Endo/Repro Exam 2: Pathology OB/GYN, Breast and Female Genitalia (Dr. Menon)
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
What type of inflammatory disease of the breasts?
- Infection of breast associated with lactation
- Seen during early weeks of breast-feeding
- Breast erythematous and painful
- S. aureus gain access to tissue through cracks and fissures in nipple & areola
- Treatment-Antibiotics
Acute mastitis
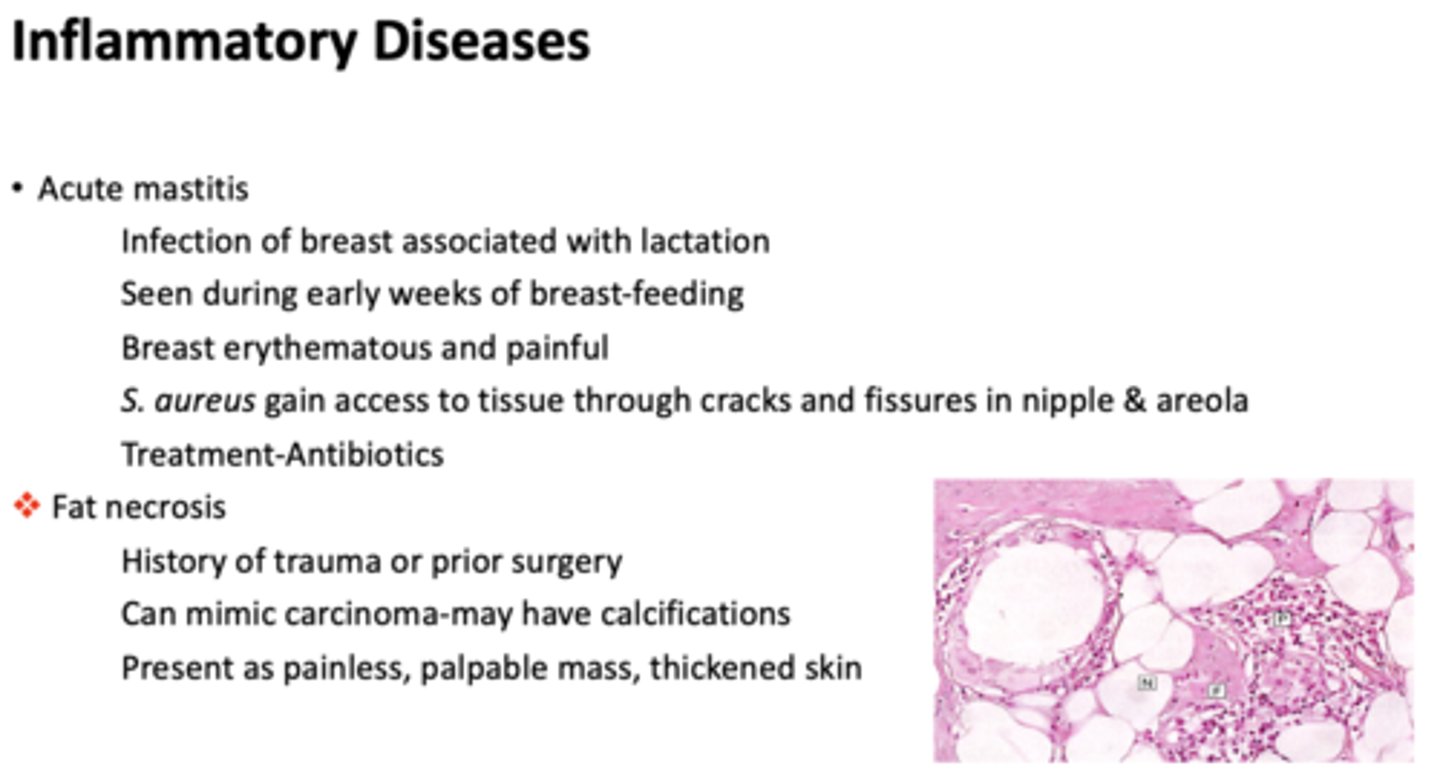
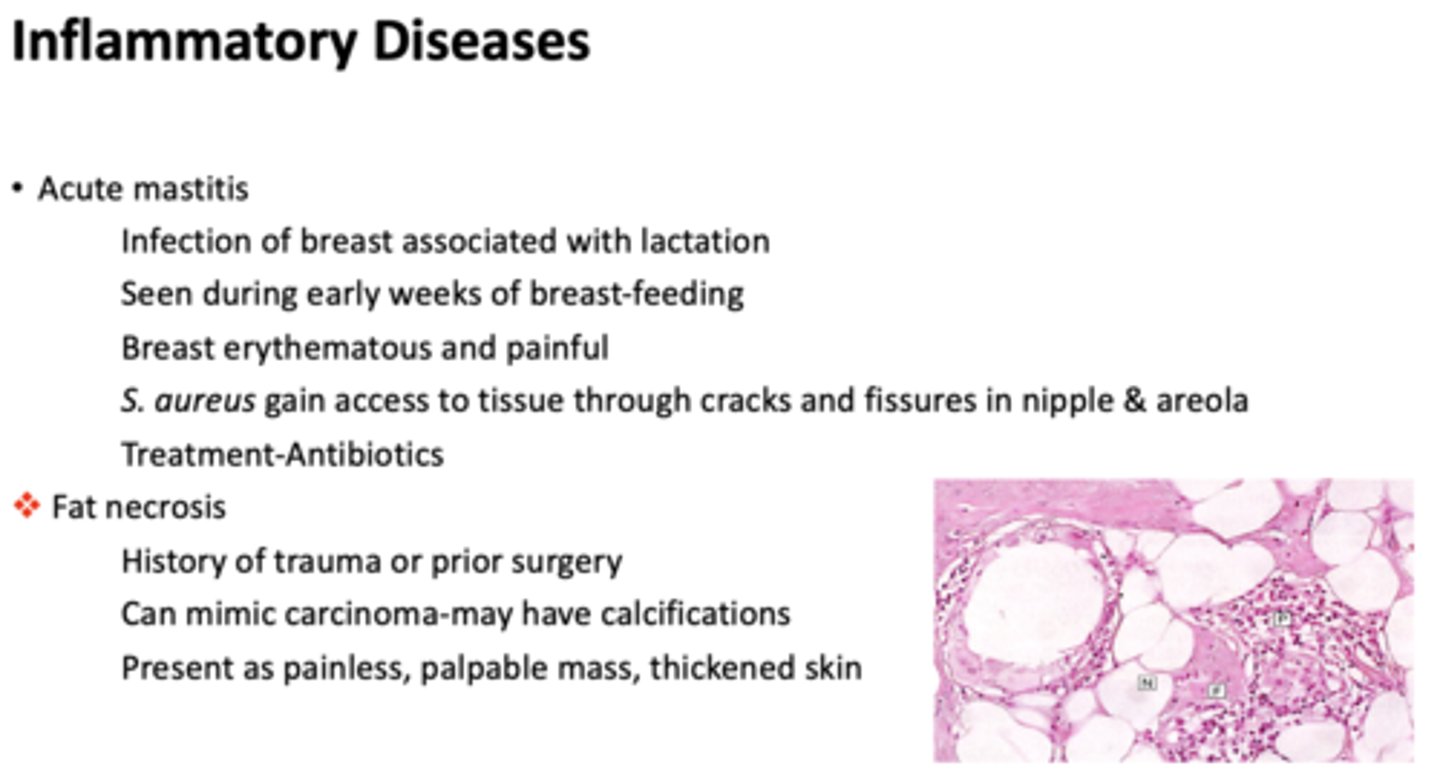
What type of inflammatory disease of the breasts?
- History of trauma or prior surgery
- Can mimic carcinoma-may have calcifications
- Present as painless, palpable mass, thickened skin
fat necrosis
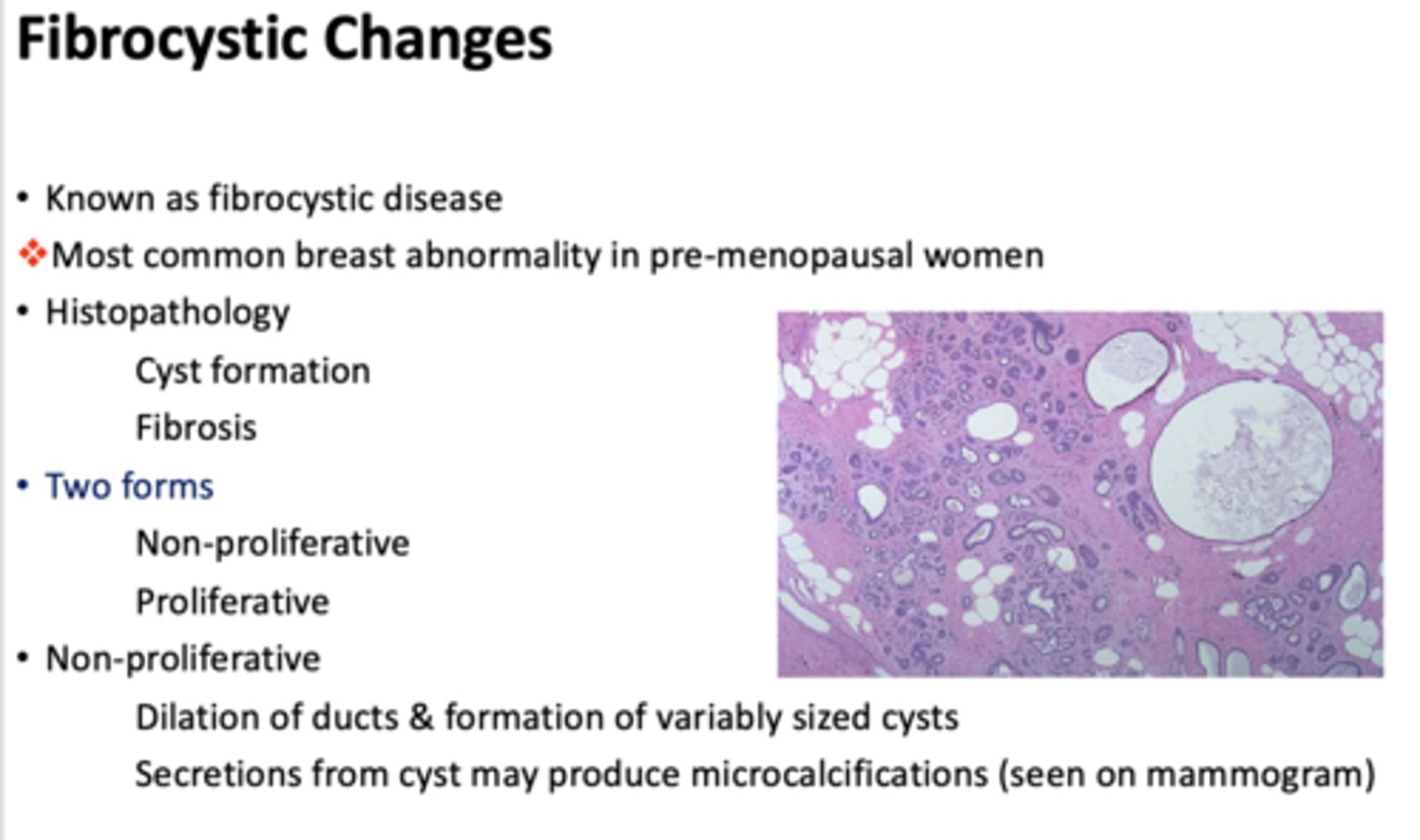
what is the most common breast abnormality in pre-menopausal women?
fibrocystic disease
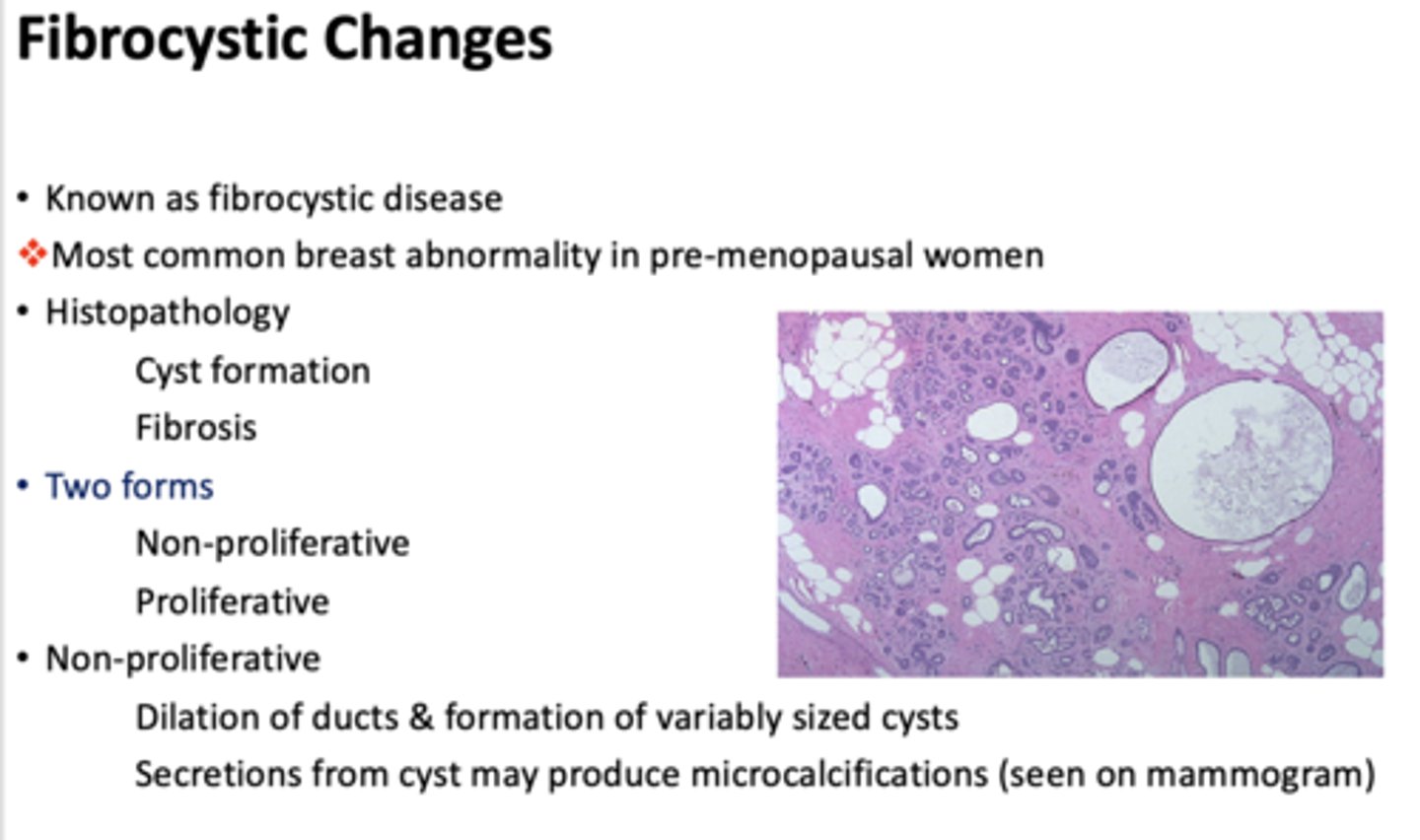
What type of fibrocystic disease?
- Dilation of ducts & formation of variably sized cysts
- Secretions from cyst may produce microcalcifications (seen on mammogram)
non-proliferative
What type of fibrocystic disease?
- Can be bilateral & multifocal
- Increased risk of carcinoma for both breasts
proliferative

