chapter 13 hair skin and nails
1/176
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
177 Terms
largest organ system
skin
how many sqft does skin take up
20 sqft
skin protects the body from
environmental stesses
epidermis
outer highly differentiated layer
basal cell layer
forms new skin cells
outer horny cell layer is made up of
keratinized cells
dermis
inner supportive layer
connective tissue
collagen
elastic tissue
located in the dermis
beneath epidermis and dermis
subcutaneous layer of adipose tissue
subcutaneous layer stores
fat for energy, aids in cushioning/protection and provides increased mobility
Skin color is determined by
melanin, carotene, hemoglobin
melanin
brown pigment
carotene
yellow-orange pigment
red purple tones
underlying vascular bed
threads of keratin
hair shaft and bulb matrix
types of hair
lanugo, vellus, terminal
lanugo hair
also known as Vellus Hair, is the soft, white and downy hair found on the body; usually lacking a medulla
terminal hair
Long, coarse, pigmented hair found on the scalp, legs, arms, and bodies of males and females.
follicle
cyclical with active and resting phases
Sebaceous glands
secrete sebum (oil) into the hair follicles where the hair shafts pass through the dermis
sebum
secreted lipid substances through hair follicles
lubricate skin and form emulsion
sweat glands
eccrine and apocrine
eccrine glands
These glands produce sweat.
apocrine glands
produce a thick, milky secretion and open into the hair follicles
nails
hard plates of keratin on the dorsal edges of the fingers and toes
skin is
washable, waterproof and rugged producing protective and adaptive properties
functions of the skin
protection, prevents penetration, perception, temperature regulation, identification, communication, wound repair, absorption and excretion, production of vitamin D
lanugo
fine downy hair of newborn infant
vernix caseosa
Waxy or "cheesy" white substance found coating the skin of newborn humans
milia
Benign, keratin-filled cysts that can appear just under the epidermis and have no visible opening in newborns
children's skins and hair
epidermis thickens darkens and becomes lubricated
hair growth accelerates
adolescents hair skin and nails considerations
secretions from apocrine sweat glands increase
subcutaneous fat deposition increase
secondary sex characteristics
increase in metabolism in pregnant people leads to
increase secretion of sweat and sebaceous glands to dissipate heat
fat deposits are laid down as
maternal reserves for nursing a baby
in pregnancy expected skin color changes
due to increased hormone levels
In aging adults: elasticity
Loses elasticity; skin folds and sags
In aging adults: sweat and sebaceous glands
decrease in number and functions, leaving skin dry
Aging adults: Senile purpura
discoloration due to increasing capillary fragility
In aging adults: Skin breakdown due to multiple factors
cell replacement is slower and wound healing is delayed
In aging adults: hair matrix
Functioning melanocytes decrease, leading to gray fine hair
Genetic attributes of dark-skinned individuals afford protection against skin cancer due to ________.
melanin
increased likelihood of skin cancer in
whites than in black and Hispanic populations
succession of genetic mutations leading to
increased chromosome sensitivity to sun damage
most important environmental risk factor for skin cancer is exposure to
ultraviolet (UV) radiation both from sun and indoor tanning sourceschanges genetic makeup
increased risk for melanoma r/t increased number of
sunburns during ones lifetime
keloids
Nodules formed in wound healing due to excessive collagen, increased TGF-Beta activity
impact of measles
highly contagious pathogen
subjective data health history questions
Past history of skin disease, allergies, hives, psoriasis, or eczema?
Change in pigmentation or color, size, shape, tenderness?
Excessive dryness or moisture?
Pruritus or skin itching?
Excessive bruising?
Rash or lesions?
Medications: prescription and over-the-counter?
Hair loss?
Change in nails' shape, color, or brittleness?
Environmental or occupational hazards?
Self-care behaviors?
additional history questions for infants and children
Does child have any birthmarks?
Any change in skin color as a newborn? Does child have any rash or sores?
Does child have diaper rash?
Does child have any burns or bruises?
Has child been exposed to contagious or communicable disease?
Does child have habits such as nail biting or twisting hair?
Which steps are taken to protect child from sun exposure?
additional health questions for adolescents
Skin problems such as pimples, blackheads
additional health history questions in aging adults
What changes have you noticed in your skin in past few years?
Any delay in wound healing?
Any other skin pain?Any change in feet: toenails, bunions, wearing shoes?
Have you had any falls?
History of diabetes or peripheral vascular disease?What do you do to care for your skin?
preparation
control external variables that impact change skin color
focus on being attentive to skin characteristics
equipment needed
Strong direct lighting, gloves, penlight, and small centimeter ruler
woods light
ultraviolet light used for diagnosing skin conditions
complete physical examination
Skin assessment integrated throughout examination
Scrutinize the outer skin surface first before you concentrate on underlying structures
Separate intertriginous areas (areas with skinfolds) such as under large breasts, obese abdomen, and groin, and inspect them thoroughly
These areas are dark, warm, and moist and provide perfect conditions for irritation or infection
Always inspect feet, toenails, and between toes
regional physical examination
-Individuals may seek health care for skin problems and assessment focused on skin alone.
-Assess skin as one entity; getting overall impression helps reveal distribution patterns.
color
general pigmentation, freckles, moles, birthmarks,
-widespread color change (pallor, erthrma, cyanosis, jaundice
temperature
use backs of hands to palpate person
skin should be warm, and temperature equal bilaterally
hands and feet might be slightly cooler in a cool environment.
moisture
diaphoresis, dehydration
texture
normal skin feels smooth and firm with even surface
thickness
observe for thickened areas (callus formation)
edema
assess for fluid accumulation in the interstitial space
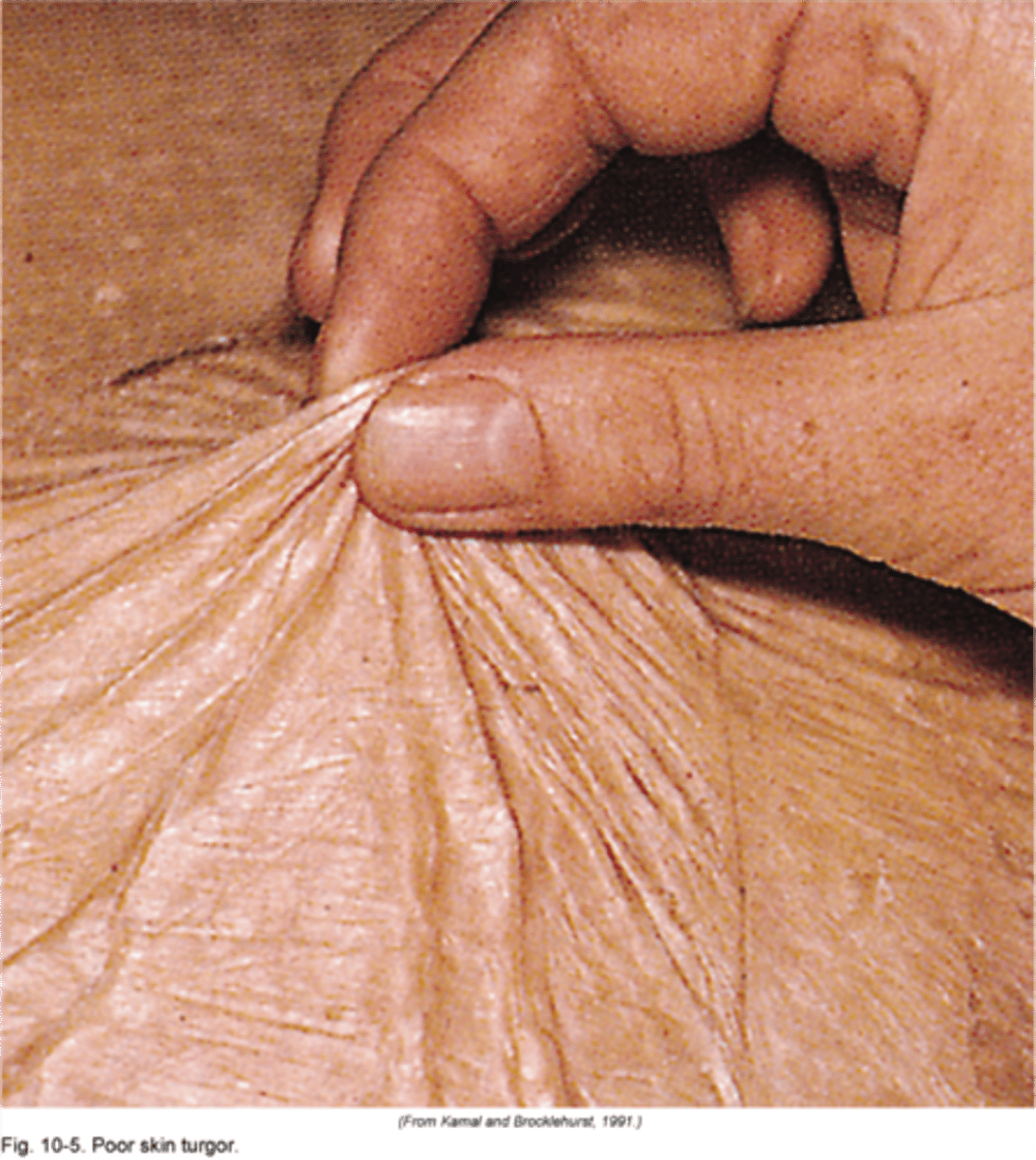
mobility and turgor
assess skin elasticity
vascularity or bruising
Assess for presence of tattoos and/or variations
Lesions: if any are present, note the following:
ØColor
ØElevation
ØPattern or shape
ØSize
ØLocation and distribution on body
ØAny exudate: note color and odor
ØUse a Wood's light (ultraviolet light filtered through special glass) to detect fluorescing lesions.
