translational - W7
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
RNA types and functions
Messenger (mRNA) = Carries genetic information from DNA to the ribosome. Synthesised by RNA pol II
Ribosomal (rRNA) = Structural component of ribosomes. Synthesised by RNA pol I
Transfer (tRNA) = Adaptor molecules between amino acid and mRNA. Synthesised by RNA pol III
how do antibiotics work?
have same translation process as eukaryotes except their ribosomes have 70s subunit instead of 80s subunit
antibiotics exploit this difference by targeting bacterial ribosomal subunits to preferentially inhibit bacterial protein synthesis.
typical recognition sequence by which intron can be spliced out
introns recognised by a GT on 3’ end of first exon and AG on 5’ end of second exon
UTR
Untranslated region – contains promoters and regions that do not fall into mature protein
snRNA function
small nuclear RNA
In spliceosomes involved in excising introns that allow exons to come together
important for base pairing and other interactions with pre-mRNA
spliceosome energy source
uses ATP hydrolysis as energy source to produce a complex series of RNA-RNA rearrangements
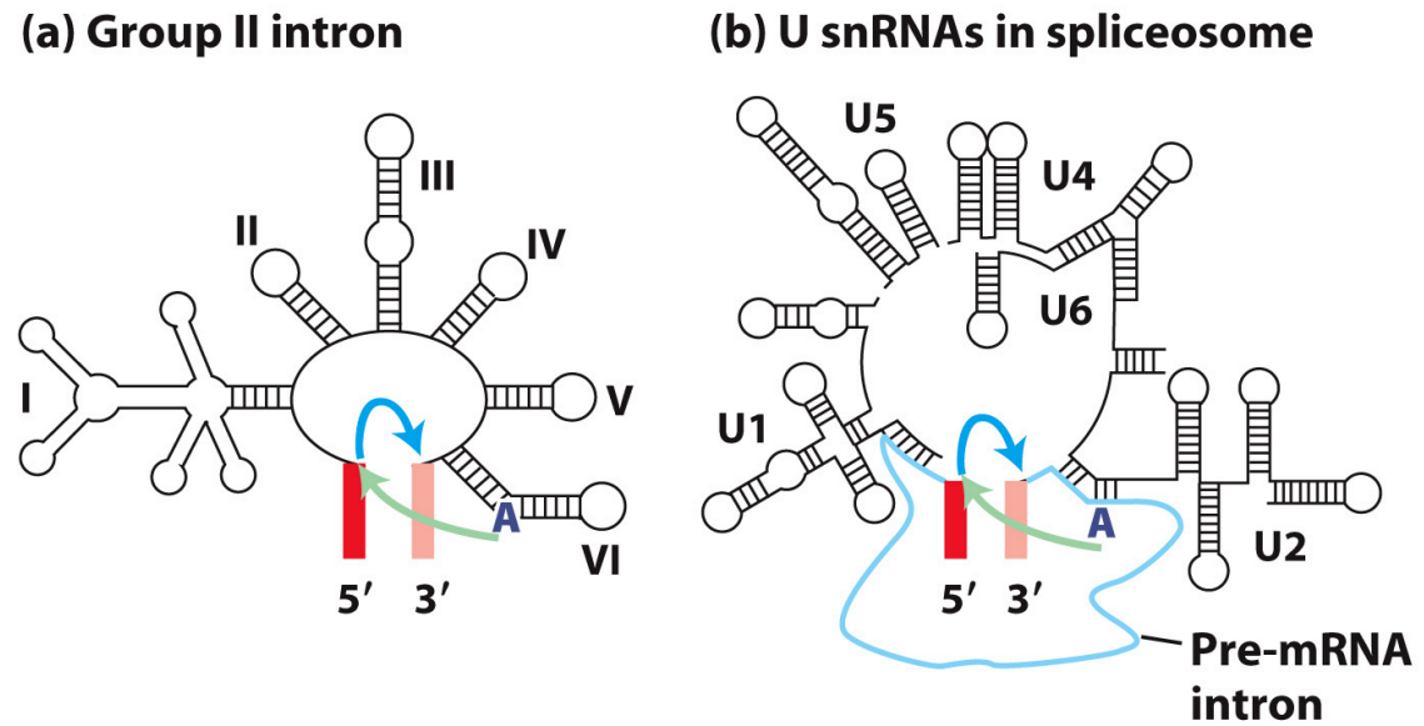
What Are Group II Introns?
a type of self-splicing RNA—they can remove themselves from RNA transcripts without any proteins or external enzymes.