What type of fibrocystic disease are the following examples?
- Epithelial hyperplasia
- Sclerosing adenosis
- Intraductal papilloma
proliferative

What type of proliferative fibrocystic disease?
- Can resemble carcinoma in-situ
- Presence of more than two cell layers
- Can see ductal papillomatosis
- Atypical hyperplasia (ductal/lobular)- increased risk for invasive carcinoma
epithelial hyperplasia

What type of proliferative fibrocystic disease?
- Less common
- Can mimic carcinoma-clinical and morphologic features
- Has hard, rubbery consistency like breast carcinoma, calcifications may be present
- Intralobular fibrosis & proliferation of small ducts & acini
sclerosing adenosis

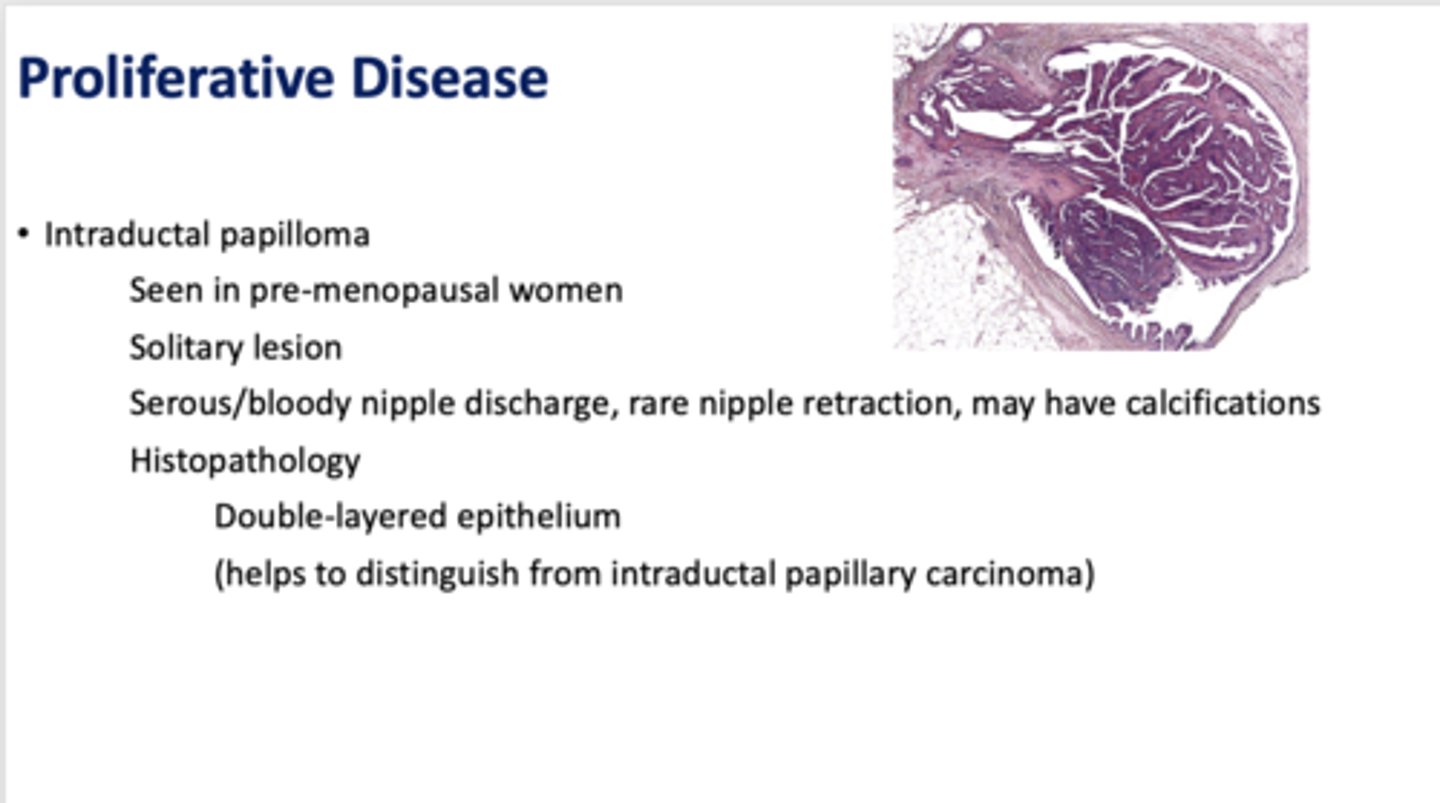
What has the following characteristics:
- Seen in pre-menopausal women
- Solitary lesion
- Serous/bloody nipple discharge, rare nipple retraction, may have calcifications
- Histopathology
- - Double-layered epithelium
- - (helps to distinguish from intraductal papillary carcinoma)
Intraductal papilloma
Most common benign tumor of the breast:
fibroadenoma

What has the following characteristics:
- Affects young women around 3rd decade
- Presents as a solitary, movable mass
- May present with calcifications
- Can be bilateral
fibroadenoma

What has the following characteristics:
- Enlargement of male breast
- Results from excess estrogen
- Causes:
- - Liver cirrhosis (liver metabolizes estrogen)
- - Anabolic steroids
- - Klinefelter syndrome
Gynecomastia

What is the most common malignancy of women?
breast carcinoma

Which of the following is not considered an etiology/Risk factors for breast carcinoma?
a. Age and estrogen stimulation
b. Race/Ethnicity
c. Overexpression of HER2/Neu
d. BRCA gene (tumor suppressor gene)
e. Family history/Previous history
f. Nulliparity
g. Late birth of first child-after age 30
h. Early menarche/late menopause
i. None of the above
i. None of the above (all are risk factors - see image)

