Travel Geography – Key Concepts for Final Exam (DTT 1213)
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards cover the Ring of Fire, tectonics, hazardous destinations, Malaysian forest types, a traditional Sabah dish, and related key facts for the DTT 1213 Travel Geography final.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What is meant by the Pacific “Ring of Fire”?
The ring of Fire is a string of volcanoes and sites of seismic activity, or earthquakes, around the edges of the Pacific Ocean Roughly 90 percent of all earthquakes occur along the Ring Of Fire, and the ring is dotted with 75 percent of all active volcanoes on Earth. The Ring of Fire is not quite a circular ring. There are 15 countries in the Ring of Fire.
Countries that lie within the Ring of Fire.
Possible answers: Indonesia, Japan, Philippines, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, United States, Chile, Canada, Guatemala, Russia, Peru, Solomon Islands, Mexico, or Antarctica.
Give two examples of dangerous tourism destinations mentioned in the notes.
Examples include: Kawah Ijen Lake (Indonesia), Kathmandu (Nepal), Aceh (Indonesia), areas of Japan prone to earthquakes, or regions of the United States with active volcanoes (e.g., Hawaii).
Identify the three main types of Malaysian forest highlighted in the notes.
1) Dipterocarp Forest, 2) Swamp (Peat Swamp) Forest, 3) Mangrove Forest.
Describe a key characteristic of Dipterocarp Forests in Malaysia.
They have a dense canopy with diverse hardwood species such as Meranti, Balau, and Kapur.
Give two typical tree species found in Malaysian Swamp (Peat) Forests.
Examples: Koompassia malaccensis (Kempas) and Gonystylus spp. (Ramin). Other acceptable species: Calophyllum spp. (Bintangor), Shorea platycarpa (Meranti paya), Sapotaceae sp. (Nyatoh), Cratoxylum spp. (Geronggang), Vatica spp. (Resak).
What unique root adaptations are common in Mangrove Forest plants?
Taproots, stilt roots, and pneumatophores that allow the plants to anchor in mud and obtain oxygen in tidal environments.
Which genus of trees dominates true Malaysian mangrove stands?
Rhizophora spp. (mangroves).
What is Ambuyat and in which Malaysian state is it a traditional dish?
Ambuyat is a sticky, glue-like starch paste traditionally eaten in Sabah (also in Brunei and Sarawak).
What utensil is traditionally used to eat Ambuyat and how is it employed?
A double-pronged bamboo stick called a Candas; diners twirl the paste around the prongs to form a bite-sized portion before dipping it into sauce.
Explain why Swamp Forest soils are usually acidic and waterlogged.
They form on deep peat (up to ~6 m) that retains water, leading to low oxygen levels and high acidity from accumulated organic matter.
Why are mangrove forests important to coastal ecosystems?
They stabilize shorelines, reduce erosion, provide nursery habitats for marine life, and act as buffers against storm surges.
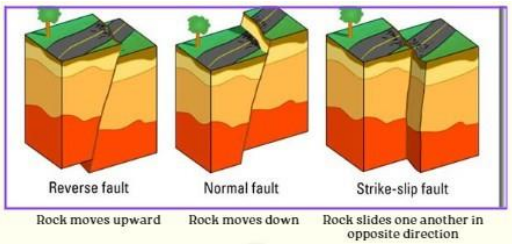
Illustrate plate tectonic movement
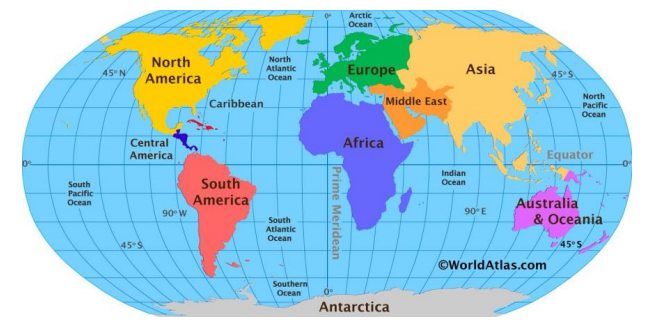
Label the name of continents