Cystic Fibrosis, Asthma, and Spinal Cord Injury Overview
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
130 Terms
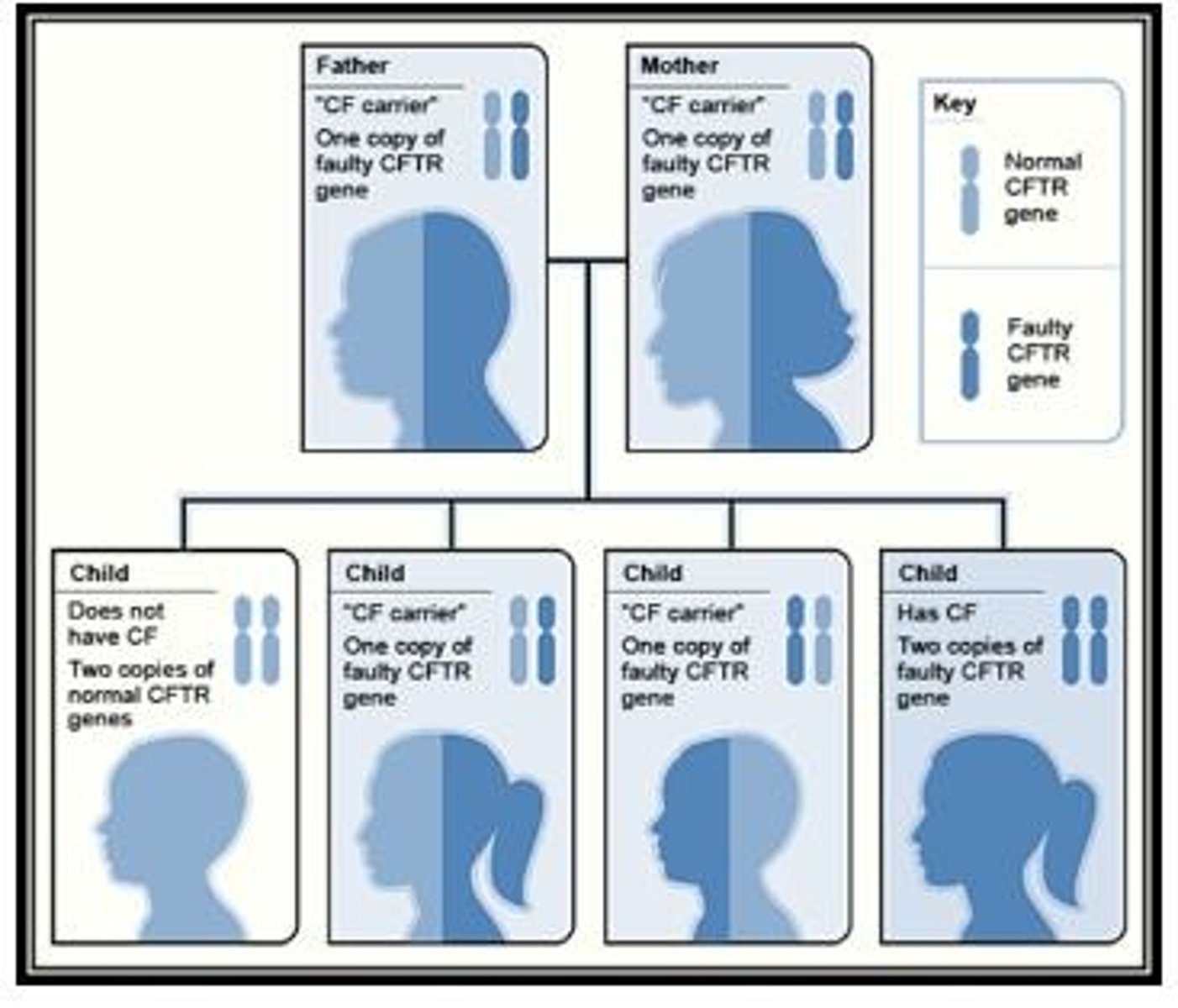
Cystic Fibrosis
Congenital exocrine gland disease affecting lungs and pancreas.
- affects GI and respiratory systems
- HEREDITARY
Median Age of Survival (Cystic fibrosis)
Average lifespan for cystic fibrosis patients is 37 years.
Diagnosis for Cystic Fibrosis
10% diagnosed in late teens or later.