What is the most common quadrant for breast carcinoma?
upper outer quadrant
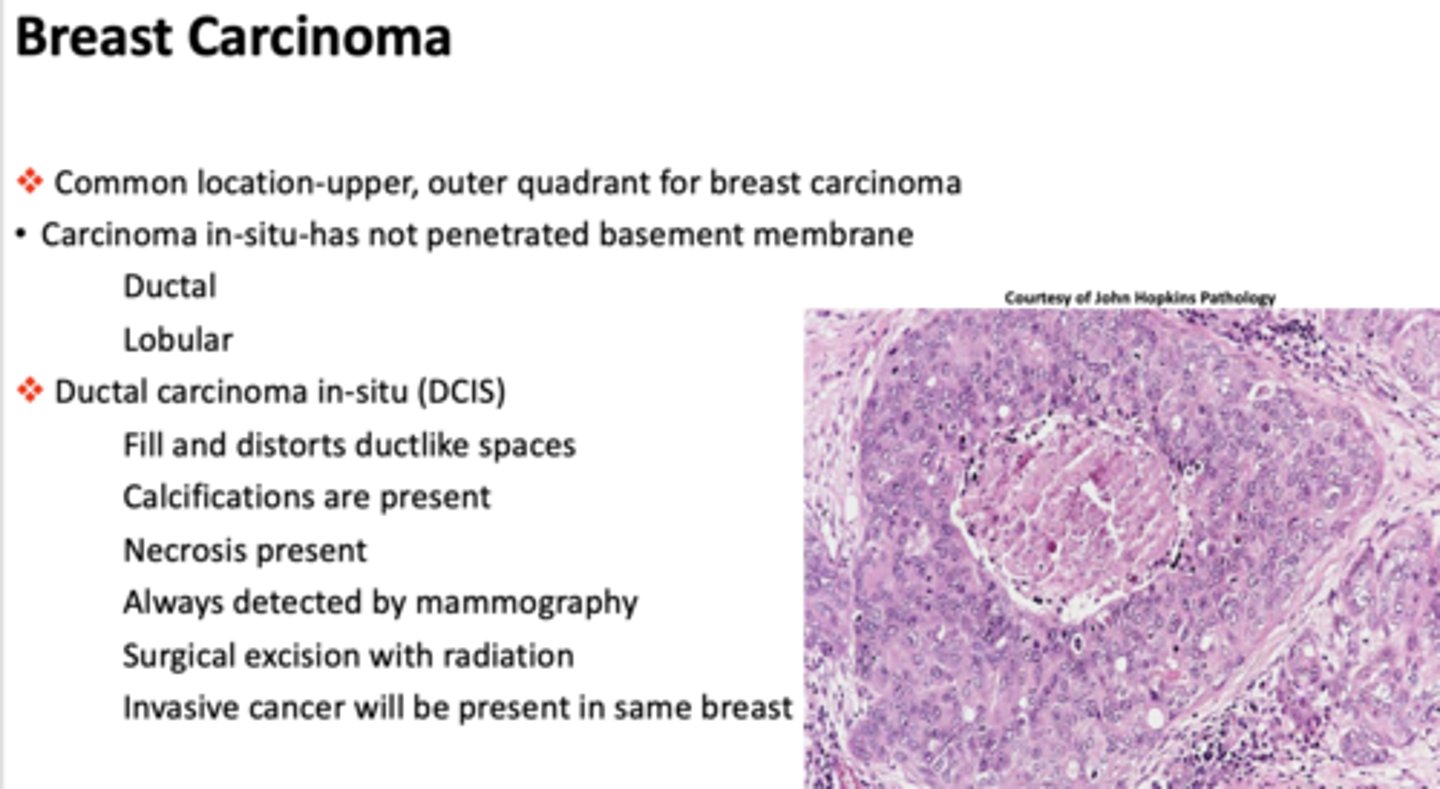
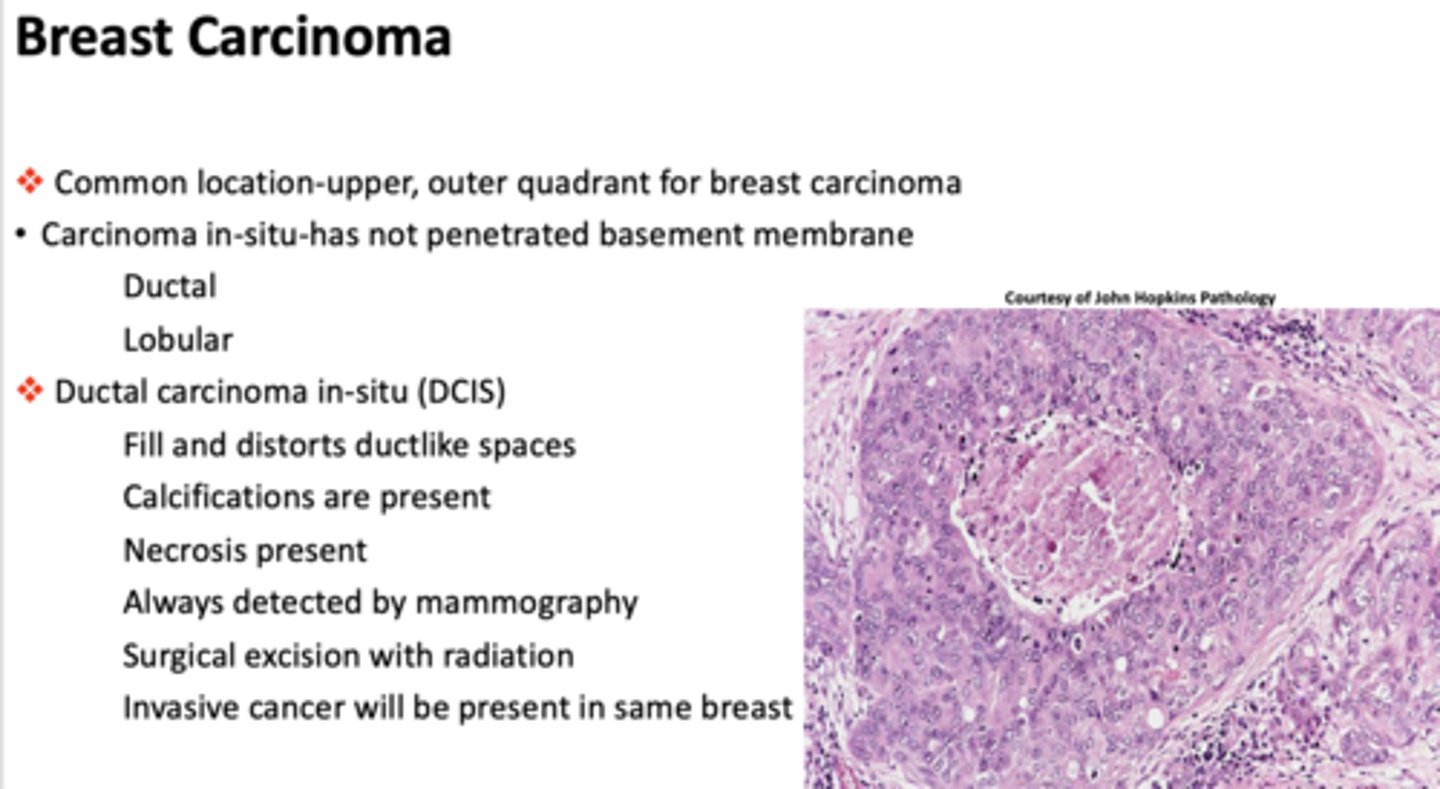
What breast condition is the following?
- Fill and distorts duct-like spaces
- Calcifications are present
- Necrosis present
- Always detected by mammography
- Surgical excision with radiation
- Invasive cancer will be present in same breast
ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
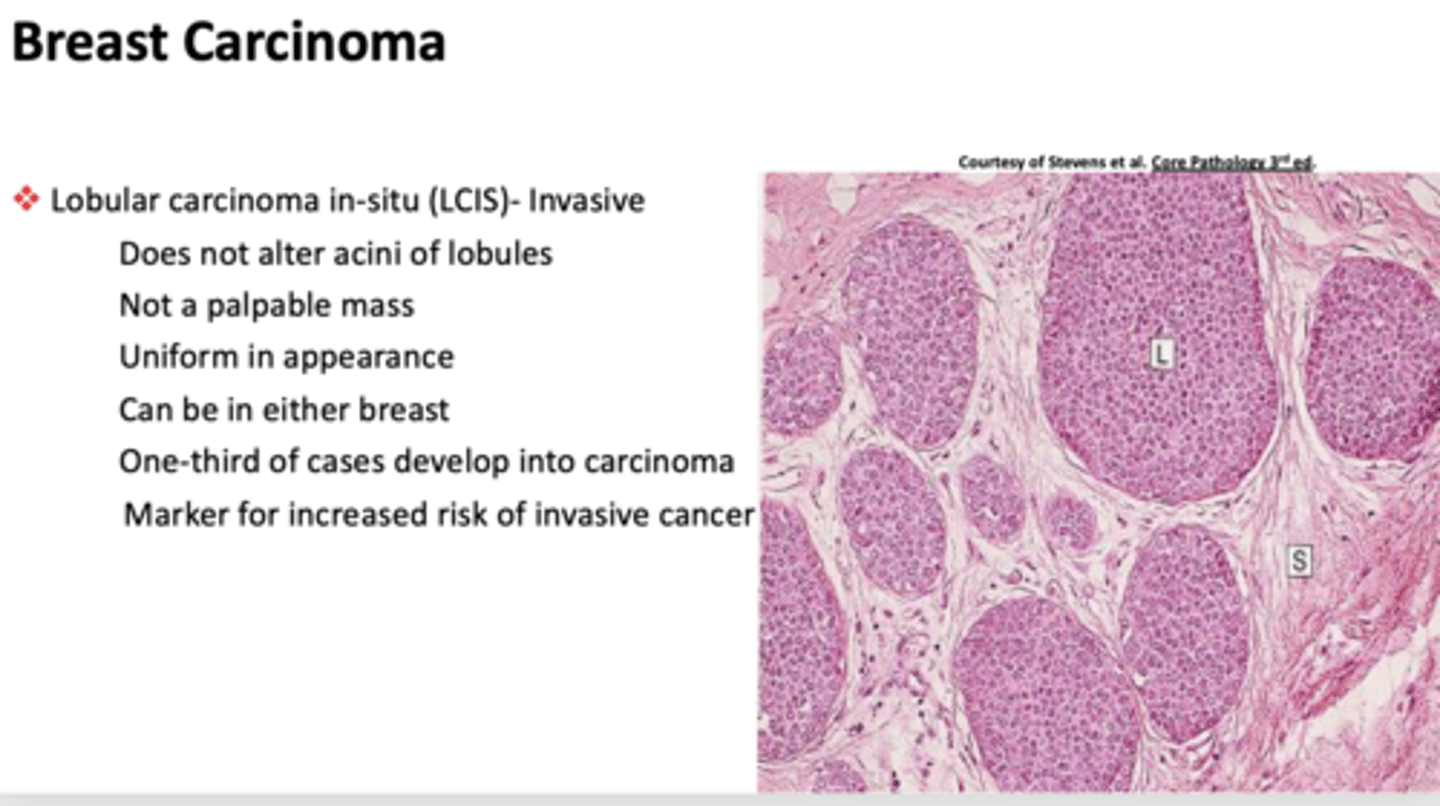
What breast condition is the following?
- Does not alter acini of lobules
- Not a palpable mass
- Uniform in appearance
- Can be in either breast
- One-third of cases develop into carcinoma
- Marker for increased risk of invasive cancer
lobular carcinoma in-situ (LCIS)
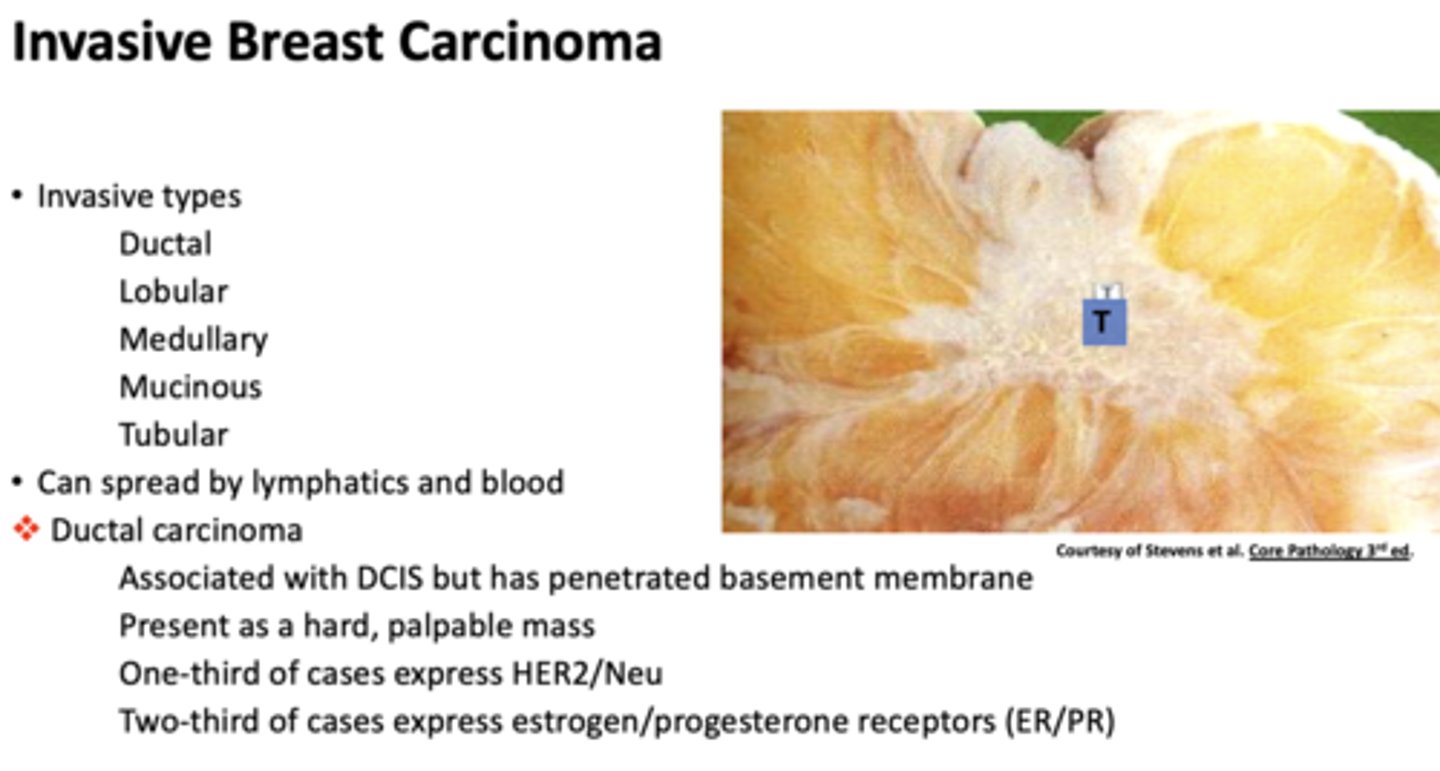
what is the most common form of invasive breast carcinoma?
ductal carcinoma
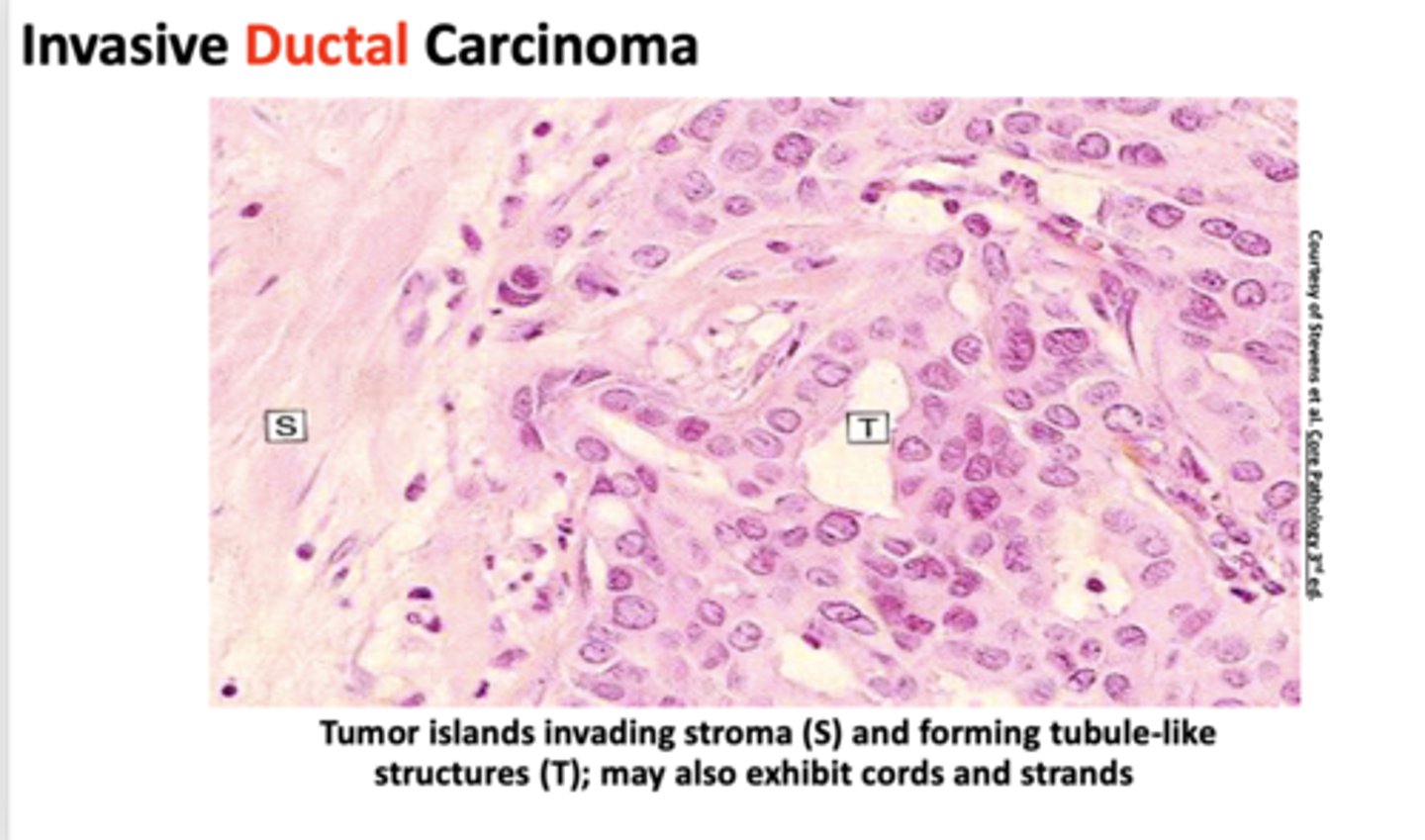
What form of invasive breast carcinoma?
- Associated with DCIS but has penetrated basement membrane
- Present as a hard, palpable mass
- One-third of cases express HER2/Neu
- Two-third of cases express estrogen/progesterone receptors (ER/PR)
ductal carcinoma
What form of invasive breast carcinoma?
- Identical to LCIS but has penetrated basement membrane
- Cells invade in single file line
- Majority express estrogen/progesterone receptors
- Rare expression of HER2/Neu
lobular carcinoma
What form of invasive breast carcinoma?
- Occur with women with BRCA1 mutation
- Triple negative (does not express estrogen, progesterone, HER2/Neu)
Medullary carcinoma
What does the prognosis depend on for invasive breast carcinoma?
- Presence of hormone receptors-slightly better prognosis
- Axillary lymph node status-most important factor in absence of distant metastasis
What is the 10-year survival if no nodal involvement?
70-80%
invasive breast carcinoma can metastasis to what 5 locations?
- Bone
- Lung
- Liver
- Oral cavity
- Ovaries (Krunkenberg tumor)
Where does the following occur?
- Inflammatory diseases on skin can affect region
- - Psoriasis
- - Eczema
- - Dermatitis
- More prone to superficial infections
- Malignancies can occur
- - Squamous cell carcinoma
- - Basal cell carcinoma
- - Melanoma
Vulva