They do this by forming a lariat structure and carrying out two transesterification reactions, which are chemically similar to the steps in pre-mRNA splicing in eukaryotic cells.

Evolutionary Hypothesis - Self-splicing group II introns
Scientists hypothesise that spliceosomal snRNAs evolved from ancient group II introns.
Over time, as cells became more complex, self-splicing introns may have lost their ability to act independently and instead gave rise to snRNAs, which now act in trans (i.e. they assist in splicing other RNA molecules rather than themselves).
This transition allowed for greater control and regulation of RNA processing in complex cells.
There is growing evidence that group II does occur, but most splicing in humans is through spliceosome
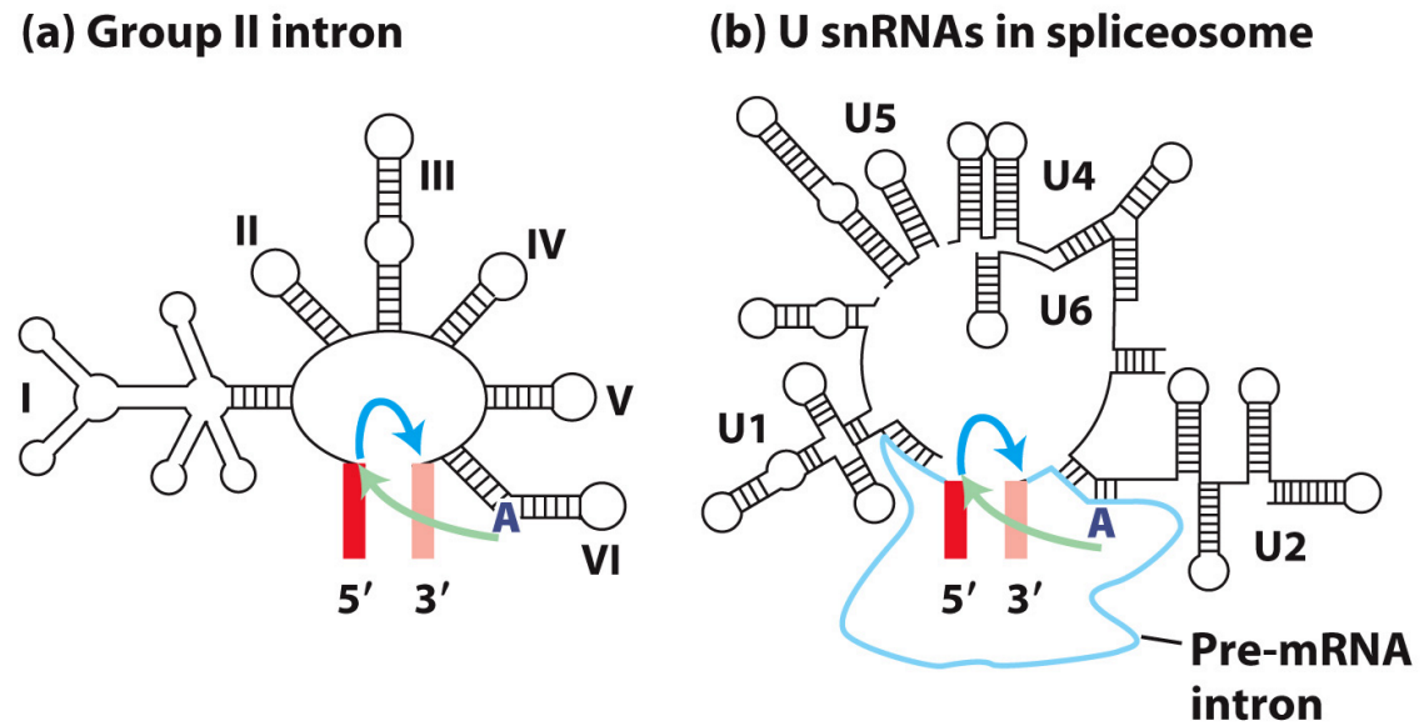
CD44 Isoform - cause and implications
extensive alternative splicing, producing multiple isoforms.
