API 20E & Quiz 7
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
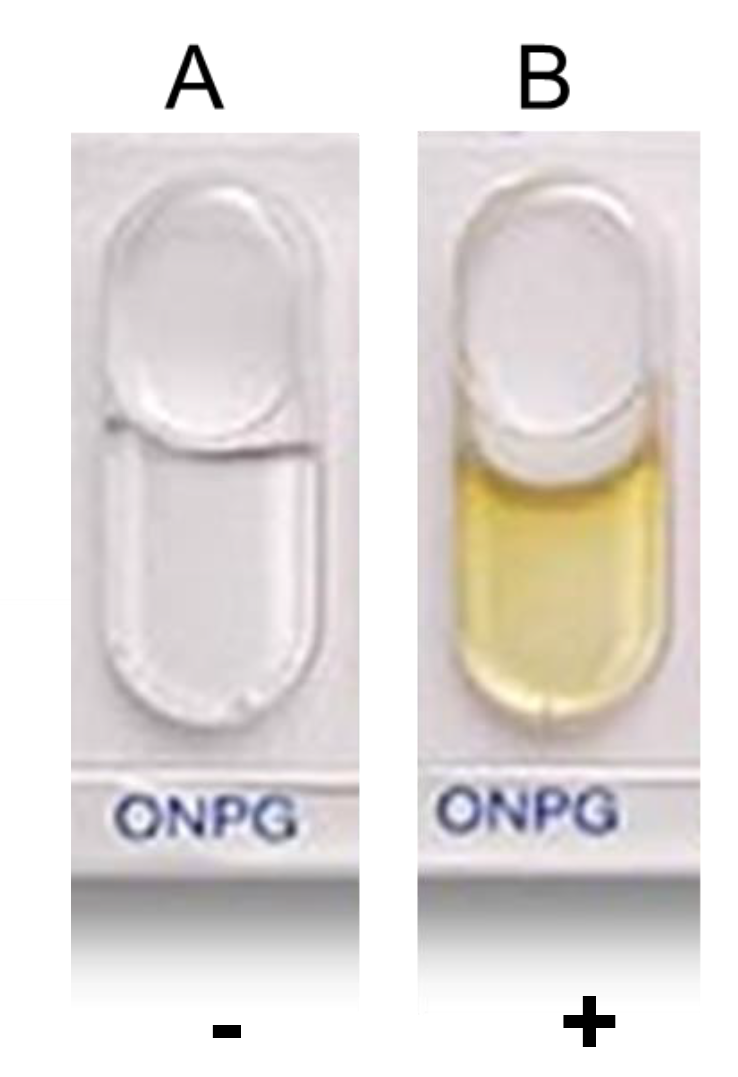
ONPG
To determine if bacteria can produce beta-galactosidase.
Positive test will turn yellow. Clear is negative.
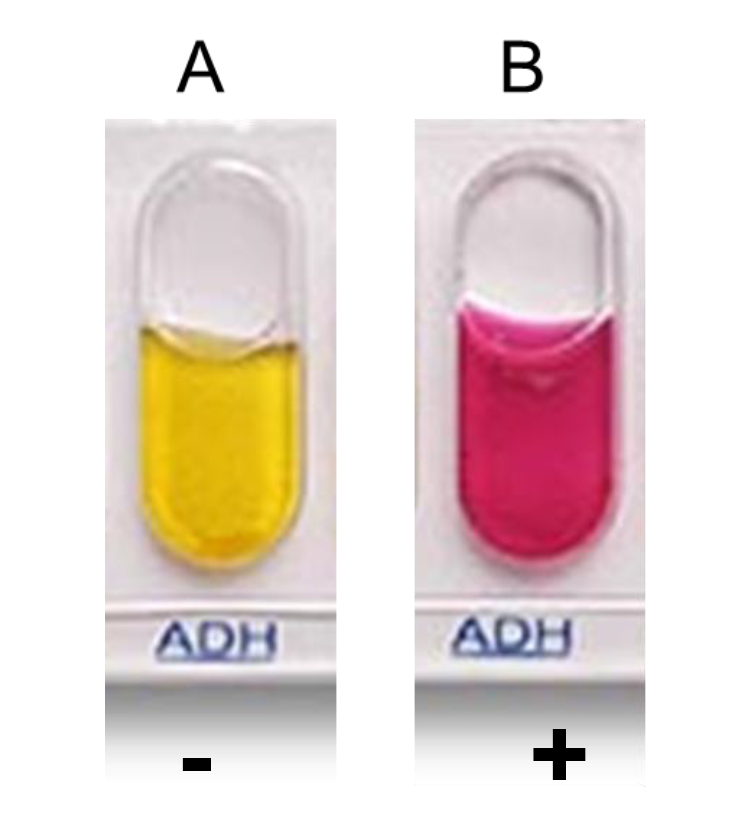
ADH
Arginine Dehydrolase
Determines whether bacteria can express arginine dehydrolase or not.

