Option D - Hazardous environments
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Hazard
A potentially damaging natural event that poses a threat to people, property, or the environment
Disaster
When a hazard actually causes significant harm
Risk
The likelihood of a hazard causing harm, influenced by exposure, vulnerability and capacity to respond
Vulnerability
How susceptible people or places are to harm from a hazard
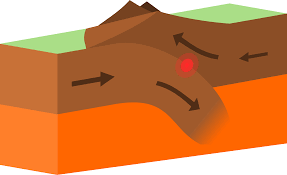
Convergent (destructive) boundary
Plates move toward each other, oceanic plate subducts beneath continental plate

Divergent (constructive) boundary
Plates move away from each other, magma rises to form new crust

Transform (conservative) boundary
Plates slide past each other, no crust is created or destroyed
Convection cells
Heat from the Earth’s core causes hot magma to rise and cooler magma to sink into the mantle
Ridge push
A divergent (constructive) boundary, magma rises to form new crust (e.g. mid-ocean ridges), as magma cools and hardens, it forms elevated ridges, gravity causes the new crust to slide down the slop, pushing plates apart
Slab pull
At convergent (destructive) boundary, a denser oceanic plate subducts underneath a lighter plate, as the oceanic plate sinks into the mantle, it pulls the rest of the plate with it
Soil creep
The micro-movement of individual soil particles downslope
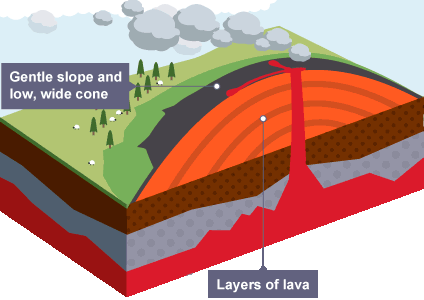
Shield volcano
A broad, gently sloping volcano formed by low viscosity, basaltic lava that flows easily and spreads over large areas
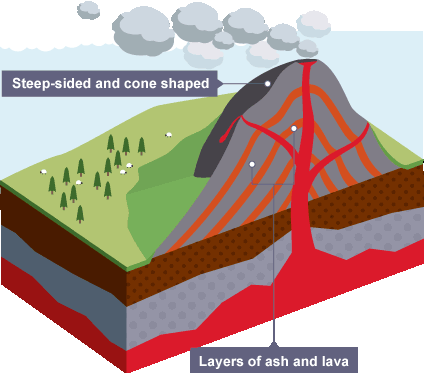
Composite volcano (stratovolcano)
A steep, cone-shaped volcano made of alternating layers of lava, ash, volcanic rock which eruptions are explosive and dangerous
Lava
Molten rock that erupts onto the Earth’s surface from a volcano
Pyroclastic flow
A fast-moving, deadly cloud of hot gas, ash, and volcanic rock that races down the side of a volcano during an explosive eruption
Lahar
A volcanic mudflow made of ash, rock, and water, often triggered by rainfall or melting ice on a volcano
Epicenter
The point on the Earth’s surface directly above the focus of an earthquake
P-wave
A type of seismic wave that compresses and expands the ground that is fast and shakes the ground in the direction they travel
S-wave
A seismic wave that moves the ground up and down or side to side, slower
Love waves
A type of surface seismic wave that moves the ground side to side horizontally, causing intense shaking and damage
Rayleigh waves
A type of surface seismic wave that move the ground in a rolling, elliptical motion, similar to ocean waves
Liquefaction
The process by which an earthquake’s violent movement makes soil lose its structural integrity