ALL PRE-LABS
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
When Grignard reagent is added to carbon dioxide, grignard reagent is acting as:
(Lab2: grignard reaction)
Nucleophile
Why is it extremely important to make sure your equipment is absolutely dry in the step of generating Grignard reagent?
(Lab2: grignard reaction)
Formed Grignard reagent quickly reacts with water
When comparing phenyl bromide and benzoic acid which compound do you expect to have a higher polarity?
(Lab2: grignard reaction)
Benzoic acid
When comparing benzoic acid and sodium benzoate, which compound do you expect to have a better solubility in water? (Lab2: grignard reaction)
Sodium benzoate
How would you characterize your product for Lab 2: grignard reaction?
Melting point and IR analysis

(Lab 3-polymerization)
Polyamide via step-growth mechanism
What promotes polymerization of styrene in the experiment?
(Lab 3-polymerization)
Free radicals formed by decomposition of benzoyl peroxide
Nylon 6, 10 is an example of
(Lab 3-polymerization)
Condensation polymer
Polystyrene is an example of
(Lab 3-polymerization)
Addition polymer
Why does addition of borax to the polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) affect its physical properties?
(Lab 3-polymerization)
Due to formation of boron cross-linking sites between PVA chains
Nitration of aromatic compounds is an example of
(Lab 3-polymerization)
Electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction
How can you determine which isomer you obtained from the nitration experiments?
(Lab 3-polymerization)
Melting point and NMR analysis
How can you determine the purity of the products that you obtained from the nitration experiment?
(Lab 3-polymerization)
Melting point and NMR

