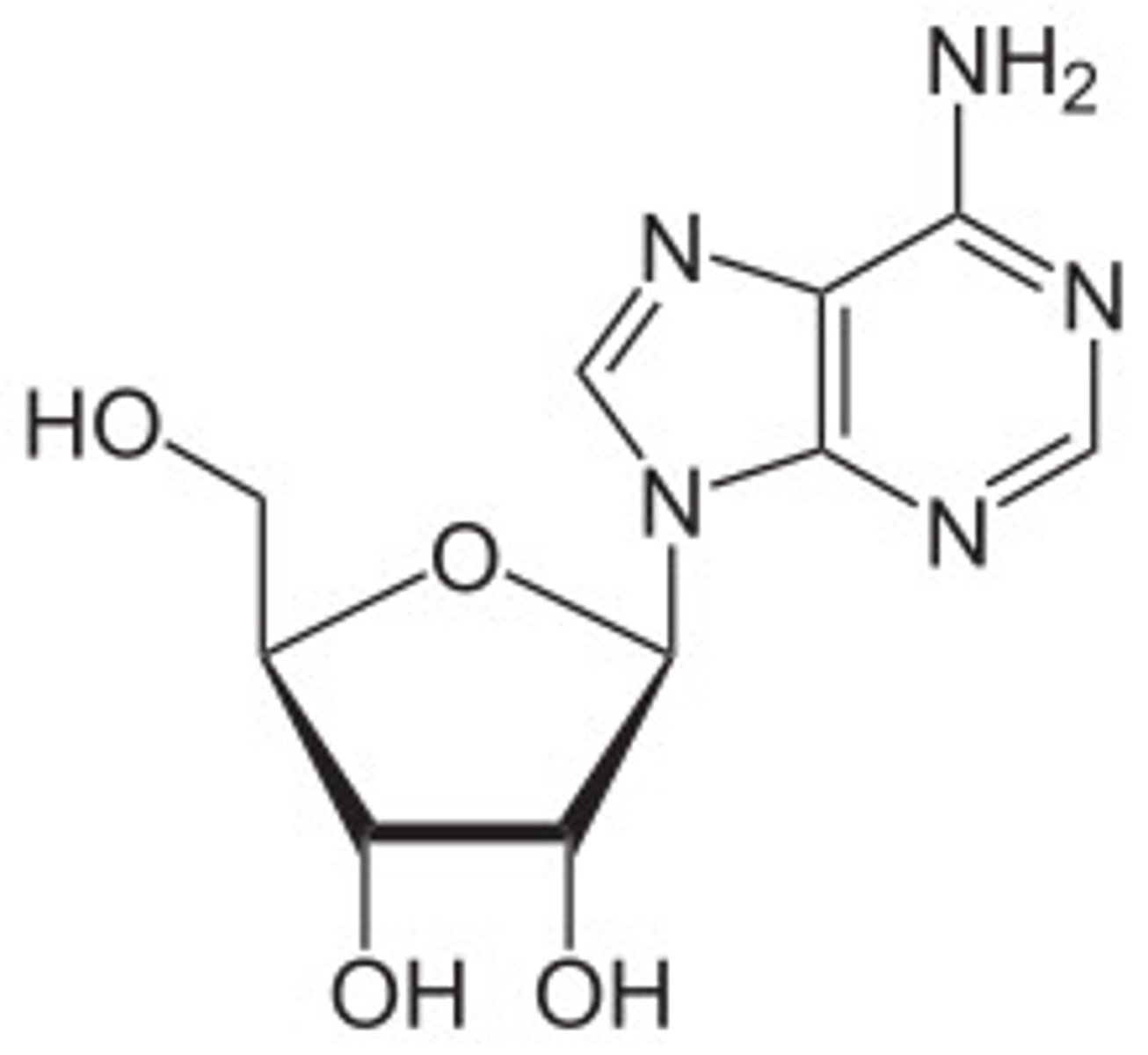
CRB Recall an earlier lesson on nucleotides, where Adenine and Adenosine were compared. Draw out Adenosine.
Note that Adenine became Adenosine when the sugar bound to to the Nitrogenous base, so you must draw the sugar!
In what way does anabolism rely on cellular respiration?
The building up of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids needed to sustain life is an energy-requiring process. Cellular respiration supplies this energy in the form of ATP.
Draw the structure of ATP.
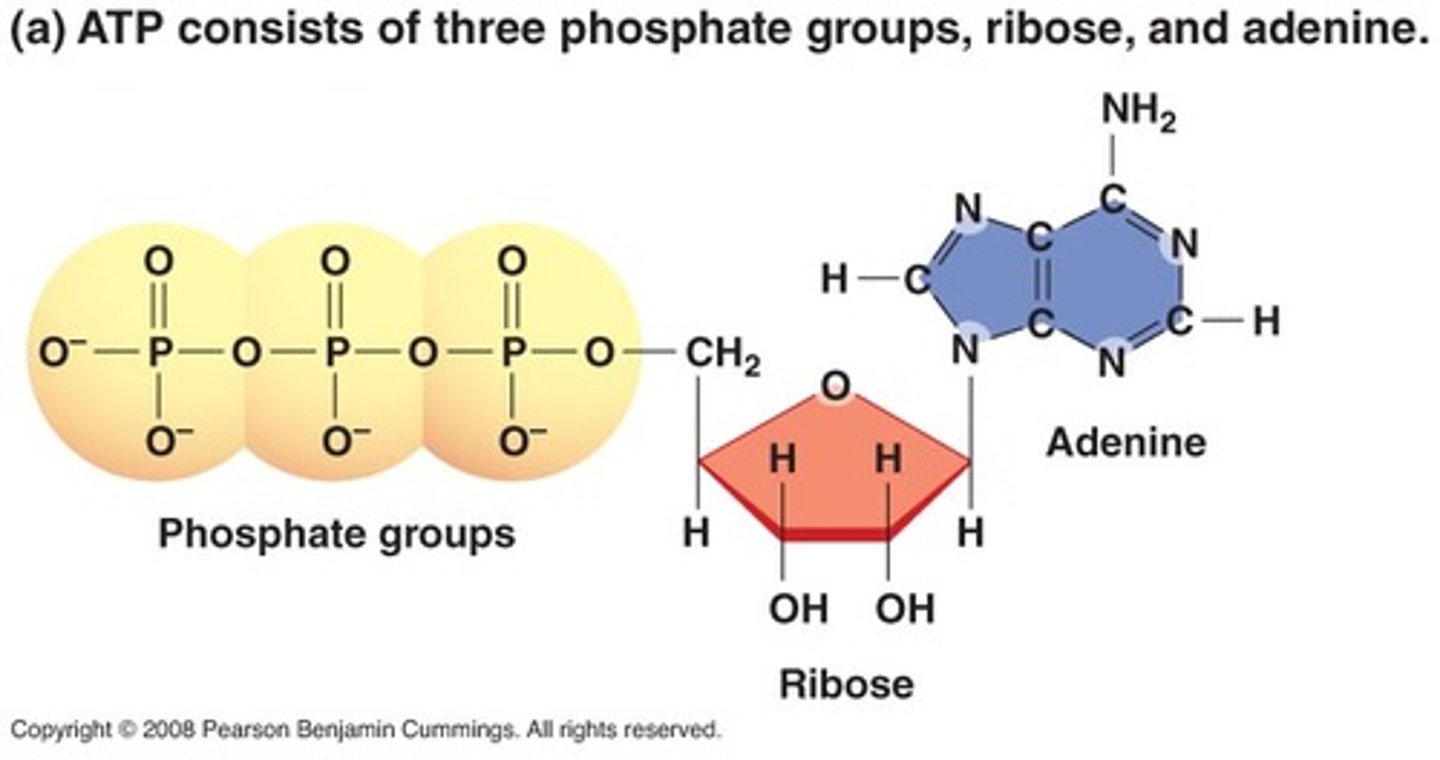
CRB Fill in the blanks: The Nitrogenous Base is bound to Ribose's Carbon number ________, whereas the Phosphate Groups are bound to Carbon number ________.