hair color
due to melanin production
hair texture
Characteristics range from fine to thick to curly to straight and may be affected by use of hair care products
hair distribution
review gender patterns of hair distribution
hair lesions
Identification by looking at scalp and dividing hair into sections
shape and contour nails
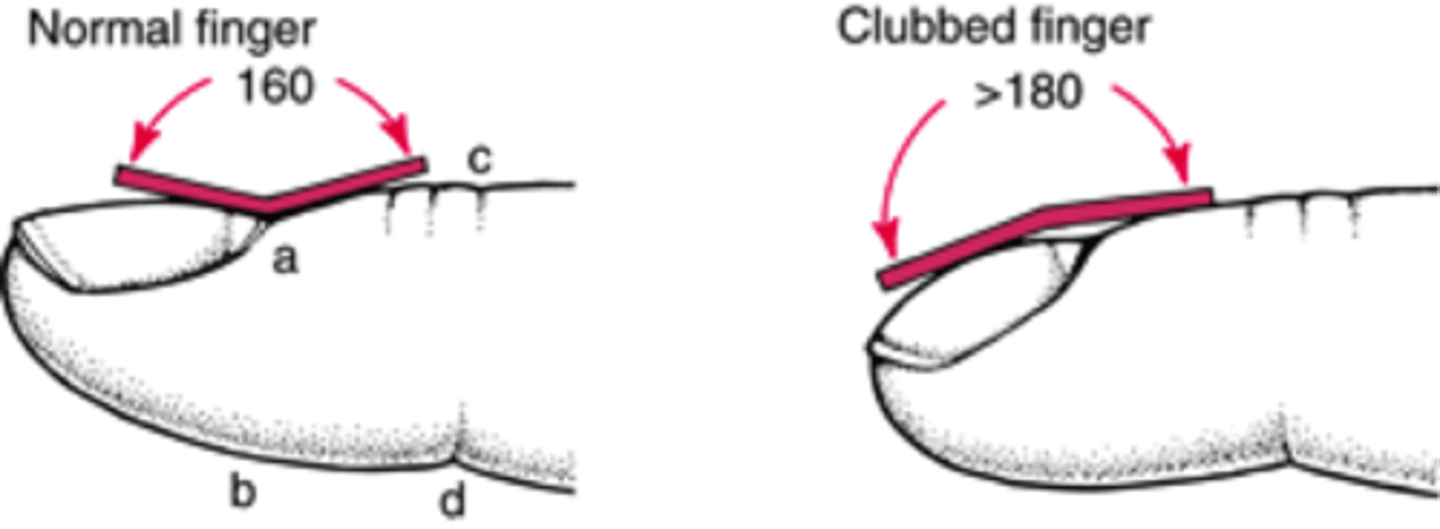
Profile sign: view index finger at its profile and note angle of nail base; it should be about 160 degrees
nails consistency
observe for smooth, regular, not brittle or splitting, uniform nail thickness
nail color
Translucent nail plate to pink nail bed below
Note ethnic variations
nail capillary refill
Depress nail edge to blanch and then release, noting return of color; indicates status of peripheral circulation.
clubbing
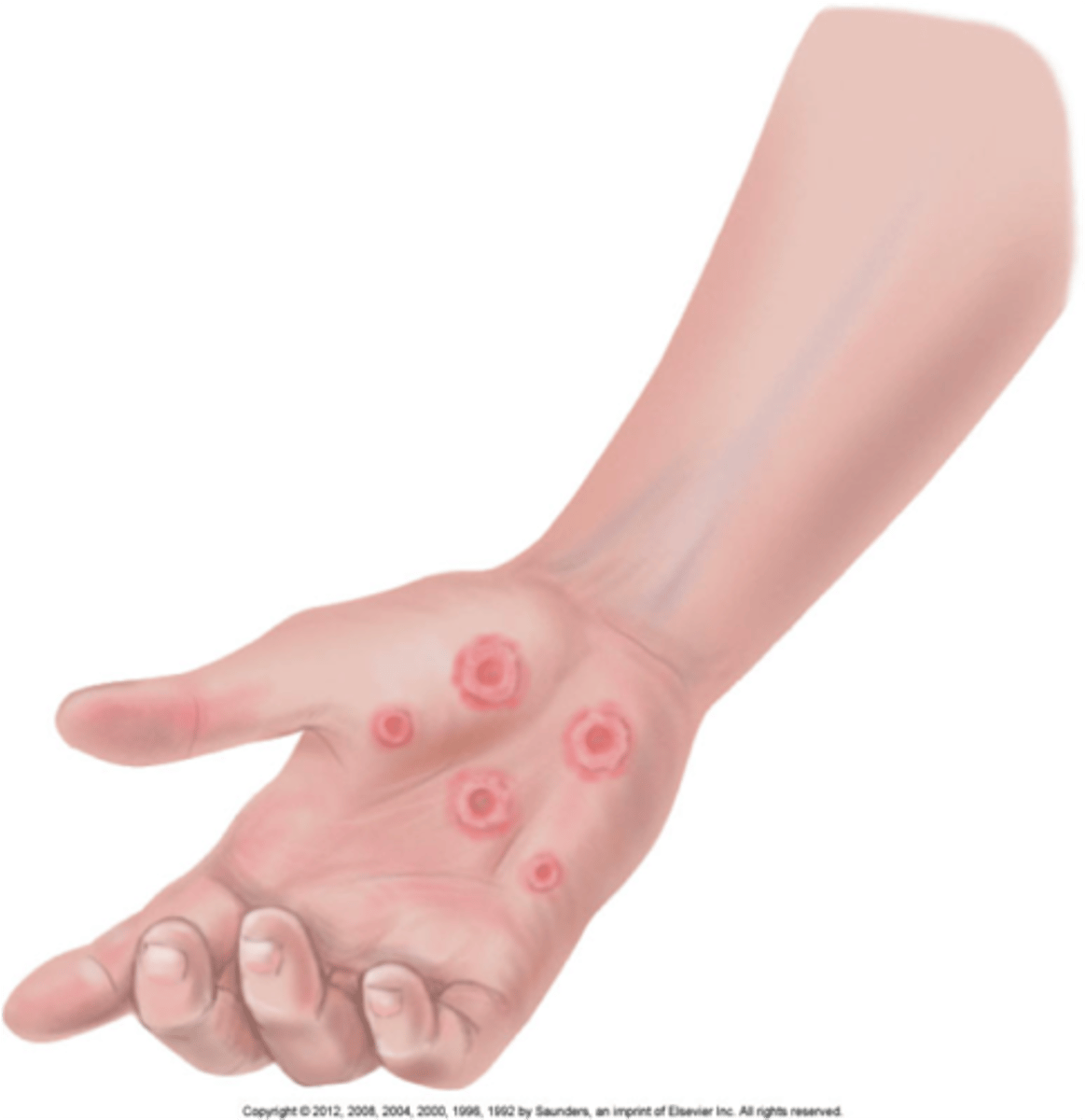
ABCDEF skin assessment
A: asymmetry
