8.3 Solid Domestic Waste
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
The Big Picture
Waste is diverse and increasing in volume as we gain more stuff and as the population grows
Domestic waste = household waste
Increase in e-waste
Increase in recycling efforts and composting
Waste needs to be managed
Solid Domestic Waste (SDW) (trash)
Industry & urbanization increased the amount of SDW due to:
Increase in waste creation → more ppl buy more stuff
Decrease in quality of life in cities → due to more trash
Increase in waste led to unsanitary conditions & disease outbreaks (like cholera)
Case Study: London
1846- Nuisance Removal & Disease Prevention Act (initial regulation of waste management)
1874- first incinerators
1875- Public Health Act (waste bins & waste collection by open trucks)
open trucks = problem bc waste can fall out
1920s- closed trucks for collection
1938- modern hydraulic compactors
As waste increased, management of it improved
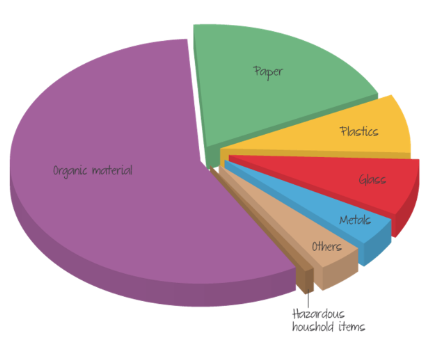
Types of SDW
Organic material (food waste, clothing)
Paper, plastic, metal, glass (medical waste, batteries, e-waste, paint, household chemicals, etc.)
Hazardous waste
Other waste (ceramic, rock, ash, soil)
Linear v.s. Circular Economies
Linear
Make smth → use it → dispose of it → wasteful + damaging
Circular
Goods are designed to reenter the system naturally, be recycled, or used again.
Restorative.
Biological nutrients (compost)
Technical nutrients (recycling e-waste)
Bad SDW
Non-biodegradable waste
Doesn’t break down
Plastic: made from crude oil
Toxic Waste
Batteries & e-waste
E-waste can be recycled to an extent
Landfills
Must be lined to avoid leaching
Smaller is more easily monitored
Waste must be compacted to reduce volume
Needs to be covered to reduce smell, vermin, litter dispersal
Dumps have a lifespan
Dependent on: compressibility of waste, thickness of the layers, frequency of compaction, amount added each day
Advantages
mass disposal (easy)
lower cost
create jobs
Disadvantages
can negatively affect communities
methane creation
takes up space
limited storage/life
Waste to Energy
Landfills create methane when waste breaks down
Methane is often burned off through flares → creates more pollution
Methane can be captured (thru wells) and used to generate electricity (advantage)
Incineration
Burns waste
Creates ash, flue gas (which contains PM + pollutants), and heat
Electricity can be generated from the heat
Helpful when space for landfills is limited
Advantages and disadvantages?
Adv.
less space than landfills
create jobs
can create energy
may last longer than a landfill
Disadv
to build them
create pollution (scrubbers to reduce)
need to dispose of ash
Recycling
The 3 Rs
Reduce
Reuse
Recycle
Design Phase
less use of raw materials → less waste
lower energy consumption
Reuse, repurpose, donate
Transform original product into something new
Recycling is far from perfect
Need infrastructure to process materials
Indefinite recyclability: glass, metals
Limited recyclability: paper/cardboard (5-7 times)
Nor really recyclable: plastic (only 1-2 times)
Composting
Food waste can generate a lot of methane in landfills
Composting keeps the food waste out of landfills
When composting, need to control amounts of C & N, monitor moisture, control pests, ensure heat to speed up breakdown process
Combines the 3 R’s
Aerobic decomposition (uses O2 — does not release CH4)
Dealing with Pollution
All of the strategies discussed are for managing pollution
The strategy used depends on the localities culture, economic status, available technology, and the local politics
Educate (cheap) → Legislate (laws about…) → Remediate (most costly: clean up the mess)
educate abt how to separate trash
ex: rinse ur recyclables, sustainable purchasing, how to compost
The Circular Economy Model
Ellen MacArthur (see page 10) sailed around the world and likened Earth to a boat
Linear economy: take → make → use → dispose
Circular economy: take, make, use → reuse, repair, remake, remove waste, regenerate natural resources
3 Principles
Eliminate waste & pollution
Linear economy is wasteful; resources are finite
Product design allows for resources to re-enter the economy
Circulate products & materials
Technical cycle: maintain/ reuse entire products (they can have a life after you’re done with it)
Biological cycle: food by-products can be composted or anaerobically digested; use waste to replenish soil to grow more food
Regenerate nature
Shift focus from extraction to regeneration
Regenerative agriculture: crop growth to enhance soil health, ranching in harmony with grasslands
Uses of circular economy model (strengths)
Regenerate natural systems
Reduce GHG emissions
Improve local food networks/ support local communities
Extend life of products to reduce waste
(Educate) consumers to change habits
Limitations of circular econ. model
Lack of environmental awareness by consumers & companies
Lack of political will to push education of circular use
Lack of regulations for recycling of products
Not all waste is recyclable/ reusable
Lack of finances to support recycling of goods
Push edu of circular use