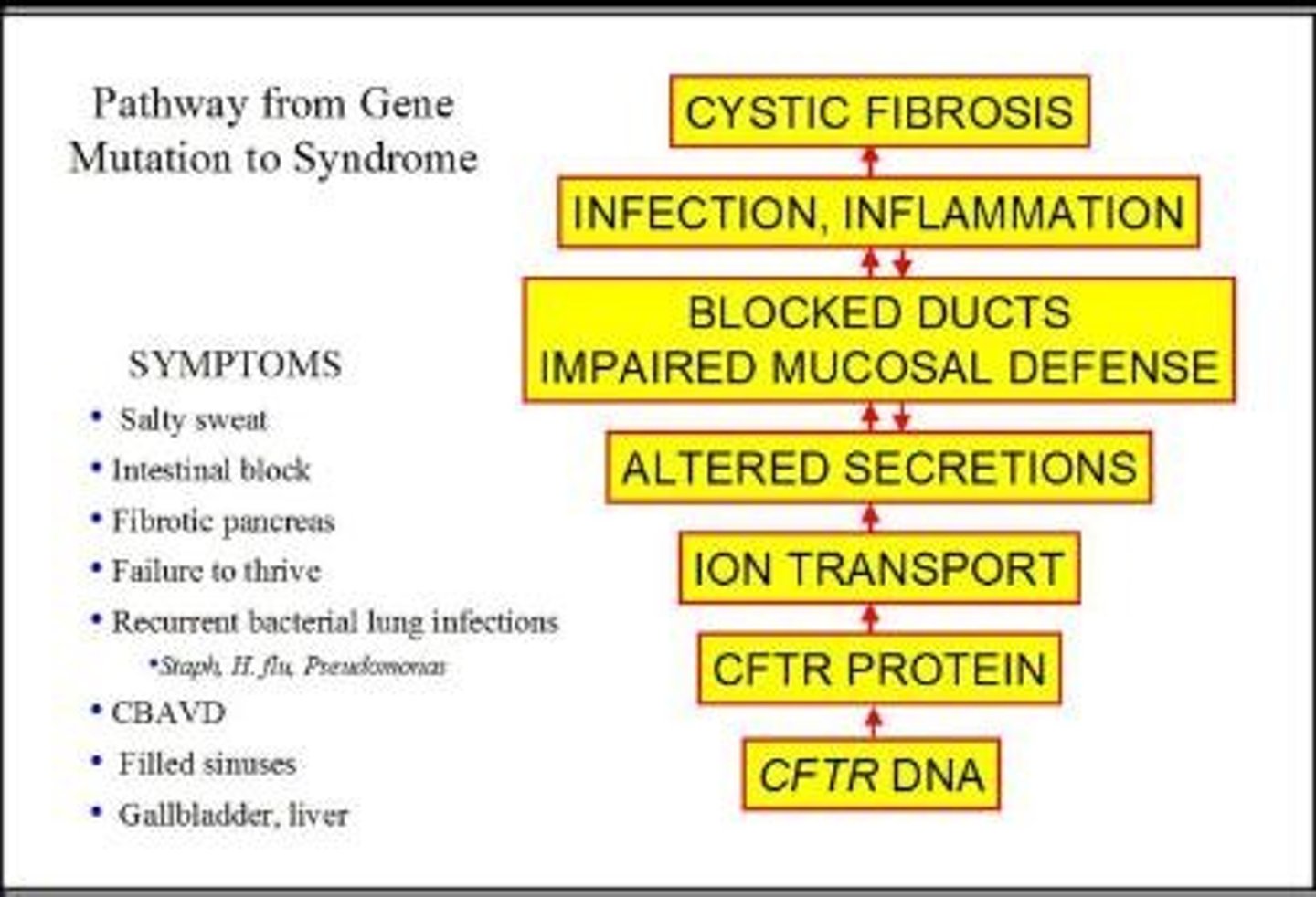
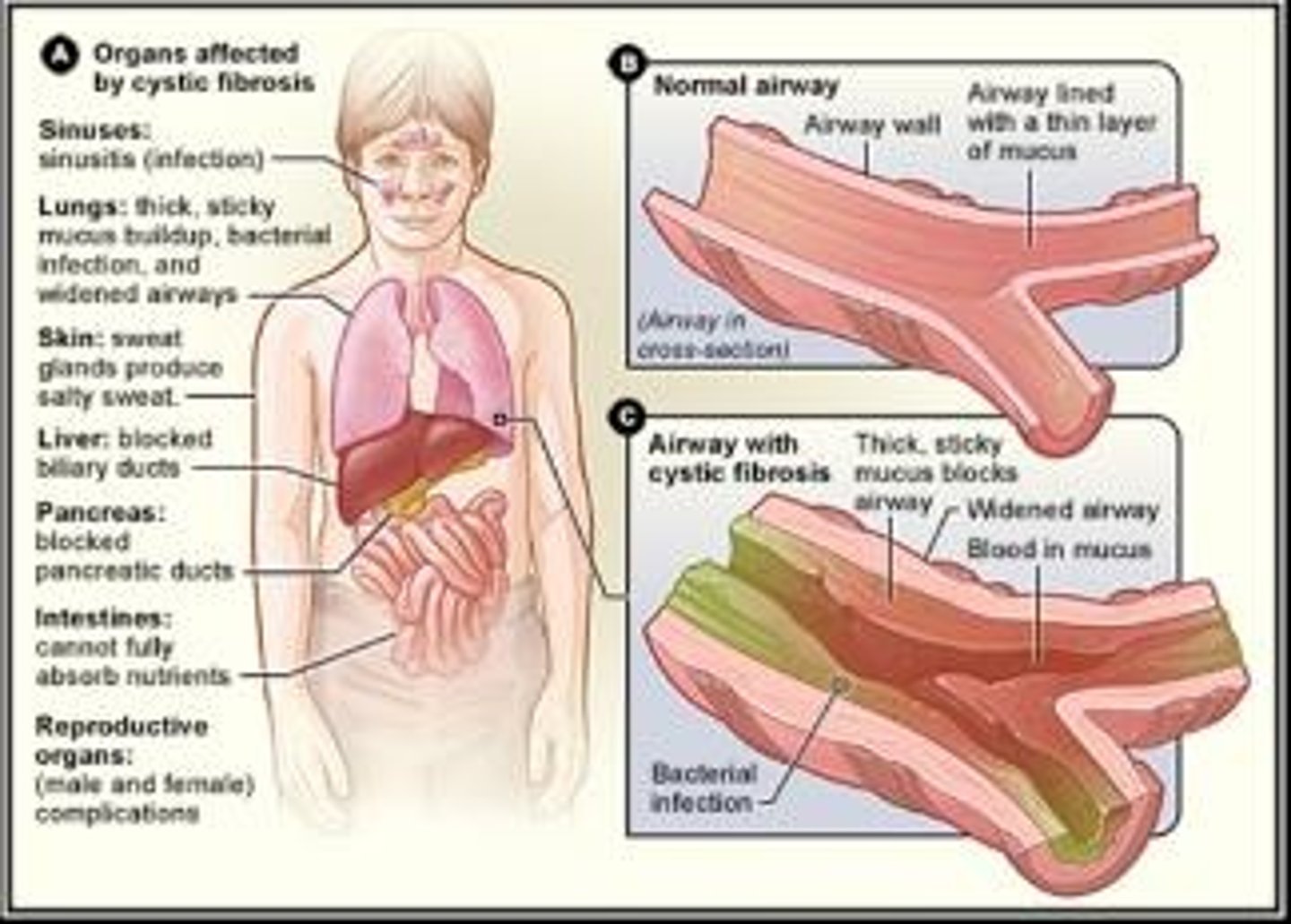
Symptoms of Cystic Fibrosis
• Progressive lung damage
• Delayed growth
- Failure to gain weight normally during childhood
- Excessive appetite but poor weight gain
• Salty-tasting skin
- High concentration of sodium & chloride in sweat
• Persistent coughing, wheezing, pneumonia
• Production of abnormally thick mucus
Cystic Fibrosis Vest
Device that vibrates chest to aid mucus clearance.
- can also use cup shaped hand percussion
Oxygen Therapy (Cystic Fibrosis)
Supplemental oxygen to assist breathing in patients.
- help open airways
Enriched Diet (Cystic Fibrosis)
High caloric intake with fats and proteins.
Life Span Cystic Fibrosis
average lifespan 37 years due to lung complications
Complications with Cystic Fibrosis
• Chronic respiratory infection
• Bowel problems (i.e. gallstones, intestinal obstruction, etc.)
• Coughing up blood
• Diabetes
• Infertility
- 95% - sperm transport
- 50% -cervical mucus
• Liver disease or liver failure, pancreatitis, biliary cirrhosis
• Malnutrition
• Pneumonia
Managing cystic fibrosis
- Encourage coughing to clear out mucus
• Cystic fibrosis is not a communicable disease
- Dietary issues
- Precautions to minimize respiratory infections
- Fluid intake before, during, & after exercise.
- Obtain physician's approval before participating in any activity
Asthma
Chronic lung disease causing airway inflammation.