B: border irregularity
C: color variations
D: diameter greater than 6 mm
E: elevation or evolution
F: funny looking—"ugly duckling" —different from others
infant skin color
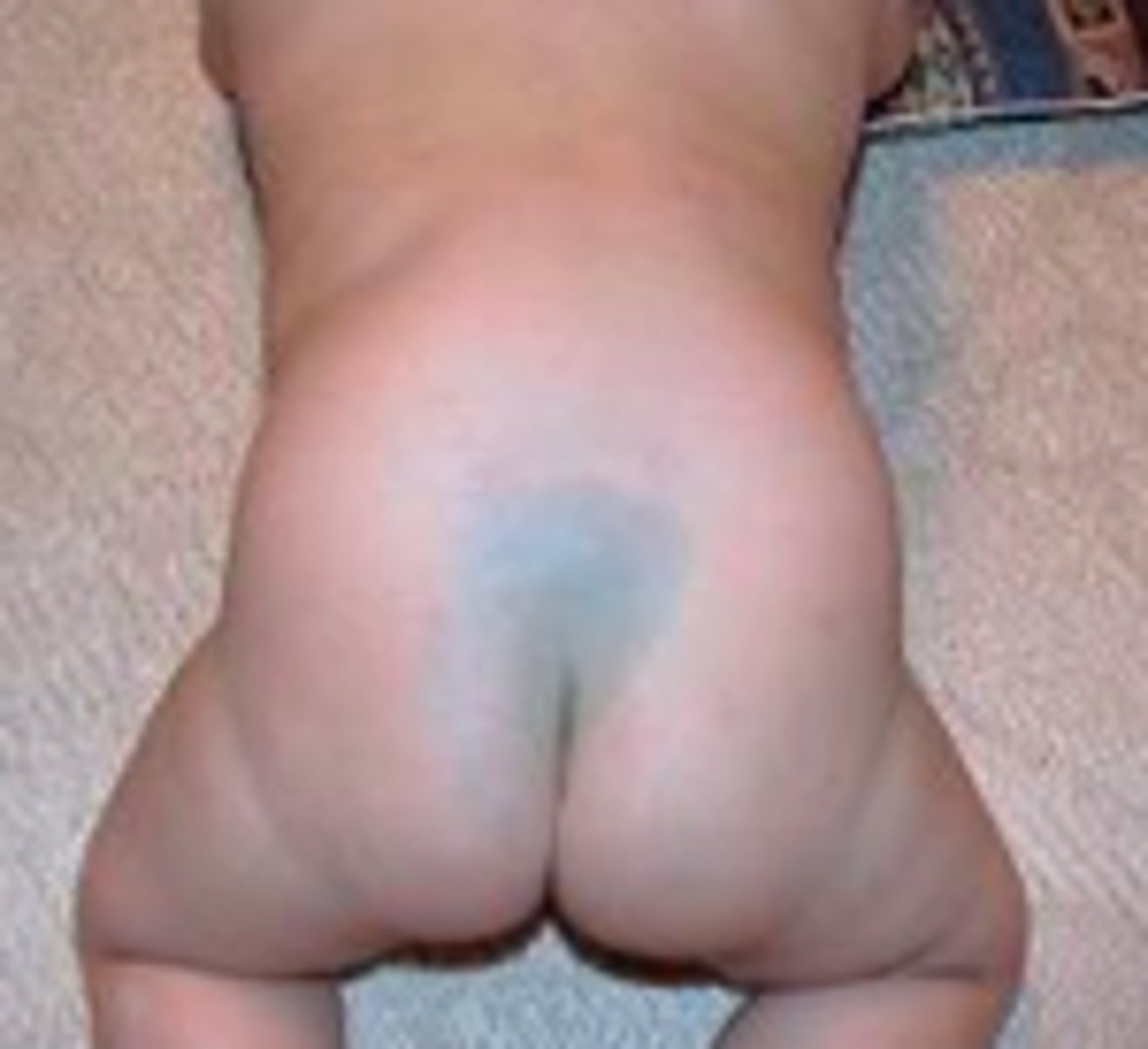
Mongolian spot
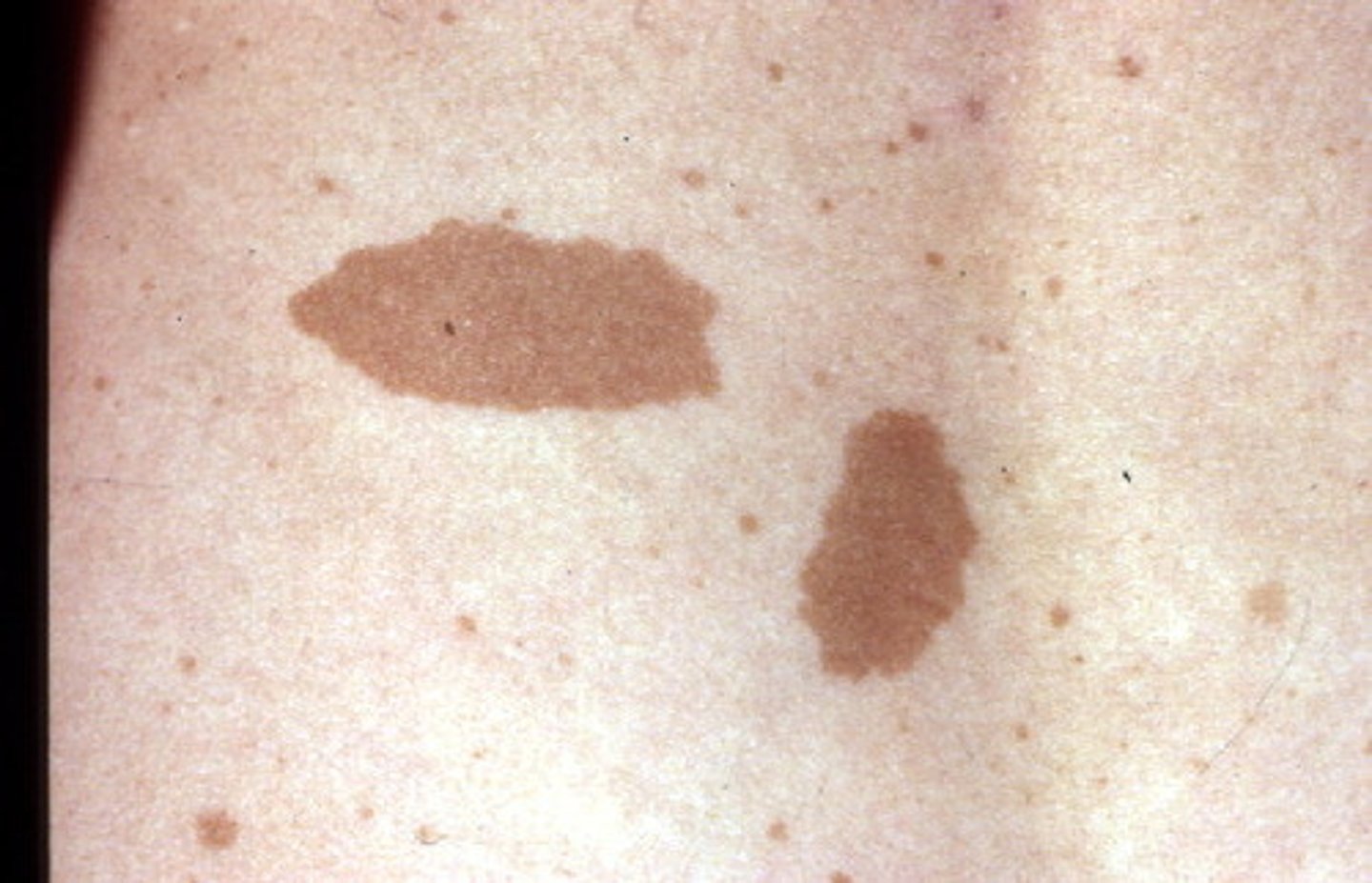
Café-au-lait spot
Mongolian spot
Café-au-lait spot
infant skin color changes
Harlequin color change
Erythema toxicum
harlequin color change
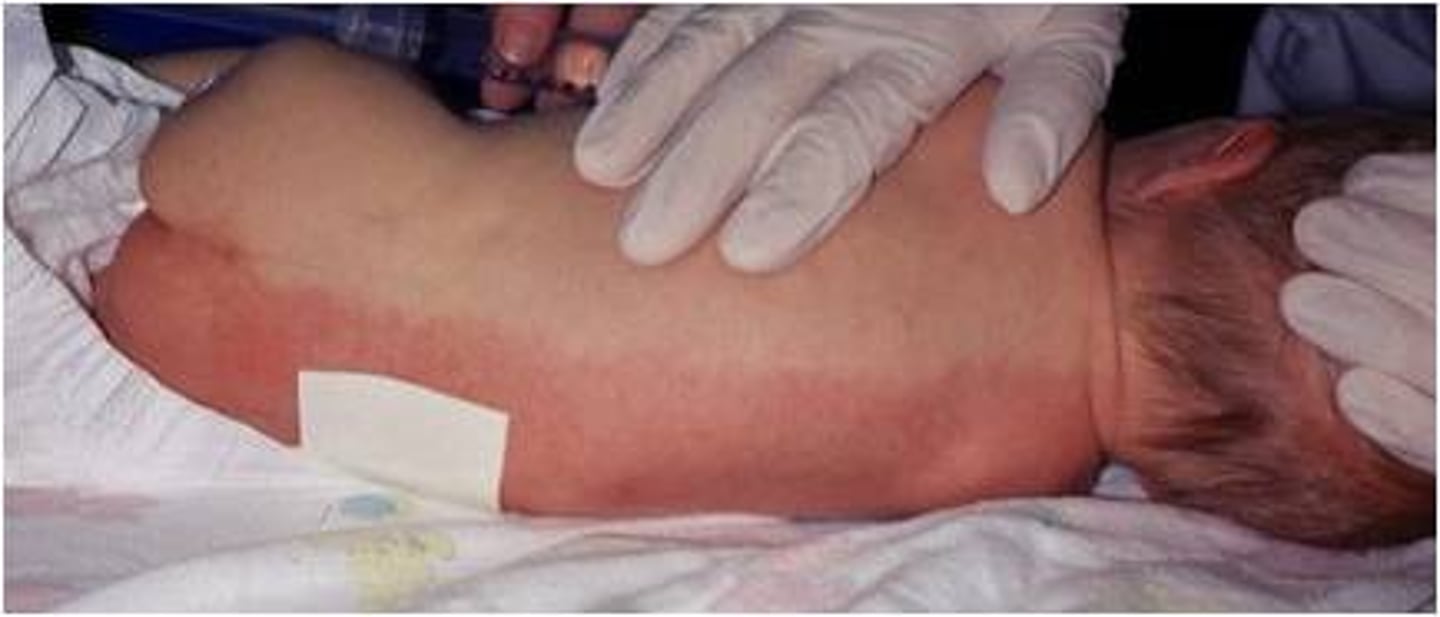
Erythema toxicum
pink rash that appears suddenly anywhere on the body of a term newborn during the first 3 weeks.
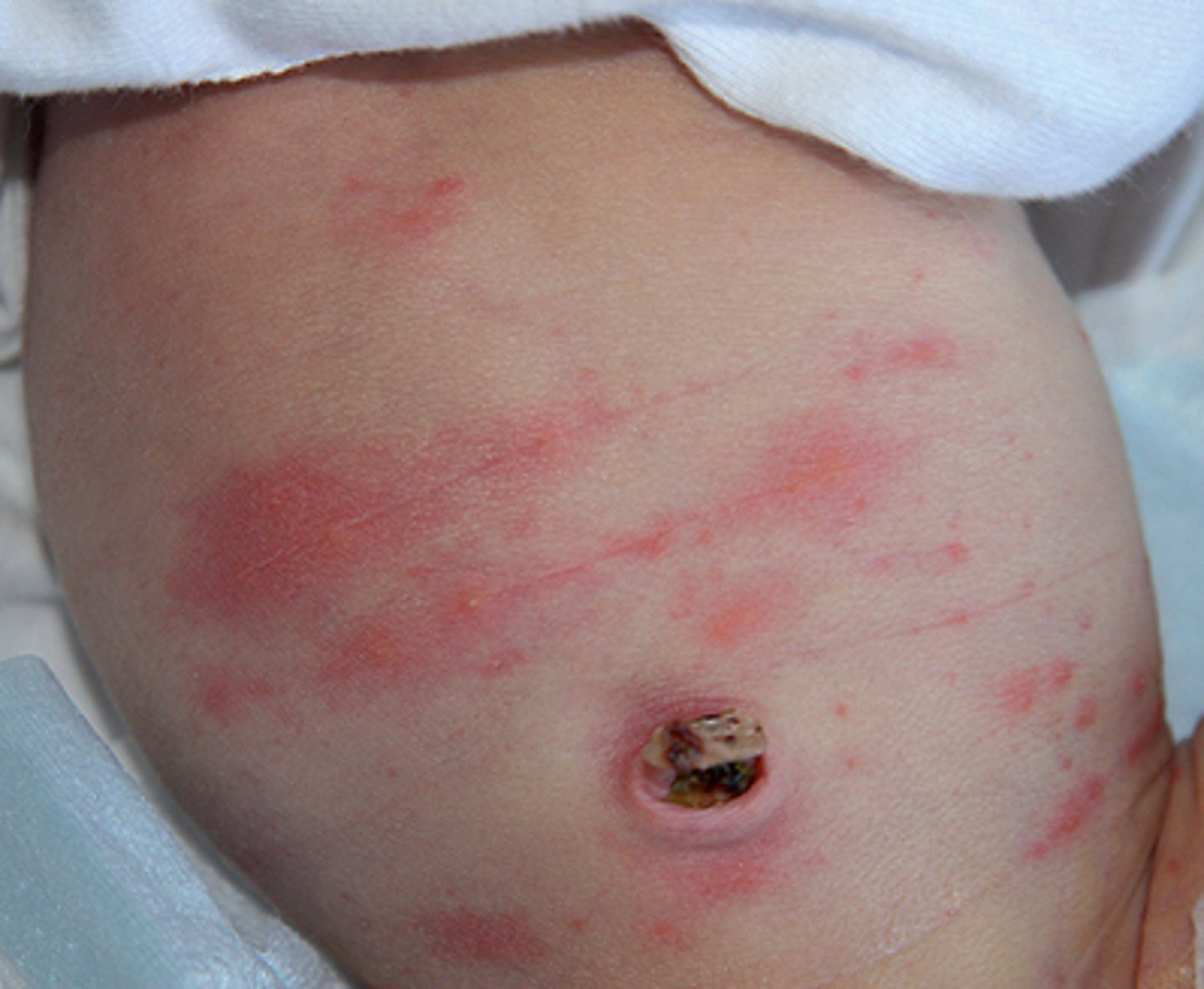
temporary cyanotic conditions in infants
acrocyanosis and cutis marmorata
acrocyanosis
Temporary cyanotic condition, usually in newborns resulting in a bluish color around the lips, hands and fingernails, feet and toenails. May last for a few hours and disappear with warming.
