Sustainable Solvents
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Solvent
Substance that dissolves or disperses other substances.
Largest Uses of Solvents
46% in paints, 9% in pharmaceuticals.
Role of Solvents
Facilitates mixing and increases reaction rates.
Heat Dissipation
Solvents aid in maintaining temperature stability.
Higher Yield
Solutions transfer more efficiently than solids.
Solvent Production
Most solvents derived from fossil fuels.
Energy Intensity
More synthesis steps increase energy consumption.
Flash Points
Low flash points indicate high flammability risk.
Ethers
Form explosive hydroperoxides in oxygen presence.
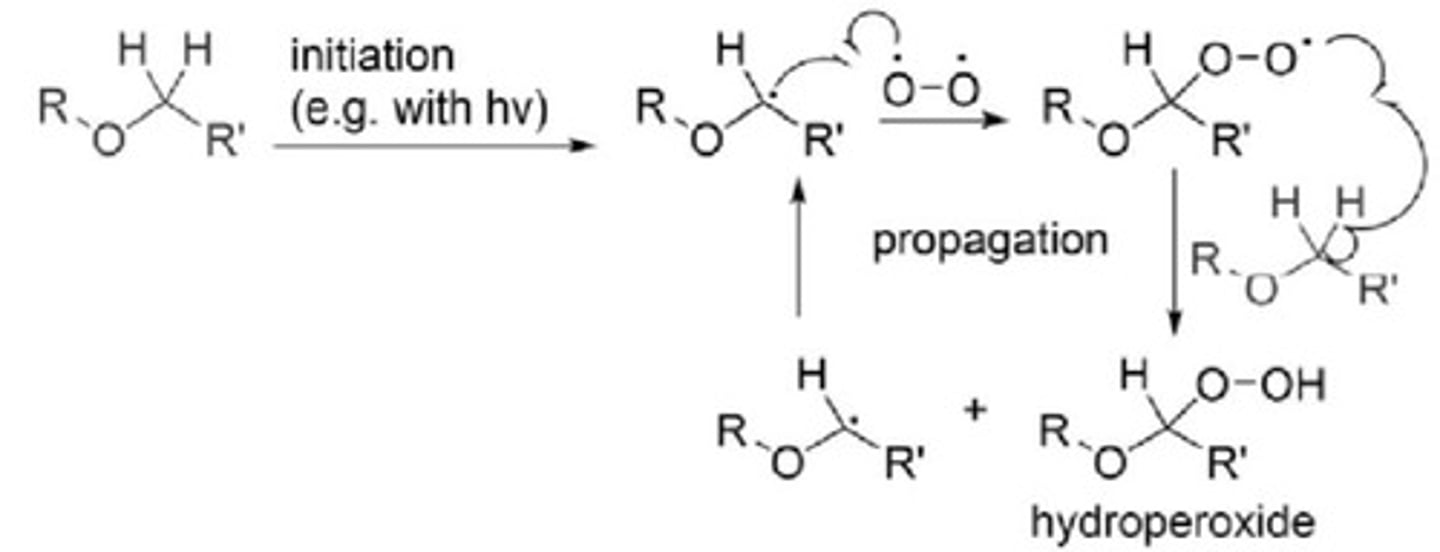
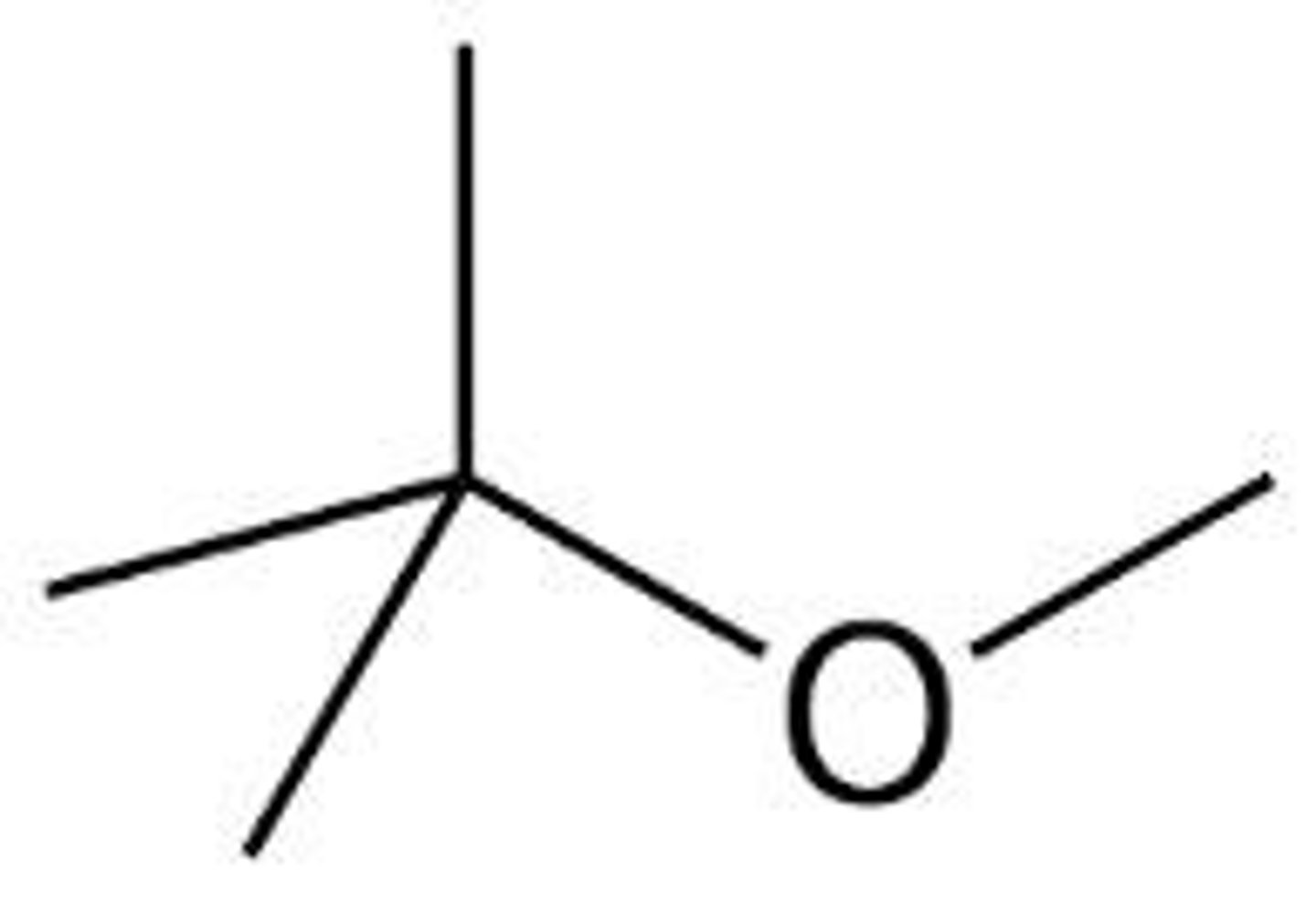
Methyl Tert-Butyl Ether (MTBE)
Alternative to diethyl ether, contaminates groundwater.
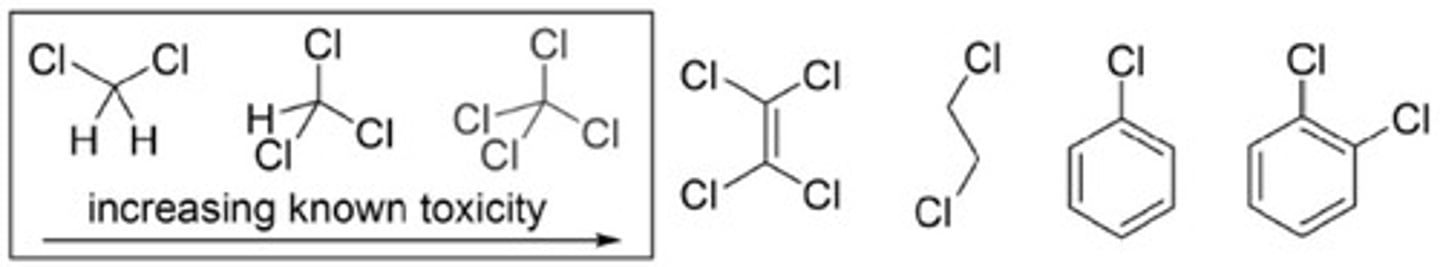
Chlorinated Solvents
Non-flammable but toxic with health risks.
Choosing a Solvent
Consider availability, cost, and previous usage.
Transition State Stabilization
Ability to stabilize reaction intermediates.
Aprotic Solvents
Solvents without reactive protons.
Boiling Point
Critical for solvent volatility and application.
Sustainability
Environmental impact of solvent production and use.
Solvent Guides
Recommendations against using chlorinated solvents.