- creates difficulty breathing
- recurrent periods of wheezing, chest tightness, shortness of breath, and coughing
Airway Function Asthma
- inflamed airways
- react strongly to certain inhaled substances
- muscles around airways tighten
- make more mucus
Asthma Triggers
Include dust, pets, weather changes, and exercise.
Symptoms of Asthma
- cough (w/ or w/o phlegm
- shortness of breath (worsens with exercise)
- wheezing
Exams and testing asthma
- stethoscope
- chest x- ray
- lung function test
- peak flow measurement
Treatment goals for asthma
- control swelling
- stay away from triggers
- prevent attacks (medications)
- quick relief (medications)
Long-term Asthma Medications
- prevent symptoms
- people w/ moderate- severe asthma
- taken daily
Inhaled Steroids
Prevent airway swelling to control asthma.
Quick-relief Drugs
prevent symptoms by preventing airway swelling
- rescue inhalers
- can be used before exercising
Chronic Respiratory Infections
Common complication of cystic fibrosis.
Coughing Up Blood
Serious symptom indicating potential lung complications.
Diabetes in Cystic Fibrosis
Occurs due to pancreatic dysfunction affecting insulin.
Infertility in Cystic Fibrosis
95% of males and 50% of females affected.
C5 spinal injury
Most common site for spinal cord injuries.
Hyperflexion injury
Forward bending injury to the cervical spine.
Hyperextension injury
Backward bending injury to the cervical spine.
Axial loading
Vertical compression of the spinal cord.
Rotation injury
Excessive head rotation beyond normal range.
Penetration injury
Injury from objects like guns or knives.
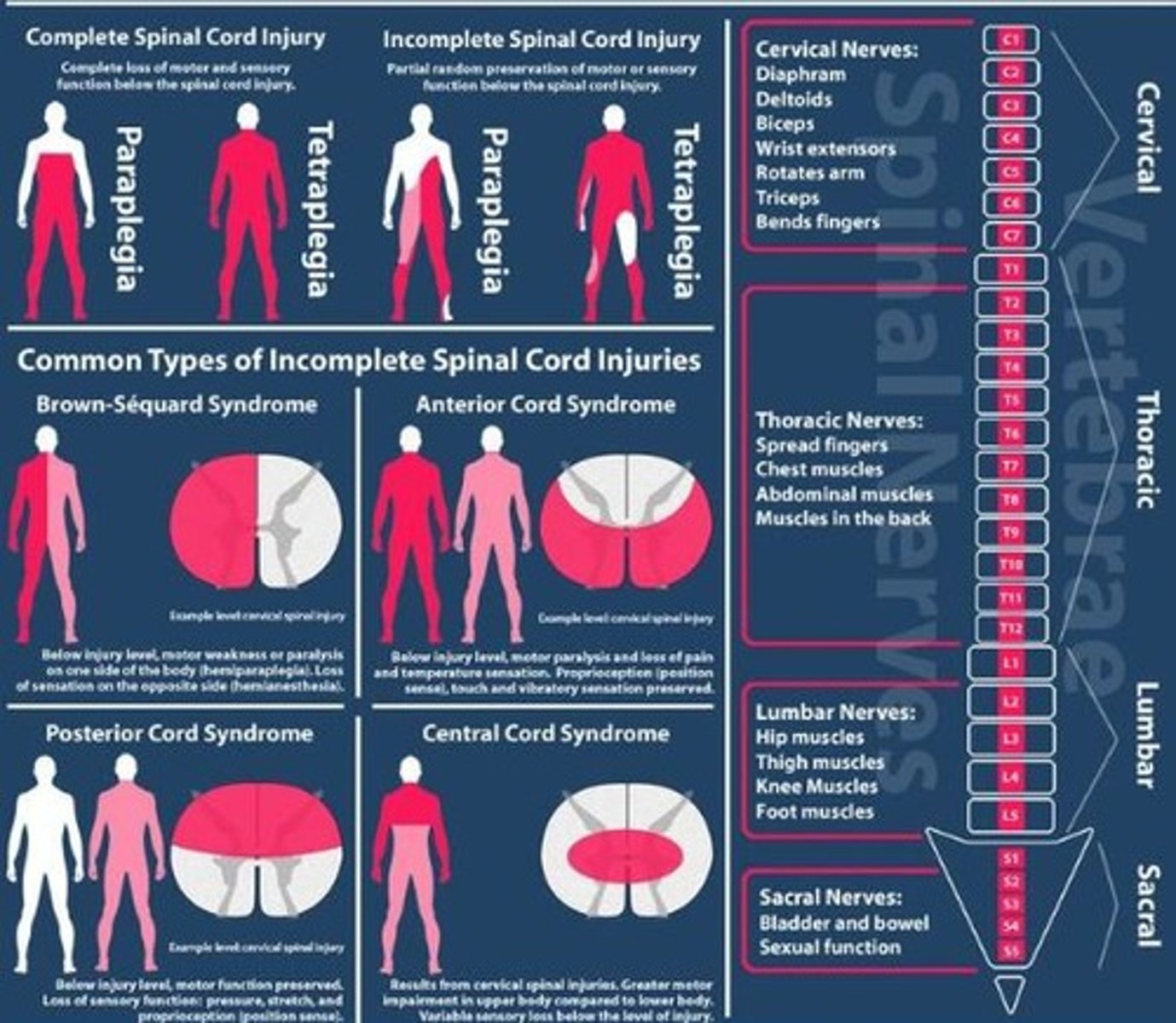
Spinal injury classification
- level
- complete or incomplete
- tetraplegia or paraplegia
Level
• Most distal uninvolved nerve root segment w/normal function
- Normal function = muscles innervated by the most distal nerve root
• At least a 3+/5 MMT grade indicating sufficient strength for functional use
Complete lesion
- no sensory or motor function below the lesion
- caused by a complete transection ( or severing), severe compression
Incomplete lesion
•Preservation of some sensory or motor function
•Often from contusions, pressure on the cord or swelling w/in spinal canal
•Clinical picture is unpredictable
Tetraplegia
Paralysis of all four limbs and trunk.
- includes respiratory muscles
- cervical lesions
Paraplegia
•All or part of the trunk & both lower extremities
- Thoracic, lumbar or sacral lesions
Spinal Shock
•Immediately following SCI a period of areflexia
- Not clearly understood
- Characterized by absence of all reflex activity, flaccidity, & loss of sensation below the level of the lesion
- Can last hours to weeks, but typically subsides w/in 24 hours
Nerve Tracts spinal cord
• Many spinal cord injuries have ascending & descending nerve tracts stunned
• w/o activity, these fibers atrophy
