L21 Population Genetics & Natural Selection
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards for Population Genetics & Natural Selection concepts.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Population
Localized group of individuals of the same species
Gene Pool
Total aggregate of genes (and their alleles) in the population at one time
Why we need to estimate genotype frequencies in population
To predict how many individuals will inherit genetic disease, and how many are carriers.
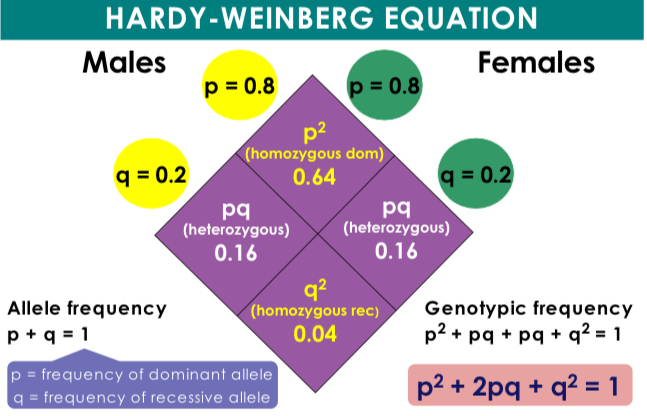
Hardy-Weinberg Equation
p² + 2pq + q² = 1; used to predict genotype frequencies in a population
Causes of change in allele frequency
Random genetic drift, mutation, gene flow/ migration, founder effect, bottleneck effect, natural selection or non-random mating.
Random Genetic Drift
A random change in allele frequencies due to sampling error over generations
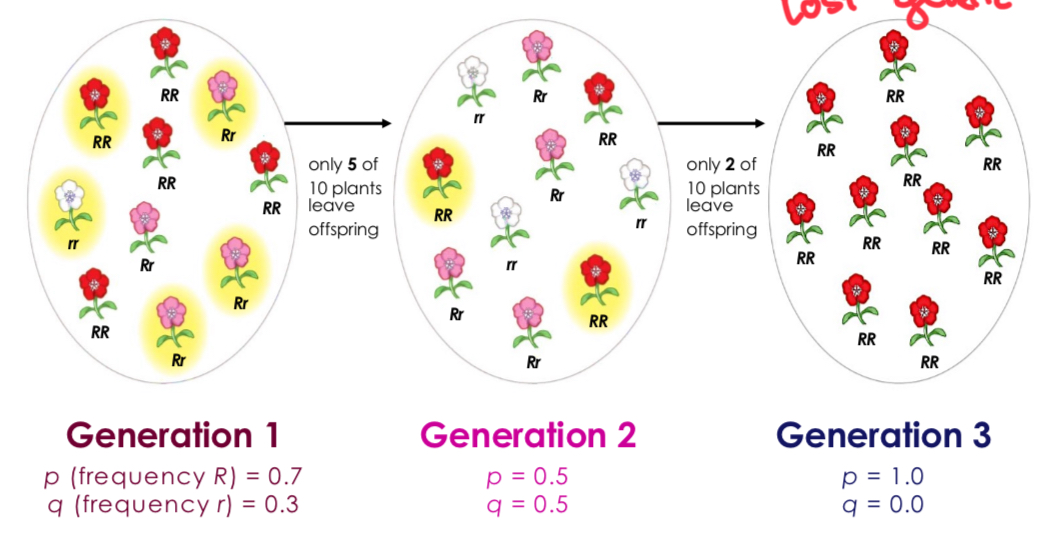
Bottleneck Effect
Population reduction that results in loss of genetic diversity because when population increases again it will consist only of the remnants.
