Energy, Heat, and Temperature Unit
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
What is Energy?
The ability to do work or produce heat.
What is Thermal Energy?
The total kinetic energy from the random motion (vibration, rotation, translation) of atoms/molecules in a substance.
What is Heat?
The transfer of thermal energy between objects due to a temperature difference.
What is a Manipulated Variable?
The factor intentionally changed or tested in an experiment.
What is a Responding Variable?
The outcome measured in an experiment; it changes in response to the manipulated variable.
What is a Controlled Variable?
Factors kept constant in an experiment to ensure a fair test.
What is Temperature?
A measure of the average kinetic energy (speed of movement) of particles in a substance.
What is Celsius?
A temperature scale where water freezes at 0^ ext{o} ext{C} and boils at 100^ ext{o} ext{C} (at standard pressure).
What is the Kelvin Scale?
An absolute temperature scale where 0{ ext{ K}} (absolute zero) is the point of minimum particle motion.
What are the parts of a Thermometer?
Sensor: The part that absorbs/releases heat (e.g., the bulb with liquid).
Signal: The physical change indicating temperature (e.g., liquid rising/falling).
Responder: The scale (numbers) that interprets the signal.
What is Matter?
Anything that has mass and takes up space (volume).
What is Mass?
The amount of "stuff" (particles) in an object.
What is Volume?
The amount of space an object occupies.
What are the three states of matter?
Solid, Liquid, Gas (and Plasma).
What is Expansion?
Increase in volume (particles move faster, spread out) when heated.
What is Contraction?
Decrease in volume (particles slow down, move closer) when cooled.
What is Kinetic Energy?
Energy of motion (movement).
What is Potential Energy?
Stored energy (e.g., a stretched spring).
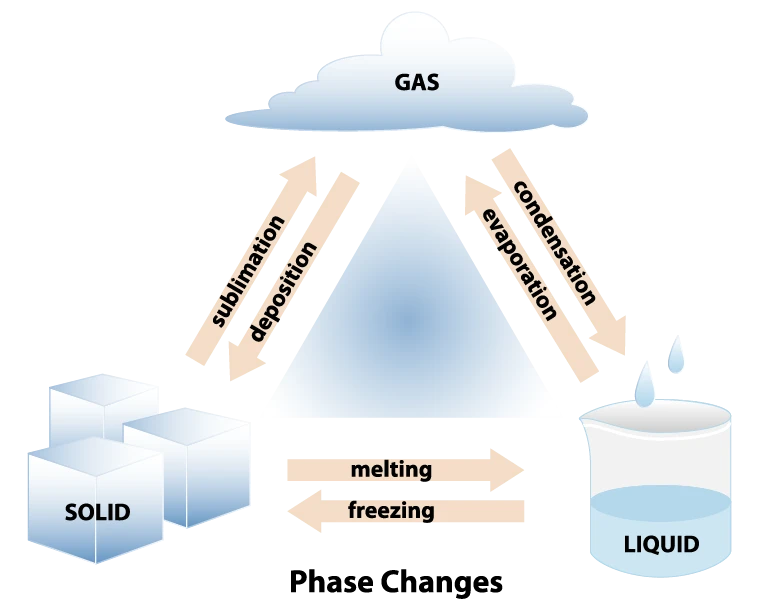
What are Phase Changes?
Fusion (Melting): Solid to Liquid.
Solidification (Freezing): Liquid to Solid.
Evaporation (Vaporization): Liquid to Gas.
Condensation: Gas to Liquid.
Sublimation: Solid to Gas.
What is Energy?
The ability to do work or produce heat.
What is Thermal Energy?
The total kinetic energy from the random motion (vibration, rotation, translation) of atoms/molecules in a substance.
What is Heat?
The transfer of thermal energy between objects due to a temperature difference.
What is a Manipulated Variable?
The factor intentionally changed or tested in an experiment.
What is a Responding Variable?
The outcome measured in an experiment; it changes in response to the manipulated variable.
What is a Controlled Variable?
Factors kept constant in an experiment to ensure a fair test.
What is Temperature?
A measure of the average kinetic energy (speed of movement) of particles in a substance.
What is Celsius?
A temperature scale where water freezes at 0^ ext{o} ext{C} and boils at 100^ ext{o} ext{C} (at standard pressure).
What is the Kelvin Scale?
An absolute temperature scale where 0{ ext{ K}} (absolute zero) is the point of minimum particle motion.
What are the parts of a Thermometer?
Sensor: The part that absorbs/releases heat (e.g., the bulb with liquid).\n\n- Signal: The physical change indicating temperature (e.g., liquid rising/falling).\n\n- Responder: The scale (numbers) that interprets the signal.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n
What is Matter?
Anything that has mass and takes up space (volume).\n\n
What is Mass?
The amount of \"stuff\" (particles) in an object.\n\n
What is Volume?
The amount of space an object occupies.\n\n
What are the three states of matter?
Solid, Liquid, Gas (and Plasma).\n\n
What is Expansion?
Increase in volume (particles move faster, spread out) when heated.\n\n
What is Contraction?
Decrease in volume (particles slow down, move closer) when cooled.\n\n
What is Kinetic Energy?
Energy of motion (movement).\n\n
What is Potential Energy?
Stored energy (e.g., a stretched spring).\n\n
What are Phase Changes?
Fusion (Melting): Solid to Liquid.\n\n- Solidification (Freezing): Liquid to Solid.\n\n- Evaporation (Vaporization): Liquid to Gas.\n\n- Condensation: Gas to Liquid.\n\n- Sublimation: Solid to Gas.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n
What are Energy sources?
An object or material that can transfer energy to other objects.
What is an Insulator?
Materials that slow or block the transfer of heat through conduction (and other methods), often by trapping air or due to low thermal conductivity.
What is a Conductor?
Materials that allow easy transfer of heat through conduction, typically metals, due to free-moving electrons.
What is Conduction?
The transfer of thermal energy from one particle to another in a solid (or between objects in direct contact) through collisions, without the overall movement of the material itself.
What is Convection?
The transfer of thermal energy through a fluid (liquid or gas) by the macroscopic movement of the warmer, less dense particles rising and cooler, denser particles sinking, creating a circular flow called a convection current.
What is Radiation?
The transfer of thermal energy in the form of electromagnetic waves, which can travel through a medium or a vacuum (empty space).