(Lab 3-polymerization)
Ortho

(Lab 3-polymerization)
5
Fischer esterification is a reaction that combines ___to yield an ester and water.
(Lab 5: Fischer esterification)
An alcohol and an acid (with catalysis)
An esterification process is what kind of reaction?
(Lab 5: Fischer esterification)
Condensation
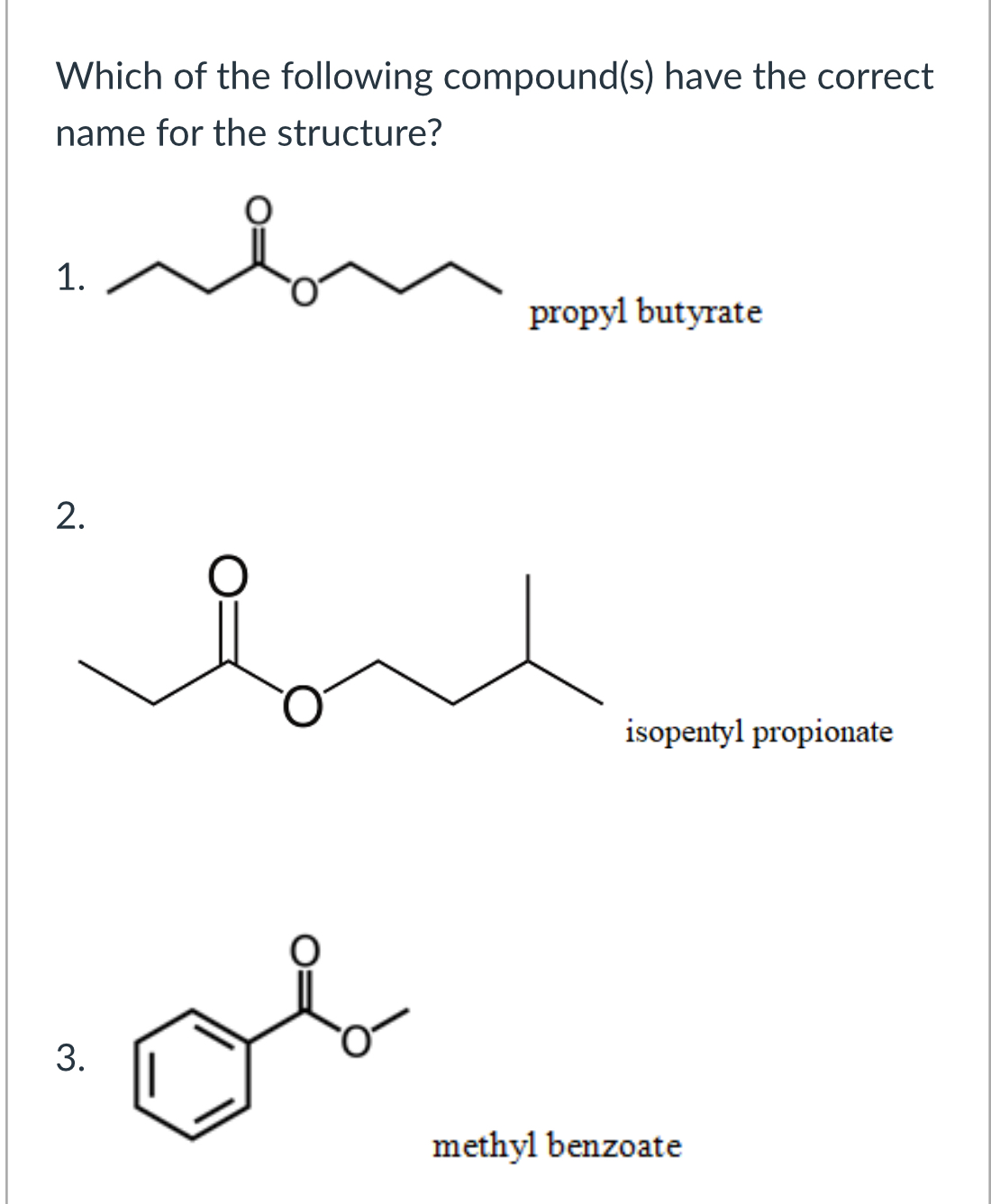
(Lab 5: Fischer esterification)
2 and 3
Which of the following compounds will have the lowest boiling point? (estimate the size, polarity and ability to form hydrogen bonding):
(Lab 5: Fischer esterification)
Methyl acetate
What functional group will be formed in today’s synthesis of aspirin?
(Lab 6: aspirin synthesis)
Ester
What is the role of H2SO4 in this reaction?
(Lab 6: aspirin synthesis)
Catalyst
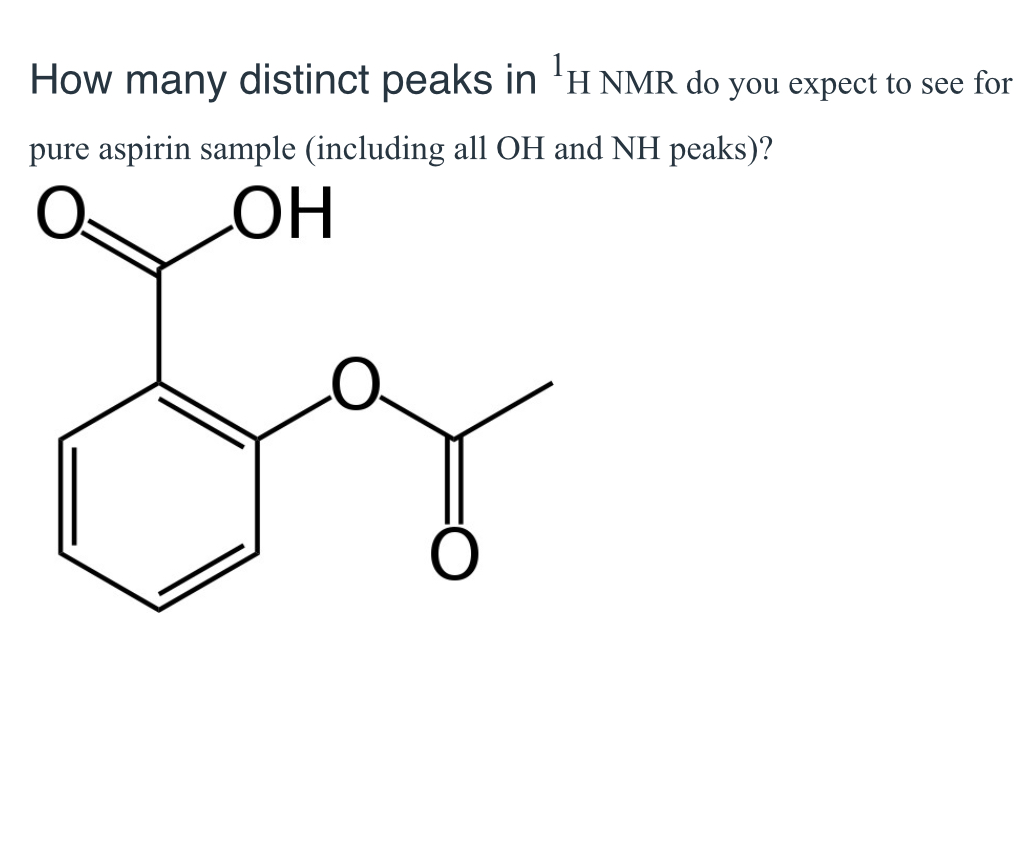
(Lab 6: aspirin synthesis)
6
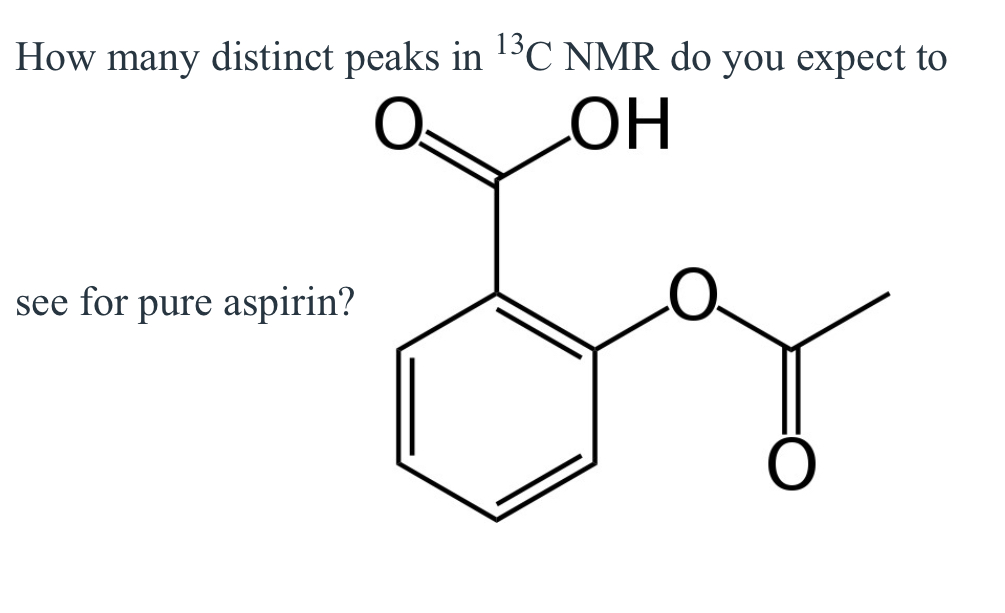
