biomolecules 2
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
carbohydrates
molecules that contains carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms
also known as a saccharide
single saccharide (monosaccharide), two monosaccharides (disaccharide), few linked monosaccharides (oligosaccharide), many monosaccharide (polysaccharide)
monosaccharide
simple sugar units
they have the empirical formula = (CH2O)n where n = 3-7 carbons
they are poly-hydroxy aldehydes or ketones
n = 3 carbons: triose
n = 5 carbons: pentose
n = 6 carbons: hexose
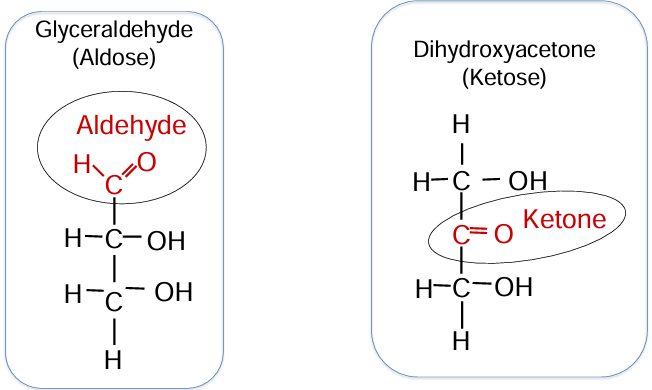
triose
glyceraldehyde (aldose) - aldehyde is on carbon 1
dihydroxyacetone (ketose) - ketone is in the middle
pentoses
important pentoses in biology:
ribose, deoxyribose - nucleotides (ATP, NAD), nucleic acid (DNA/RNA)
ribulose, xylulose - hexose-monophosphate shunt
xylose - glycoproteins
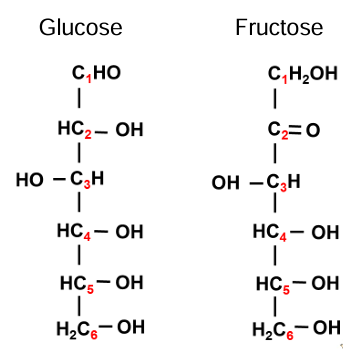
hexose
same chemical formula but different structures
these structures are called isomers
glucose: fruit juices, starch, glycogen, lactose, maltose, cane sugar
fructose: fruit juices, honey, cane sugar
galactose: milk (lactose)
mannose: plants and gums
cyclisation of monosaccharides
in an aldose, the carbonyl group is at C1
C1 in cyclized aldose = anomeric carbon
beta = OH group in up, alpha = OH group is down
in a ketose it all happens at carbons 2
glycosidic bond
the name or type of bond depends on the number of the connected carbons, the position of the anomeric hydroxyl group
if the OH group is in the alpha configuration it is an alpha bond and vice versa
example: lactose = beta-galactose + glucose
bod is between carbon 1 of beta-galactose and carbon 4 of glucose
bond is beta(1→4) glycosidic bond)
carbohydrates can also bond to non carbohydrate structures (purines, aromatic rings, proteins, lipids)
disaccharides
maltose: glucose alpha(1→4) glucose
lactose: galactose beta(1→4) glucose
polysaccharides
n > 12-hundreds
variations can occur in the chain: monosaccharides, glycosidic bonds, branch points, structure
example: amylopectin branched every 24-30 residues
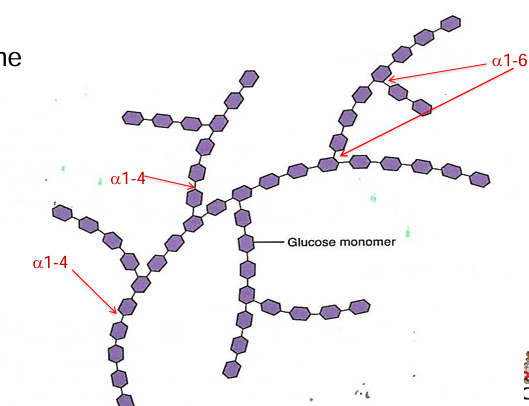
polysaccharide functions
storage in animals
glycogen: a homopolymer of glucose. branched every 12-14 residues (alpha1-4, alpha1-6)
storage in plants:
starch: a homopolymer of glucose; composed of amylose(non branches helical structure)
amylopectin (branched every 24-30 residues)
structure in plants
cellulose: homopolymer of glucose, long straight chains (beta1-4)
lipids
heterogeneous group of water insoluble (hydrophobic) organic molecules
functions:
major source of energy in the body
structural components of cells and organelles
involved in cellular signaling events e.g. steroids
fatty acid
hydrophobic hydrocarbon chain with terminal carboxyl group (unsaturated and saturated)
cis configuration means that two hydrogen atoms adjacent to the double bond stick out on the same side of the chain
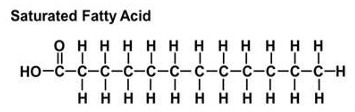
saturated FAs
carbon to carbon bonds are single
contain no double bonds
fully reduced or saturated with hydrogen atoms
highly flexible due to free rotation around single bonds
unsaturated FAs
contain double bonds - one db = monosaturated, more than one = polysaturated
if 2 or more db bonds: bond is spaced at 3 carbon intervals
position is specified by distance from carboxy end: e.g. ▲6 (delta 6) double bond is between carbon 6 and 7
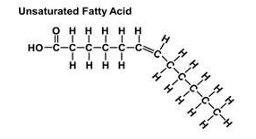
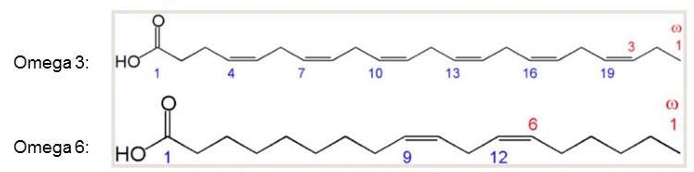
omega FA
omega refers to the position of the double bond from the omega end of the FA chain
omega 3 refers to the position of the final double bond, which is three carbons from the omega or tail end of FA
classification of lipids
fatty acids and their derivatives
lipids containing glycerol
neutral lipids: mono, di, tri-acylglycerol
charged lipids: phospholipids
lipids not containing glycerol
steroids, sphingolipids
lipoproteins and lipopolysaccharides
essential FAs
nutritionally essential as we cannot synthesize them in the body
linoleic acid (omega-6 FA)
alpha-linolenic acid (omega-3 FA)
triglycerides
made up of 3 FAs and glycerol
the principal storage form of energy in the body
stored in adipose tissue
diglycerol and monoacylglycerol
DAG
potent intracellular signaler
mobilization of calcium
MAG
breakdown product of TAG in fat digestion
phospholipids
major component of cell membrane
they are amphipathic: hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails
the hydrophilic head is negatively
sphingolipids
sphingosine + FA + R
when R if hydrogen → ceramide
when R is phosphocholine → sphingomyelin
when R is sugar → glycosphingolipid
steroids
contain a characteristic fused ring with a hydroxyl or keto group on carbon 3
one of the most essential steroids is cholesterol
functions as a metabolic precursor of vitamin D, bile acids, steroid hormone
plays a key role in structure of membranes
other major steroid classes: bile acids (24 carbons), progesterone (21 carbons) androgens (19 carbons), estrogens (18 carbons)
lipoprotein
spherical particles found in plasma that transport lipids including cholesterol
hydrophobic core of triacylglycerols and cholesterol esters
phospholipid layer associated with cholesterol and protein