(A) 5, 1
(B) 1, 5
(C) 1, 3
(B) 3, 1
(B) 1, 5
The Nitrogenous Base is bound to Ribose's Carbon number 1, whereas the Phosphate Groups are bound to Carbon number 5.
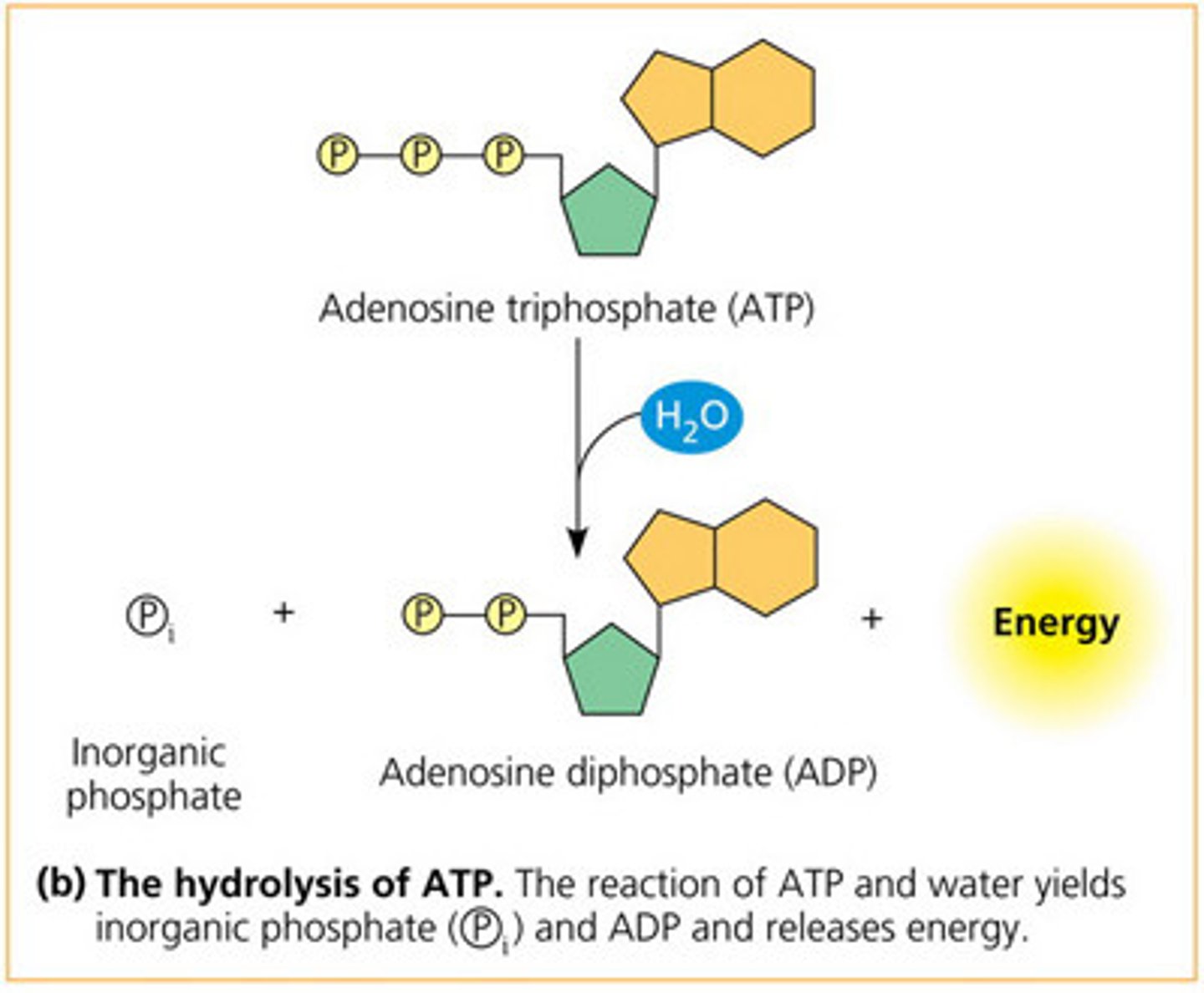
When ATP is hydrolyzed, what two products will result?
(A) ATP and Pi
(B) ADP and PPi
(C) AMP and Pi
(D) ADP and Pi
(D) ADP and Pi
When ATP is hydrolyzed, ADP and an inorganic phosphate (Pi) are the products. This reaction will release energy that can be used to drive important cellular reactions.