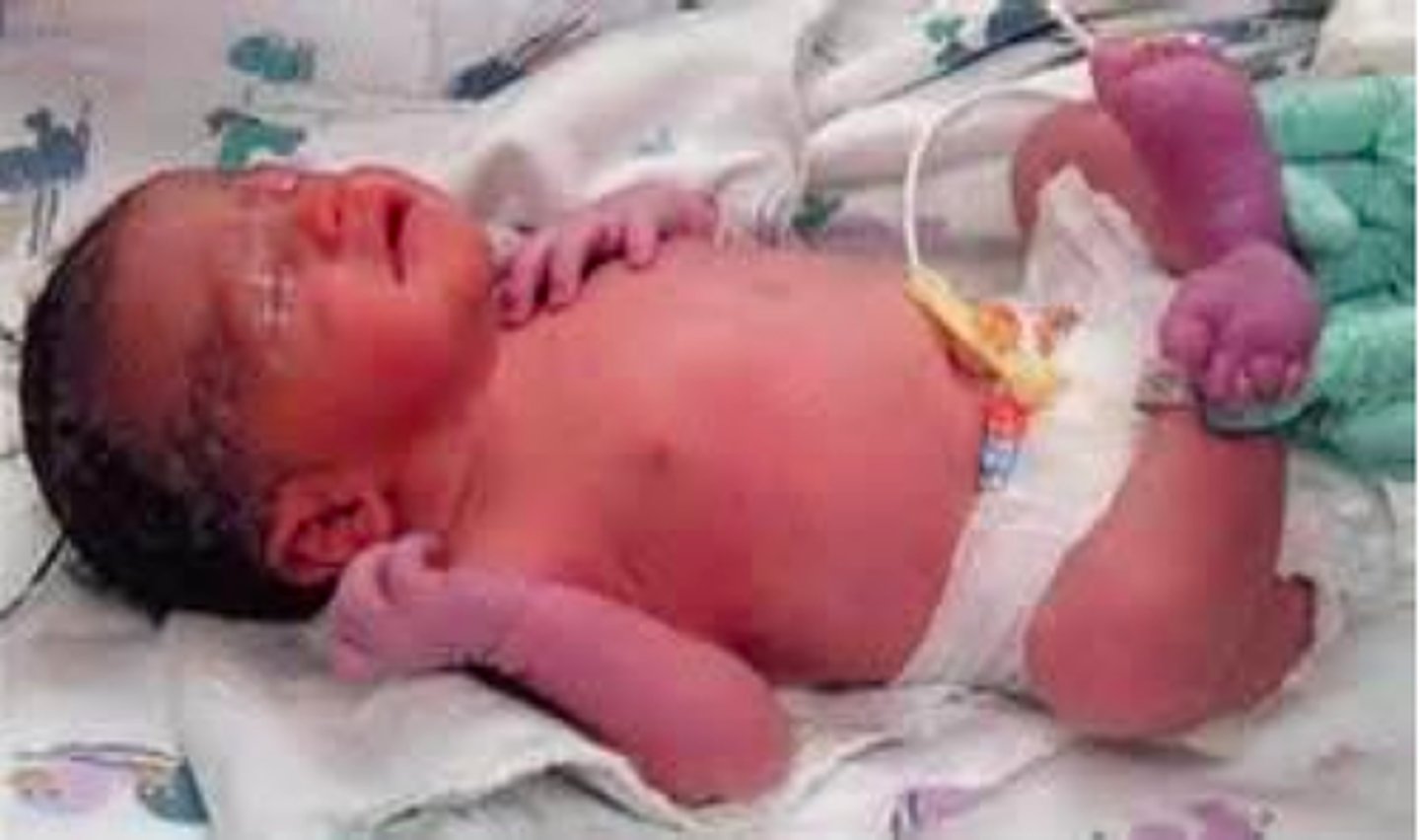
cutis mamorata
transient mottling in the trunk and extremities
in response to cooler room temperatures in babies
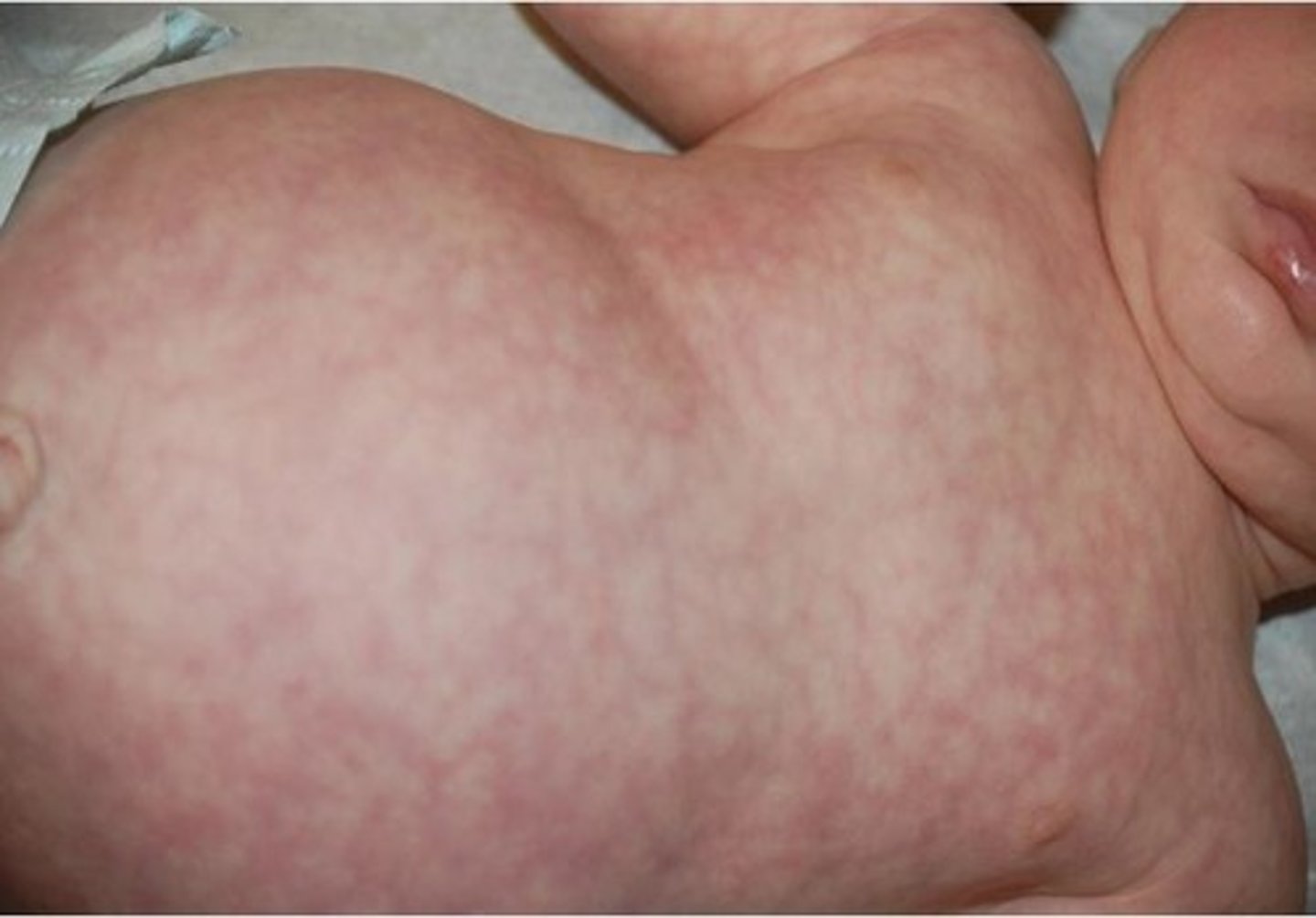
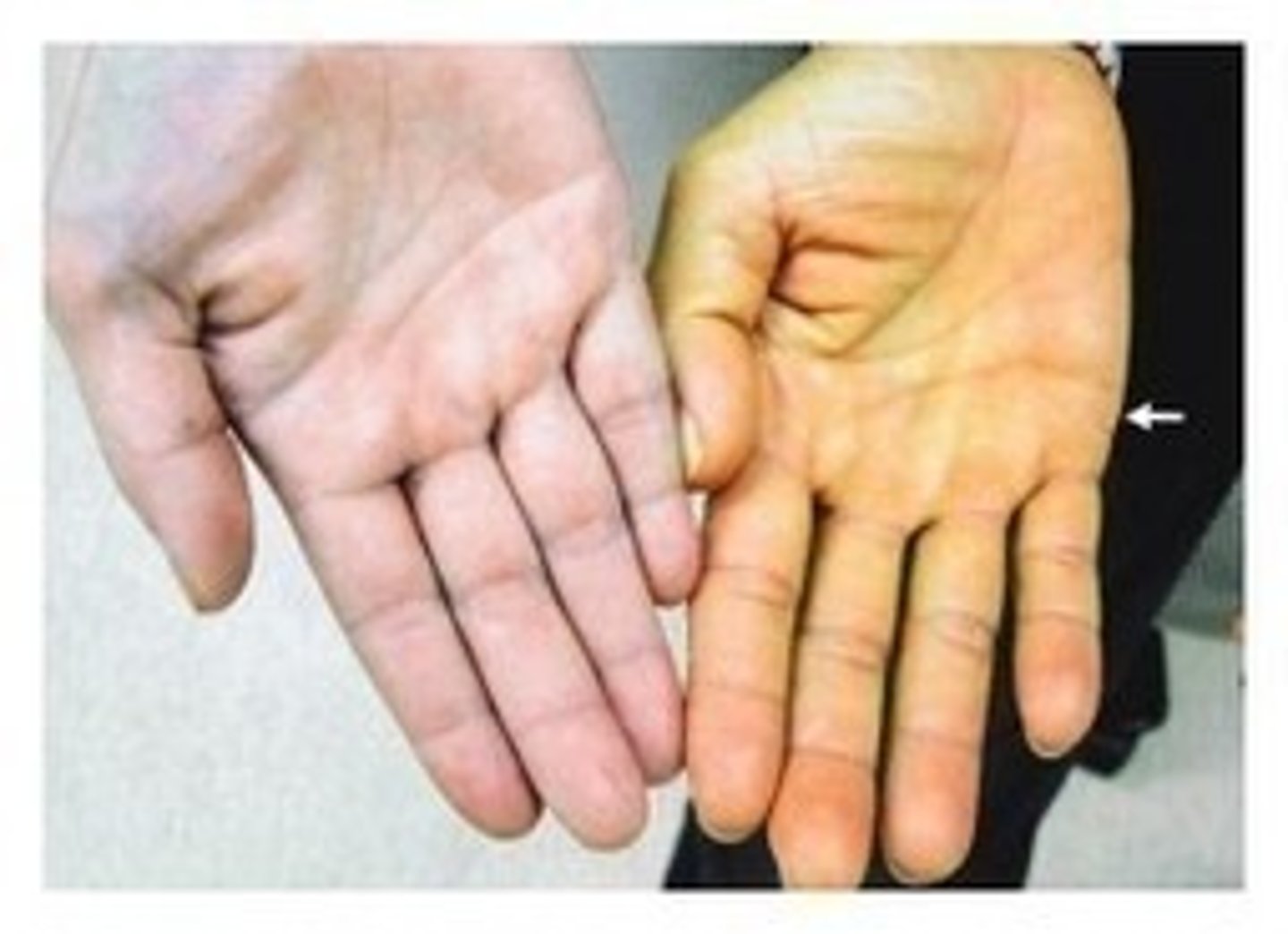
physiological jaundice in infants
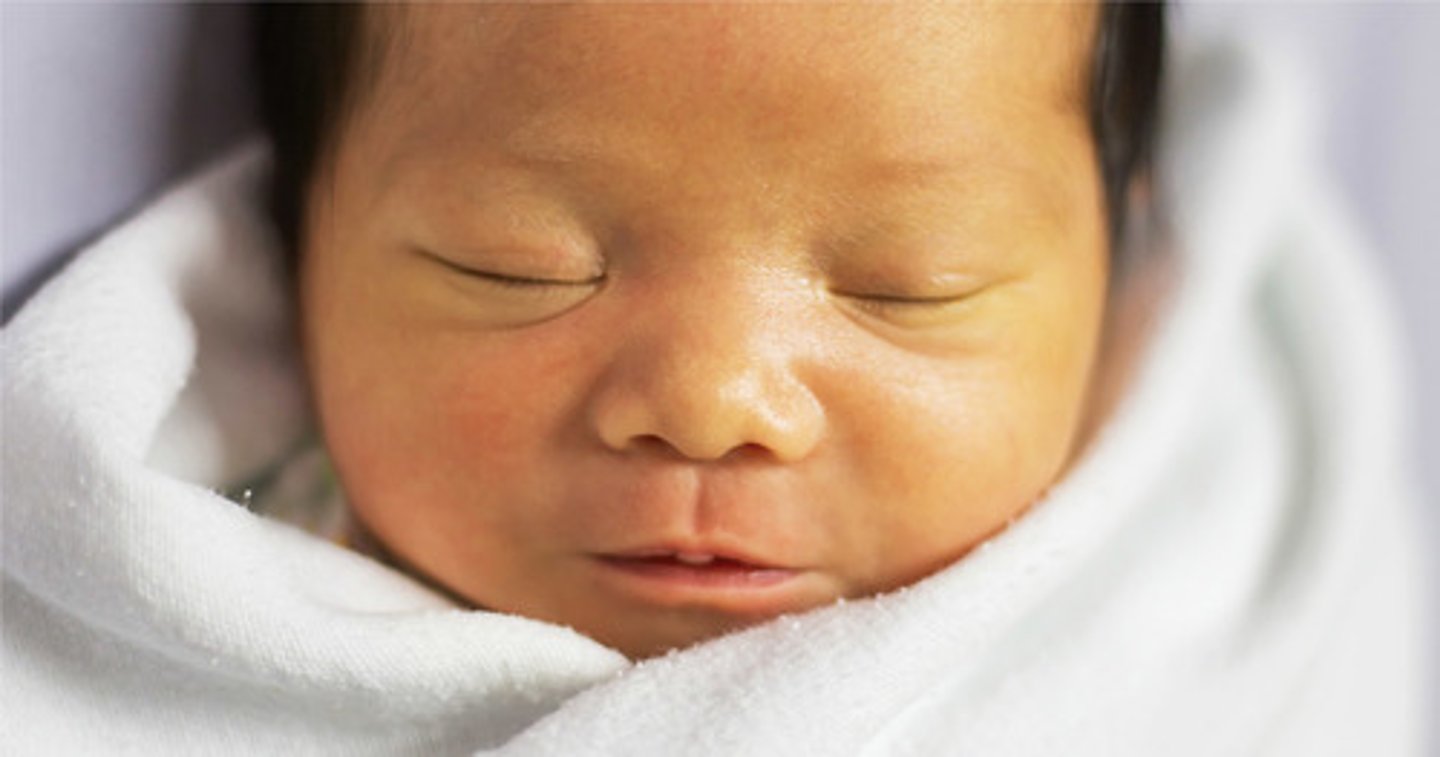