• When muscles are stimulated w/electrodes &/or exercise, nerve tracts sometimes partly revive
Anterior Cord Syndrome
Usually caused by cervical flexion
- Motor function is lost bilaterally
- Pain & temperature sensation are lost bilaterally
Brown-Sequard Syndrome
• Result of hemisection of spinal cord (gunshot or stab wound)
- Ipsilateral paralysis, loss of proprioception & vibration
- Contralateral loss of pain & temperature sense
Cauda Equina Injuries
Injuries below L1 vertebra causing lower motor neuron lesions.
- usually incomplete
• Results in flaccidity, areflexia, and impairment of bowel & bladder function
• Regeneration of peripheral nerves is possible
Central Cord Syndrome
• Hyperextension injuries
- Impairment of function in the upper extremity > lower extremity
- High % of patients will attain ambulatory function
Posterior Cord Syndrome
• Very rare
- Compression by tumor or infarction of the posterior spinal artery
- Motor function is preserved
Clinical Manifestations Spinal Cord
- motor paralysis
- sensory loss
- respiratory dysfunction
- impaired temperature control
- spasticity
Bowel and bladder dysfunction
- Sexual Dysfunction
Motor Paralysis (Spinal cord)
Following SCI there will be either complete or partial loss of muscle function below the level of the lesion
Sensory Loss (spinal cord)
Disruption of ascending sensory fibers results in or absent sensation below the level of the lesion
Respiratory Dysfunction Inhalation
- Diaphragm & external intercostals
• Impairments = decreased chest expansion & lowered inspiratory volume
Respiratory Dysfunction Expiration
- Abdominals and internal intercostals
• Impairments = decrease expiratory efficiency
Impaired Temperature Control Spinal Cord
• Hypothalamus can no longer control cutaneous blood flow or sweating below the lesion
• Lose the ability to shiver, absence of thermoregulatory sweating below the level of the lesion
Spasticity Spinal Cord
• Characterized by hypertonicity, hyperactive stretch reflexes, & clonus
- Below lesion level after spinal shock subsides
- Gradually increases during first 6 mo & plateaus by 1 year
Bowel Dysfunction Upper motor lesion
Spastic bowel
Bowel Dysfunction Lower motor lesion
Flaccid Bowel
Sexual Dysfunction Male Spinal cord
erection and ejaculation are possible depending on the level of the lesion and complete/ incomplete
Sexual Dysfunction Female Spinal Cord
mended and fertility remain unchanged
Post Injury Spinal Cord
Prevention of secondary complications
- Diaphragmatic breathing
- Strengthening
- Assisted coughing
- Abdominal support
Post Spinal cord injury Maintaining ROM
Facilitating movement in available musculature
- Pull ROM daily except when contraindicated
ROM Spinal Cord Contraindications
- paraplegia : hip flex> 90 (w/ combined hip and knee flexion)
- Tetraplegia: motion of head and neck
- Stretching of the shoulders
Peyton Manning's Injury
Cervical disc herniation affecting spinal function.