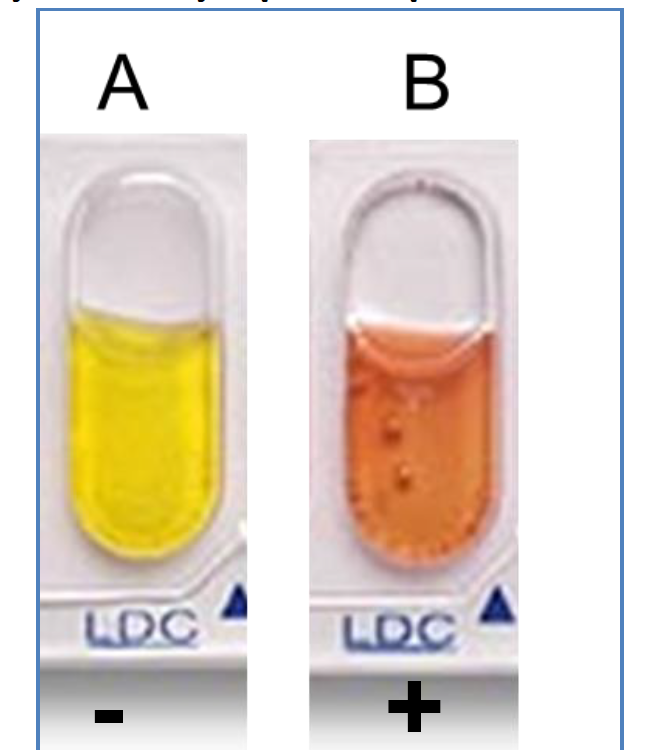
LDC
Lysine Decarboxylase
Determine whether bacteria can decarboxylate lysine by Lysine decarboxylase.
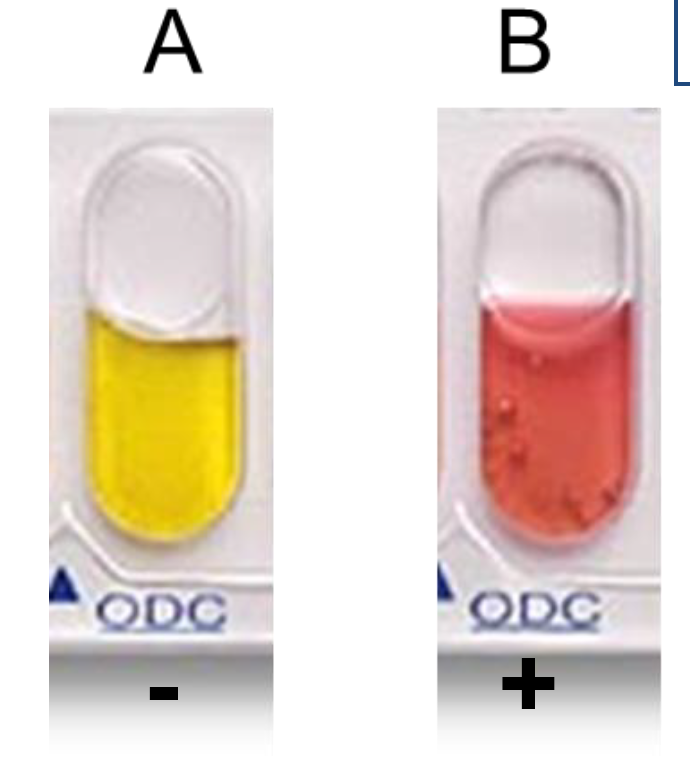
ODC
Ornithine Decarboxylation
Determine whether bacteria can decarboxylate ornithine by ornithine decarboxylase
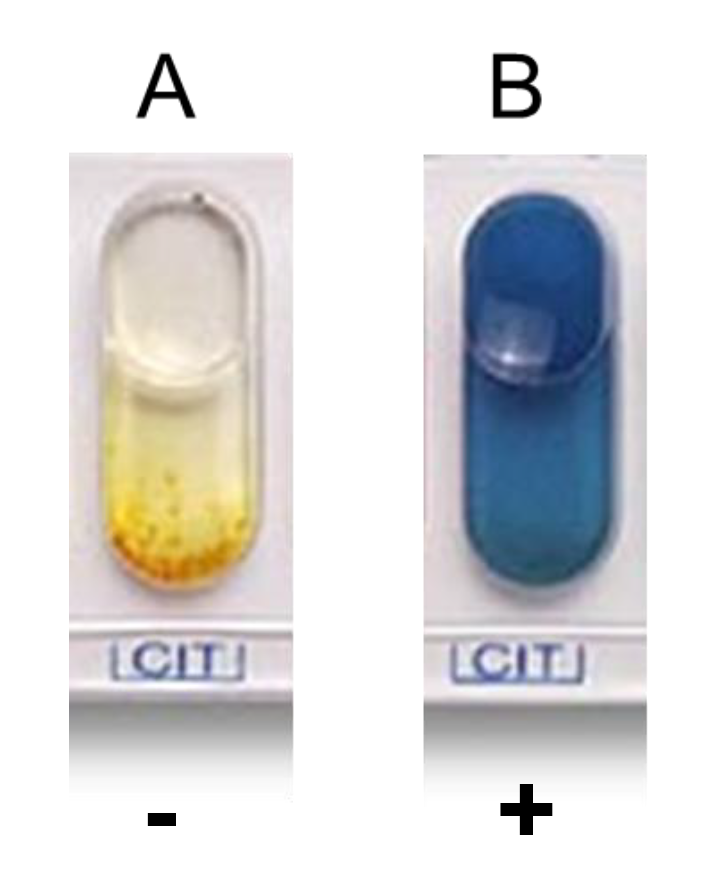
CIT
Citrate Test (CIT)