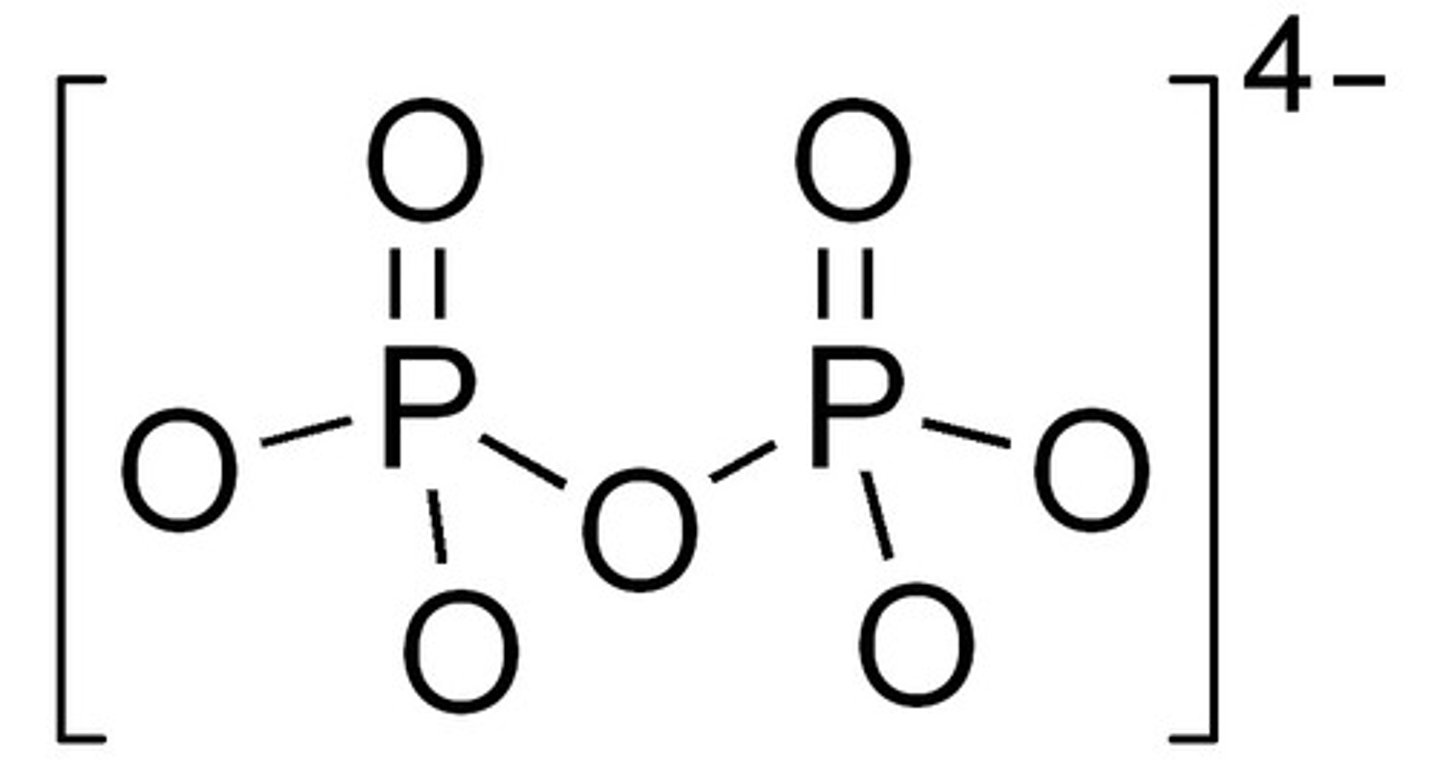
CRB Notice the PPi answer choice in the previous card. The i in each of the answers stands for Inorganic, but what does the PP truly stand for?
(A) Phosphate Phosphate
(B) Pyrophosphate
(C) Peculiar Phosphate
(D) Polyphosphate
(B) Pyrophosphate
CRB True or false? The energy that is freed when ATP is hydrolyzed cannot be saved, so it is useful that ATP is a mid-level energy carrier.
True. The energy that is freed when ATP is hydrolyzed cannot be saved, so it is useful that ATP is a mid-level energy carrier.
CRB Which of the following are considered High-Energy Electron Carriers?
I. NADPH
II. NADH
III. FADH2
(A) II only
(B) I and II only
(C) I and III only
(D) I, II and III
(D) I, II and III
Each of the following are considered High-Energy Electron Carriers:
I. NADPH
II. NADH
III. FADH2
CRB Which of the following statements about Flavoproteins are true?
I. Flavoproteins are common in the Mitochondria and Chloroplasts.
II. Flavoproteins are modified vitamin B2, and include FAD and FMN.
III. Flavoproteins also act as Prosthetic Groups for enzymes that oxidize fatty acids, decarboxylate Pyruvate ,and reduce Glutathione.
(A) I only
(B) I and II only
(C) II and III only
(D) I, II and III
(B) I and II only
Each of the following statements about Flavoproteins are true:
I. Flavoproteins are common in the Mitochondria and Chloroplasts.
II. Flavoproteins are modified vitamin B2, and include FAD and FMN.
III. Flavoproteins also act as Coenzymes for enzymes that oxidize fatty acids, decarboxylate Pyruvate, and reduce Glutathione.
CRB In which of the following ways are ATP formed?
I. Substrate Level Phosphorylaton
II. Oxidative Phosphorylation
III. Substrate level Ribosylation
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) I and II only
(D) II and III only
(C) I and II only
ATP can be formed by either Substrate Level Phosphorylation or Oxidative Phosphorylation.
Draw the ATP hydrolysis mechanism starting with ATP and two water molecules.