carotenemia in infants
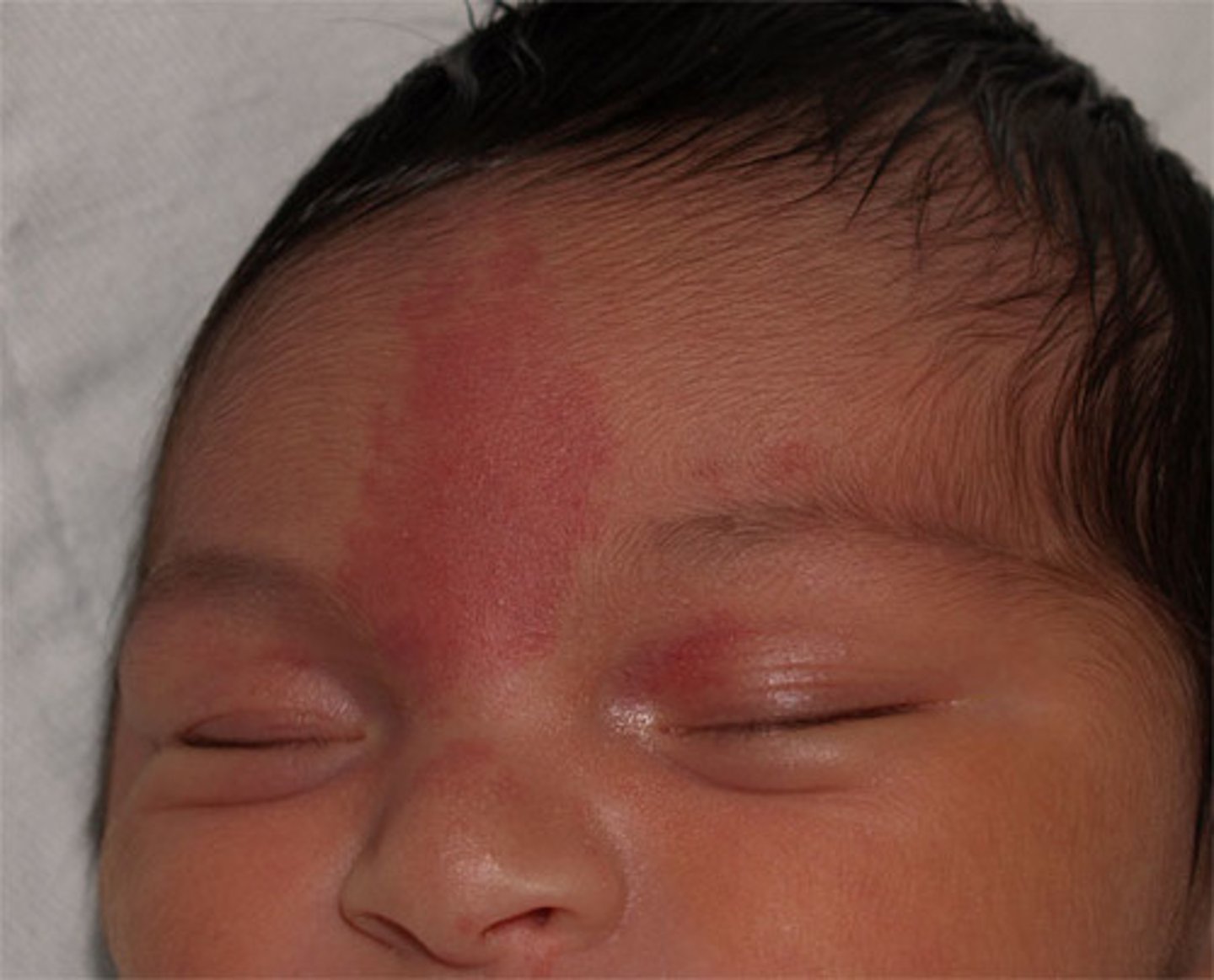
nevus simplex
"stork bite", pink red capillary on face or neck
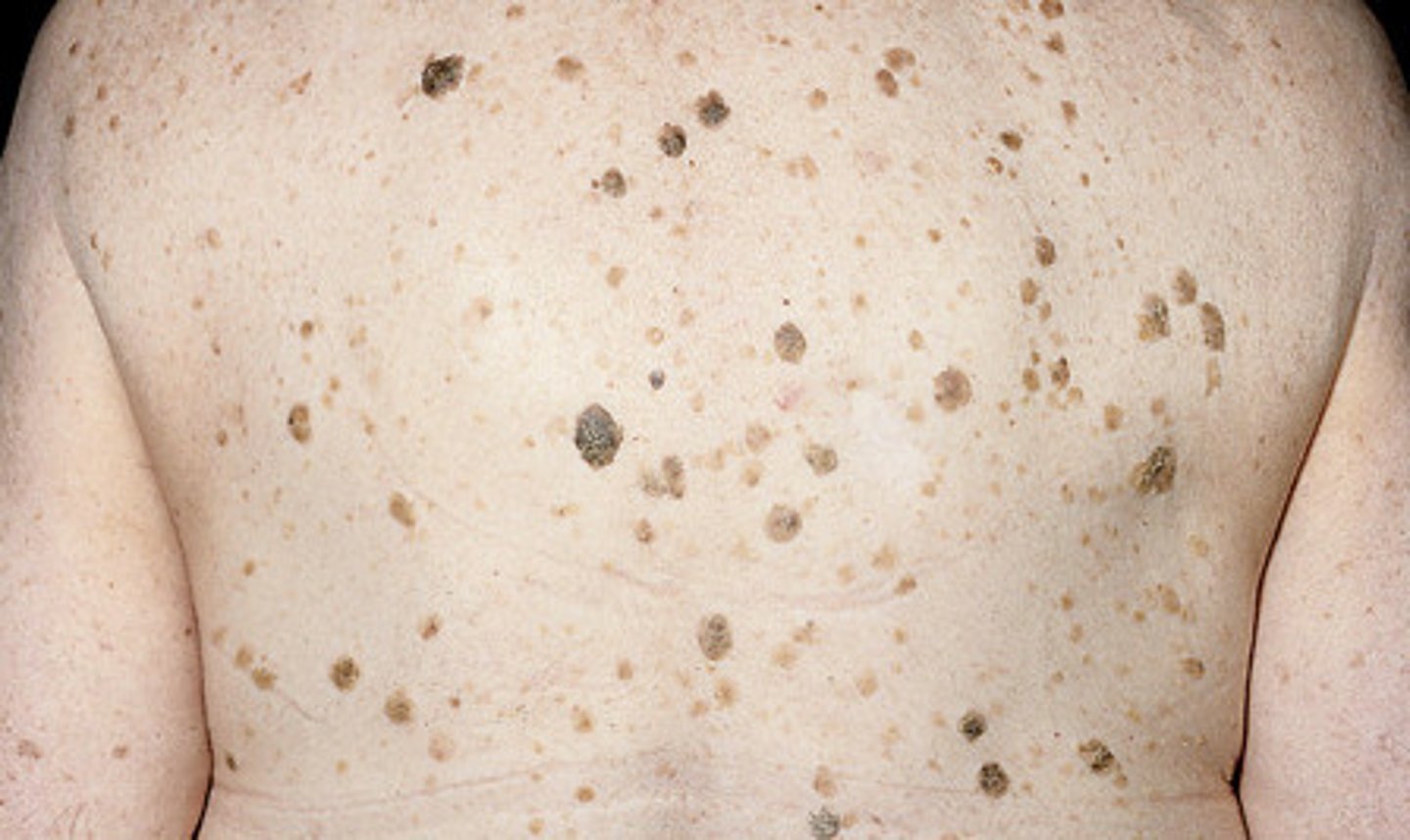
aging skin color and presentations
solar lentigines (liver spots
keratoses - seborrheic or actinic
liver spots

