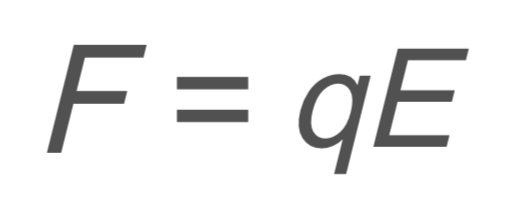MCAT Physics Equation
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
teehee
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Gravity
Fgrav → force of gravity
m → mass
g → the acceleration due to gravity
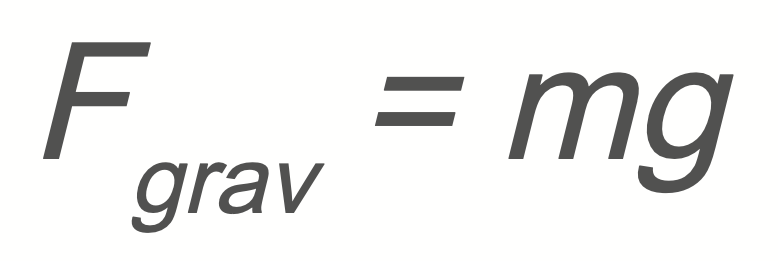
Gravity
g → gravity
t → time
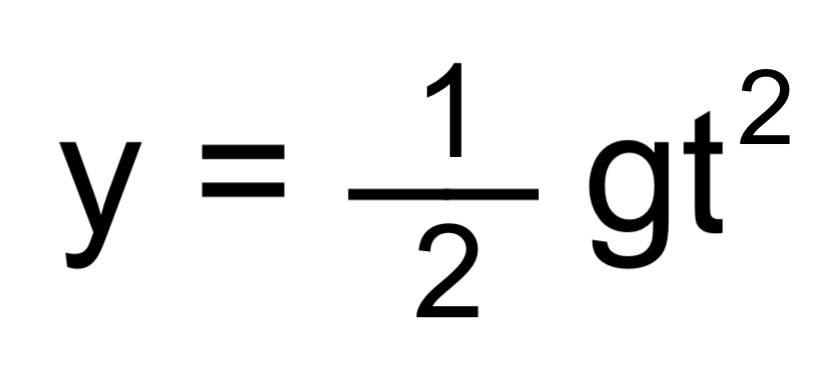
Kinematics
v → velocity
v0 → initial velocity
a → acceleration
t → time
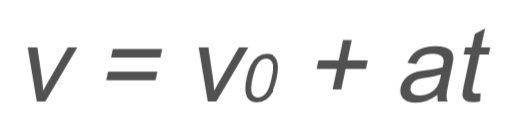
Kinematics
d → displacement
v0 → initial velocity
t → time
a → acceleration
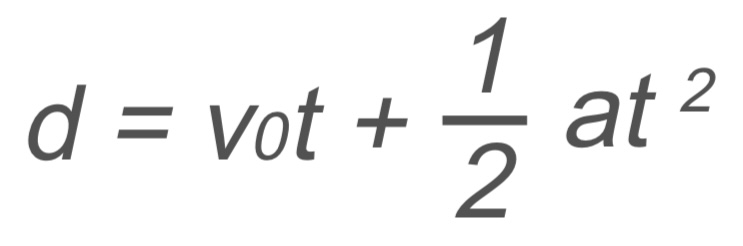
Kinematics: Acceleration Equation
vf2 → final velocity
vi2 → initial velocity
a → acceleration
d → displacement
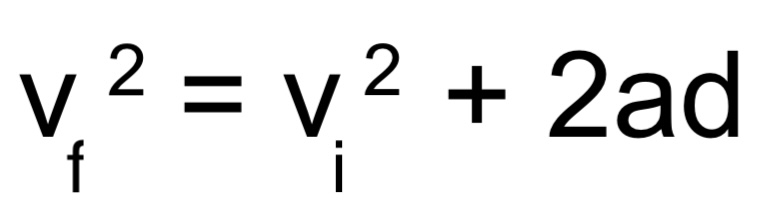
Kinematics
d → displacement