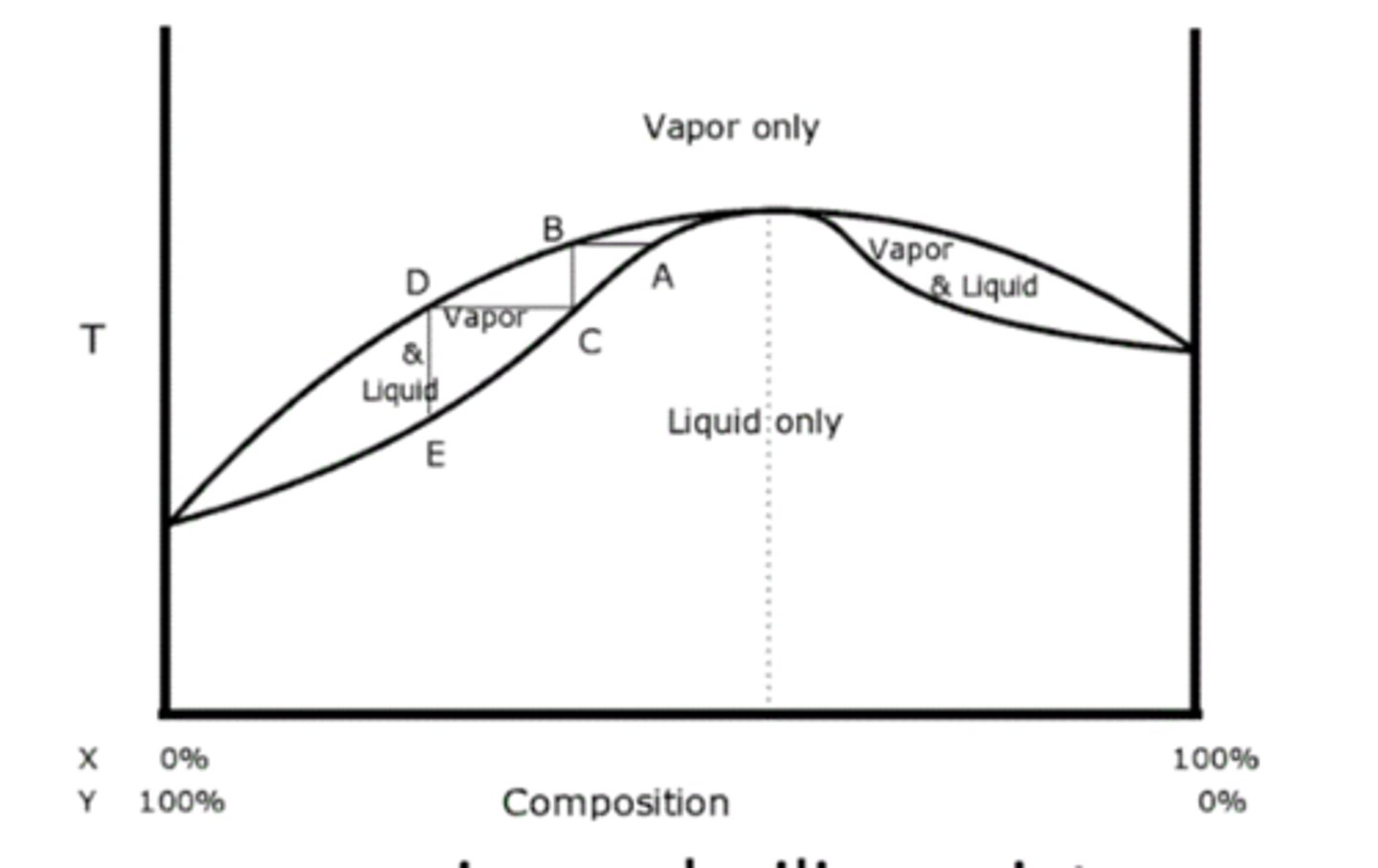
Azeotropes
Mixture with constant composition during boiling.
Positive Azeotropes
Lower boiling point than individual components.
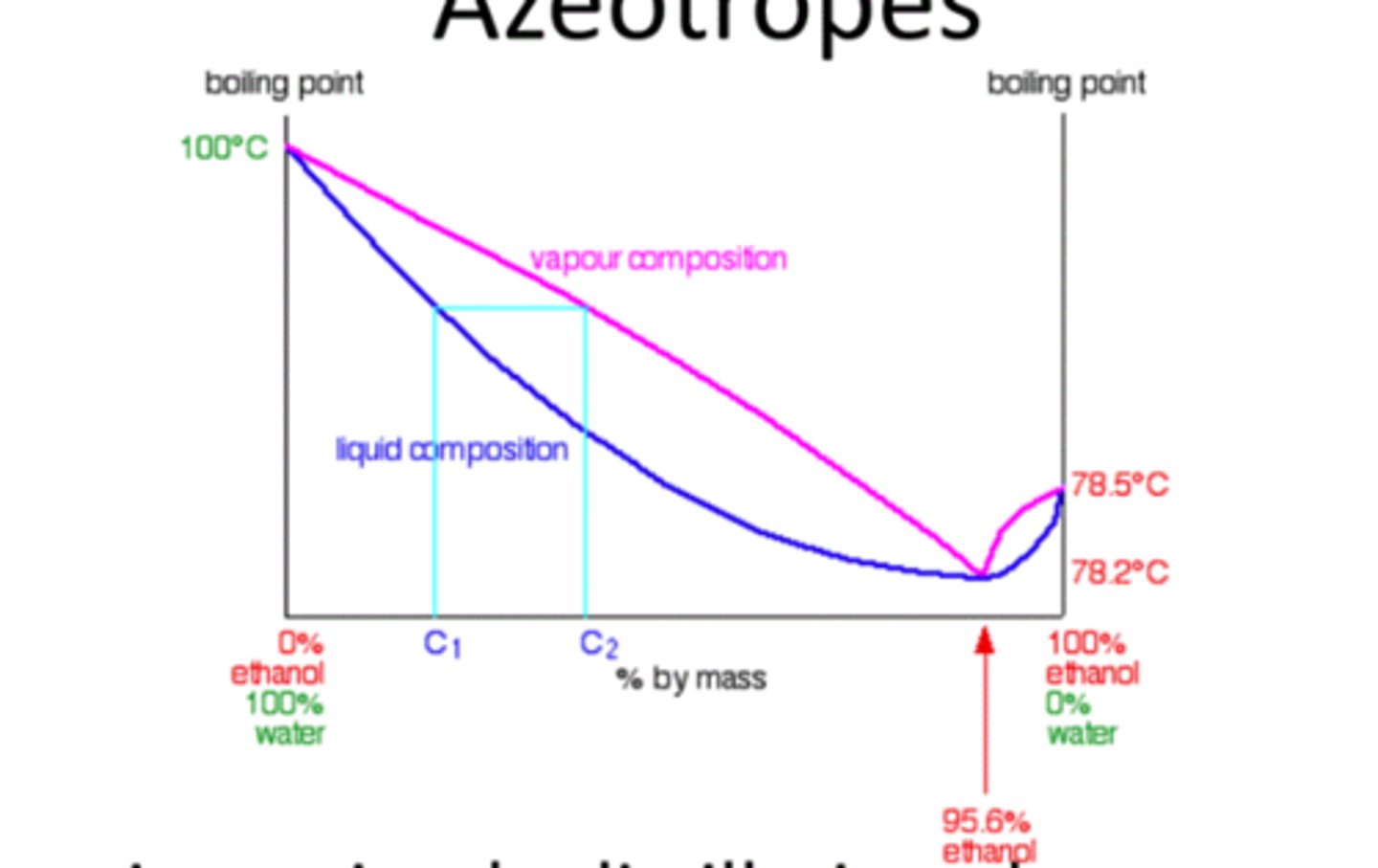
Negative Azeotropes
Higher boiling point than individual components.
Supercritical Solvents
Solvents above critical temperature and pressure which acts like a gas and a liquid
Water as Solvent
Good for salts; poor for non-polar compounds.
CO2 Solvent Limitations
Poor solvent; requires expensive pressurization equipment.
Advantages of Supercritical Solvents
No surface tension, low toxicity, tunable density.
Disadvantages of Supercritical Solvents
Requires high pressure; industry reluctance to change.
Supercritical CO2
Formed at high pressure; non-toxic and sustainable.
Benefits of Supercritical CO2
Cheap, abundant, recyclable, high diffusion rate.
CO2 Evaporation
Leaves no solvent residues in final product.
Stereoselectivity Control
Varying fluid density affects reaction selectivity.
ScCO2 vs Hexane
ScCO2 replaces toxic hexane in extraction.
Co-solvent for ScCO2
Adding 1-10% acetone/methanol increases polarity.
Supercritical Fractionation
Temperature and pressure changes separate different fractions.
Advantages of ScCO2 Extraction
Less structural damage than traditional extraction methods.
Industrial Uses of ScCO2
Decaffeination, extraction of hops, and nutraceuticals.
Hydrogenation with ScCO2