(Lab 6: aspirin synthesis)
9
The nucleophilic reagent used in Wittig reaction is called:
(Lab 7: Wittig reaction)
ylide
The electrophile used in today’s Wittig reaction is:
(Lab 7: Wittig reaction)
Aldehyde
How will you generate an ylide in today’s experiment?
(Lab 7: Wittig reaction)
Deprotonating a phosphonium salt with sodium hydroxide
Which functional group is generated in the process of Wittig reaction between an aldehyde and ylide?
(Lab 7: Wittig reaction)
Alkene
In today’s experiment, we purify the final product by
(Lab 7: Wittig reaction)
Recrystallization
How will you break your polyethylene terephthalate (PET) sample?
(Lab 8: braking down plastics)
By heating it with a strong base
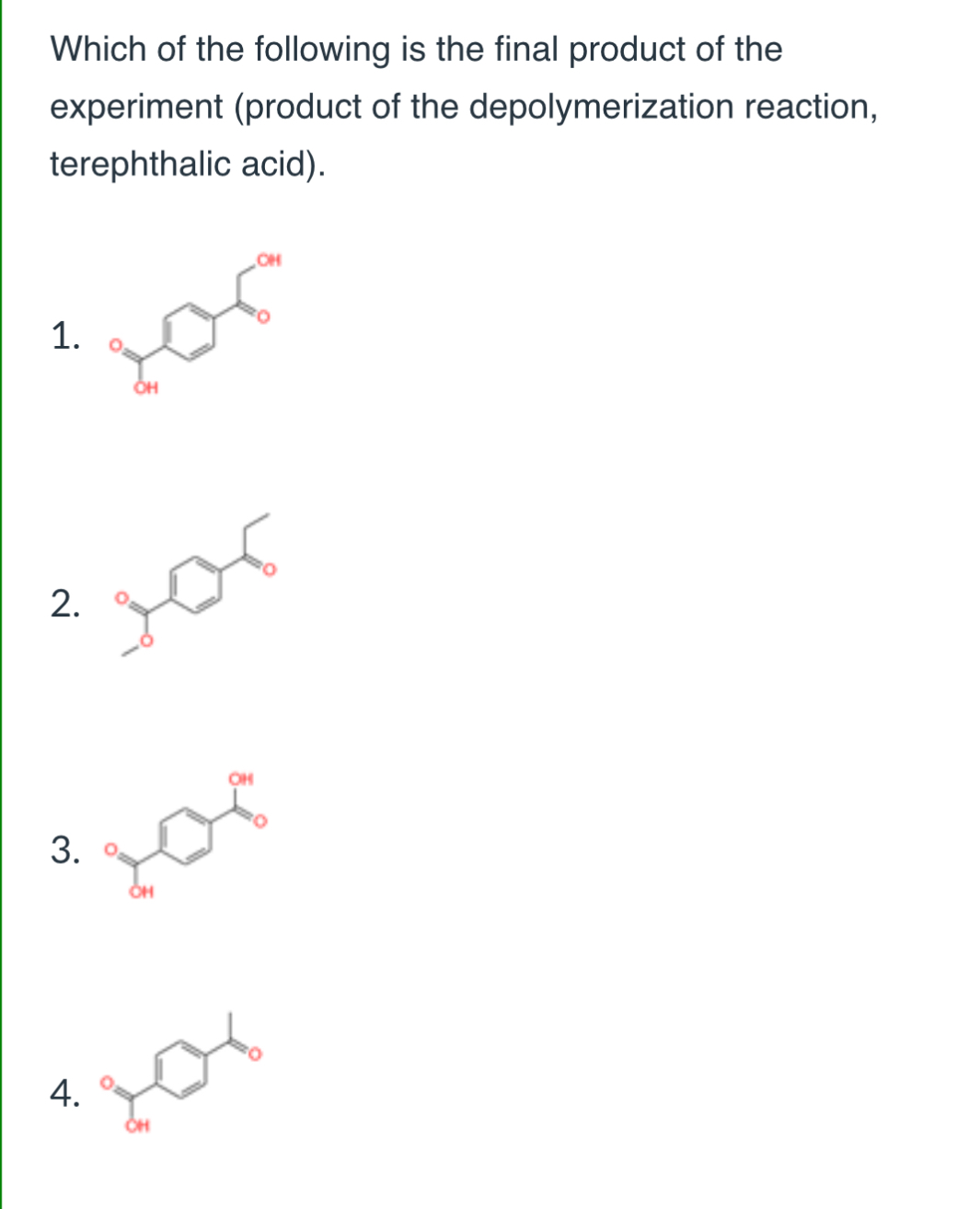
(Lab 8: braking down plastics)
3
Which of the following characteristics peaks are you expecting to see from your product in the IR spectrum?