vavg → average velocity
t → time
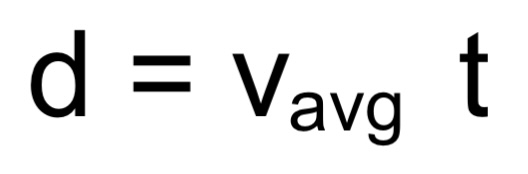
Projectile Motion: Horizontal Component
y → y-axis
vf → final velocity
t → time
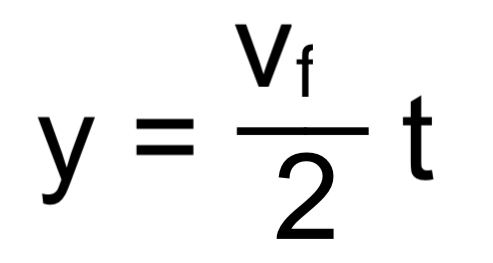
Projectile Motion: Vertical Component
y → y-axis
v0 → initial velocity
u →
t → time
g → gravity
t → time
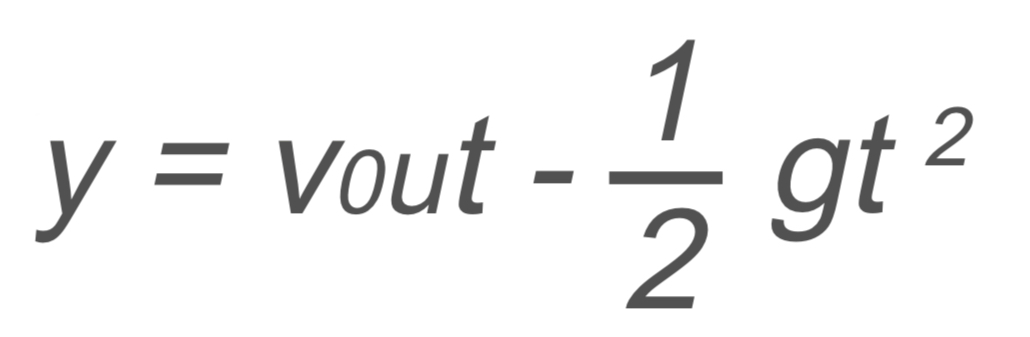
Work, Energy, and Power: Kinetic Energy
KE → kinetic energy
m → mass
v → velocity
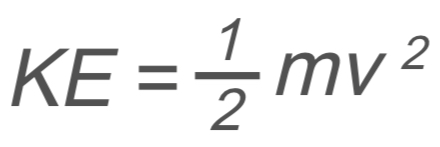
Work, Energy, and Power: Gravitational Potential Energy
PE → gravitational potential energy
m → mass
g → gravity
h → height
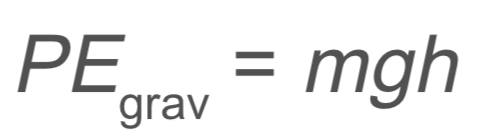
Work, Energy, and Power: Total Mechanical Energy
E → total energy
KE → kinetic energy
PE → potential energy

Torque
τ → torque