ScCO2 dissolves H2 completely; selective reactions.
Impregnation of Polymers
Rapid penetration of pores using supercritical fluids.
Dry Cleaning with ScCO2
Safer alternative to cancer-causing perc solvent.
Supercritical Water
Requires extreme conditions; highly corrosive.
Properties of Supercritical Water
Non-toxic, miscible with toluene above 308°C.
Water Autodissociation
Causes strong acidity and alkalinity in supercritical water.
Subcritical Water
Extracts compounds from herbs using 20x less energy than steam.
Chemical Rearrangements
Transformations of molecular structures in chemistry.
Oxidation with scH2O
Destructive breakdown of contaminants into simple molecules.
Benefits of scH2O oxidation
Achieves 99.9999% destruction of contaminants.
Waste treatment performed at the location of generation.
Competitive cost
Public acceptance - General public is comfortable with water-based treatments.
Disadvantages of a Solvent Free Reaction
As products form, the polarity of the solution may change, which may cause the reagent to dissolve more and more quickly --> this may lead to a runaway reaction
Mechanochemistry
Reactions achieved by grinding solid materials together.
Ball Mills
Grinding method adaptable for various batch processes.
Disadvantages of a Batch Process
Requires cleaning before reuse (in ball milling)
Alternative to ball mills
Twin Screw Extruders - Flow alternative for continuous solid reactions.