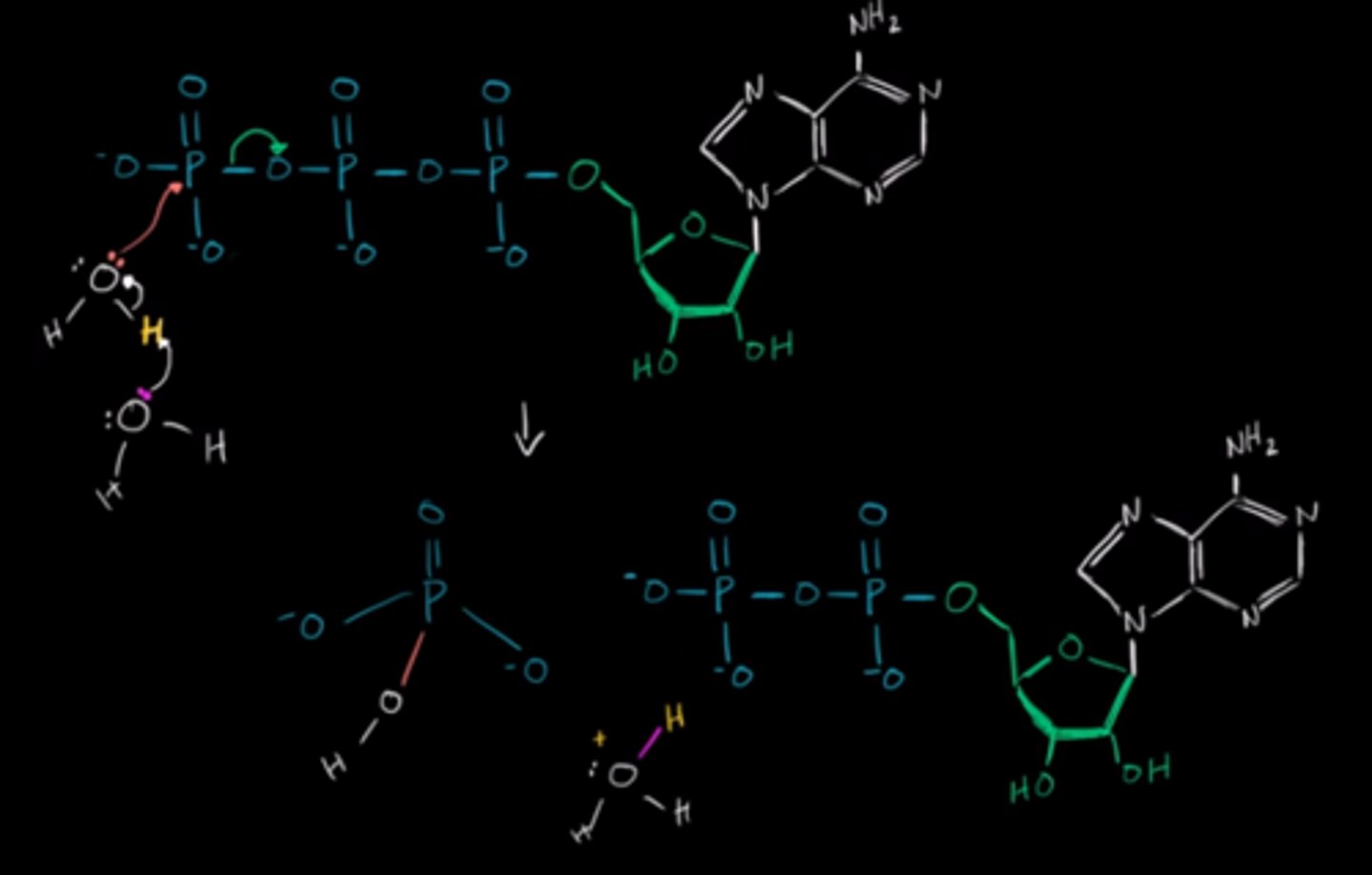
CRB True or false? Reaction coupling is what can make the energy freed by ATP hydrolysis able to drive other, less favorable reactions forward.
True. Reaction coupling is what can make the energy freed by ATP hydrolysis able to drive other, less favorable reactions forward.
CRB Fill in the blanks:
ATP can undergo a(n) ____________, where a Phosphate group is added to a(n) ___________, affecting its conformation and activity.
(A) Oxidative Phosphorylation, RNA
(B) Oxidative Phoshporylation, Protein
(C) Phosphoryl Group Transfer, RNA
(D) Phosphoryl Group Transfer, Protein
(D) Phosphoryl Group Transfer, Protein
ATP can undergo a Phosphoryl Group Transfer, where a Phosphate group is added to a protein, affecting its conformation and activity.
CRB True or false? When ATP is formed by a Substrate Level Phosphorylation, that is also a Phosphoryl Group Transfer from a higher-energy molecule to a lower-energy molecule.
True. When ATP is formed by a Substrate Level Phosphorylation, that is also a Phosphoryl Group Transfer from a higher-energy molecule to a lower-energy molecule.
Gibb's free energy (∆G) is positive for a certain reaction. Do the products or the reactants have a higher free energy?
If ∆G is positive for a certain reaction, the products will have a higher free energy.
∆G is positive for a certain reaction. This means that the reaction __________ energy and is _________________.
(A) requires, spontaneous
(B) requires, non-spontaneous
(C) releases, spontaneous
(D) releases, non-spontaneous
(B) requires, non-spontaneous
∆G is positive for a certain reaction. This means that the reaction requires energy and is non-spontaneous. Non-spontaneous reactions will not naturally occur unless coupled with highly exergonic, or spontaneous reactions.
Hydrolysis of phosphate groups in ATP is what type of reaction?
(A) Exergonic
(B) Endergonic
(C) Isometric
(D) Isotonic
(A) Exergonic
Hydrolysis of phosphate groups in ATP is an exergonic process (a process in which the change in Gibb's Free Energy of the reaction is negative- products are at a lower energy level than the reactants.)
