Dogs- Everything
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
149 Terms
The top of the foot is the ____ aspect
Dorsal
The bottom of the foot (with pada) is the ______ aspect
Palmar/plantar
The head is _____ to the tail
Cranial
The tail is ____ to the head
Caudal
The nose is ____ to the ear
Rostral
The ear is ____ to the nose
Caudal
The spine is _____to the flank
Medial
The flank is ____ to the spine
Lateral
The elbow is ______ to the carpus
Proximal
The carpus is _____ to the elbow
Distal
The spine is ______ to the sternum
Dorsal
The sternum is ____ to the spine
Ventral
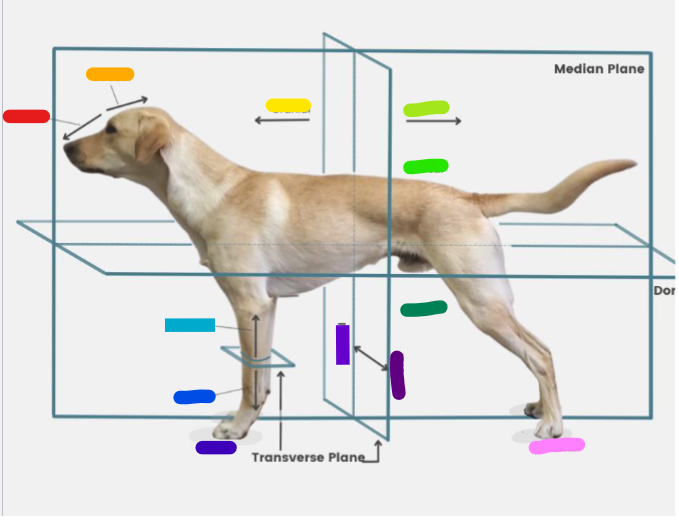
What is the red?
Rostral
What is the orange?
Caudal
What is the yellow?
Cranial
What is the light green?
Caudal
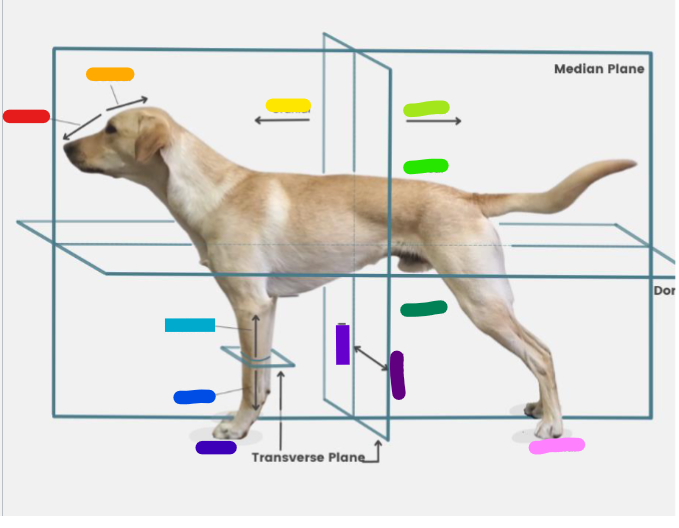
What is the green?
Dorsal
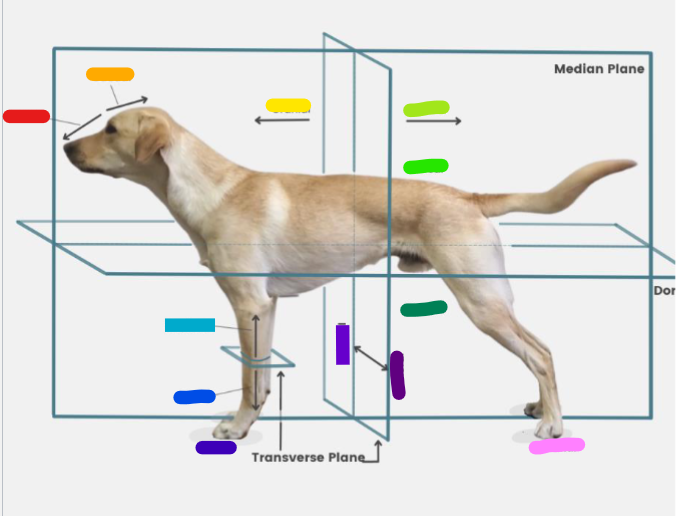
What is the dark green?