Advantages of Polar Aprotic Solvents
Dissolve polar and non-polar compounds effectively (and some salts)
Are miscible with organic and aqueous compounds
Stabilise polar transition states (so can have an increasing effect on the rate of reaction)
DMSO
Polar aprotic solvent
Enhances pharmaceutical absorption through skin.
NMP
Polar aprotic solvent
Used as a paint stripper solvent.
Disadvantages of polar aprotic solvents
-Generally quite toxic
-All PA solvents contain N or S so if theyre incinerated they produce SOx and NOx
-The synthesis of DMSO produces lots of negative byproducts (CO2, H2S, NOx)
Green Polar Aprotic Solvents
-DMSO and DMF are environmentally friendly examples.
-Carbonates (cyclic and acyclic) are being looked at as new alternatives (eg. propylene carbonate)
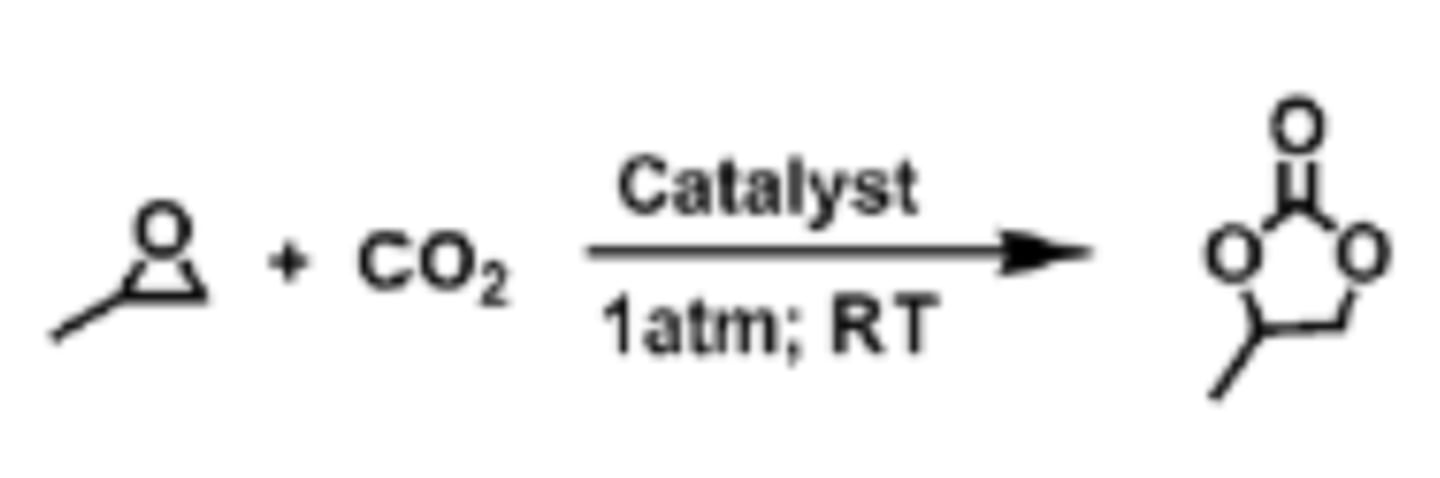
Ethylene Carbonate
Green PA solvent, but solid at room temperature which can be off-putting to companies
Ethylene Oxide
-Used to make ethylene carbonate
-Carbon negative because the reaction takes in CO2
-Croda can manufacture ethylene oxide from bioethanol
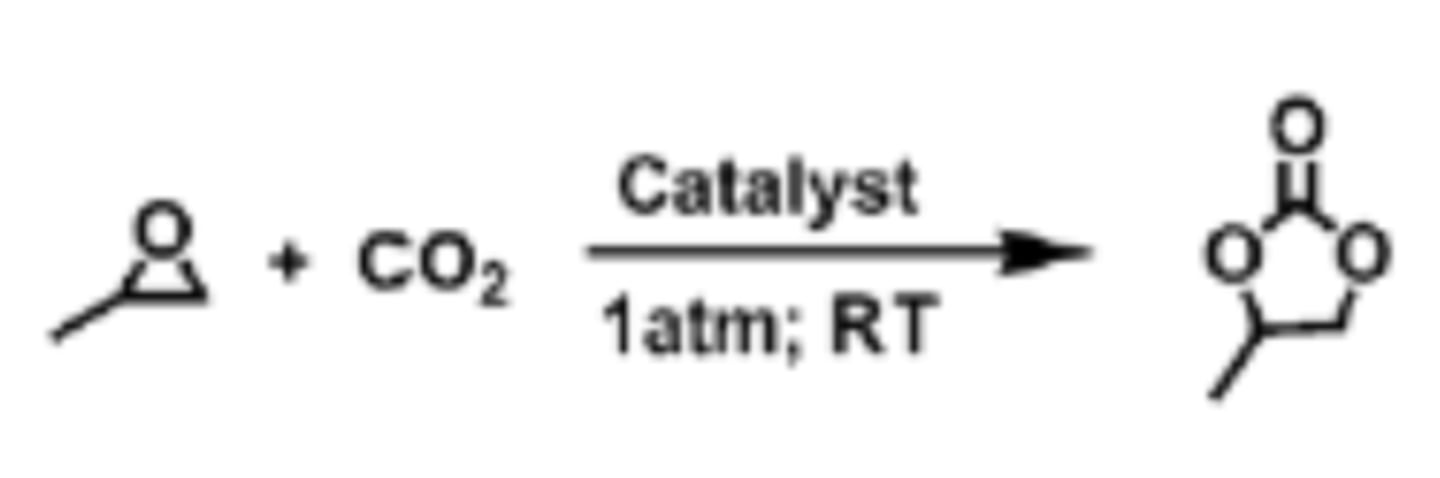
EtOCOOEt
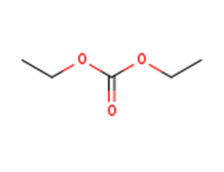
Green PA solvent
Used as a solvent alternative to DCM or toluene.