keratoses
raised, thickened areas of pigmentation that look crusted, scaly, and warty
aging moisture
xerosis
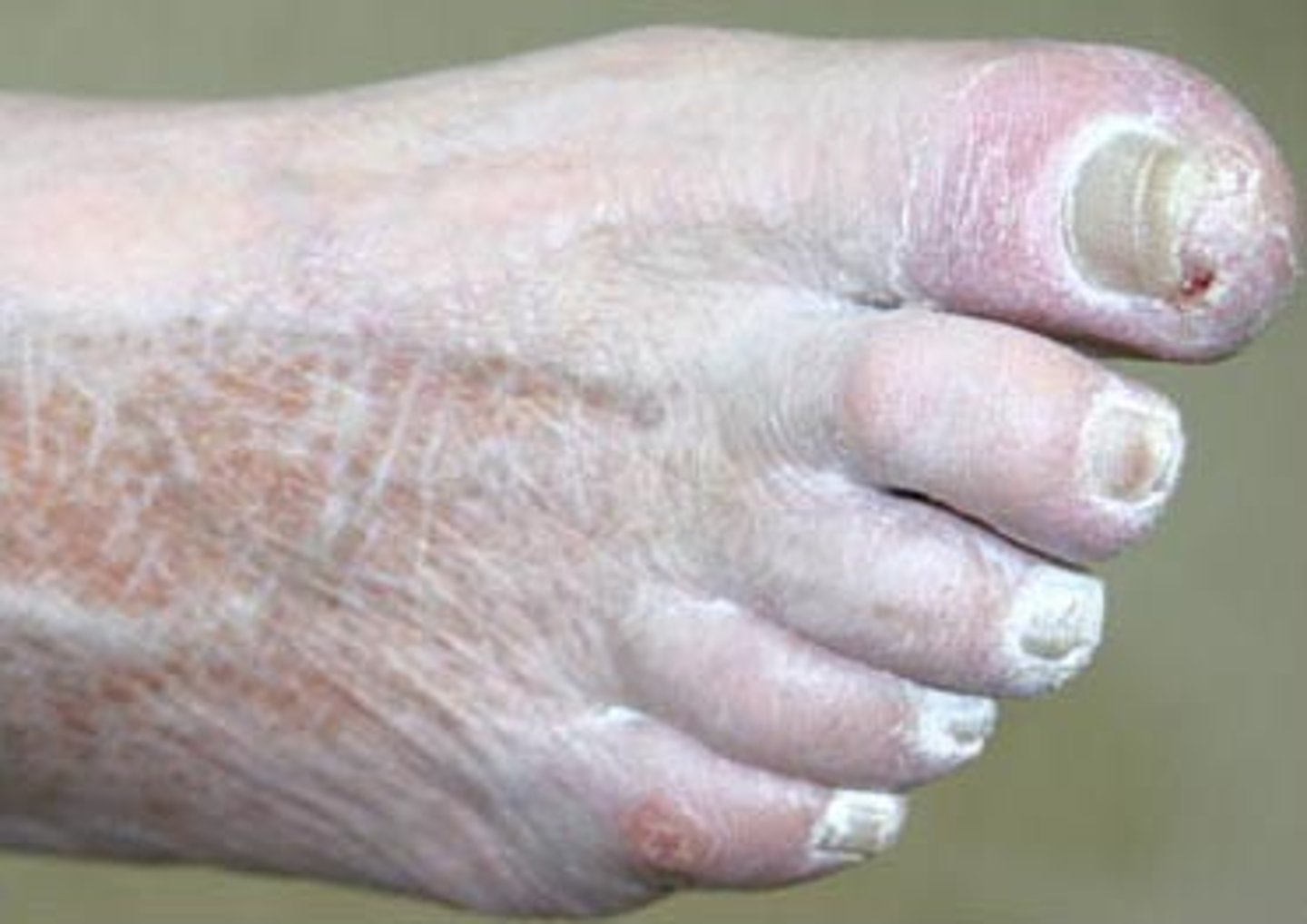
aging skin texture
skin tags or acrochordons
sebaceous hyperplasia
aging skin thickness
Thin parchment as subcutaneous fat decreases Decreased