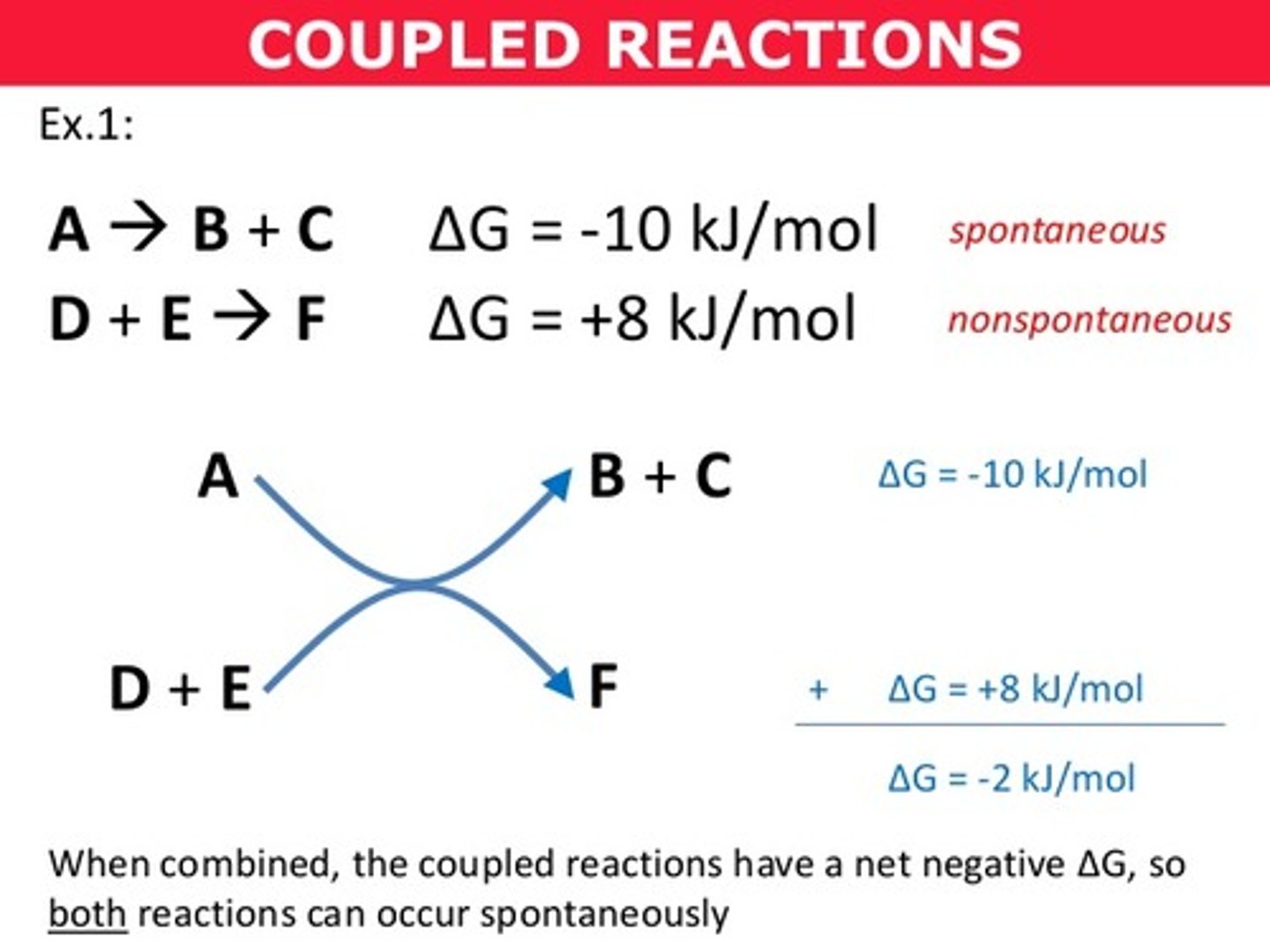
Describe the process of "coupling" two reactions?
A non-spontaneous reaction can be driven forward using the energy released from a spontaneous reaction. We are "coupling" these two reactions together in a way that the overall change in Gibb's free energy is negative, making the overall process spontaneous.
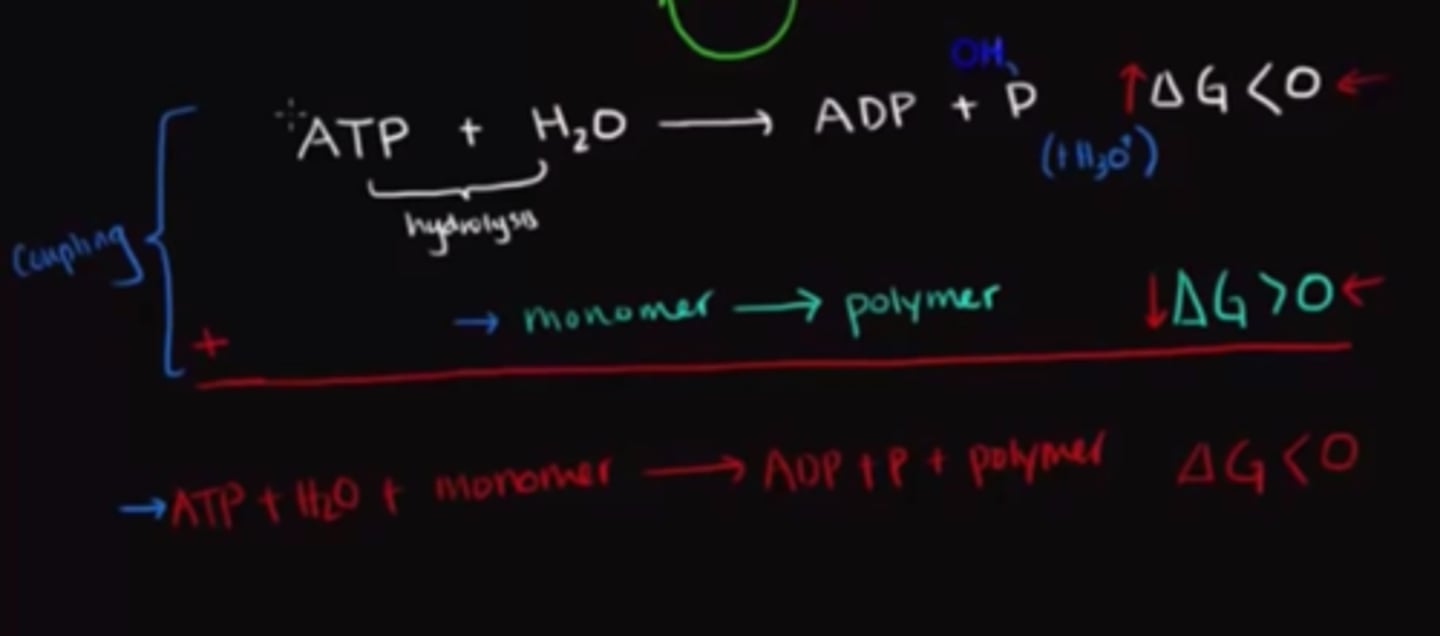
True or False? Coupled reactions tend to occur simultaneously.
True. Coupled reactions tend to occur simultaneously.
