I HATE CNCM
Abruptio Placenta
A complication of late pregnancy or labor characterized by premature (early) partial / complete separation of the placenta from the uterus. Primary Cause is unknown
Occurs mostly around
25 wks of pregnancy
2nd leading cause of
Bleeding the 3rd; occurs in 1:300 pregnancies
Other terms
accidental miscarriage, ablatio placenta
Type I / Classic Type
Concealed, covert, central type. Placenta separates at the center, causing blood to accumulate behind the placenta. External bleeding not evident. Signs of shock are not proportional to the amount of external bleeding.
Type II / External bleeding type
Marginal, overt. Placenta separates at the margins. External bleeding (old, dark red) is usually proportional to the amount of internal bleeding. May be complete / incomplete depending on the degree of placental detachment
Type III / Mixed
Some part of the blood collects inside (concealed), and some parts expelled out (revealed)
Signs and Symptoms
Early Stages there may be no symptoms
Sudden onset abdominal pain
Contractions that seem continuous and won’t stop
Painful vaginal bleeding 3rd trimester
Rigid, board-like, and painful abdomen
Enlarged uterus disproportionate to the AOG
Decreased fetal movement and heart rate due to lack of nutrients and oxygen
If in labor: tetanic contractions with the absence of alternating contractions and relaxations of the uterus
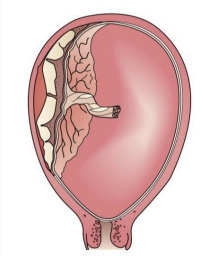
Partial separation (concealed hemorrhage)
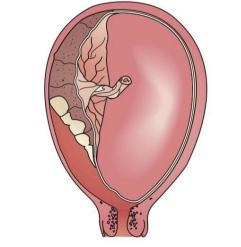
Partial Separation (Apparent Hemorrhage)
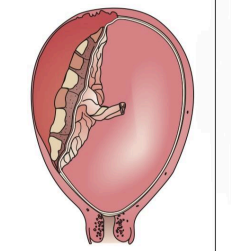
Complete Separation (Concealed Hemorrhage)
Grade 0
No symptoms of separation are apparent from maternal / fetal signs
Diagnosis is made after birth when placenta is examined and a segment of the placenta shows a recent adherent clot on the maternal surface
Grade 1
Minimal separation; not enough to cause vaginal bleeding and changes in maternal vital signs
No fetal distress or hemorrhagic shock occurs
Grade 2
Moderate separation
No evidence of fetal distress
Uterus is tense and painful on palpation
Grade 3
Extreme Separation
Maternal hypovolemic shock and fetal death will result if without immediate intervention
Complications
Hemorrhagic Shock
Couvelaire Uterus
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
CVA cerebrovascular accident from DIC
Hypofibrinogenemia
Renal failure
Infection
Prematurity; fetal distress/ demise (IUFD)
Couvelaire Uterus
The bleeding behind the placenta may cause some of the blood to enter the uterine musculature causing the uterine muscles not to contract well once the placenta is delivered
Therapeutic Management / Treatment
Assess and monitor vaginal bleeding
Place woman on bedrest in lateral position to prevent pressure on vena cava
Obtain blood sample for fibrinogen level
Insert large gauge IV catheter into large vein for fluid replacement
Monitor FHR and measure maternal vital signs every 5-15 minutes
Administer oxygen to the mother by mask (limits fetal anoxia)
Administer IV fluid, plasma, or blood as ordered
Nursing Implementation
Maintain bedrest
Careful monitoring: maternal VS, FHT, labor onset/progress, I&O oliguria/anuria, uterine pain, bleeding
Administer IN fluid, plasma, or blood as ordered
Prepare for an emergency birth either per vagina or CS
Observe for associated problems after delivery
Observe for associated problems after delivery
Poorly contracting uterus (Couvelaire uterus) > postpartal hemorrhage
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) > hemorrhage and possibly CVA
Hypofibrinogenemia > postpartal
hemorrhage