Isoform expression is tissue- and cell-type-specific = functional diversity.
Splicing determines binding capabilities and cellular localisation.
CD4 Isoforms & Cancer
CD44 isoforms are often upregulated in cancers, especially at the cell surface.
Promotes tumour cell migration, invasion, and metastasis.
Acts as a biomarker of cancer stem cells and supports epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT).
Soluble CD44 in serum correlates with tumour burden and metastasis, particularly in colon and gastric cancers.

What is involved in post-transcription control for RNA stability?
5′ Cap = methylated GTP added “backwards” → protects against 5′→3′ exonuclease degradation.
3′ Poly-A tail = adenine chain added to 3′ end → protects against 3′→5′ exonucleases.
Function: Both caps help ensure mRNA stability and proper translation.
Effect: More stable mRNA = longer lifespan in cytoplasm → more protein production.
Significance of mRNA decay
Once transported to cytoplasm, RNA reside time is controlled
Each RNA molecule has defined lifespan and decays at a specific rate
RNA lifespan (decay rate) = stability = controls how much protein is made:
↑ Decay rate = ↓ protein production.
↓ Decay rate = ↑ protein production.
Therefore… greater RNA stability = detectable for longer periods of time in the cytoplasm
RNA Binding protein (RBP)
RBPs influence RNA stability by binding to regions of mRNA just upstream or downstream from coding regions
UTR’s role in stabilisation
RBP bind to UTRs to influence stability:
Can stabilise or destabilise mRNA.
UTRs also regulate mRNA localisation, stability and protein translation.
post-transcriptional gene/ quality control purpose
ensure that improperly processed mRNA are degraded → constituent nucleotides can be reused for other purposes
performed by nuclear exonucleases + exosome complex
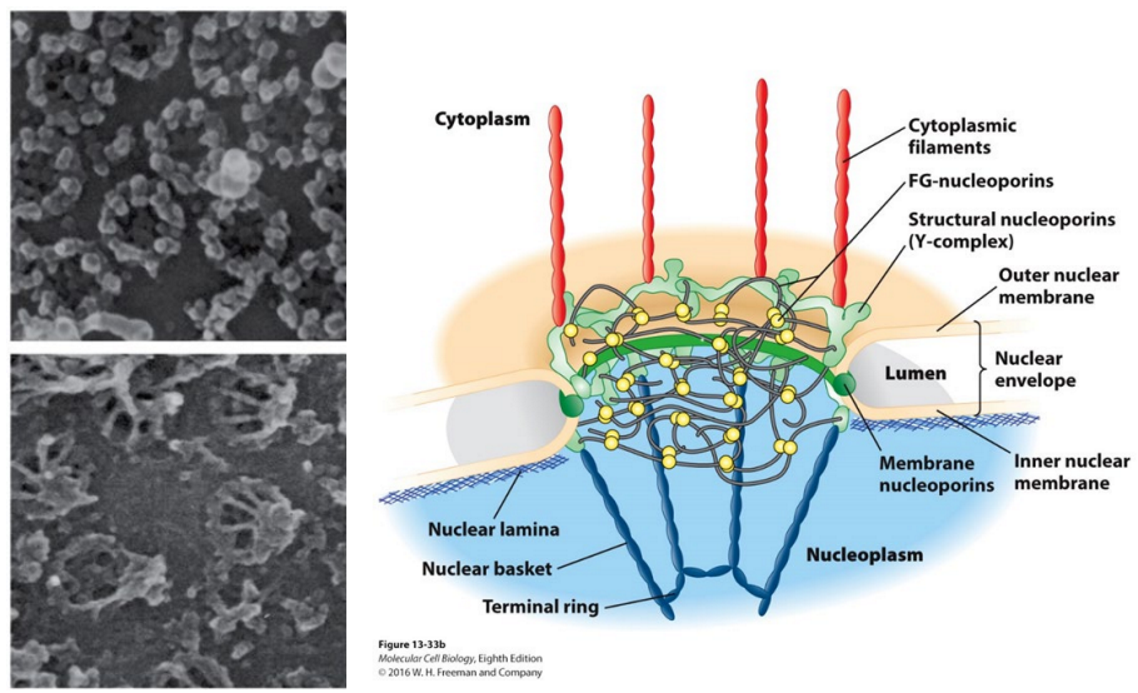
Function of nuclear pore complex
Exports mature mRNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm for translation.
