Cell Structure and Function
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Cell Theory
All organisms consist of cells
The cell is the basic unit of structure for all organisms
All cells arise from preexisting cells
Micrometer
unit of measurement for cells
Nanometers
unit of measurement for subcellular structures and molecules
Angstrom (Å)
0.1 nm
Limit of resolution
how far apart objects must be to appear as distinct
Resolving Power
ability to see fine details
Categories of proteins
Enzymes
Structural proteins
Motility proteins
Regulatory proteins
Transport proteins
Signaling proteins
Receptor proteins
Defensive proteins
Storage proteins
Disulfide bonds
covalent bonds formed between cysteine amino acids
Intramolecular disulfide bonds
bonds that form between cysteines in the SAME polypeptide
Intermolecular disulfide bonds
bonds that for between cysteines in DIFFERENT polypeptides
Primary structure
amino acid sequence
Secondary structure
local folding of the polypeptide that results from hydrogen bonding
Motifs
units of secondary structure consisting of short stretches of alpha helices and beta sheets
Tertiary structure
3D conformation, the hydrogen bonding is maximized in the overall fold of the protein
Quaternary structure
interactions between monomeric proteins to form multimeric units, the level of organization concerned with subunit interactions and assemby
Monomeric proteins
proteins that consist of a single polypeptide
Multimeric proteins
proteins that consist of two or more polypeptides
RNA
contains five-carbon sugar, responsible for information transmission
DNA
deoxyribose, has genetic information
Types of nucleotides
Adenine
Guanine
Thymine
Uracil
Cytosine
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek
the first person to observe living cells
Enzymes
serve as catalysts of chemical reactions in the body
Structural proteins
provide physical support and shape to cells and organelles
Motility proteins
play key roles in the contraction and movement of cells and intracellular materials
Regulatory proteins
responsible for control and coordination of cellular functions
Transport proteins
involved in he movement of other substances into, out of, and within the cell
Signaling proteins
mediate communication between cells in an organism
Receptor proteins
enable cells to respond to chemical stimuli from their environment
Defensive proteins
provide protection against disease
Storage proteins
serve as reservoirs of amino acids
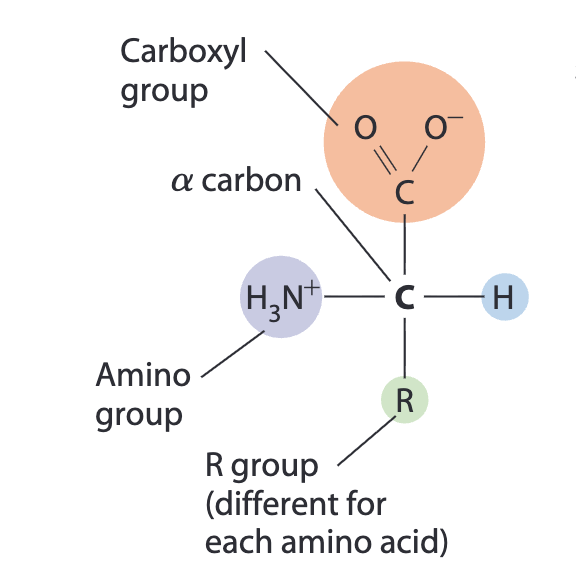
Structure of an amino acid
carboxyl group, amino group, hydrogen atom, R group, and alpha carbon
Condensation reaction
the process of stringing individual amino acids together into a linear polymer by adding each new amino acid to the growing chain
Peptide bond
a C—N bond linking two amino acids