Founder Effect
Reduced genetic variation when a new population is founded by a small number of individuals
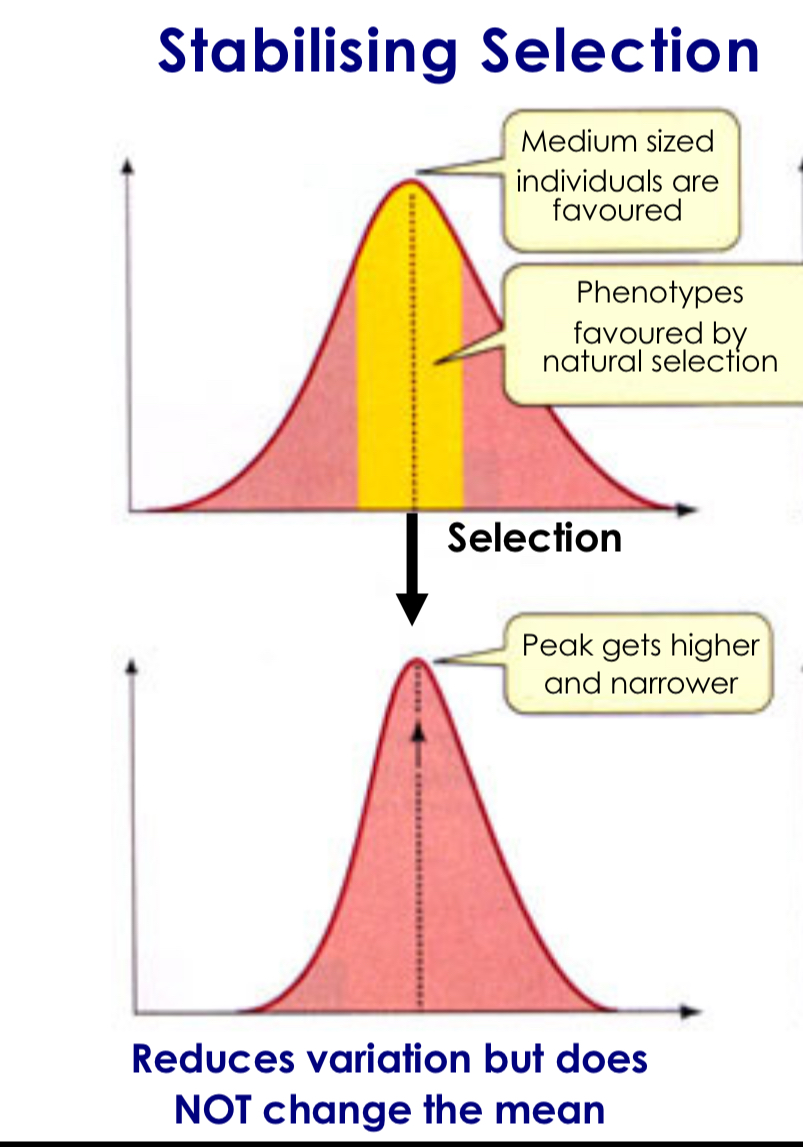
Stabilizing Selection
Natural selection that favors intermediate variants by acting against extreme phenotypes
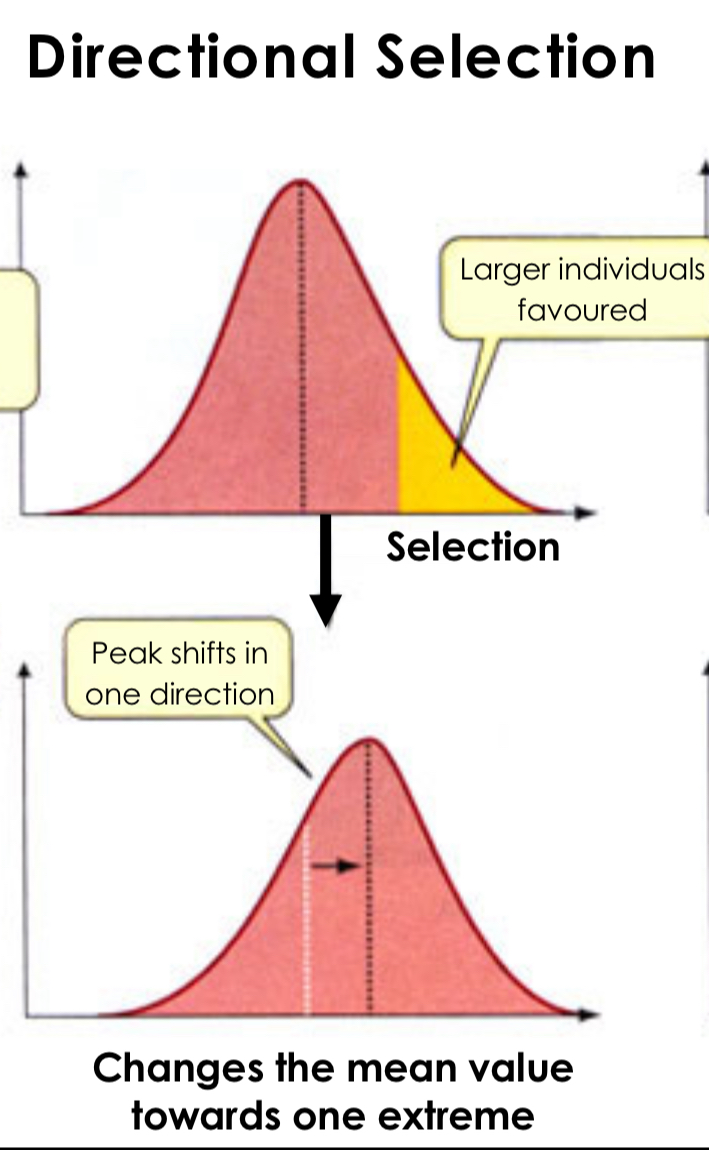
Directional Selection
Natural selection that favors one extreme phenotype, causing a shift in the population's genetic variance toward that extreme over time.