• The discs of the spine are the cushions between the vertebrae. These discs can become damaged and put pressure on the nerves surrounding the spinal cord.
• When pressure is put on these nerves, typical symptoms include arm pain, numbness, and weakness. In addition, a damaged disc can cause neck pain.
Obesity
Obesus- to eat away
Obesity causes, incidence, and risk factors
- Caloric balance/diet
- Biology
- Socialization/society
- Medical problems/medicines
Signs and tests for obesity
- Physical exam
Physical Exam
- Anthropometric measures
• Body mass index (BMI)
• Waist circumference
gynoid(pear) android (apple)
• Skin fold measurements
- Clinical measures
• Bod Pod
• DEXA
BMI Classification underweight
<18.5 kg/m2
BMI Classification Normal
18.5-24.9 kg/m2
BMI Classification Overweight
25-29.9
BMI Classification Obese- Class 1
30.0-34.9
BMI Classification Obese- Class 2
35-39.9
BMI Classification- Class 3
>_ 40
Skin fold measurements minimal
Men: 5%
women: 8%
Skinfold measurements below average
Men: 5-15%
Women :14-23%
skinfold measurements above average
men: 16-25%
women: 24-32%
skinfold measurements at risk
men: >25%
women: >32%
Waist circumference
Measurement around the abdomen indicating fat distribution.
Gynoid obesity
Fat distribution resembling a pear shape.
Android obesity
Fat distribution resembling an apple shape.
Bod Pod
Device measuring body composition via air displacement.
DEXA
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry for body composition.
treatment for obesity
Lifestyle
- diet
- physical activity
- life management
Medications
Surgery
Obesity Complications
- Cardiovascular disease
- Bone & joint problems (i.e. osteoarthritis)
- High blood cholesterol & triglycerides
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Fatigue
- Diabetes (High blood sugar (glucose)
Obesity and diabetes
90% of diabetes cases are Type II
- Almost 90% of those with Type II Diabetes are overweight or obese
- Abdominal adiposity