mobility and turgor Decreased hair growth, nail growth, and brittle nails
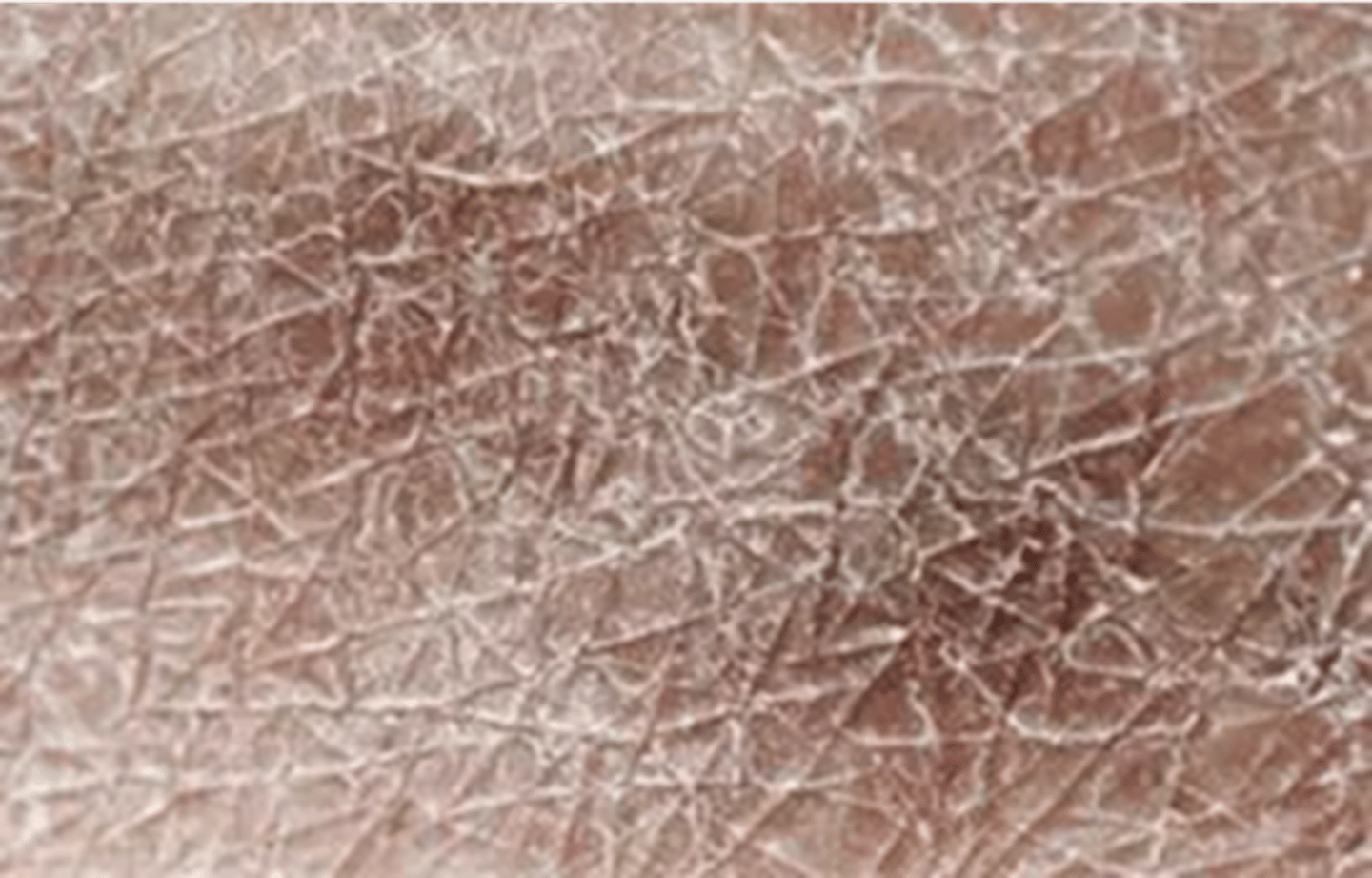

annular or circular
begins in center and spreads to periphery
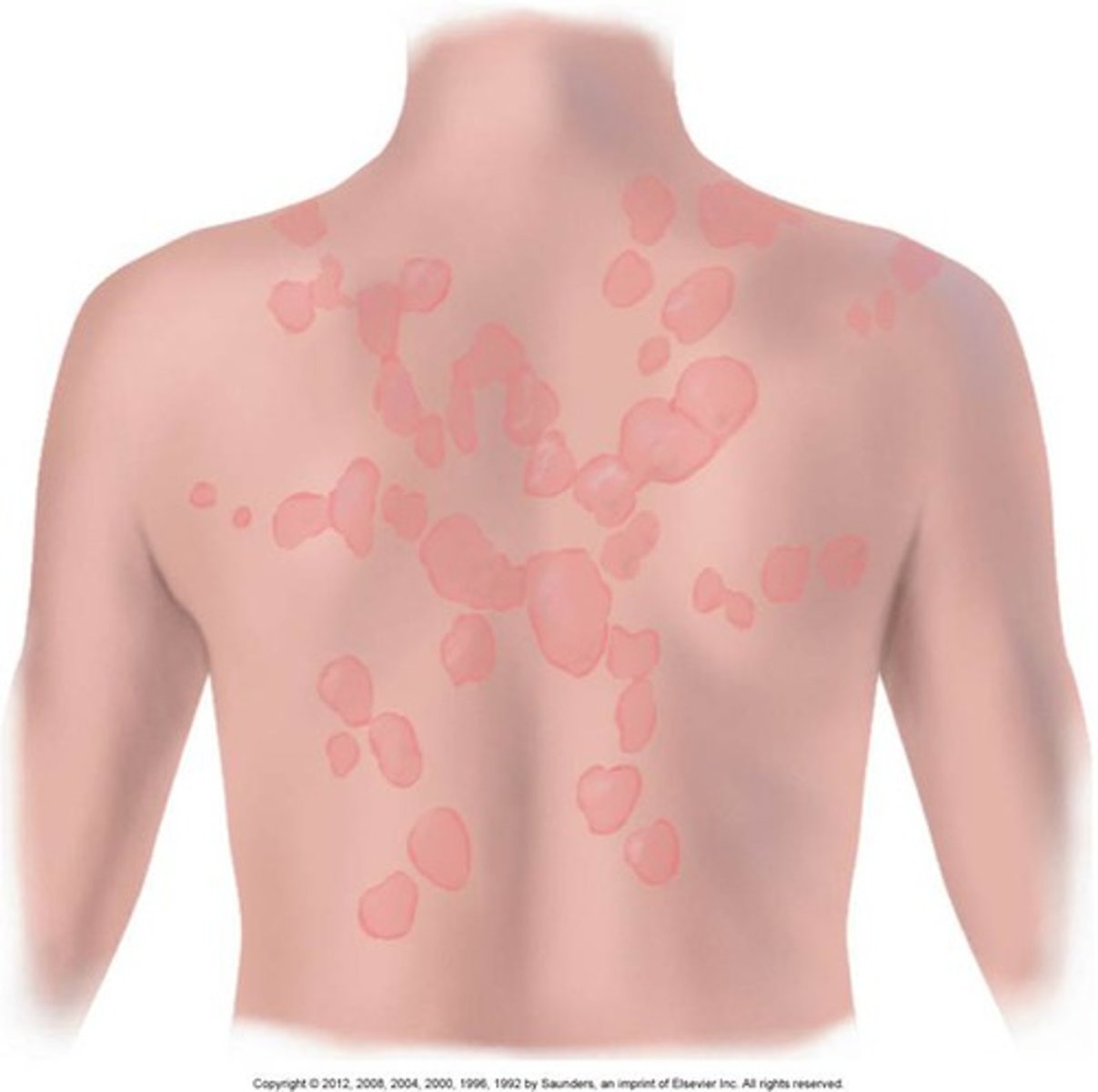
confluent
skin lesions that run together
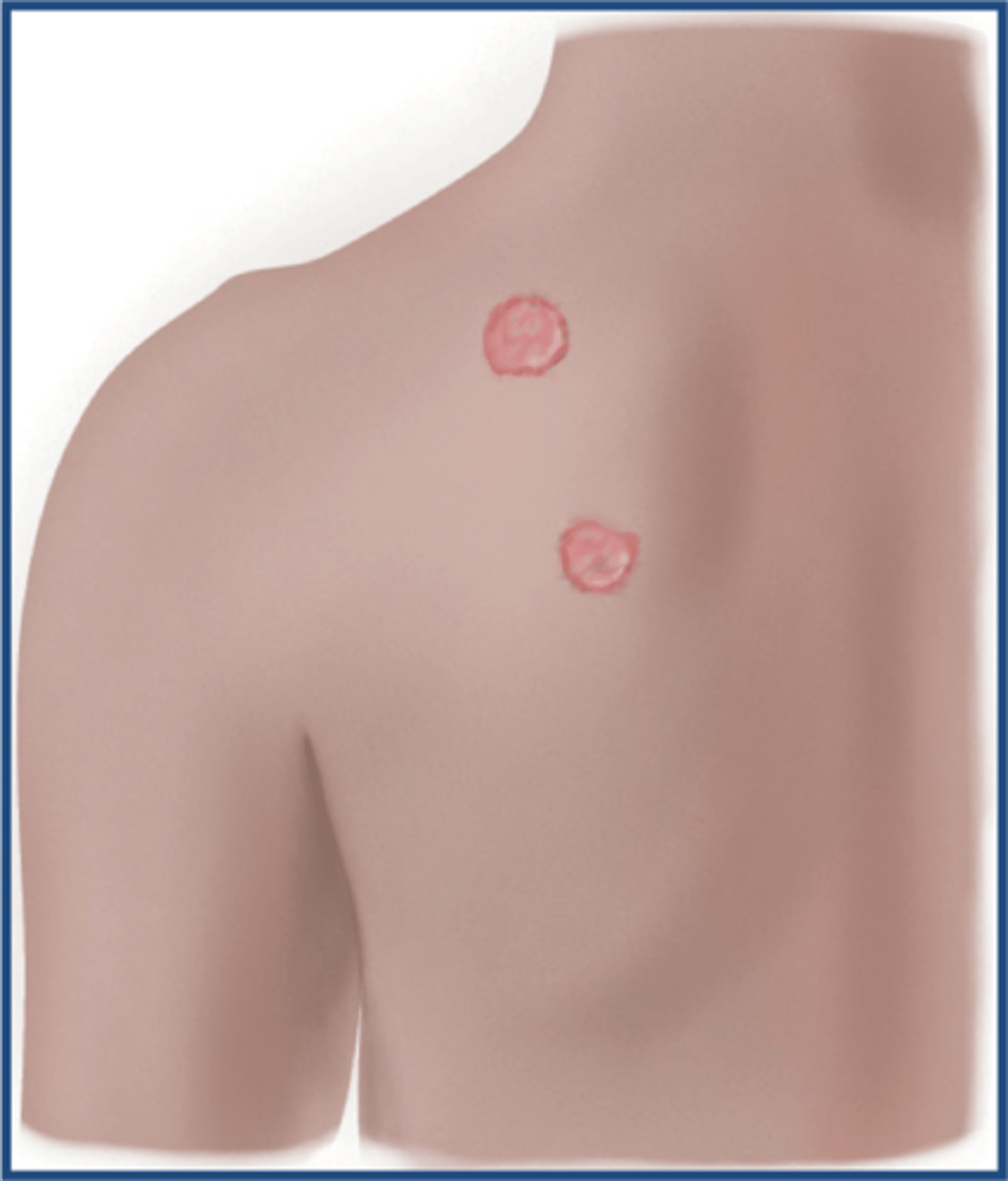