Ventral
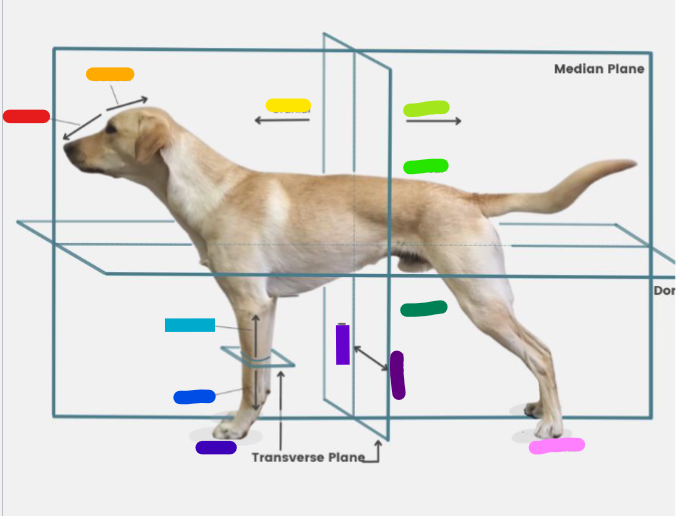
What is the light blue?
Proximal
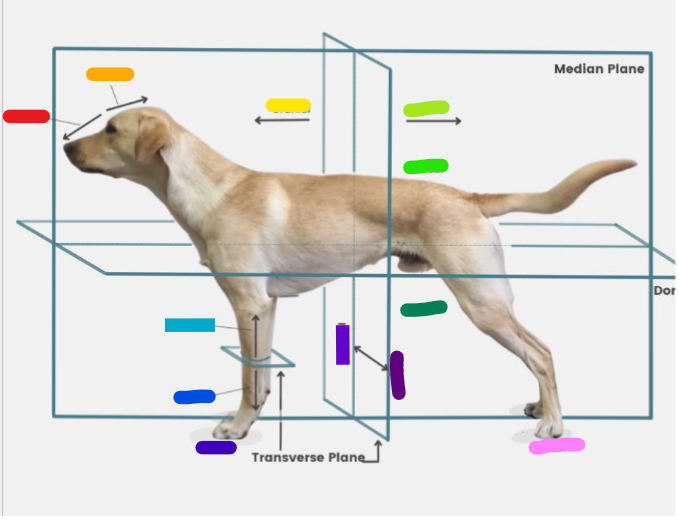
What is the blue?
Distal
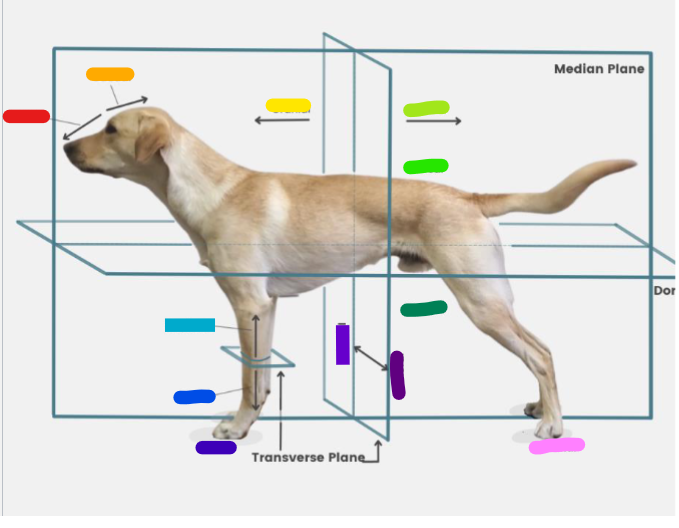
What is the dark blue?
Palmar
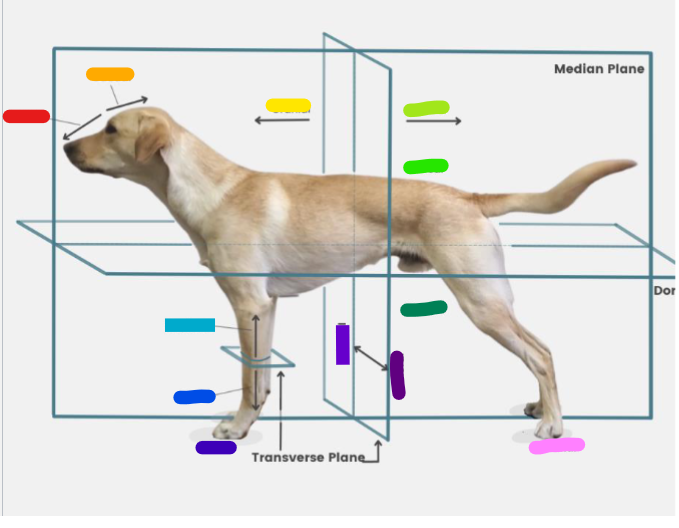
What is the purple?