diabetes
high levels of blood sugar
Related to the body turning food into energy (diabetes)
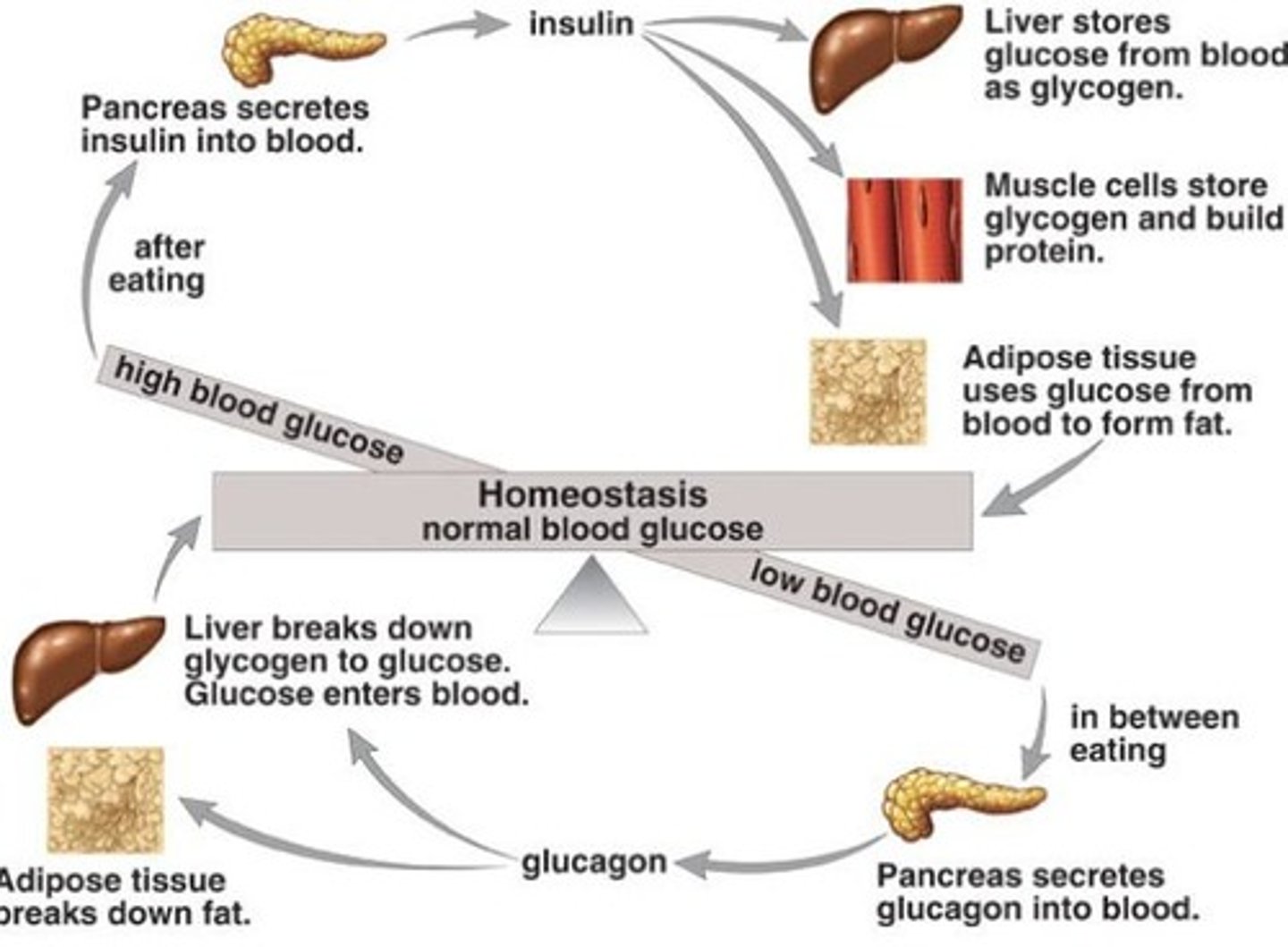
- Sugar (glucose) enters the bloodstream
- Pancreas makes insulin
People w/ diabetes have high blood sugar
- Body cannot utilize sugar
- Pancreas does not make enough insulin
- Cells do not respond to insulin normally
• Affects more than ~29 million Americans
Type 1 diabetes
• Can occur at any age
• Most often diagnosed in children, teens, or young adults.
• Body makes little or no insulin.
• Insulin injection
• Exact cause unknown
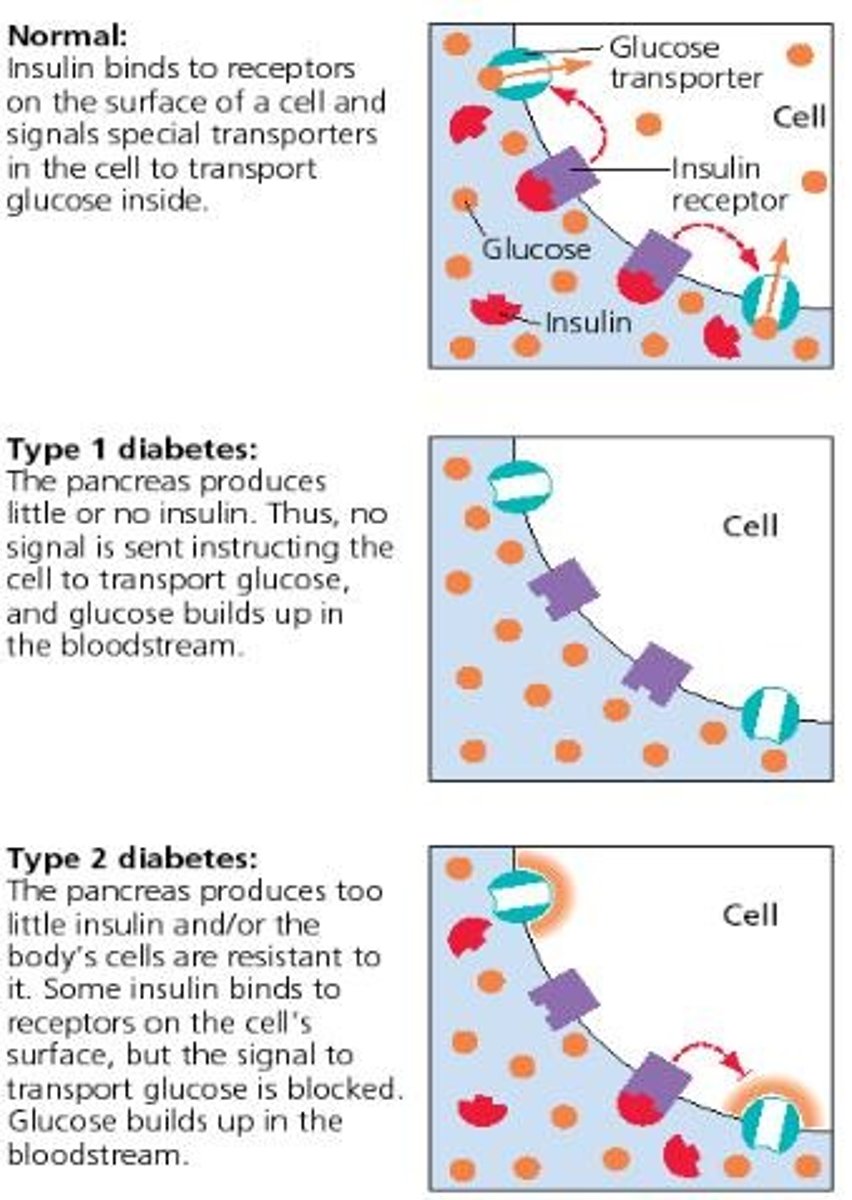
Type 2 diabetes
• Most of diabetes cases
- Doesn't produce enough insulin
- Cells are resistant to insulin, or both
• Often occurs in adulthood
• Related to obesity
Gestational diabetes
• High blood sugar
• Develops at any time during pregnancy
- In a woman who does not have diabetes.
• Develops in 2-5% of pregnant women
Prevention > treatment (Diabetes)
• Taking preventative measures will result in the largest decrease in obesity rates
• ~ 20% maintain weight loss after 1 year
• Treatment methods are expensive - insulin can be up to $80 every 7-10 days
Screening for Diabetes
• Screening for type 2 diabetes in people who have no symptoms is recommended for:
- Overweight children who have other risk factors for diabetes, starting at age 10 and repeated every 2 years
- Overweight adults (BMI=25+) & have other risk factors
- Adults over age 45, repeated every 3 years
Treatment for diabetes
No cure for diabetes
Medicines, diet, and exercise to control blood sugar
Prevent symptoms and problems
diabetes complications
Diabetic neuropathy
Diabetic ketoacidosis
High blood sugar can lead to kidney damage
Diabetic neuropathy
• Nerve injuries caused by high blood sugar levels & decreased blood flow
- More common when blood sugar levels not well controlled
• ~50% of people w/diabetes will develop nerve damage