(Lab 8: braking down plastics)
- peak at ~1700cm & 3000cm
-broad peak at 3100-3500
What is mainly responsible for a drastic difference in solubilities in water between terephthalic acid and potassium terephthalate?
(Lab 8: braking down plastics)
Ionic nature of COOK groups
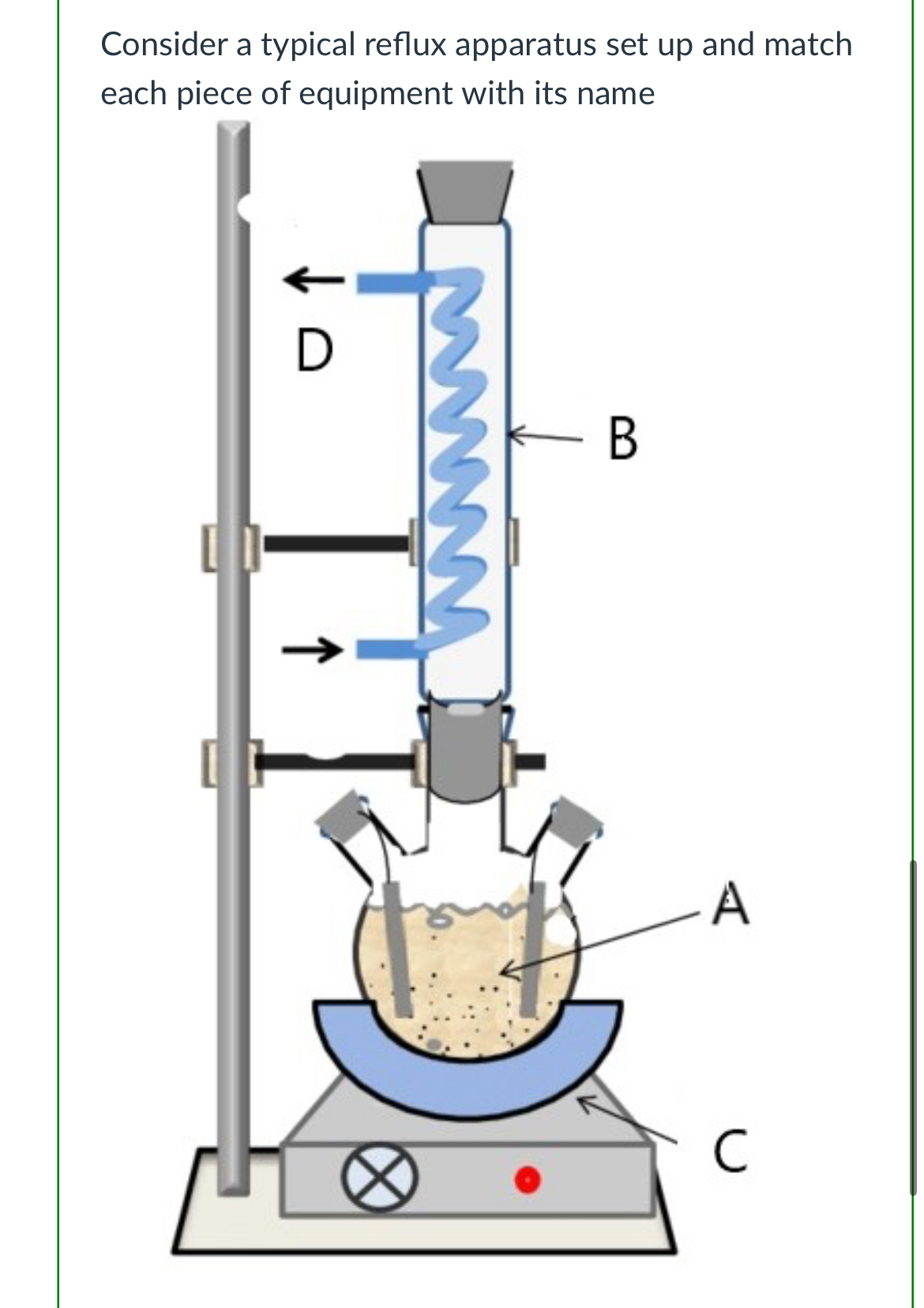
(Lab 8: braking down plastics)
A- reaction mixture
B- reflux condenser
C- heating mantle
D- water running through condenser to help condense the vapors
Aldol condensation reaction is used extensively in organic synthesis to make
(Lab 9: Aldol Condensation)
C=C bonds
Enolate ion is a very strong:
(Lab 9: Aldol Condensation)
Nucleophile
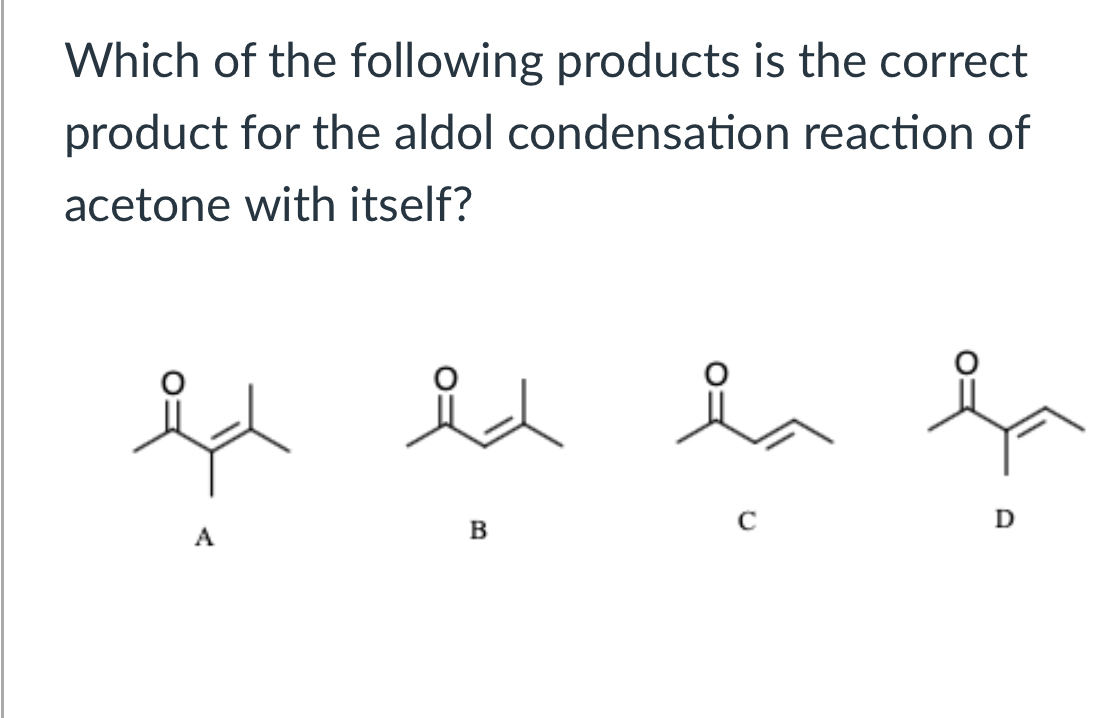
(Lab 9: Aldol Condensation)
B
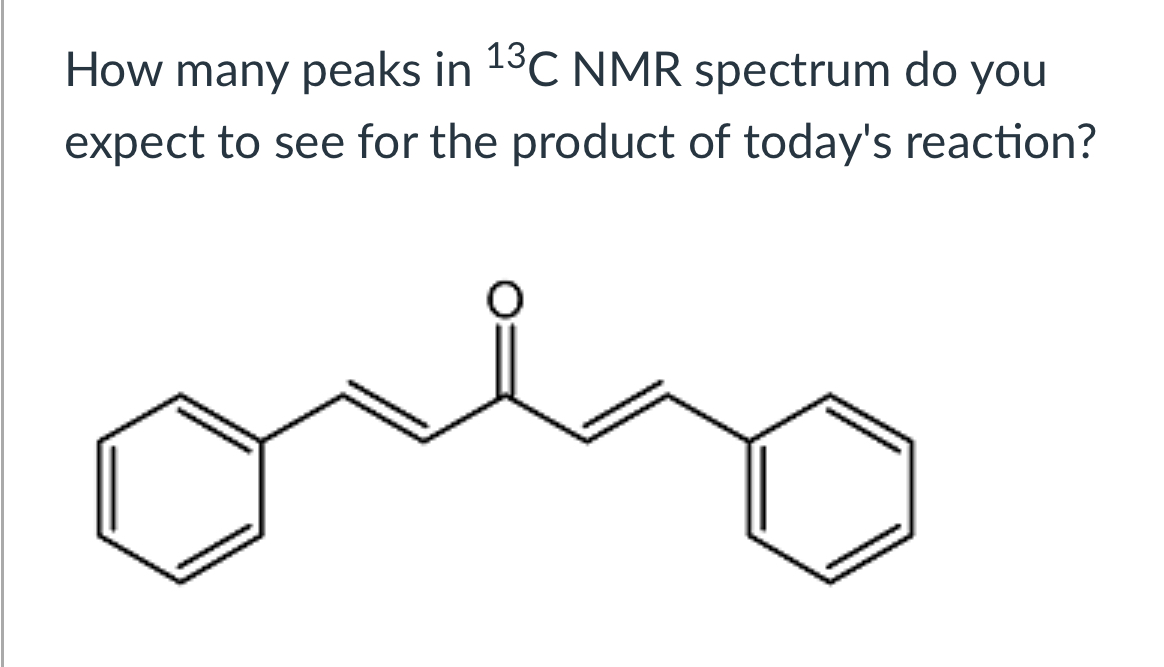
(Lab 9: Aldol Condensation)
7
During recrystallization step is very important to:
(Lab 9: Aldol Condensation)
Use minimal amount of solvent in order to create supersaturated solution
Which of the following is the unstable acid that is generated upon reaction of sodium nitrite with hydrochloric acid?
(Lab 10: Azo Dyes)
HNO2
What’s the purpose of the initial mixing of sulfanilic acid with aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution?
(Lab 10: Azo Dyes)
To solubilize the staring acid
What will happen if the diazonium salt is not kept cooled and it is allowed to warm up?
(Lab 10: Azo Dyes)
It decomposes at room temperature
Methyl orange is used as an acid-base indicator. Describe the color change that is expected when you added excess acid to the basic solution of methyl orange.
(Lab 10: Azo Dyes)
Color changes from yellow to red
Which method is used to analyze methyl orange in this experiment?
(Lab 10: Azo Dyes)
UV-Vis spectroscopy