What STI is the following?
- DNA virus
- Affect vagina, vulva, cervix
- Develop 3-7 days after transmission
- Red papules that form vesicles which become painful ulcerations
- Very common
- Look identical in oral cavity
herpes simplex virus (HSV)

What STI is the following?
- Heal within 1 to 3 weeks
- Persist indefinitely
- Transmission occurs during active phase
- Highest risk if active during delivery (C-section needed)
Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV)

What type of infection is the following?
- Most common - Candida (yeast) infection
- Disturbance in vaginal microbial ecosystem
- Have pruritus, erythema, or curdlike discharge
Fungal infection

What STI is the following?
- Caused by large protozoan organism
- Sexually transmitted disease affects vagina and cervix
- Can be asymptomatic
- Develops within 4 days to 4 weeks
- Presents as yellow, frothy discharge
- Cervix can have a fiery, red appearance- “strawberry cervix”
Trichomonas

What vulvar disease is the following?
- Exophytic lesion
- Can be single or multiple, if multiple (vulvar papillomatosis)
Squamous papilloma

What vulvar disease is the following?
- Known as genital wart
- Sexually transmitted disease
- Caused by HPV 6/11
- Can be solitary or multifocal
- Presents as an exophytic, papillary lesion
condyloma acuminatum

What vulvar disease is the following?
- Caused by syphilis
- Organism, spirochete Treponema pallidum
- Seen in 2nd stage
- Presents as broad-based plaques
condyloma lata

what is the most common cause of pelvic inflammatory disease?
gonorrhea

What vulvar disease is the following?
- Common cause gonorrhea
- Infection in vulva/vagina and spreads upward
- Present as pelvic pain, adnexal tenderness, fever, vaginal discharge
pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)

Acute complications of this vulva disease include:
- Peritonitis
- Bacteremia
- Suppurative arthritis
pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)

Chronic complications of this vulva disease include:
- Infertility
- Tubal/intestinal obstruction
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Pelvic pain
pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)

What vulvar disease is the following?
- Uncommon malignancy, but most common histologic type is squamous cell carcinoma
- Have two forms (HPV related, not HPV related)
Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN)/Vulvar carcinoma

What type of vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN) is the following?
- Caused by HPV 16
- Seen in middle-aged women
- Prolonged HPV infection
- Develops from classic VIN-white or slightly raised, pigmented lesion
- VIN can present as carcinoma in-situ or Bowen disease
Basaloid and Warty Carcinoma (HPV-related)

Histopathology of what disease is...
- Epidermal thickening
- Nuclear atypia
- Increased mitotic figures
- No cell maturation
Basaloid and Warty Carcinoma (HPV-related)

What type of vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN) is the following?
- Not HPV related
- Seen in older women
- Have long standing lichen sclerosus or squamous cell hyperplasia
- Arises from VIN simplex (differentiated VIN)-atypia of basal cell layer with normal appearing cells within superficial layers
Keratinizing Squamous Cell Carcinoma

which type of vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN) is more common?
Keratinizing Squamous Cell Carcinoma