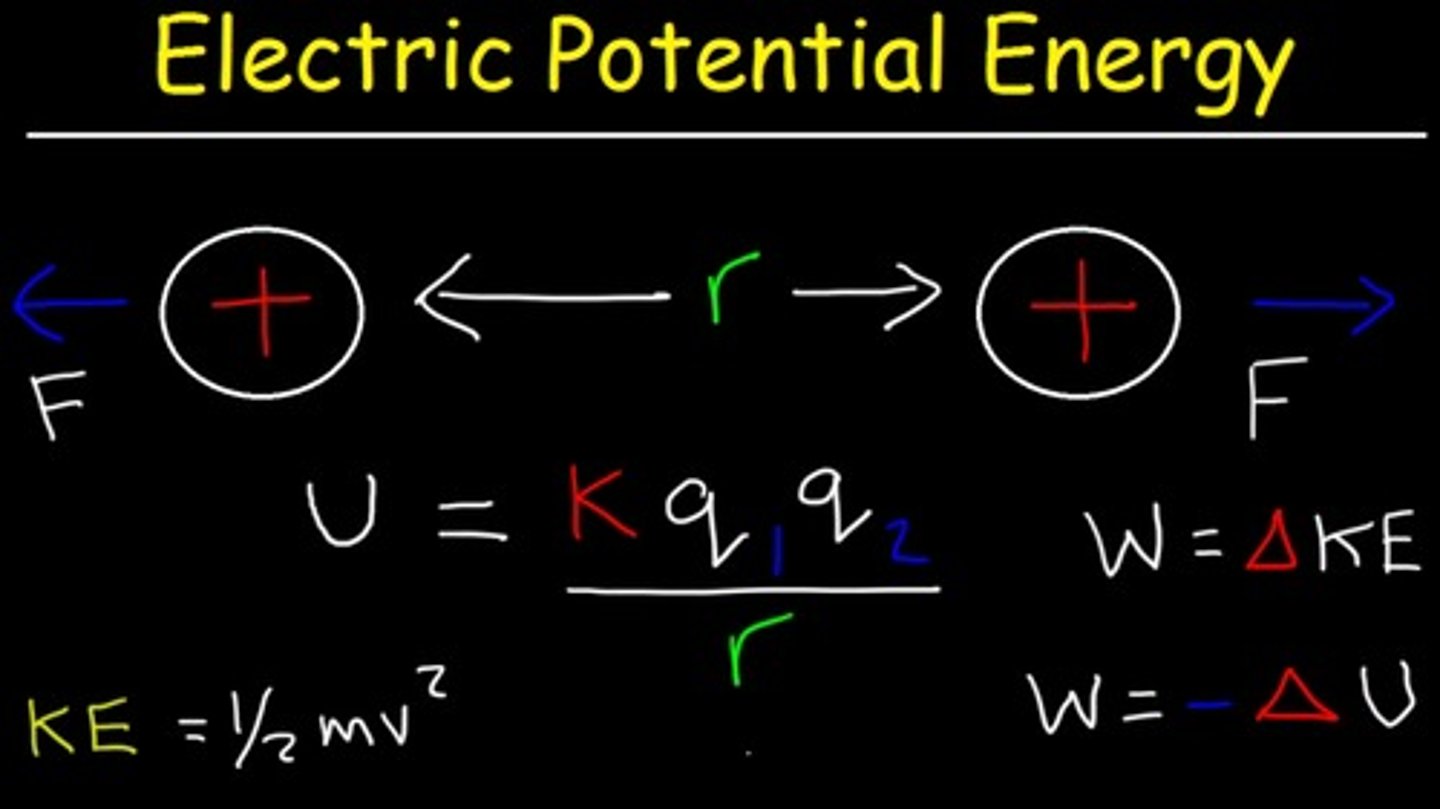
ATP has three phosphate groups directly next to one another. What about this structure makes ATP a high-energy molecule?
Phosphate groups are very negatively charged, and negatively charged groups do not want to be next to each other. This is a high-energy situation.
Think about it like two similar charges being next to each other. The closer the charges, the higher the electric potential energy. As these charges separate, the high amount of electric potential energy is converted into kinetic energy.
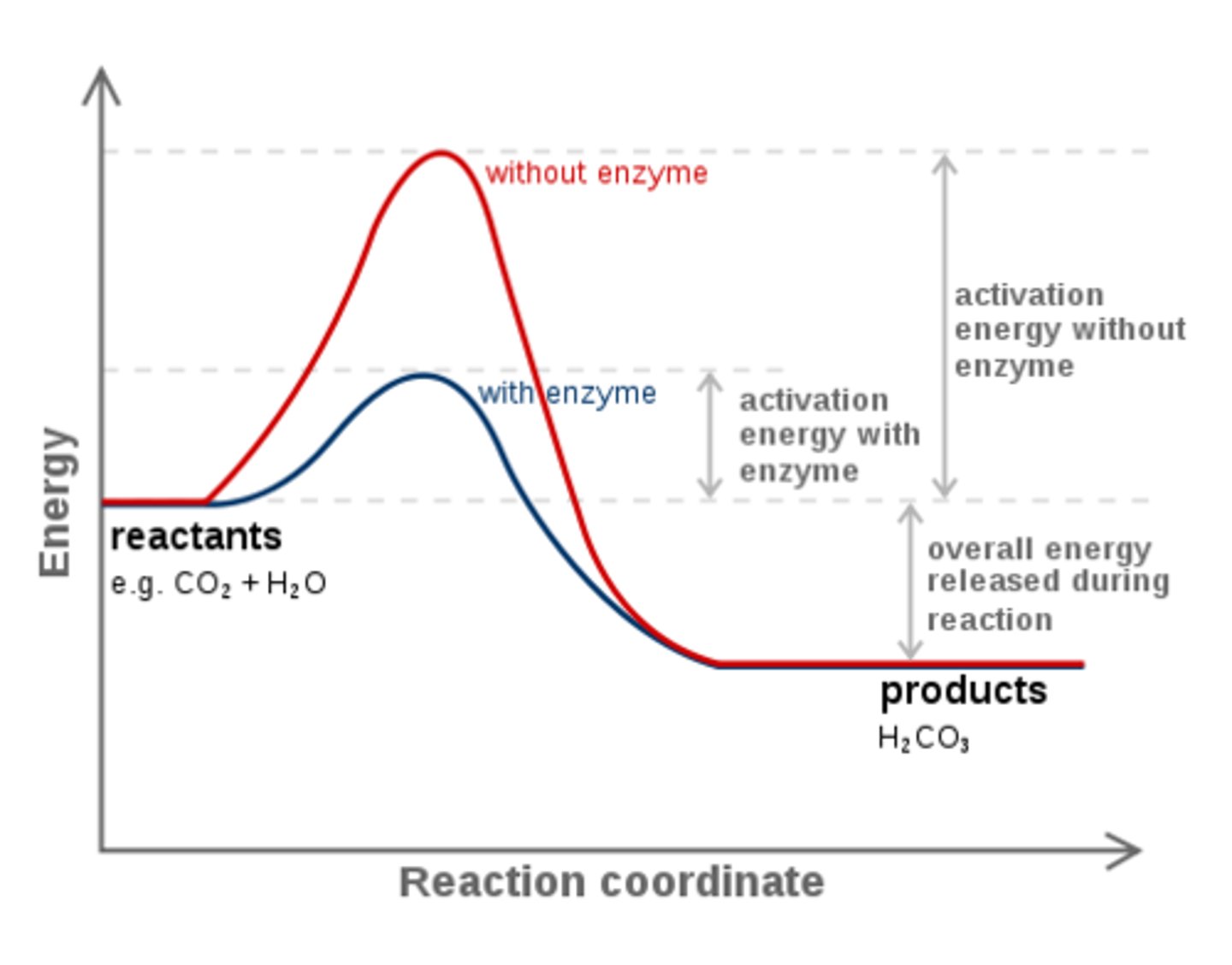
If ATP hydrolysis has a very negative ∆G value, why doesn't ATP hydrolyze spontaneously all the time? How is our body able to control when ATP hydrolysis occurs?