To determine whether bacteria can utilize citrate as a sole carbon source by producing citrase.
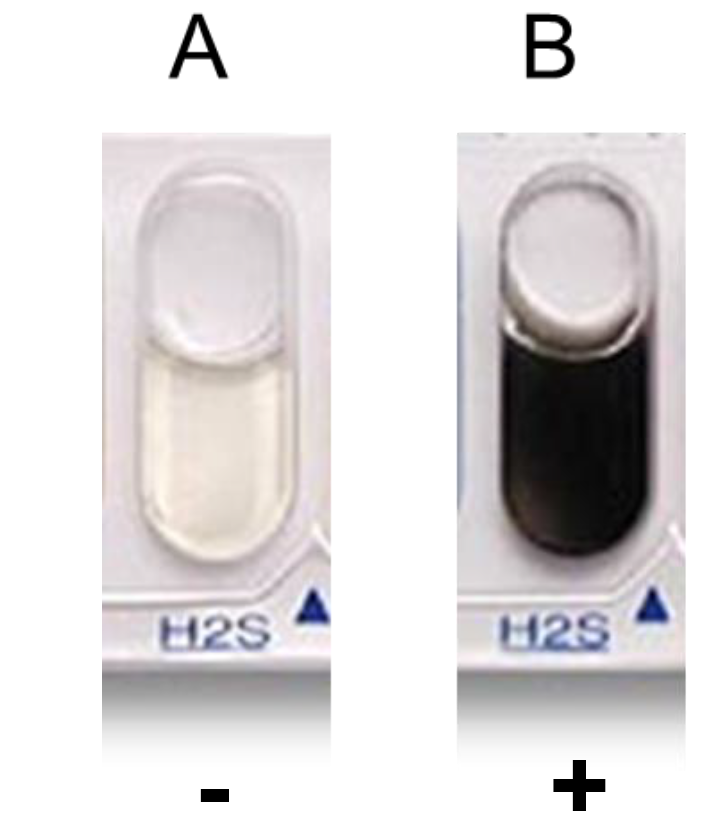
H2S
Hydrogen Sulfide Test (H2S)
Determine whether bacteria can produce hydrogen sulfide by producing thiosulfate reductase
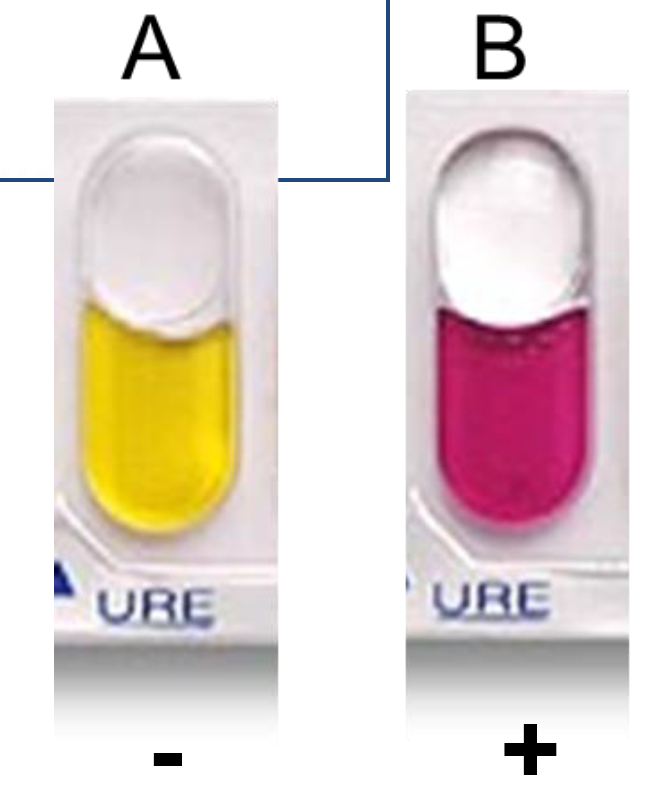
URE
Urease (URE)
Determine if bacteria can hydrolyze urea by urease.