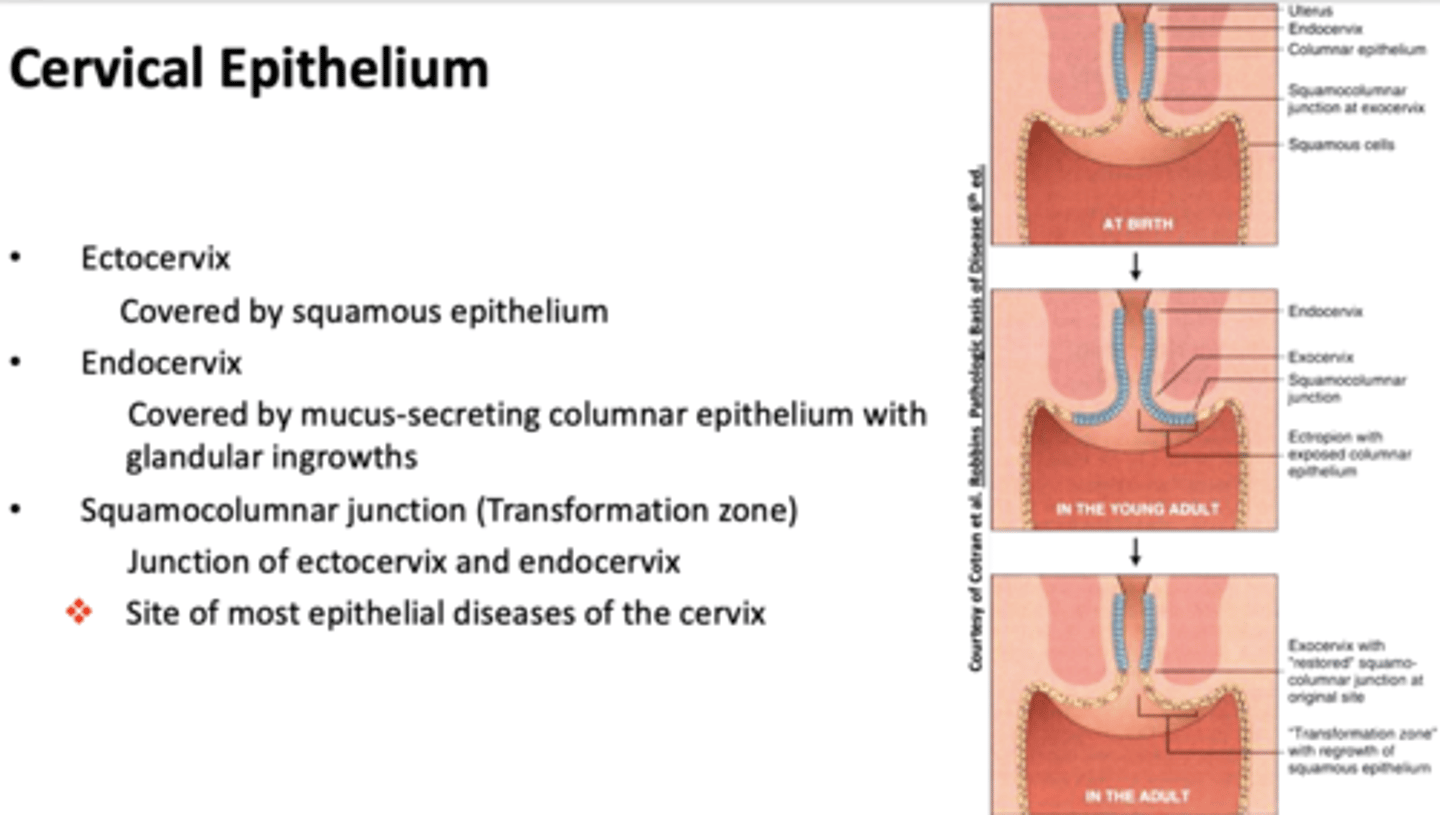
What part of the cervix is covered by squamous epithelium?
Ectocervix
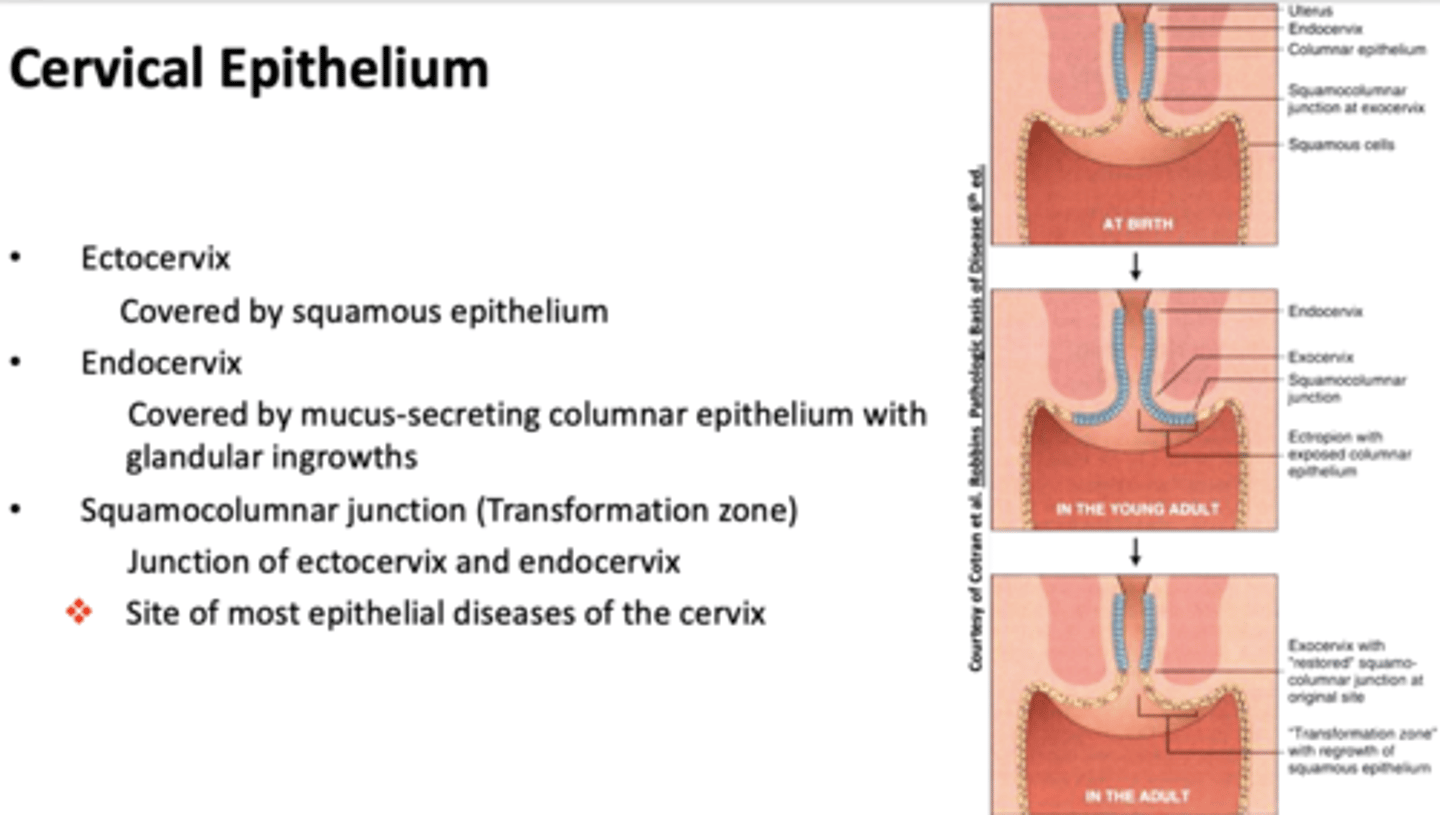
What part of the cervix is covered by mucus-secreting columnar epithelium with glandular ingrowths?
Endocervix
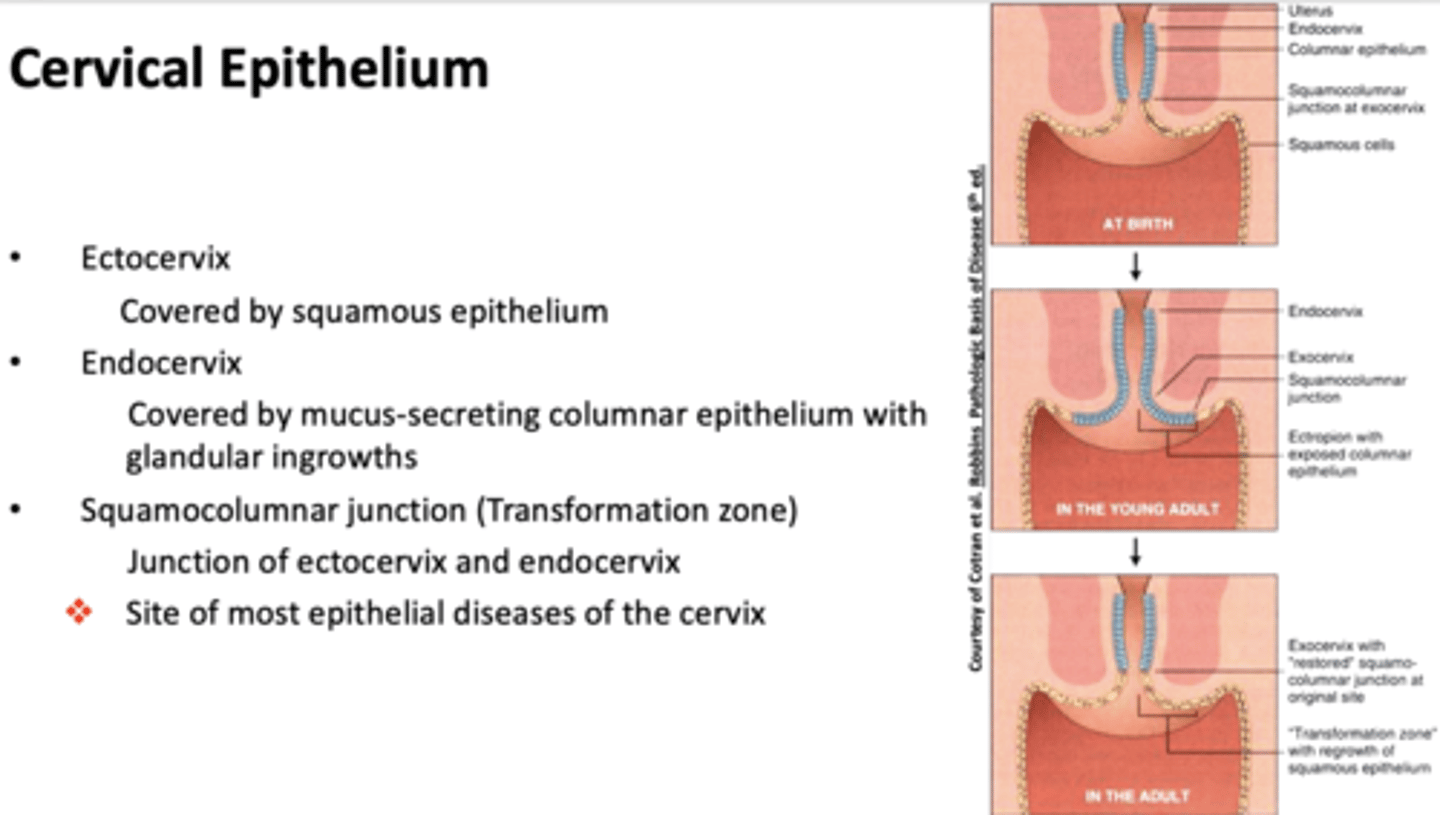
what is the site of most epithelial diseases of the cervix?
squamocolumnar junction (transformation zone)
What type of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN)/squamous intraepithelial lesions (SIL)?
- Known as low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL)
- Productive HPV infection
- Does not progress directly to carcinoma
- Ten times more common (80% have high risk HPV-16, 18)
- Involve the lower one-third of the cervical epithelium
CIN 1 (LSIL)

What type of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN)/squamous intraepithelial lesions (SIL)?
- Known as high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL)
- High risk for progression to carcinoma
- Involve the upper two-thirds of the cervical epithelium
CIN 2 & CIN 3 (HSIL)

What has a 100% high risk of HPV 16?
CIN 2 and CIN 3 (HSIL)

What is the 4th most common cancer in women?
cervical carcinoma

What has the following characteristics:
- 4th most common cancer in women
- Decrease due to effective screening, early diagnosis, therapy
- Important risk factor- HPV high risk types (Types 16, 18, 31, 33)
- Vast majority arise in transformation zone
cervical carcinoma

What has the following characteristics:
- Squamous cell carcinoma most common subtype
- Can be keratinizing or non-keratinizing
- Treatment: Hysterectomy with radiation & chemotherapy
- - Depends on staging and extent of disease
cervical carcinoma

What is a papanicolaou screening method to detect abnormal cells?
Pap smear

How can you test for HPV?
HPV DNA test

T/F: Vaccinations are available to help prevent cervical cancer and HPV-related lesions
True