Non-Reaction Solvent Uses of Carbonates
-Used in lithium ion batteries
-Propylene carbonate used in nail polish remover
-Dimethyl carbonate used as anti-knocking agent in petrol
Ionic Liquids
-Composed entirely of ions, liquid below 100°C.
-Changing the ions changes the qualities (eg. melting point, conductivity, viscosity, solvent miscibility)
-Normally a large organic cation and a weakly coordinating anion
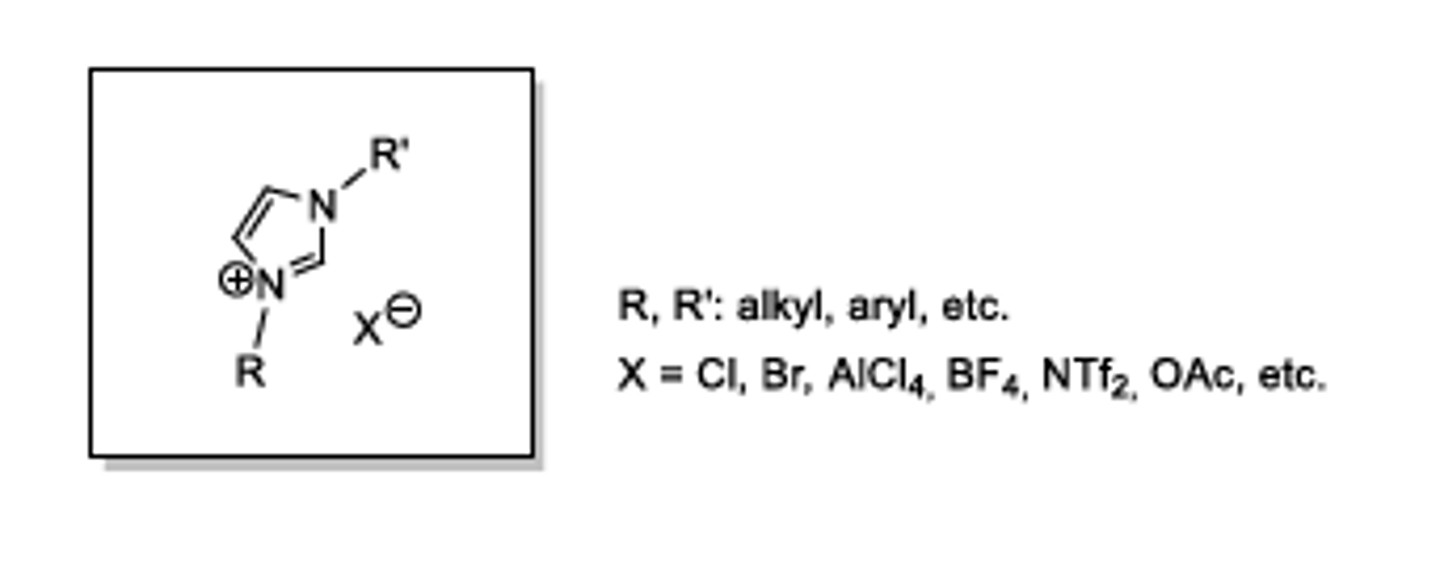
Properties of Ionic Liquids
-Dissolve a wide range of solutes
-Electrically conducting
-Good chemical and thermal stability
-Tunable qualitites by changing the ions
What does changing the cation alter in an ionic liquid?
Viscosity, conductivity and density
What does changing the anion alter in an ionic liquid?