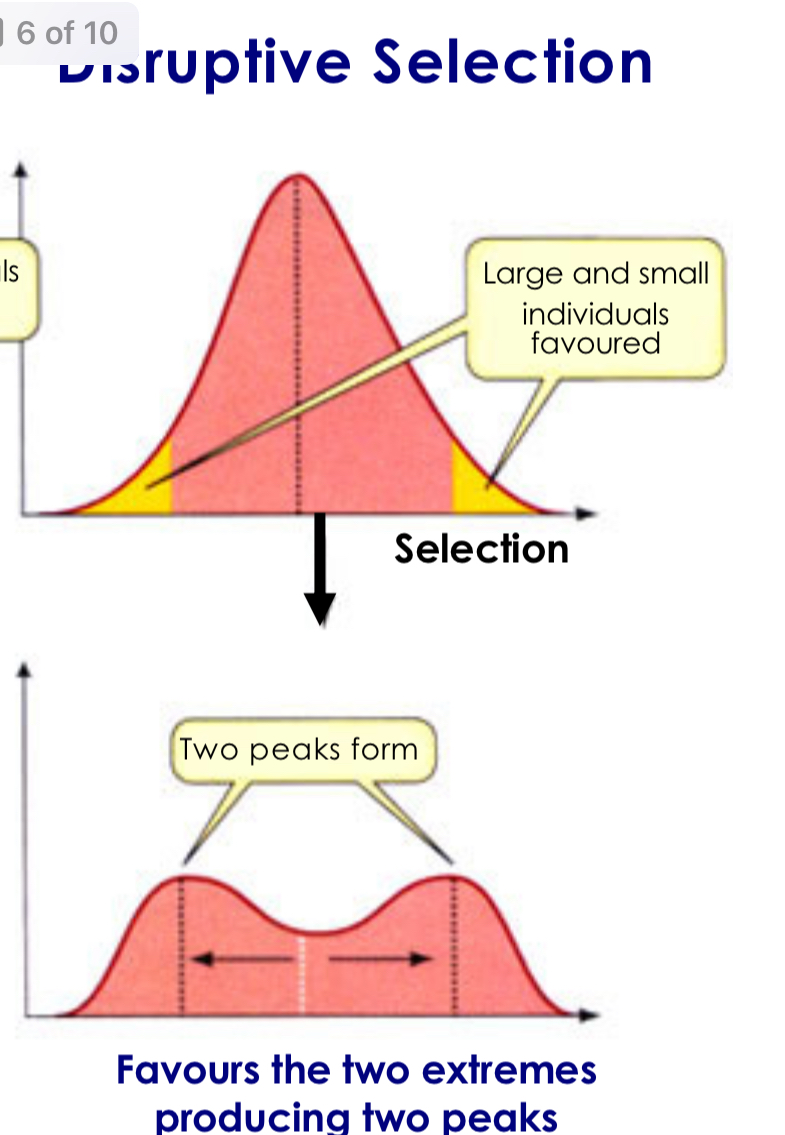
Disruptive Selection
Natural selection that favors both extremes over intermediate phenotypes
Sexual Selection
Individuals with certain inherited characteristics are more likely than other individuals to obtain mates. (eg birds with long tails)
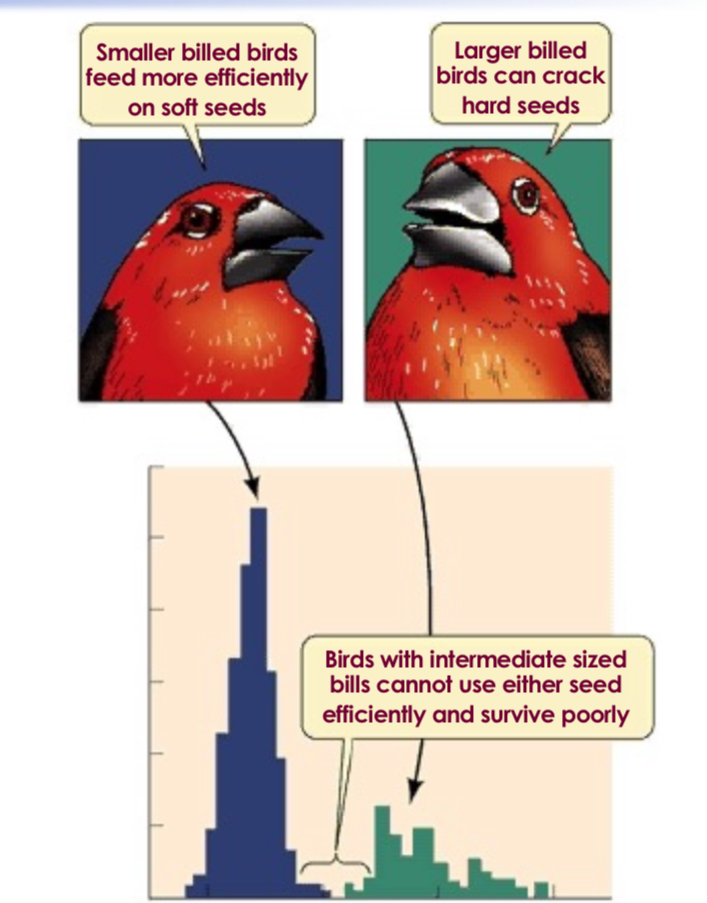
What type of selection is this?
Disruptive
Frequency-Dependent Selection
The fitness of a genotype is influenced by its frequency in a population. (how rare or common)
Spatial distribution of genetic variation (Cline)
The gradual geographical change in genetic/phenotypic composition.
Migration (Gene Flow)
Individual from one population mates with someone from another gene pool. New alleles, change in existing allele proportion and population size, makes populations more similar.
Mutation
A change in the nucleotide sequence of an organism's DNA, creating new alleles.