discrete
Distinct, separate
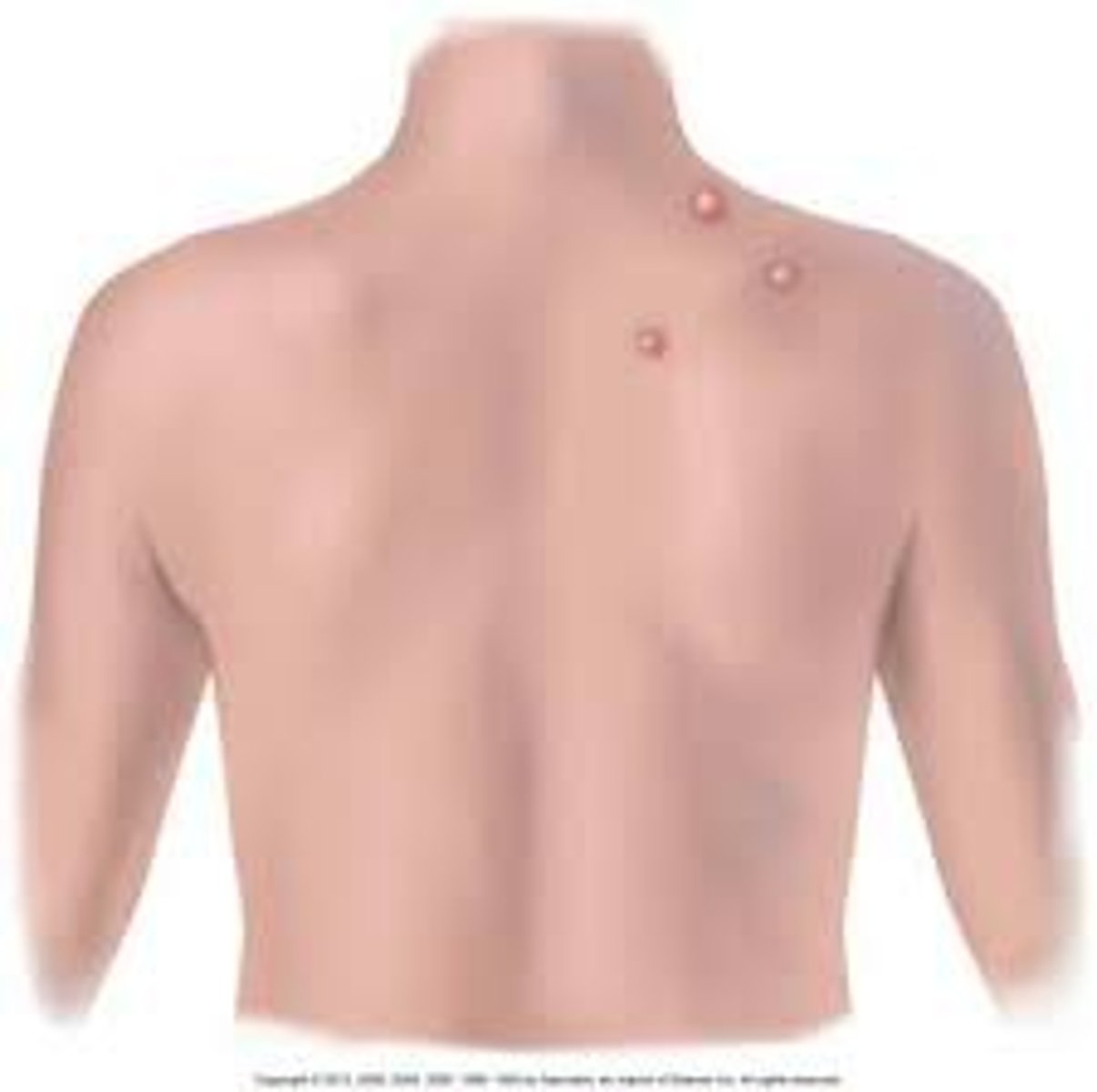
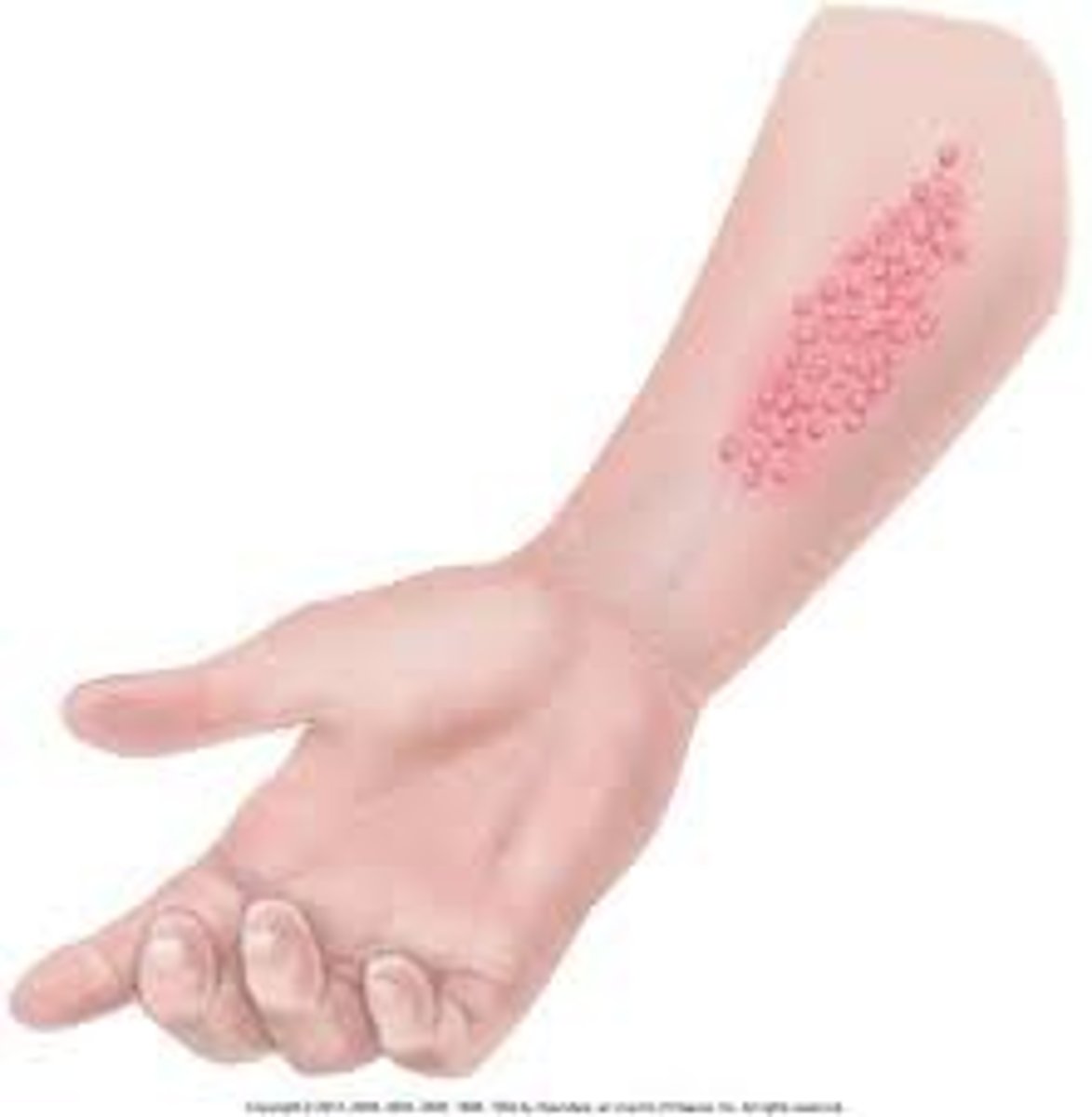
grouped
clusters of lesions
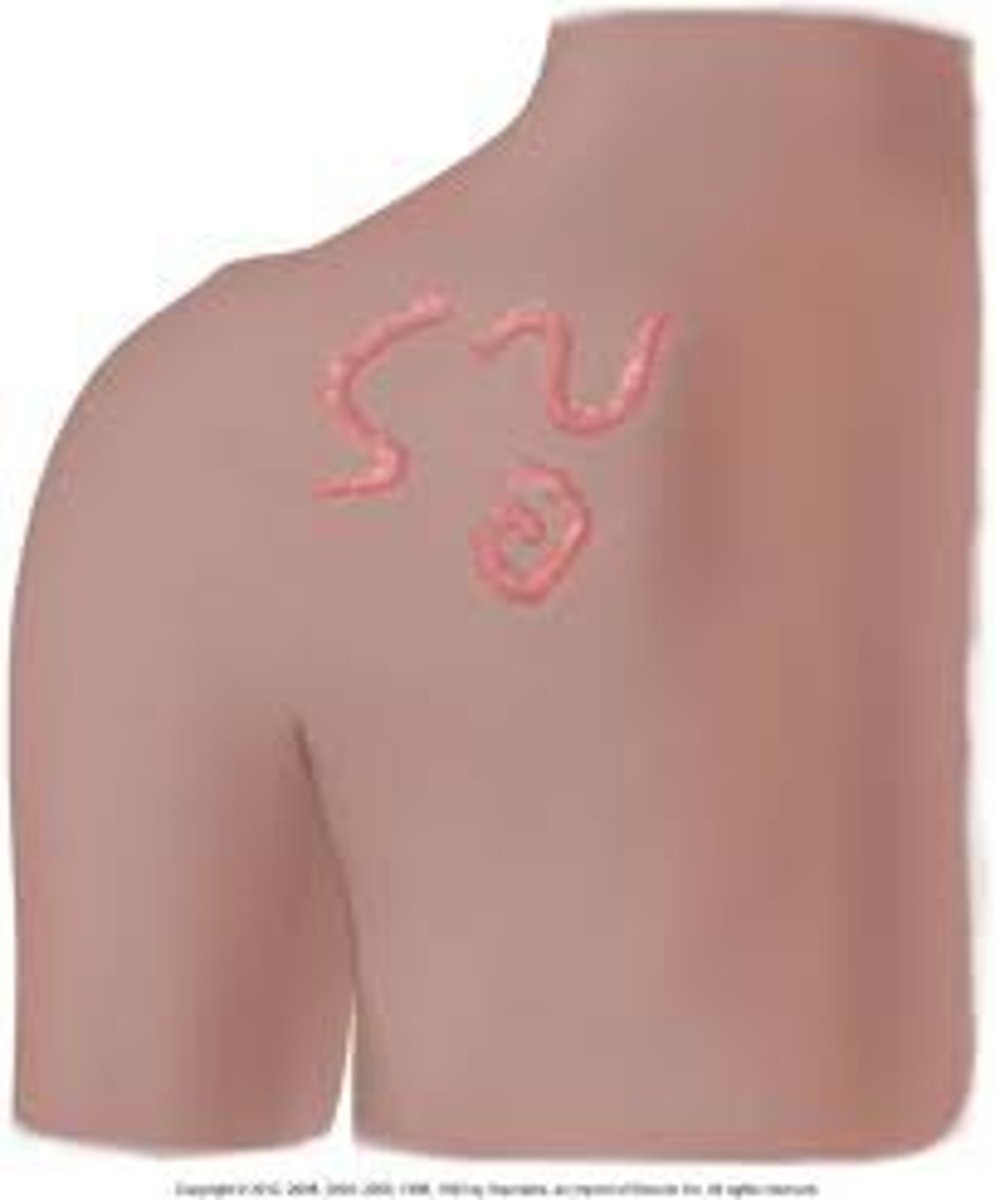
gyrate
twisted, coiled spiral, snakelike
target or iris
resembles iris of eye, concentric rings of color in lesions