Miscibility
Advantages of Ionic Liquids in Catalysis
-Low vapour pressure (less evaporation = safer)
-Dissolve a wide range of solutes
-Ionic liquids can immobilise a catalyst to prevent leaching so that it can be reused
Disadvantages of Ionic Liquids in Catalysis
-High viscosity may cause a slow rate of reaction (due to slow diffusion)
-Toxicity is unknown (longer chains persist longer in the body so generally more toxic)
-Can't be distilled (due to low vapour pressure)
-Expensive
What is the advantage of diethylamine and CO2 as an ionic liquid
Can be distilled
Deep Eutectic Solvents (DES)
Formed from hydrogen bond donor and acceptor, produces an extended hydrogen bonding network
Eutectic Point
Lowest melting point of a mixture of solids.
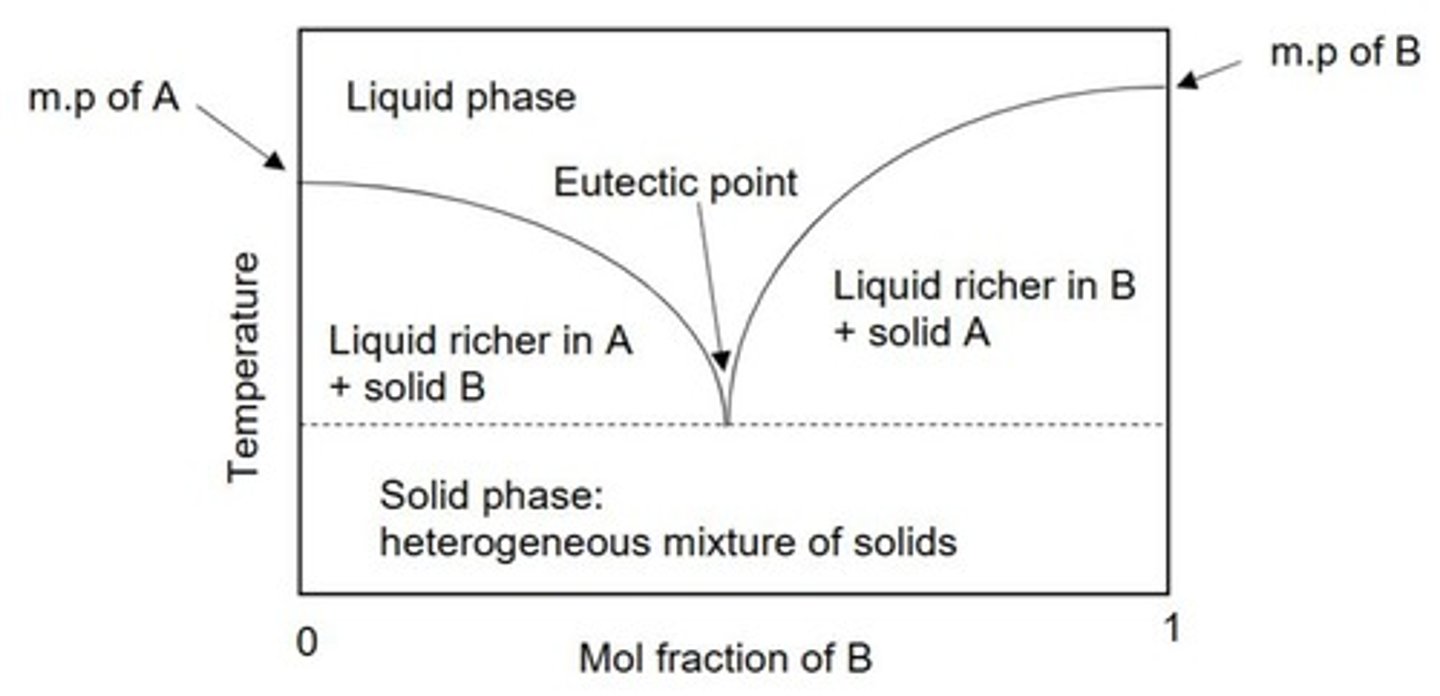
Advantages of Deep Eutectic Solvents
-Starting materials are cheap, non-toxic and abundant
-DES deactivates water (strong H-bonding environment) so water sensitive reactions can be done on the benchtop
Gas Expanded Liquids
Solvents with dissolved gas that alters properties.