Helicobacter pylori Infection
produces Urease (enzyme) leading to Ulceration of the Stomach Wall
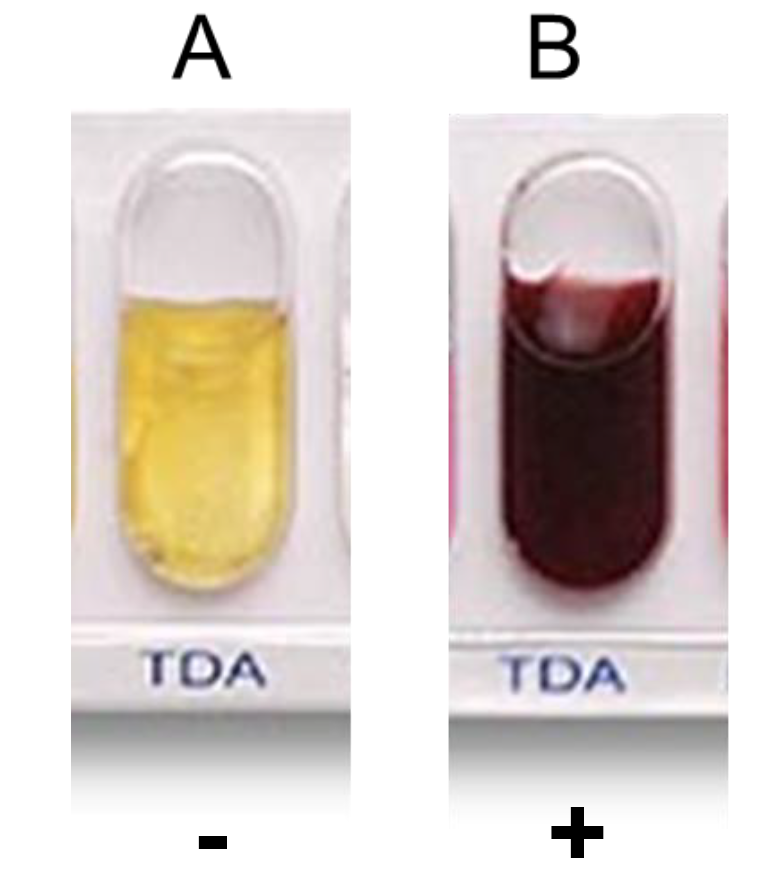
TDA*
Tryptophan Deaminase (TDA)*Determine if bacteria can deaminate tryptophan by tryptophan deaminase.
Post-incubation - TDA reagent added to determine if bacteria can deaminate tryptophan.