Medial
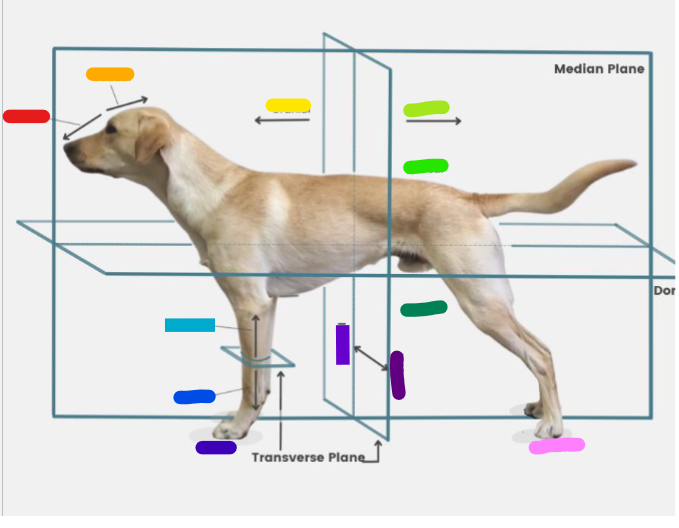
What is the dark purple?
Lateral
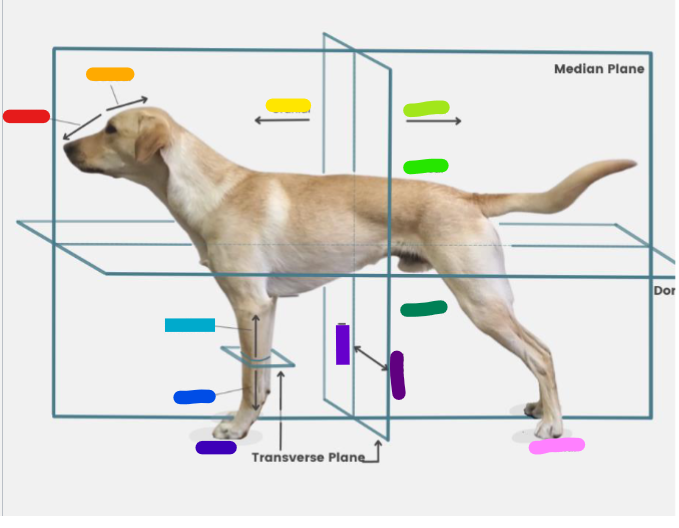
What is the pink?
Plantar
Look for this on the packaging of the dog food you are feeding to ensure it is meeting the guidelines
Associate of American Feed Control Officials (AAFCO)
Regulates the commercial pet food industry and ensures that foods are uniformly labeled and marketed
Associate of American Feed Control Officials (AAFCO)
Product has been produced to meet the guidelines set by the AAFCO but was not actually fed to dogs
Formulated foods
Product was produced to meet the guidelines and then fed to dogs to ensure it meets criteria related to growth, maintenance and reproduction of the dogs
Tested foods
What is the optimal body shape for a dog?
Hourglass and feel ribs but not see the ribs
When do pregnant dogs need more food?
4th week
What is it called when a dog gives birth?
Whelping
How much more food do lactating dogs need?
2-3 times more
When can puppies be given normal food?
3-4 weeks (puppy food with water or puppy milk replacer)
When are puppies usually weaned by?
6-8 weeks
Under California law, how long must puppies stay with their mother?
8 weeks
When do puppies grow the most?
6 months
What happens if you feed puppies too much and they grow rapidly?
Bone disorders
What happens to dogs that are on a grain free diet?
Dilated cardiomyopathy (2-4 years after a grain free diet)
How long does the average pregnancy last?
63 days
How long does a dog have to be pregnant for the dogs to survive outside the uterus?
59 days
Dogs go through the same cycle even if not pregnant
Pseudopregnancy
Temperature of a pregnant dog with drop how long before active labor?
24hrs
If going more than ___ minutes, should see a veterinarian
30 minutes
If going more than ____ between puppies, should see a veterinarian
3-4 hours
What is the first milk called?
Colostrum
Gives immunity to the puppies that is absorbed through the stomach wall
Colostrum
Calcium deficiency
Eclampsia
This condition is usually seen in smaller dogs with large litters
Eclampsia
What would you see eclampsia?
2-3 weeks after whelping (during the first month)
Restlessness, panting, whining, progresses to trouble walking on rear legs, muscle tremors and generalized stiffening
Eclampsia
Can be fatal to mom and puppies should stop nursing
Eclampsia
Where are mats most common on dogs?