Switchable Solvent
Solvent whose properties change when gas is dissolved in it
CO2 dissolved in an alcohol
Reversible forms carbonic acid - acid catalyst is generated in situ
CO2 dissolved in Water
-Produces hydrogen and acid catalyst for reduction reactions
-Reduces the production of salts in these reactions
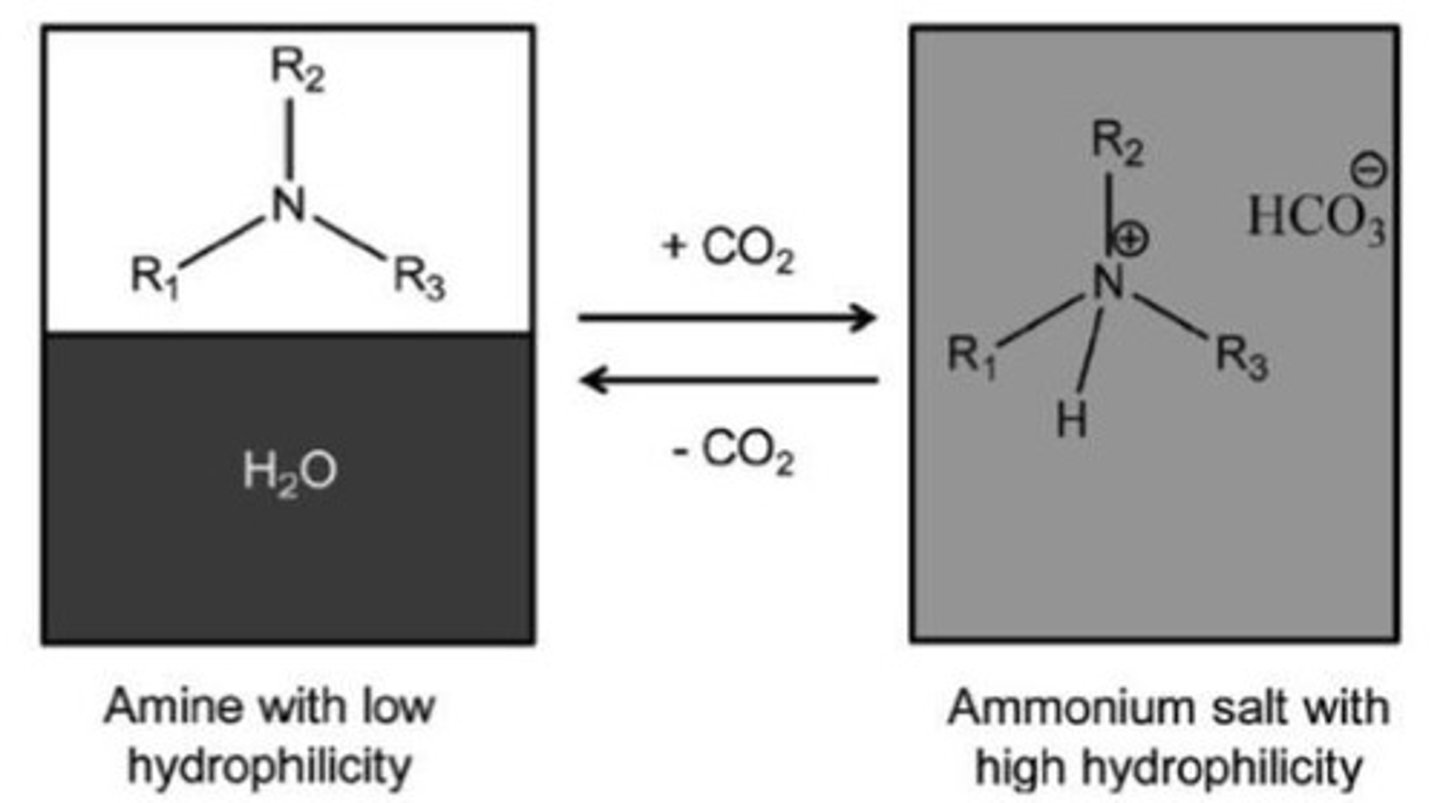
CO2 dissolved in Tertiary Amines
-Protonates the amine and produces a carbamate anion
-Aqueous phase is lost as H2O is used to make the salt, hence 2 phases to 1 phase
Class 1 Gas Expanded Liquid
Low CO2 solubility (little change in properties)
Class 2 Gas Expanded Liquid
High CO2 solubility (large expansion and very different properties)
Class 3 Gas Expanded Liquid
Medium CO2 solubility (large change in viscosity but polarity is fairly unchanged)
Advantages of Gas Expanded Liquids
-Changing the pressure changes the properties
-CO2 is easily removed by reducing the pressure
-CO2 has a fire suppressive effect
-Expansion means less organic solvent is required
-Adding CO2 reduces the polarity so organic solvents can be separated from water, which is greener than adding a solid salt (traditional method)
Disadvantages of Gas Expanded Liquids
-Require pressurisation (but only to 10s of bar)
Switchable Polarity Solvents
Solvents that change polarity with CO2.
Polystyrene With a Switchable Polarity Solvent
-Dissolves in cyclohexyldimethylamine (non-polar) and release the trapped gas
-Adding water/CO2 makes the solution polar so the polystyrene precipitates out as a powder
-Bubbling air through removes the CO2 so the organic solvent and water can be separated
Emulsion Breaking with Switchable Polarity Solvent
-Soap, oil, and water create stable emulsions
-Adding DMEA/CO2 (CO2 in tertiary amine) breaks the emulsion
-Bubbling argon through drives off the CO2, reforming the emulsion
Switchable Viscosity Solvents
When adding a gas (CO2) makes the solution highly viscous, and removing it (bubbling nitrogen through) produces a free flowing liquid.
There isn't a current use for this.