Positive test: turns reddish-brown
Negative: no color change
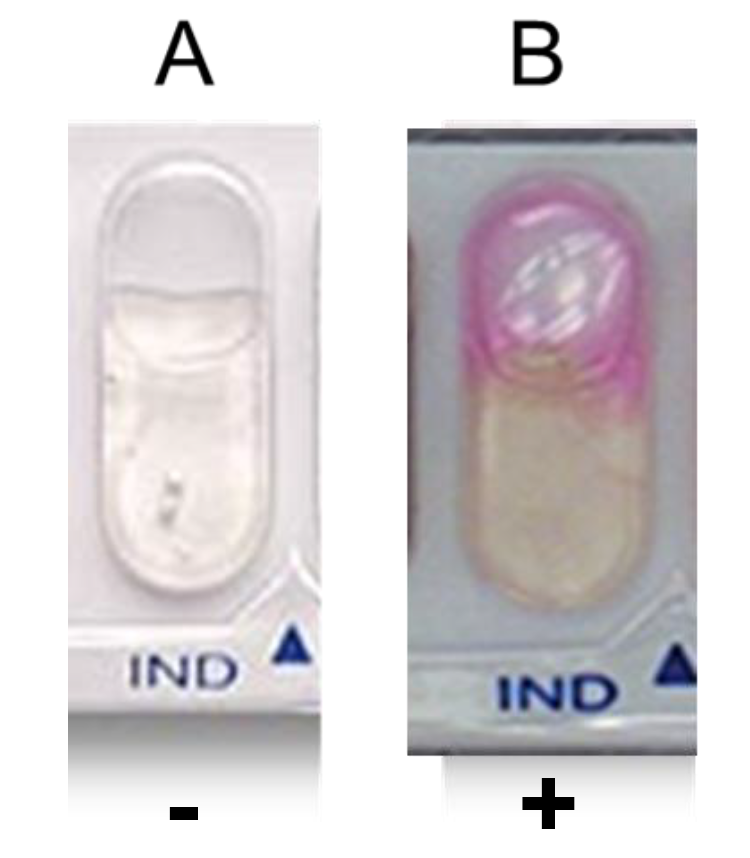
IND*
Indole (IND) Test*
Determine if bacteria can produce indole from tryptophan by tryptophanase
Post-incubation - add Kovac’s reagent to determine if bacteria can produce indole
Positive test: pink ring in cupule
Negative: no color change
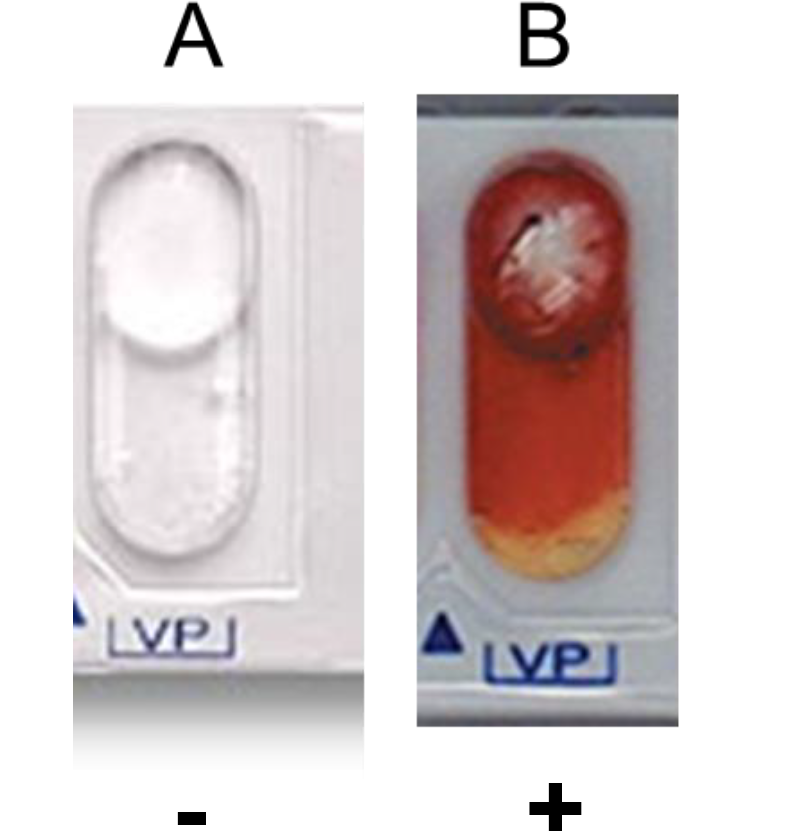
VP Test*
Voges-Proskauer (VP) Test*
To determine if bacteria produce acetoin from sodium pyruvate during 2,3-butanediol fermentation
Requires post-incubation test - 1 drop of VPA1 and 1 drop of VPA2. Wait 10 minutes.