r → distance from the pivot that the force is applied
F → force
sinθ → angle between r and F

Thermal Dynamic: First Law
ΔE → change in internal energy
Q → heat added to the system
W → work done by the system
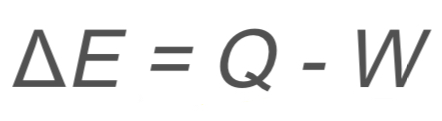
Fluids: Density
ρ → density
m → mass
v → volume
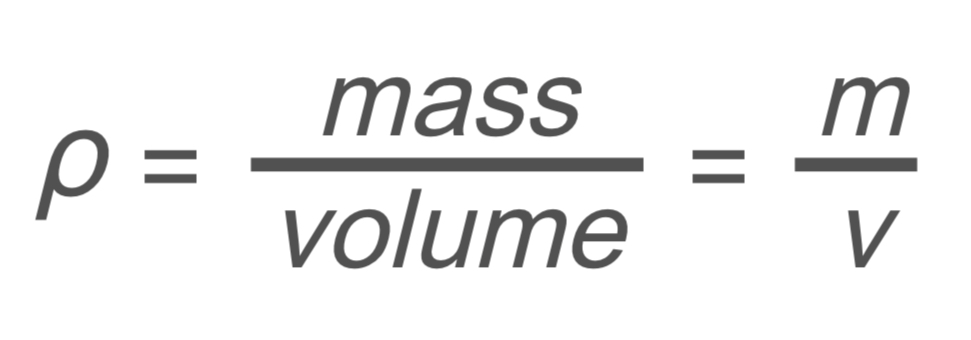
Circuits and Electrostatics: Ohms Law
V → voltage
I → current
R → resistance
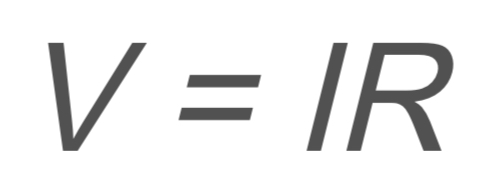
Circuits and Electrostatics: Power
P → power
I → current
V → voltage
R → resistance
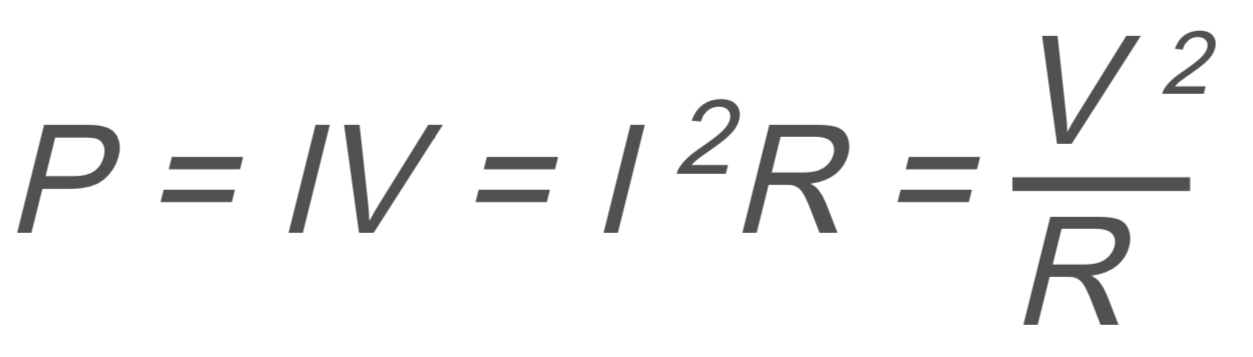
Circuits and Electrostatics: Series Resistors
RTotal → total resistance
R1 → resistance
R2 → resistance
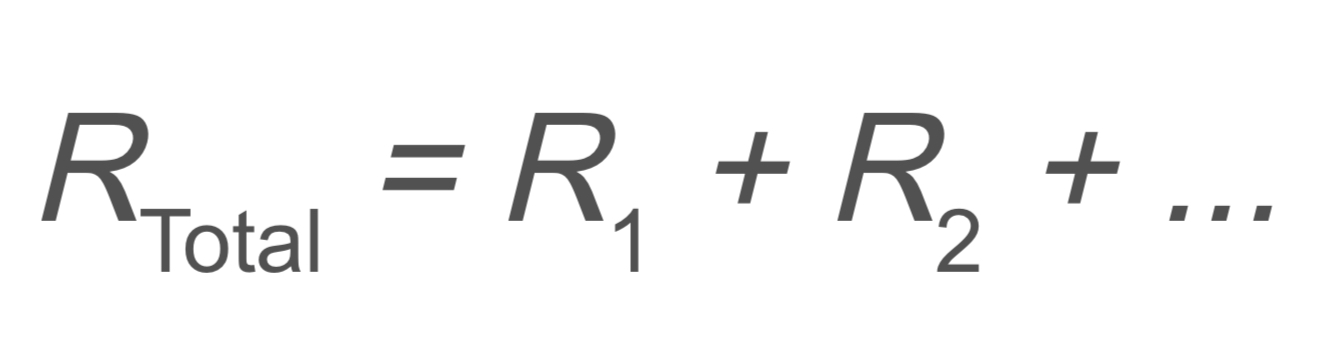
Circuits and Electrostatics: Parallel Resistors