Although ATP hydrolysis has a very negative ∆G value, the reaction has a very high activation energy (Ea). When an enzyme is used in conjunction with ATP, the Ea is lowered, allowing the reaction to occur. This way, reactions with ATP will primarily occur only in the presence of the needed enzyme.
In the following reaction, indicate the element that has been oxidized and the one that has been reduced:
2 Na(s) + FeCl2 --> 2 NaCl + Fe(s)
Sodium (Na) is oxidized, going from a 0 to +1 oxidation state
Iron (Fe) is reduced, going from +2 to a 0 reduced state.
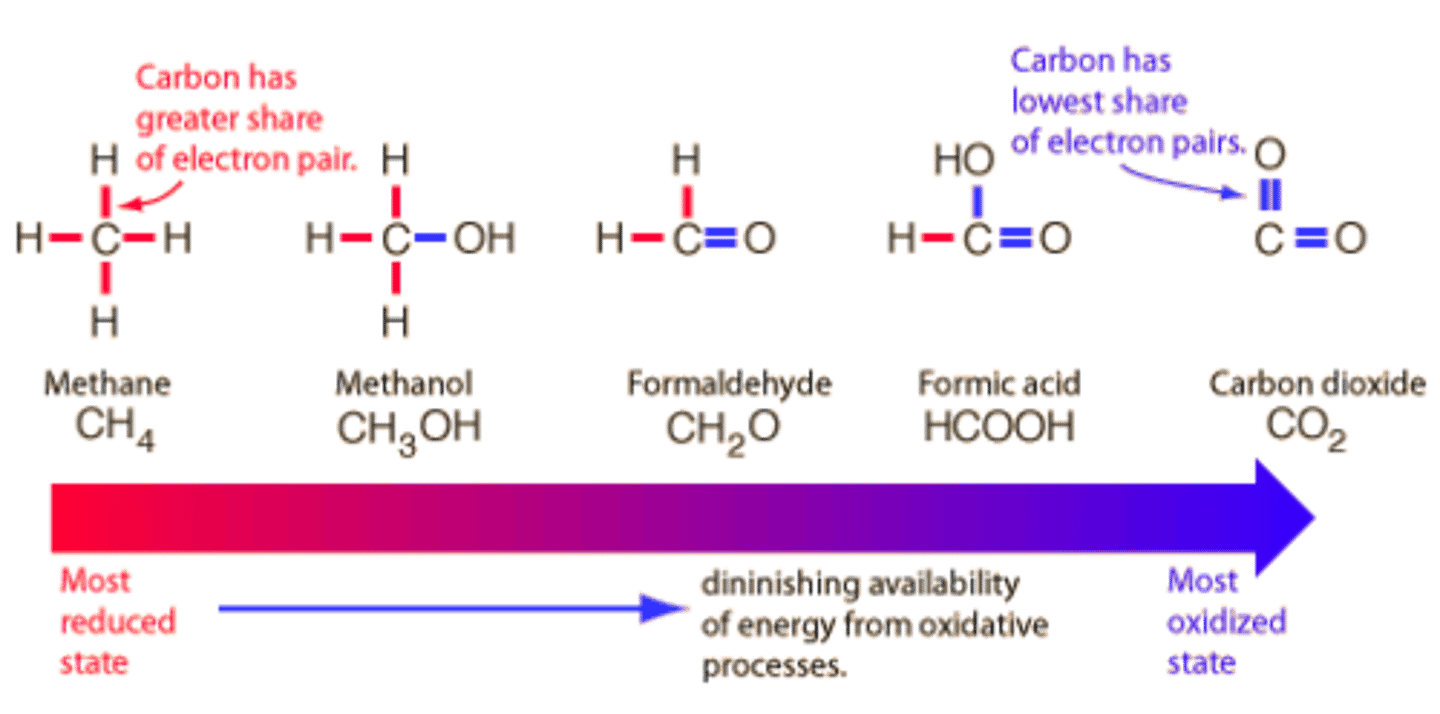
What is the definition of reduction and oxidation in terms of bonds to hydrogen and oxygen?
From a biological point of view, reduction is the gain of bonds to hydrogen atoms while oxidation is the loss of bonds to hydrogen atoms.
Additionally, reduction is the loss of bonds to oxygen atoms while oxidation is the gain of bonds to oxygen atoms.
In the following unbalanced reaction, indicate the element that has been oxidized and the one that has been reduced:
H2(g) + O2(g) --> H2O(l)
H2(g) is oxidized as it gains bonds to oxygen.