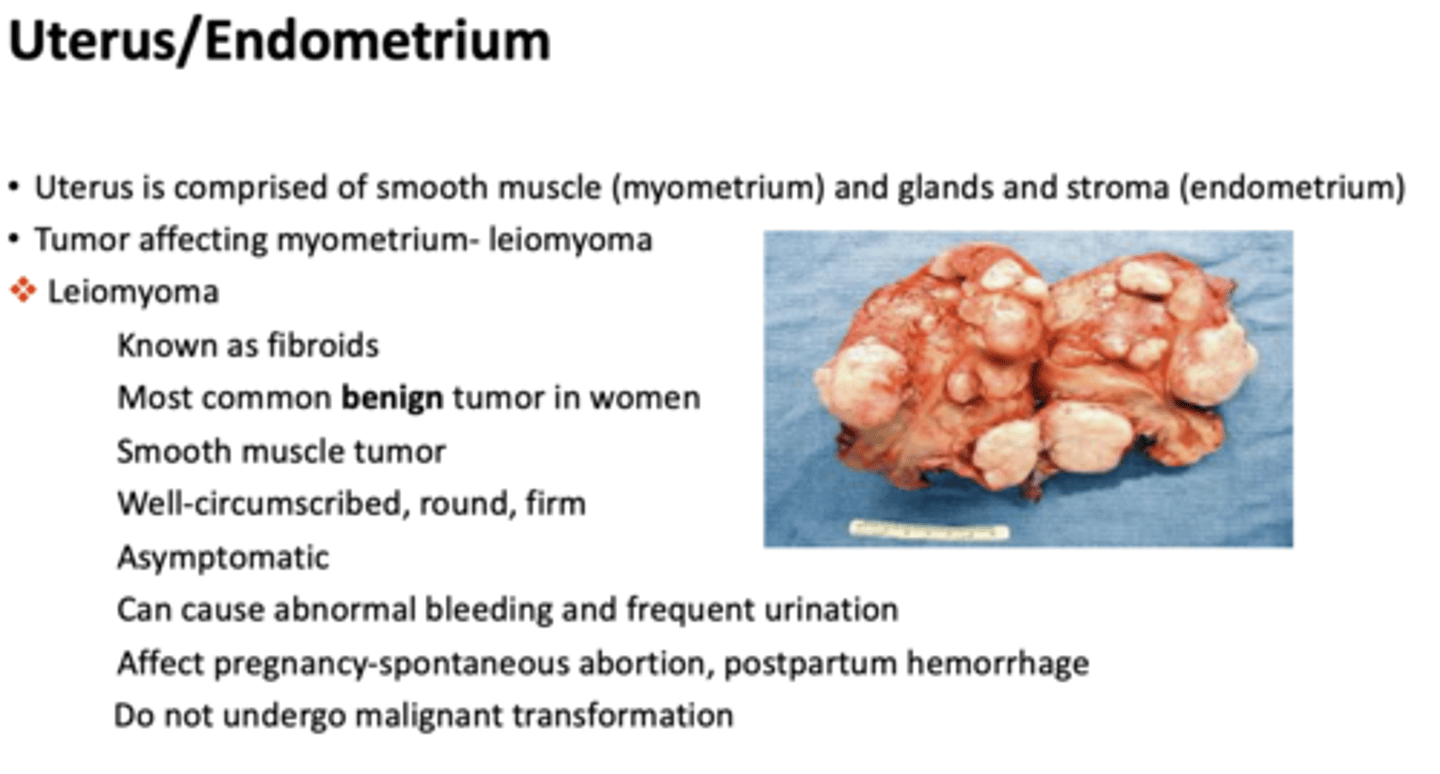
What has the following characteristics:
- Known as fibroids
- Most common benign tumor in women
- Smooth muscle tumor
- Well-circumscribed, round, firm
- Asymptomatic
- Tumor affecting myometrium
leiomyoma
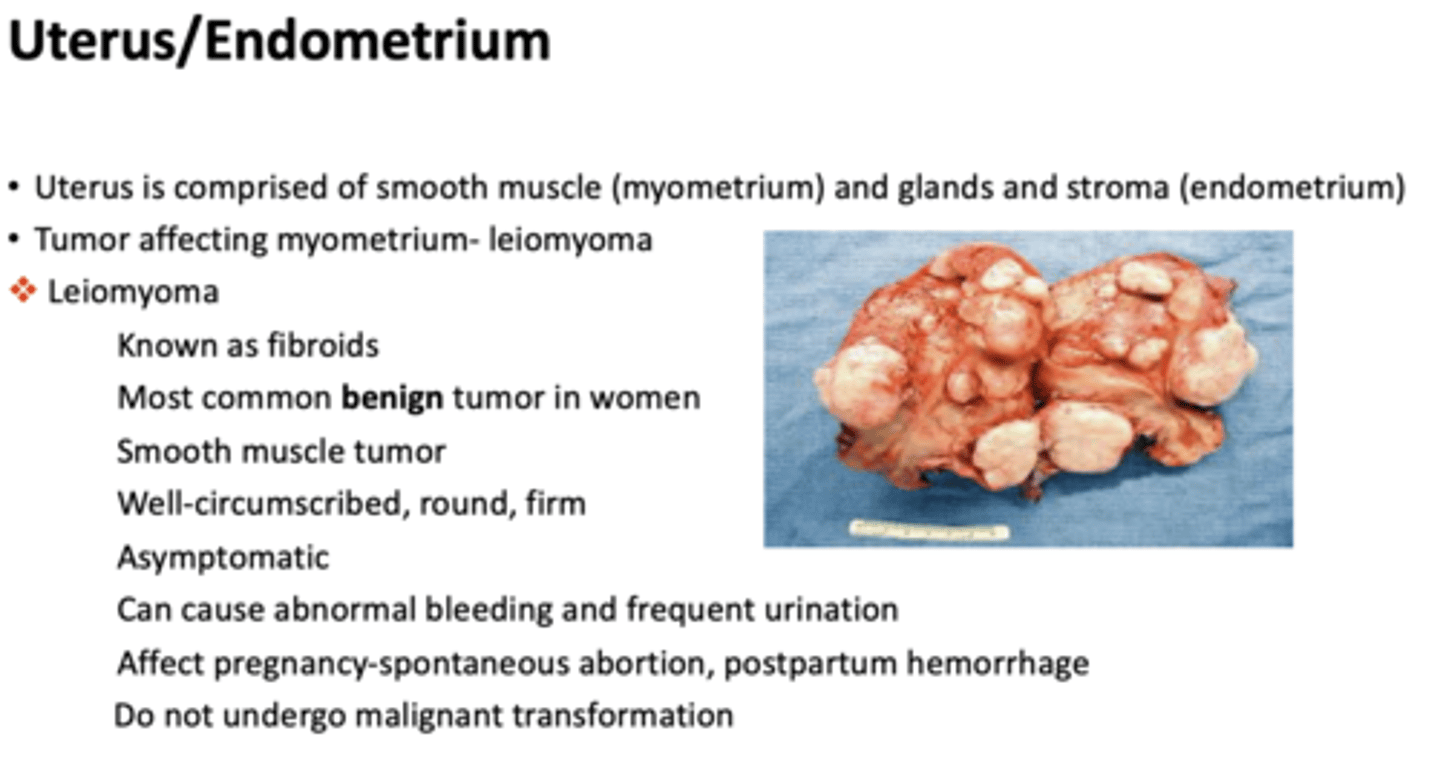
What has the following characteristics:
- Can cause abnormal bleeding and frequent urination
- Affect pregnancy-spontaneous abortion, postpartum hemorrhage
- Do not undergo malignant transformation
leiomyoma
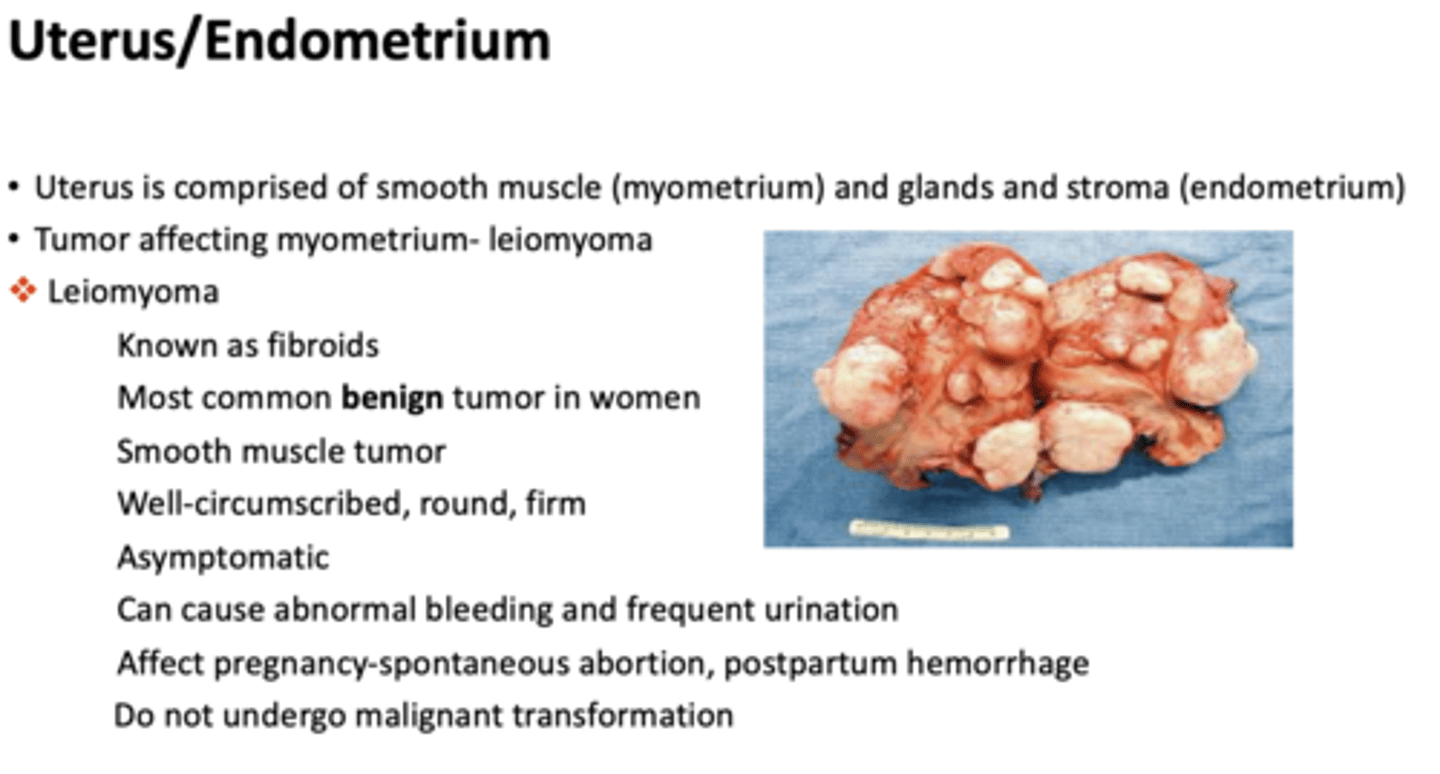
Most common benign tumor in women:
leiomyoma
What has the following characteristics:
- Presence of ectopic, abnormal endometrial tissue outside of the uterus
- Common sites: ovary, uterine ligaments, rectovaginal septum
- Can cause infertility, dysmenorrhea, pelvic pain, pain with intercourse
- Occurs in 3rd & 4th decade
- Unknown etiology
endometriosis

What has the following characteristics:
- Increased proliferation of endometrial glands
- Associated with prolonged estrogen stimulation of the endometrium
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding
- Risk factors include: Polycystic ovary syndrome, obesity, estrogen-producing tumors, estrogen therapy w/o balancing progestin
- Frequent precursor of endometrial carcinoma
endometrial hyperplasia

What is associated with prolonged estrogen stimulation of the endometrium?
endometrial hyperplasia