RTotal → total resistance
R1 → resistance
R2 → resistance
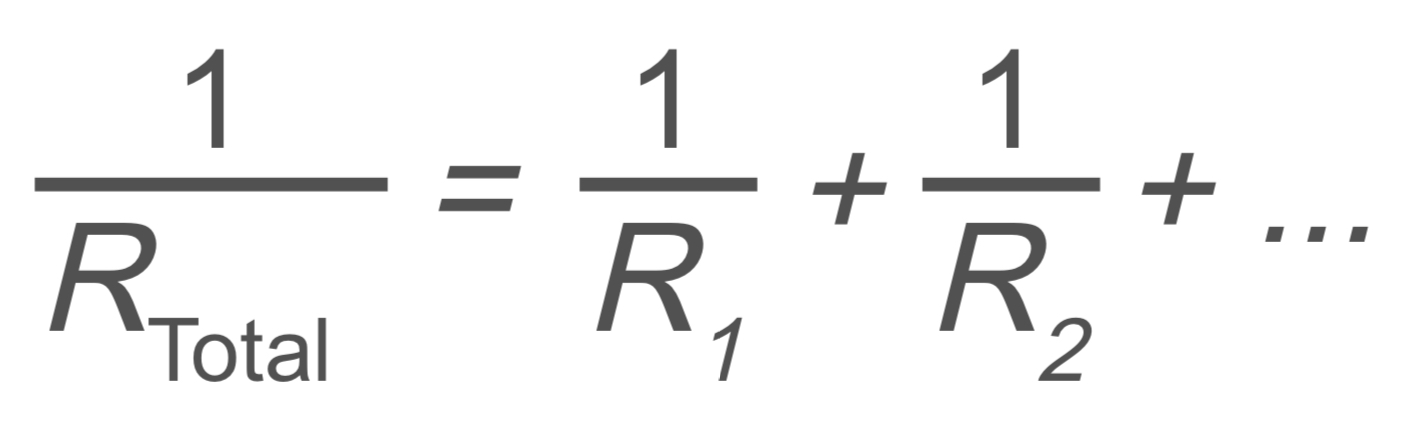
Circuits and Electrostatics: Current
I → current
Q → charges
t → time
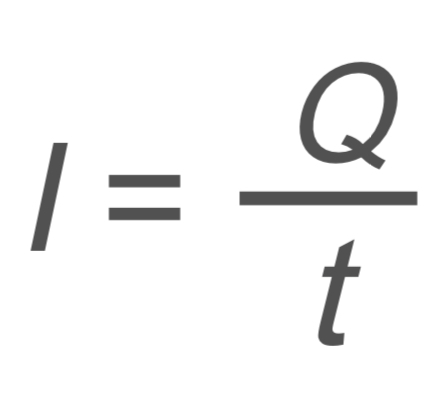
Circuits and Electrostatics: Resistance
R → resistance
ρ → resistivity
L → length
A → area
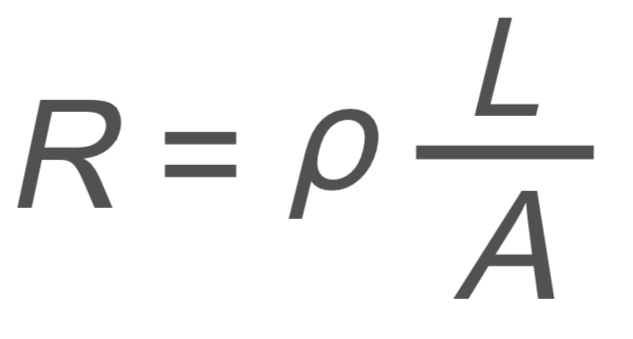
Circuits and Electrostatics: Coulomb’s Law
FE → electrostatic force
k → coulomb constant
Q1 → charges
Q2 → charges
r2 → distance
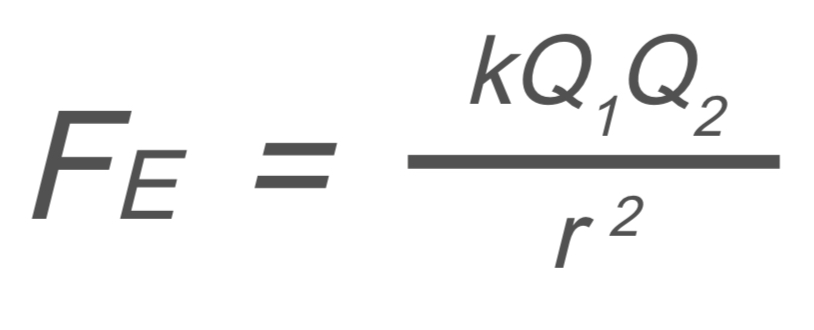
Circuits and Electrostatics: Electric Field (Point Charge)
E → electric field
k → coulomb’s constant
Q → charge
r2 → distance
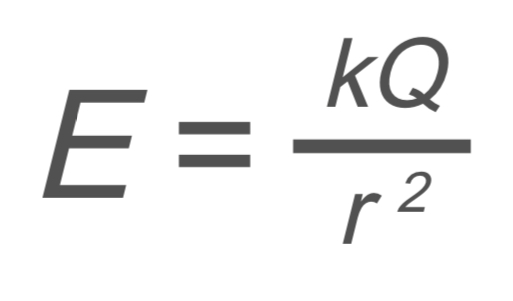
Circuits and Electrostatics: Force by an Electric Field
F → force
q → charge
E → electric field