- Most of the time symptoms do not begin until 10 to 20 years after diabetes has been diagnosed
Diabetic ketoacidosis
• Body cannot use sugar
- Because there is no insulin or not enough insulin
• Fat is used for fuel instead
- Fats are broken down, acids (ketones)build up in the blood & urine
• High ketone levels are poisonous.
diabetic ketoacidosis prevention
- Keeping an ideal body weight
• Exercise
• Diet
- Active lifestyle may prevent type 2 diabetes.
- No way to prevent type 1 diabetes
Exercise and Diabetes
• Improves blood glucose control
- While exercising glucose is pushed out of the bloodstream and into the muscles for energy
• Improved insulin sensitivity
Strength training for diabetes
•More muscle = more blood sugar stored
•30-50% of 1-repetition max
Aerobic training for Diabetes
•150+ min/week resulted in reduction in HbA1c levels
- 40-60% of VO2 max is considered moderate exercise
Overweight and Diabetes
• Overweight person needs 2-3x more insulin
- Pancreas is pushed past its limit & insulin producing cells begin to die off
• Abdominal fat cells can be harmful to the pancreas
- More damage to the pancreas & less efficient at
producing insulin
Weight loss and diabetes
• Lower body - pancreas is able to produce insulin more efficiently for the body
- Losing weight has the potential to restore blood sugar levels back to normal
• Can eliminate diabetes & lower risk of developing complications of diabetes
• Can reduce dependence on insulin therapy
ozempic Is a glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist. It works by:
stimulating insulin secretion
ozempic lowers
digestion
• Ozempic slows down gastric emptying
- Increases feelings of fullness during meals.
- It also increases the time it takes for food to leave the body.
- Suppressing liver glucose production:
• Ozempic suppresses the amount of glucose produced by the liver.
Insulin
Hormone regulating blood sugar levels.
Overweight Insulin Needs
Overweight individuals require 2-3 times more insulin.