What is the most common type of endometrial carcinoma?
Type I endometrial carcinoma
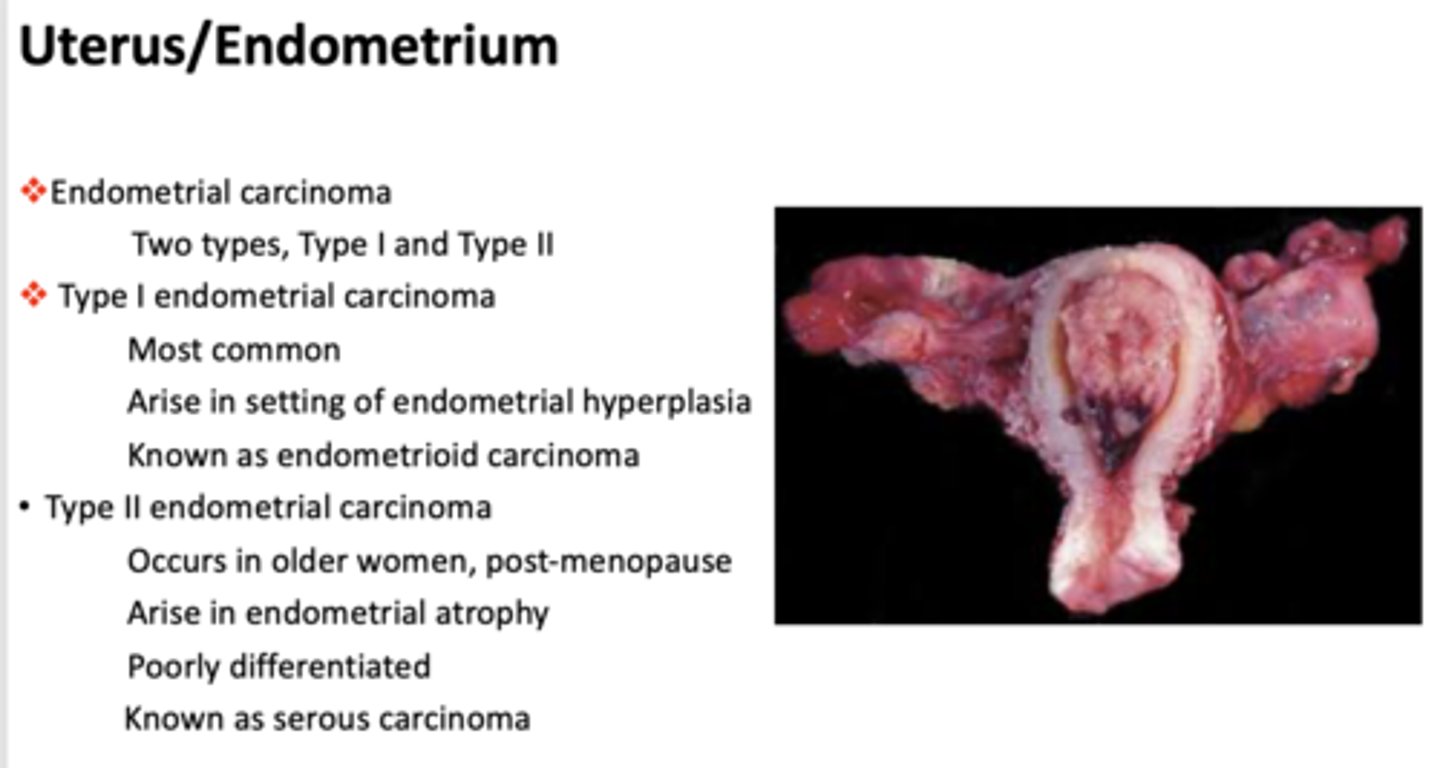
What type of endometrial carcinoma is the following?
- Most common
- Arise in setting of endometrial hyperplasia
- Known as endometrioid carcinoma
Type I endometrial carcinoma
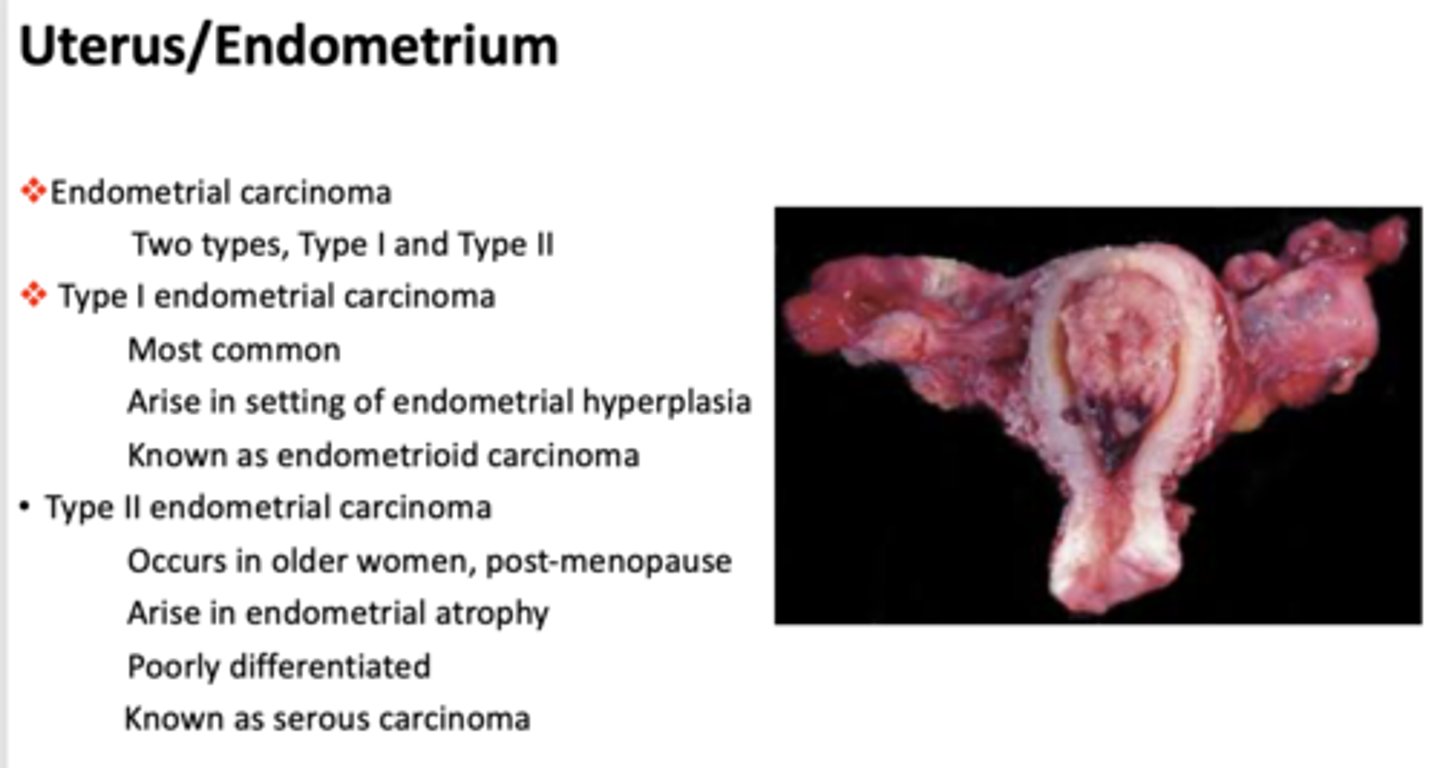
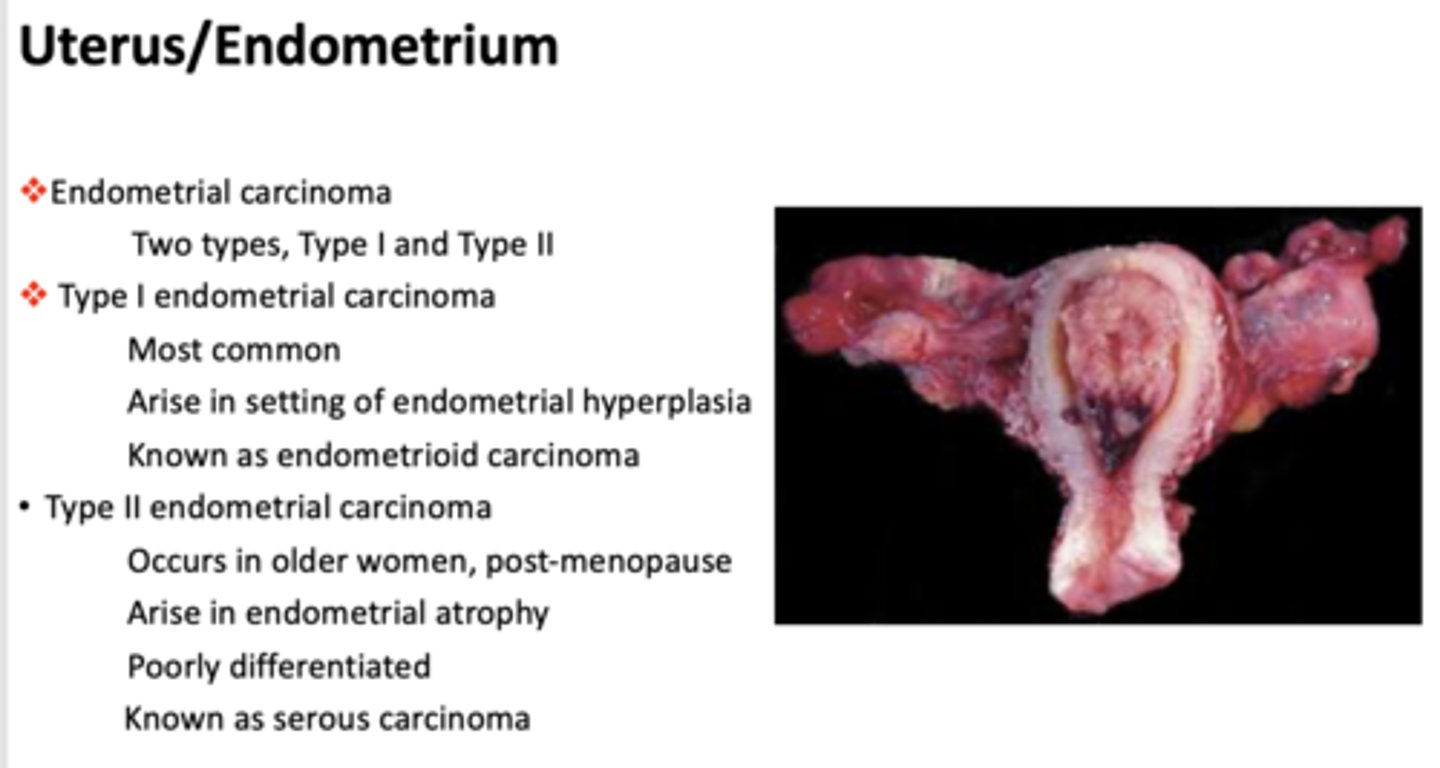
What type of endometrial carcinoma is the following?
- Occurs in older women, post-menopause
- Arise in endometrial atrophy
- Poorly differentiated
- Known as serous carcinoma
Type II endometrial carcinoma
Define the following:
Implantation of fetus in location other than uterus
ectopic pregnancy

What is the most common site of ectopic pregnancy?
fallopian tube (90%)

What is the most common cause of blood-filled fallopian tube (hematosalpinx)?
ectopic pregnancy

What has the following characteristics:
- Can occur in ovary, abdominal cavity
- Medical emergency
- Presents with severe abdominal pain
ectopic pregnancy

