Geographic Information Systems Concepts and Applications
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Shapefile
a standalone dataset. A vector data storage format for storing the location, shape, and attributes of geographic features. contains one feature class
Feature Dataset
A collection of feature classes stored together that share the same spatial reference or coordinate system and the features fall within a common geographic area. Ex: sewer lines combined with manhole locations (points and lines combined)
Meridian
measure distance in degrees East or West of the Prime Meridian
Projected/Cartesian Coordinate System
use mathematical equations to transform latitude and longitude to a planar system. Typically known as one horizontal (x) and one vertical (y)
Geographic Coordinate System
a spherical or geodetic coordinate system for measuring and communicating positions directly on the earth as latitude and longitude
Mode
The most frequently occurring number
Graphic/Linear scale
a bar marked off like a ruler with labels outlining the distances the segments represent
Fractional/ratio scale
typically represented as a ratio (1/50,000 or 1/50:000). The first number indicates one unit (inch, cm) on the map. The second number indicates the same unit actually on Earth.
Written/ verbal scale
uses words to describe the relationship between the map and landscape it depicts.
Alphanumeric Reference
refers to using numbers and letters in a grid system. Letter comes first then the number (Bingo or Battleship)
Horizontal datum
used for describing a point on the Earth's surface in latitude and/or longitude or another coordinate system
Degrees, Minutes Seconds
The unit of measure for describing latitude and longitude. A degree is 1/360th of a circle. A degree is further divided into 60 minutes and a minute is divided into 60 seconds.
Tropic of Capricorn
the parallel line currently located at 23° 26' 144.0"
International Date Line
Imaginary line extending between the North Pole and the South Pole and arbitrarily demarcating each calendar day from the next. Most of its length is located along the 180th meridian.
Attributes
Nonspatial information about a geographic feature in GIS usually stored in a table and linked to a feature by a unique identifier
Basemap
a map depicting background reference information, such as landforms, roads, landmarks, political boundaries, or satellite imagery
Coordinate System
a reference framework consisting of set points, lines, or surfaces, and a set of rules used to define the positions of points in space in either two or three dimensions
Open Data
Public data for everyone to use
Vector Data
A coordinate-based data model that represents points, lines, and polygons. Associate attribute data with each vector feature. Ex) city locations, state boundaries, and waterways
Raster
A digital surface or defined as a spatial data model that defines spaces as an array of equally sized cells arranged in rows and columns and composed of singular and multiple bands. Associates attribute data with grid cells. Ex) imagery, elevations, height data, pollution, temperature
Symbology
single symbol: one symbol for all features in the layer
Symbology
unique values: different symbols represent various attributes
Symbology
graduated colors: "used for quantitative data" different colors represent different value ranges
Symbology
graduated symbols: "used for quantitative data" symbols increase in size with increased values
Geodatabase
a "storage container" a database or file structure used primarily to store, query, and manipulate spatial data. contain multiple feature classes.
Feature Class
a collection of geographic features that have the same geometry type (point, line, polygon), the same attributes and the same spatial reference.
Longitude
a system of imaginary North and South lines called Meridians, gives east and western directions
Prime Meridian
an arbitrary meridian (line of longitude) in a geographic coordinate system which is defined to be 0°C, it divides the Eastern & Western hemispheres
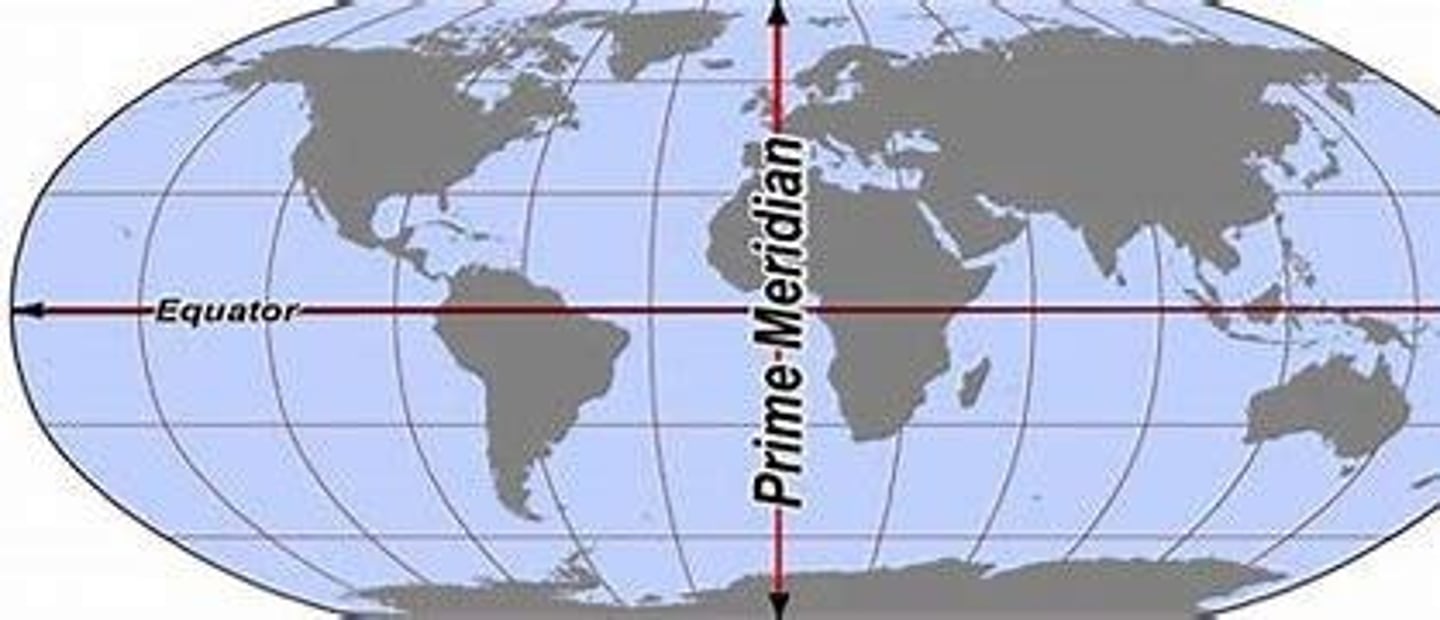
Equator
An imaginary circle around the Earth that is everywhere equidistant from the geographic poles and lines in a plane perpendicular to Earth's axis. divides earth into north and south
Latitude
is a measurement on a globe or map of location North and South of the equator.
Mean
a quantity that has a value intermediate between those of the extreme members of some set. This is found by adding the numbers and dividing by the total numbers listed.
Median
The middle value listed in and order from smallest to largest
Range
The difference between the greatest and smallest value.
Task
a predefined series of steps that walk you through a GIS workflow
Model
workflow diagrams that allow you to string multiple geoprocessing tools together and run them automatically with the click of a button
Python
a free cross-platform, open-source programming language that is used to script (GIS context) geoprocessing workflows and build custom geoprocessing tools
Map Scale
represents the ratio of map units to real world units
Crowdsourcing
a group of users can work together to gather and record information
Geodetic datum
a reference from which spatial measurements are made. AKA a reference point on a map
Vertical datum
measure of elevations or depths from a reference point. Example: sea level
Decimal Degrees
Degrees, minutes, seconds divided into decimal format
Parallel
a named line connecting all points along the same line of latitude
Arctic Circle
parallel or line of latitude around Earth at approximately 66° 30' N
Tropic of Cancer
The most northerly latitude where the sun may be seen directly overhead at noon located at 23.5° N of Equator.
Antarctic Circle
parallel or line of latitude around Earth at 66° 30' S