Positive result: turns pink
Negative result: no color change
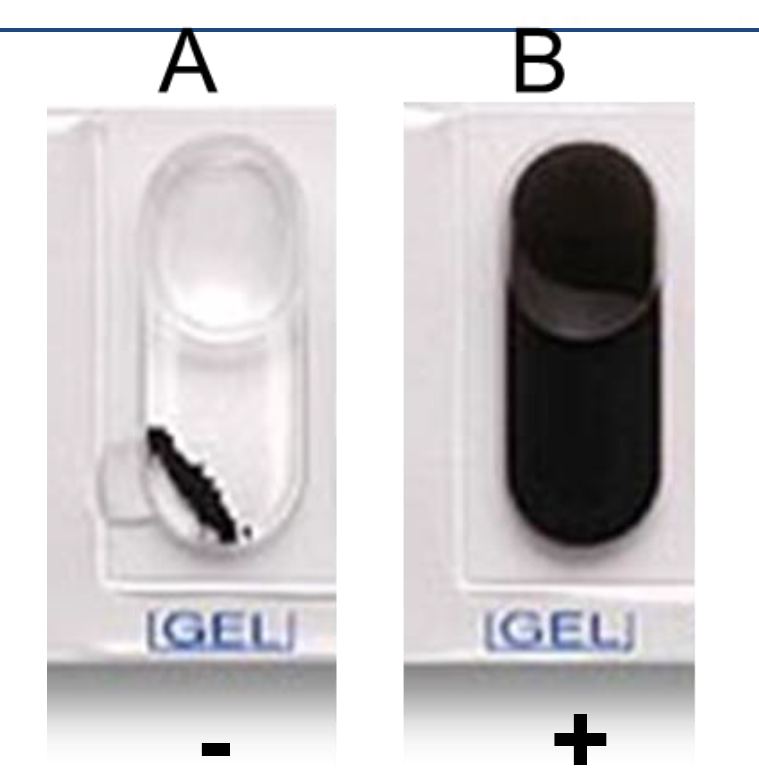
GEL
Gelatinase (GEL) Test
Determine whether bacteria can hydrolyze gelatin (Kohn’s charcoal gelatin) by gelatinase.

Carbohydrates Fermentation Test (GLU, MAN, INO, SOR, RHA, SAC, MEL, AMY, and ARA)
To determine whether bacteria can ferment or utilize a specific carbohydrate.
CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM
Cellular Respiration
Key pathways: Glycolysis ,Krebs Cycle, Electron Transport Chain
Fermentation
Key pathways: Glycolysis, Fermentation
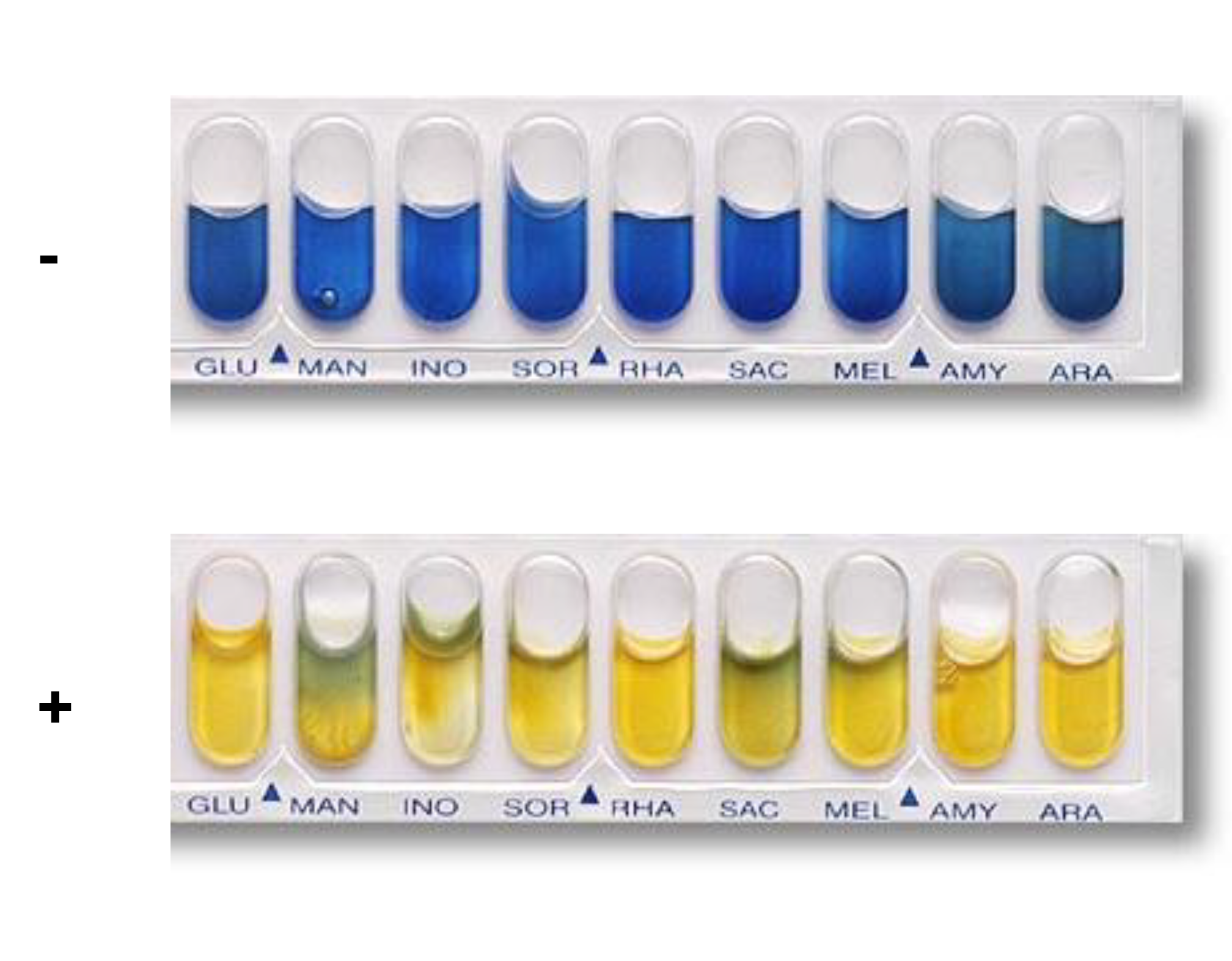
Why do we add mineral oil to a few of the API tests?
In order to create an anaerobic environment.
Add mineral oil to: ADH, LDC, ODC, H2S,URE.
Which tests require tube and cupule to be filled?
CIT
VP
GEL
Which tests required post-incubation testing?
GLU
IND
VP
MAN, INO, SOR
What is the purpose of the catalase test? Explain process of catalase test.
Purpose: to determine if bacteria are capable of producing the enzyme catalase..
During last stage of the electron transport chain (aerobic respiration), some protein may not follow path and sometimes flavoprotein (for example) bypass and will react directly with O2 to produce H2O2.
Occasionally, a superoxide radical is produced
Why are hydrogen peroxide and superoxide radicals toxic? How do organisms remove H2O2?
Hydrogen peroxide and superoxide radicals are toxic because they oxidize biochemicals and make them nonfunctional.
Most living organisms produce catalase which removes H2O2.
Add H2O2 to MAN, INO, SOR - if bubbles are produced, catalase is present (H2O2 catabolized into 2H2O and O2, water and gas).
What is the purpose of the nitrate reduction test?
To determine if bacteria reduce nitrate via anaerobic respiration.
Add reagent A (sulfanilic acid) and reagent B (alpha-napthylamine)
Red = positive for presence of nitrate reductase (
No color change = negative
Purpose of adding Kovac’s reaction to IND?
The Kovac’s reaction will react and turn fuchsia, indicating that the bacteria can produce indole (converts tryptophan to indole).
What is the purpose of the API 20E Strip Test?
To rapidly identify Enterobacteriaceae and other gram-negative rods.
What are the pH indicators in the API 20E test?
Phenol red
Bromothymol blue