Behind ears and under legs
Skin disease caused by fungus
Ringworm
Causes a round, scaly or encrusted lesion on the skin (If lesion shrinks then fungus is not present)
Ringworm
Topical antifungal drugs are used to treat and sometimes oral medication
Ringworm
Shed in the urine of infected dogs
Leptospirosis
Vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain which can be serious; symptoms 12-72 hours after infection and illness lasts 4-7 days
Salmonellosis
Carrier animals can appear healthy but carry disease causing organisms that can affect other animals and humans
Salmonellosis
Pet turtle or other reptiles are a common source of infection
Salmonellosis
Dogs and cats generally have a low likelihood of this infection (except in some areas near Mexican border and along the Atlantic coast)
Rabies
Only post-mortem tests are available
Rabies
Caused by the inhalation of an airborne virus and usually in puppies 3-6 months of age or older dogs that are not vaccinated
Canine Distemper
Starts with GI signs (diarrhea, vomiting) and/or respiratory signs; thickened keratin on nose and toe pads (can progress to pneumonia)
Canine distemper
Weeks to months later, start to have tremors to seizures (chewing gum fits)
Canine Distemper
Treatment is supportive care and trying to keep dog alive until it can recover from the virus (may not be able to control seizures and can have permanent neurological damage)
Canine Distemper
Highly contagious- spreads from urine, feces, saliva of infected dogs (or foxes, coyotes, wolves, skunks, or bears)
Infectious Canine Hepatitis
Targets liver, kidney, spleen, and lungs (Corneas may become clouded and will usually resolve after recovered)
Infectious Canine Hepatitis
Supportive care, usually recover or pass away within 36 hours of the initial signs
Infectious Canine Hepatitis
Can have mild signs (slight fever) to severe signs and death
Infectious Canine Hepatitis
Infection from ingested of material from infected dog’s feces (Can live in the environment for 6-8 months)
Canine Parvo Virus
Cardiac disease in neonatal or nursing puppies if mother is not vaccinated (usually pass away quickly)
Canine Parvo Virus
Once weaned, have the intestinal form- attacked rapidly dividing cells in the intestinal tract (Vomiting, diarrhea, not eating)
Canine Parvo Virus
Treatment is only supportive care to keep alive while the virus runs its course (3-10 days)
Canine Parvo Virus
Can be caused by many different viruses or bacteria (Bordetella, mycoplasma, parainfluenza, influenza, adenovirus, herpes virus)
Infectious Tracheobronchitis (kennel cough)
Hacking cough to gagging cough with mucous produced
Infectious Tracheobronchitis (Kennel cough)
Similar to parvovirus but they do not get as sick
Corona Virus
Highly contagious from contaminated feces (vomiting and diarrhea)
Corona Virus
Causes females to abort their pregnancy
Canine Brucellosis
Males may have swollen testicles/scrotum but also may cause atrophy
Canine Brucellosis
May not have any clinical signs
Canine Brucellosis
Is sexually transmitted and can be treated with an antibiotic to improve clinical signs but they will always remain infected (will spread disease or not be able to have a normal pregnancy)
Canine Brucellosis
Adult dogs show no signs but can infect puppies through oral nasal, feces, urine, saliva, or vaginal discharges (puppies infected before birth or within 18 days
Canine Herpes Virus
Can have a change in color of feces, difficulty breathing, abdominal pain, stop nursing and/or constant crying
Canine Herpes Virus
Usually pass quickly and treatment is not effective (Sometimes referred to as fading puppy syndrome)
Canine Herpes Virus
Systemic fungal infection from the inhalation of spores (from bat or bird droppings in soil)
Blastomycosis and Histoplasmosis
Clinical signs- coughing, rapid breathing, decreased appetite, eye problems, lameness, and skin problems (Lung lesions and skin lesions most common)
Blastomycosis
Treatment is with anti-fungal medication and usually needs a long course of treatment (6 months or longer); medications can potentially be toxic and/or make sick people
Blastomycosis and Histoplasmosis
Lung infection common with coughing, respiratory difficulty, fever and depression
Histoplasmosis
Can infect the intestinal tract and cause diarrhea and weight loss as well
Histoplasmosis
Prefers hots, dry alkaline soil; from inhalation of spores
Coccidiomycosis
Lack of appetite and weight loss then lameness, bone pain, spinal pain and coughing (usually infections the lungs then moves to the bones)
Coccidioidomycosis
Can also have fluid in the abdomen causing it to become distended and pendulous
Heart Disease
Degenerative heart valves, bacterial infection (less common), cancer, heartworms
Acquired heart disease
Cloudy white opacity of the lens
Cataracts
Usually causes blindness and can be removed surgically
Cataracts
Increased pressure within the eye
Glaucoma
From problem with production, transport or absorption of aqueous humor from the eye
Glaucoma
Pressure will cause irreversible damage to retina and optic nerve and blindness
Glaucoma
Can improve with medical management (temporarily) but will need surgery
Glaucoma
Genetic disease causing gradual retinal degeneration and loss of night vision and leads to blindness with no treatment
Progressive Retinal Atrophy (PRA)