Acts as a gateway for molecules entering and exiting the nucleus.
Structure of nuclear pore complex
channel-like structures at the interface between the nucleus and cytoplasm.
nuclear envelope contains two membrane system – separates nuclease from cytoplasm
Cytoplasm = continuous with ER membrane
ER = involved in protein synthesis
what does RNA pol I transcribe?
pre-rRNA → ribosomal components that provide components for protein translation
what does RNA pol II transcribe?
mRNA, snRNA, siRNA, miRNA → encodes protein, RNA splicing, chromatin-mediated repression, translational control
what does RNA pol III transcribe?
tRNA & other small stable RNA’s → make tRNA that transport amino acids involved in protein synthesis, snRNA involved in RNA splicing
what are non-coding RNAs?
RNAs that are transcribed but not translated into proteins, but still play have regulatory and structural functions that play important roles in gene regulation and maintaining homeostasis.
Include tRNA, rRNA, miRNA, siRNA, lncRNA, scaRNA.
function and composition of miRNA
Composition: Short, single-stranded RNAs
Post-transcriptional Role: imperfect/ perfect base pairing. Binds to 3' UTR of mRNA → represses translation or causes degradation
Relevance to Homeostasis: Controls expression of many genes (e.g. in stress, cancer, metabolism)
function and composition of siRNA
Composition: Short, double-stranded RNAs
Post-transcriptional Role: Perfect base pairing, specific to 1x mRNA. → rapid mRNA cleavage
Relevance to Homeostasis: viral defence and genome stability
function and composition of IncRNA
Composition: Long RNAs with no coding potential
Post-transcriptional Role: Guide, scaffold, or decoy for proteins/RNAs; regulate splicing and chromatin
Relevance to Homeostasis: Involved in paraspeckle formation, transcription regulation
function and composition of scaRNA
Composition: Small RNAs in Cajal bodies
Post-transcriptional Role: Modify snRNAs for splicing
Relevance to Homeostasis: Support proper mRNA processing
How do non-coding RNA’s help maintain homeostasis?
Control when and how much protein is made.
Allow the cell to quickly respond to internal signals or stress.
Prevent overproduction or misfolding of proteins.
Regulate inflammation, differentiation, metabolism, and stress responses.
what are Ribonucleoprotein Complexes (RNPs) ?
cytosolic biomolecular condensates/ complexes of RNA and proteins
form during phase separation of RNA + Protein
For SG formation, the aggregation of untranslating mRNAs at SGs requires which related proteins?`
G3BP1 and 2
what are the key enzymes in P-body’s?
key enzymes: DCP1, Xrn1 → decapping enzymes
how is p-body formation regulated?
⚡ ATPase Activity | Needed to maintain P-body structure – without ATP, P-bodies may not form |
🔁 Reversible Assembly | P-bodies can disassemble quickly if stress is removed or translation resumes |
🔧 Post-Translational Modifications (PTMs) | Regulate which proteins join or leave P-bodies: |
🧪 Stress-Dependence | P-bodies grow in number and size during stress, shrink or disappear when stress is gone |
β-thalassemia - Cause, Effect, Treatment
belongs to a group of inherited blood disorders
Cause: reduced or absent synthesis of the beta chains of haemoglobin
Effect:
low levels of haemoglobin lead to a lack of O2 in many parts of the body
shortage of TBC resulting in anaemia – can cause pale skin, weakness, fatigue and more serious complications
increased risk of developing abnormal blood clots
Treatment: regular blood transfusions

Transcriptional Error in β-thalassemia
Mutation in regulatory regions of the β-globin gene modifies transcription and RNA processing.
results in improper exon splicing or intron retention
Classified into β⁰ (no production) and β⁺ (reduced production) forms.
Nucleolus function
Makes rRNA and assembles ribosomes
Nuclear Speckles Function
Store and release splicing factors (pre-mRNA processing)
Cajal bodies function
Assemble spliceosome components (snRNPs)
Paraspeckles Function
Store and regulate RNAs that shouldn’t be translated immediately
PML bodies function
Respond to DNA damage; regulate apoptosis and stress responses