Forces doing work and their effects
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
What is work done?
The amount of energy transferred
What is power?
The rate of work being done (How fast energy is transferred)
What is the formula for work done?
Work done (J) = force (N) x Distance moved (m) or E=F x d
What is the equation for power?
Power (W)= Work done (J)/Time taken (s) or P= E/t
How can the energy of a system be changed?
Work done through forces
Electrical equipment such as a cell in a circuit transferring energy into other forms like heat energy
Heating a material which increases the kinetic energy of the material
What are non-contact forces?
Forces that can be exerted on an object without them being in contact with it
What are contact forces?
Forces that are exerted due them them being in contact with an object
What are the three main non-contact forces?
Gravity
Magnetism
Electrostatic charges
What is normal contact force?
It is a force that acts upwards in opposition to the weight of an object
What is the force of friction?
A force that acts in opposition to a pushing force trying to change the motion of an object
Friction always acts to slow an object down
What are the components of a force?
Any force can be resolved into it’s horizontal component Fx and it’s vertical component Fy
The horizontal and vertical components do not affect one another, they are independant
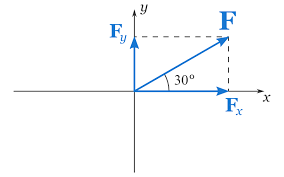
How to resolve forces by scale drawing
Decide on an appropriate scale such as 1 cm=10N
Using a ruler and protractor, draw the line to represent the force at the correct angle
Draw the horizontal and vertical components
Measure the lengths and convert to force using the same scale
Note that if you are given the vertical components instead you have to find the resultant force by making a box then drawing a line to the opposite corner and measure that
What do free-body force diagrams show?
They show the forces acting on a single object
What do free-body force diagrams need to contain?
The body the forces are acting on- this can be simplified to a box or a dot
The forces acting on the body
If there are two forces acting on different objects it is NOT a free-body force diagram
How can we see if forces are balanced on a free-body force diagram?
If the forces are balanced the line will be of equal length
If the forces are not balanced then the forces will not be of equal length
If the arrows on a free-body force diagram are not balanced, what does that tell us?
The object is moving in the direction of the biggest force
The object is accelerating
If the arrows on a free-body force diagram are balanced, what does that tell us?
The object is stationary (not moving)
OR
The object is moving at a constant speed
Why is force a vector quantity?
Because it has a size and direction
What do resultant forces determine?
Whether an object is stationary/moving at a constant speed or accelerating
What is the resultant force?
The single force that would have the same effect as all of the other forces acting on the object
If two forces are pushing a box forward with a force of 10N east each what will the resultant force be?
20N east
If one force is pushing a box forward with a force of 10N and one is pushing back with a force of 10N what will the resultant force be?
0N
If one force is pushing a box east with a force of 10N and one is pushing west with a force of 8N what will the resultant force be?
2N east
If the resultant force on an object is 0, what does that tell us?
The object is either stationary (not moving), or is moving at a constant speed
What direction will a resultant force be in if the forces act perpendicular (at right angles) to each other?
The resultant force will be a diagonal line
How can you calculate the resultant force of two angles acting perpendicular (at right angles) to each other?
If you have a scale (1cm=10N for example) you can measure the length of the diagonal line you draw to find the resultant force, so if the line was 10 cm the resultant force would be 100N
You can use Pythagoras’ theorem to calculate the hypotenuse (The slanted side)
What is a moment?
Forces which act at a distance from a pivot that can cause a turning effect or rotation
What is the formula for a moment?
Moment (Nm)= force (N) x distance from the pivot (m)
How should we measure distance between the pivot and the force?
The distance must be measured at right angles to the direction of the force
What is a pivot?
The point around which an object rotates
What is the principle of moments?
When a body is balanced, the sum of the clockwise moments is equal to the sum of the anticlockwise moments
What do levers and gears do?
Transmit the rotational effect of their forces
What does the nature of the rotation of a lever depend on?
The position of the input force- the force provided by the user of the lever
The output force- the force that results from the input force
The fulcrum- the turning point about which both forces act
What are gears?
Gears are toothed wheels put together to transmit a rotational force and motion
If one gear is moving in a clockwise direction, which way will the other gear turn?
Anti-clockwise
What is a high gear?
When a large input gear turns a smaller output gear
This leads to a high speed and a low turning effect
What is a low gear?
When a smaller input gear turns a larger output gear
This leads to a low speed and a high turning effect
What is the speed and turning effect of a large gear compared to a small gear?
A large gear will move slower than a small gear but will have a greater turning effect
A low gear leads to a low speed and high turning effect
What do levers and gears both do?
Cause rotation and can alter the size of the output force