O2(g) is reduced as it gains bonds to hydrogen.
How does the electron transport chain relate to a galvanic cell?
A galvanic cell harnesses the flow of electrons that results from a spontaneous oxidation-reduction reaction to power a resistor. The electron transport chain harnesses the flow of electrons between biomolecules that are being spontaneously oxidized/reduced to produce ATP.
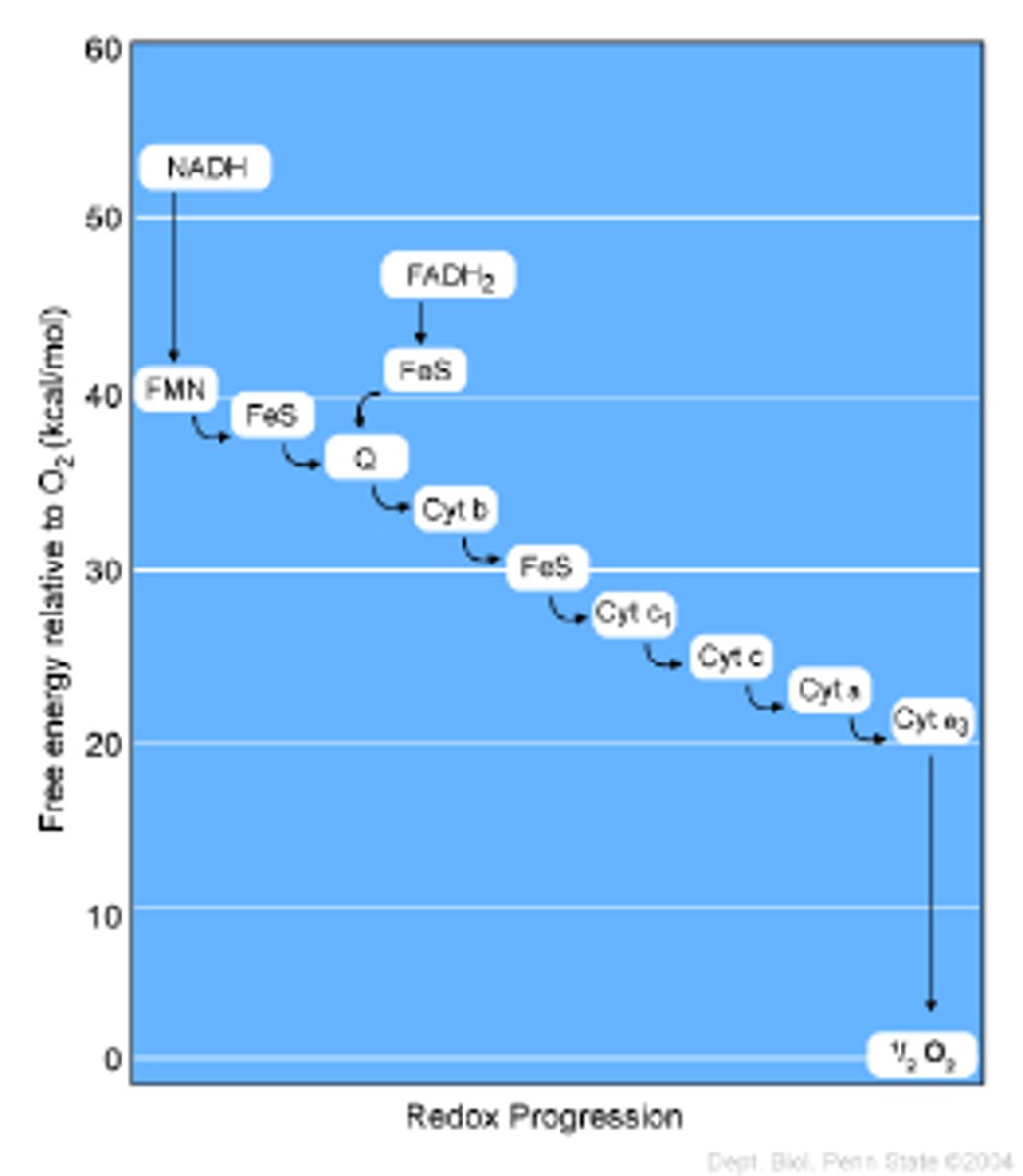
Below is the overall balanced reaction that results in the complete oxidation of glucose. Is O2(g) oxidized or reduced?
C6H12O6 + 6 O2(g) --> 6 H2O(l) + 6 CO2(g)
O2(g) is reduced as it gains bonds to hydrogen.
How does O2(g) gain electrons from glucose (C6H12O6)? (use the term "electron carrier molecule" in your explanation)
During glycolysis/Kreb's cycle, glucose (C6H12O6) donates electrons to electron carrier molecules, which will then transfer their electrons to O2(g) via the electron transport chain. This is accompanied by the transfer of an H+ proton, forming water (H2O) as a product of oxidative phosphorylation.
Which of the following are electron carrier molecules?
I. NADH
II. CO2
III. FADH2
(A) I Only
(B) I and II Only
(C) I and III Only
(D) II and III Only
(C) I and III Only
NADH and FADH2 are the electron carrier molecules that carry electrons from glycolysis/Kreb's cycle to the electron transport chain.
Why is glucose carefully broken down via many metabolic steps instead of simply combusting in a single step?
There are many reasons that glucose is not combusted in a single step. For starters, this combustion would produce energy in the form of unusable heat instead of usable ATP. Additionally, this is a kinetically unfavorable reaction due to the extremely high activation energy (Ea). Finally, if this process is not done carefully, harmful free radicals may form since we are dealing with the transfer of electrons to oxygen.
Which type of enzymes are responsible for the oxidation-reduction steps during the breakdown of glucose?
(A) Hydrolases
(B) Lyases
(C) Dehydrogenases
(D) Kinases
(C) Dehydrogenases
Dehydrogenases remove the equivalent of a hydride ion (H-) and transfer it to an electron carrier molecule.
True or False? Hydride ions contain 2 electrons.
True. Hydride ions contain 2 electrons. Think of H- as a combination of H+ and 2e-.
What products result from the following reactions?
NAD+ + 2H+ + 2e- --> ?
FAD + 2H+ + 2e- --> ?
NAD+ + 2H+ + 2e- --> NADH + H+
FAD + 2H+ + 2e- --> FADH2