What has the following characteristics:
- Risk factor for endometrial hyperplasia and endometrial carcinoma
- Associated with obesity, Type 2 diabetes, premature atherosclerosis
- Was known as Stein-Leventhal syndrome
polycystic ovary syndrome
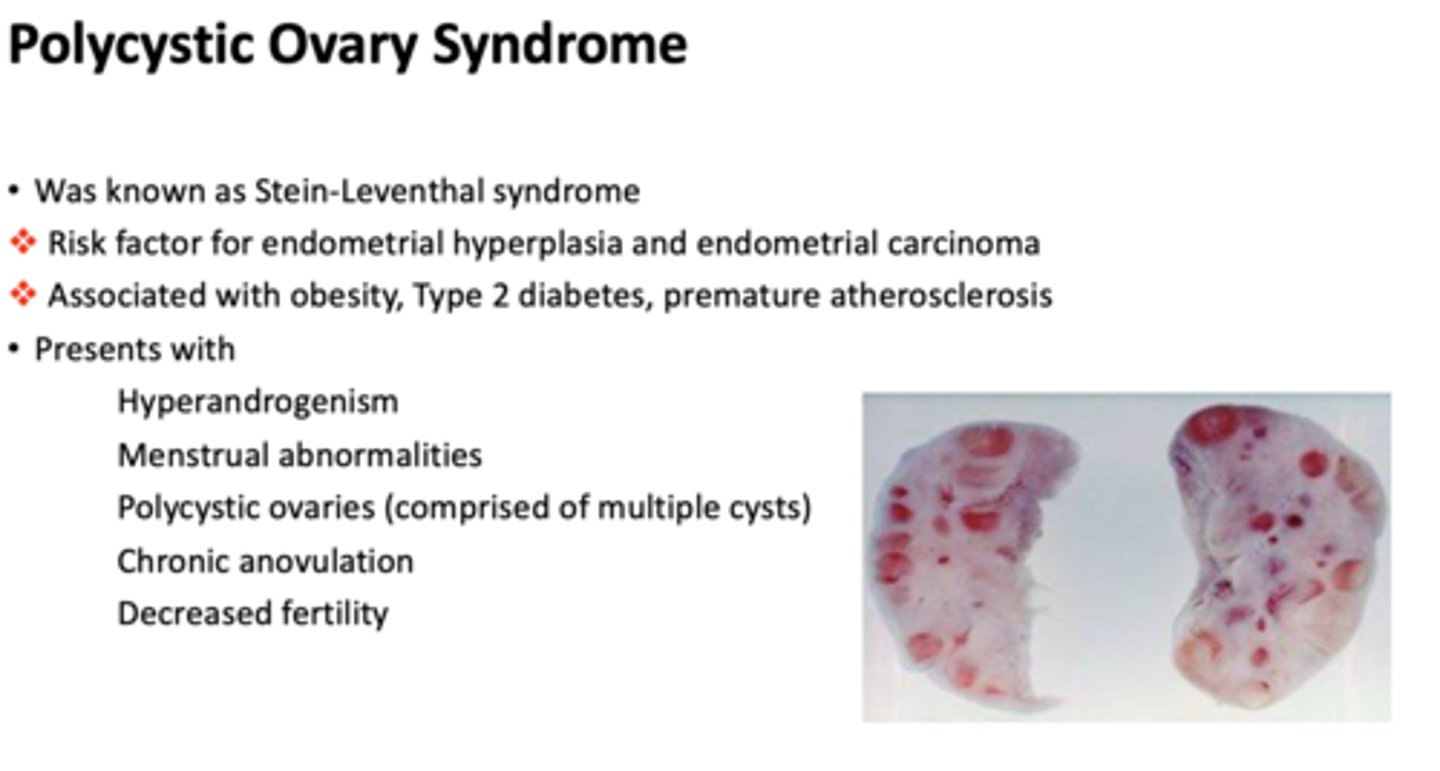
What condition presents with the following?
- Hyperandrogenism
- Menstrual abnormalities
- Polycystic ovaries (comprised of multiple cysts)
- Chronic anovulation
- Decreased fertility
polycystic ovary syndrome
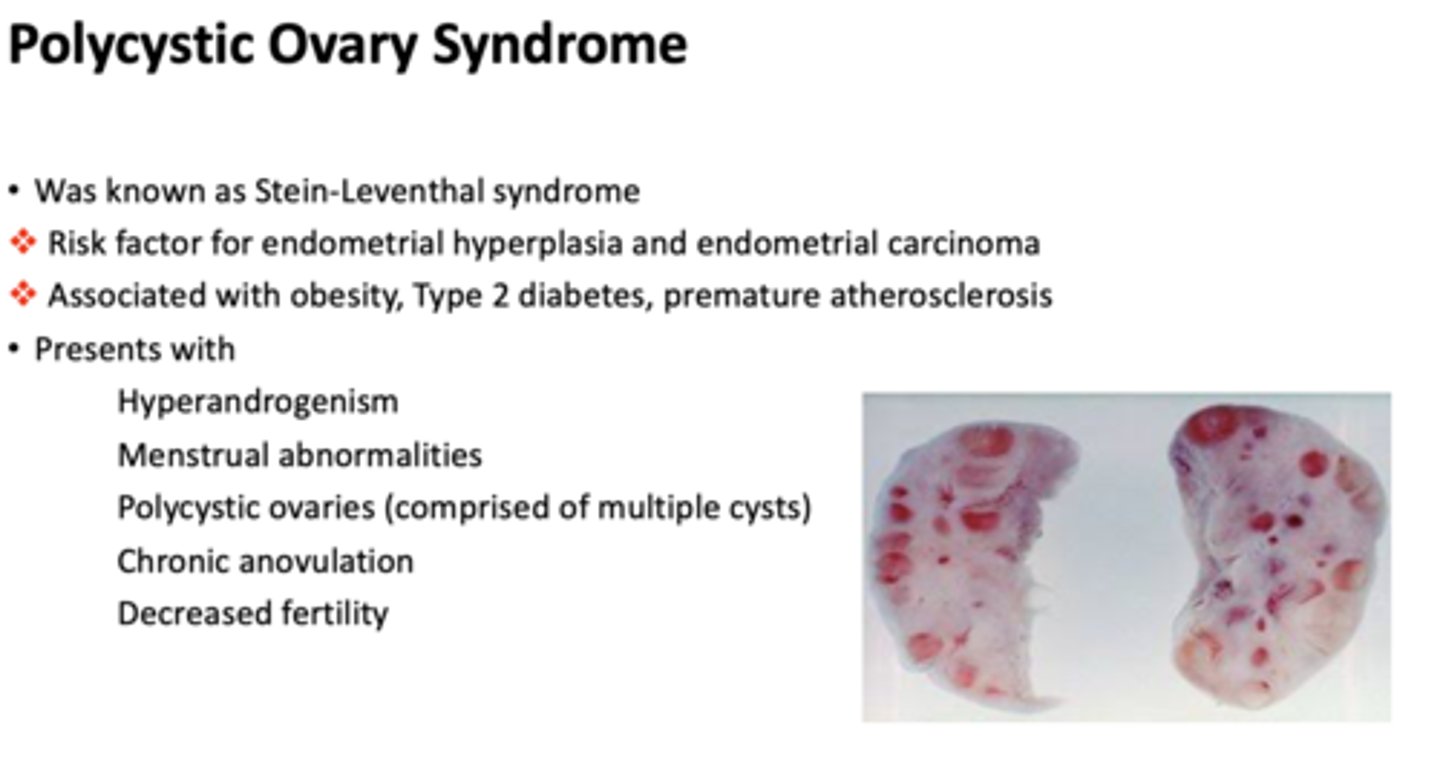
What condition is associated with obesity, Type 2 diabetes, premature atherosclerosis?
polycystic ovary syndrome
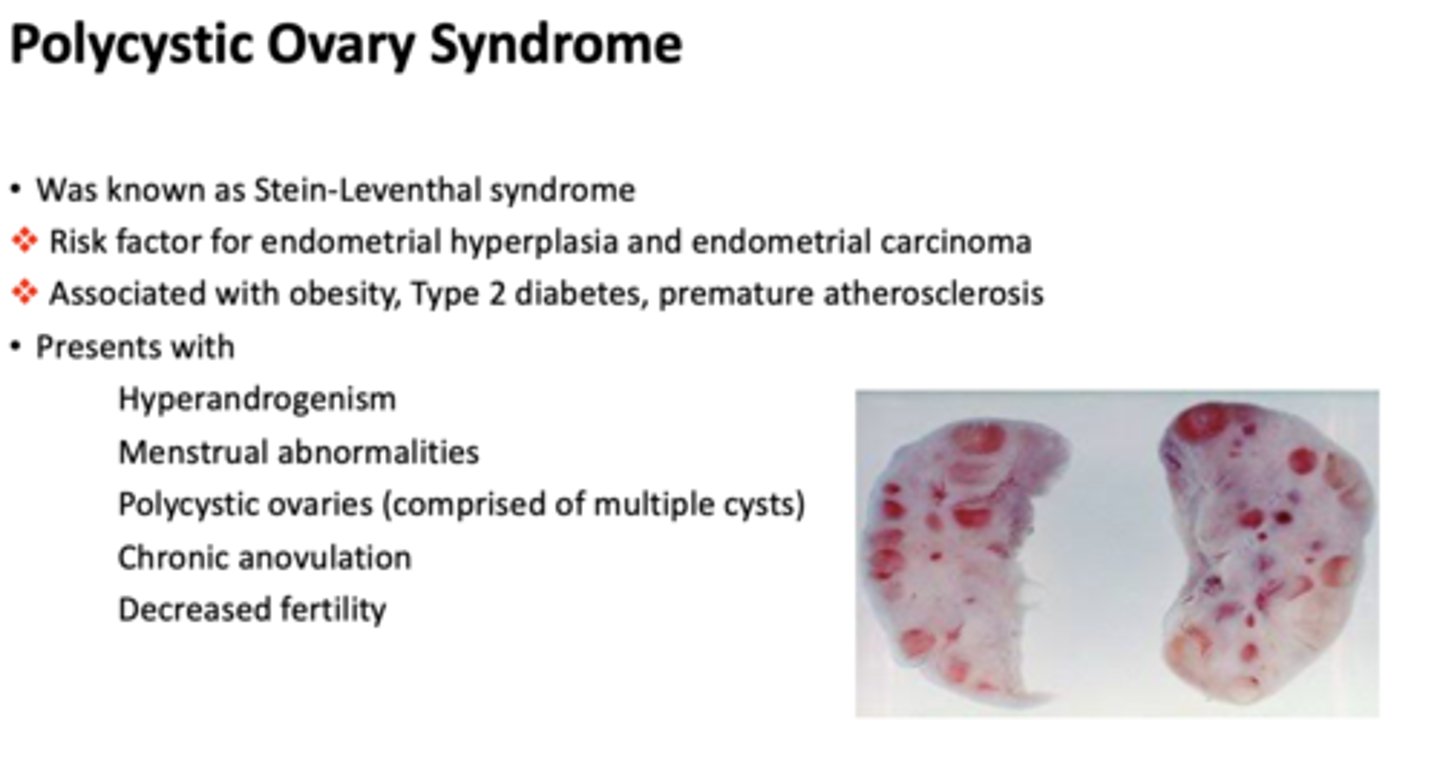
Most ovarian primary neoplasms arise from what epithelium?
müllerian
What has the following characteristics:
- Make-up 15-30% of ovarian tumors
- Majority are teratomas (15-20% of ovarian tumors)
- Three types of teratomas
- - Mature
- - Immature
- - Specialized
Germ cell tumors
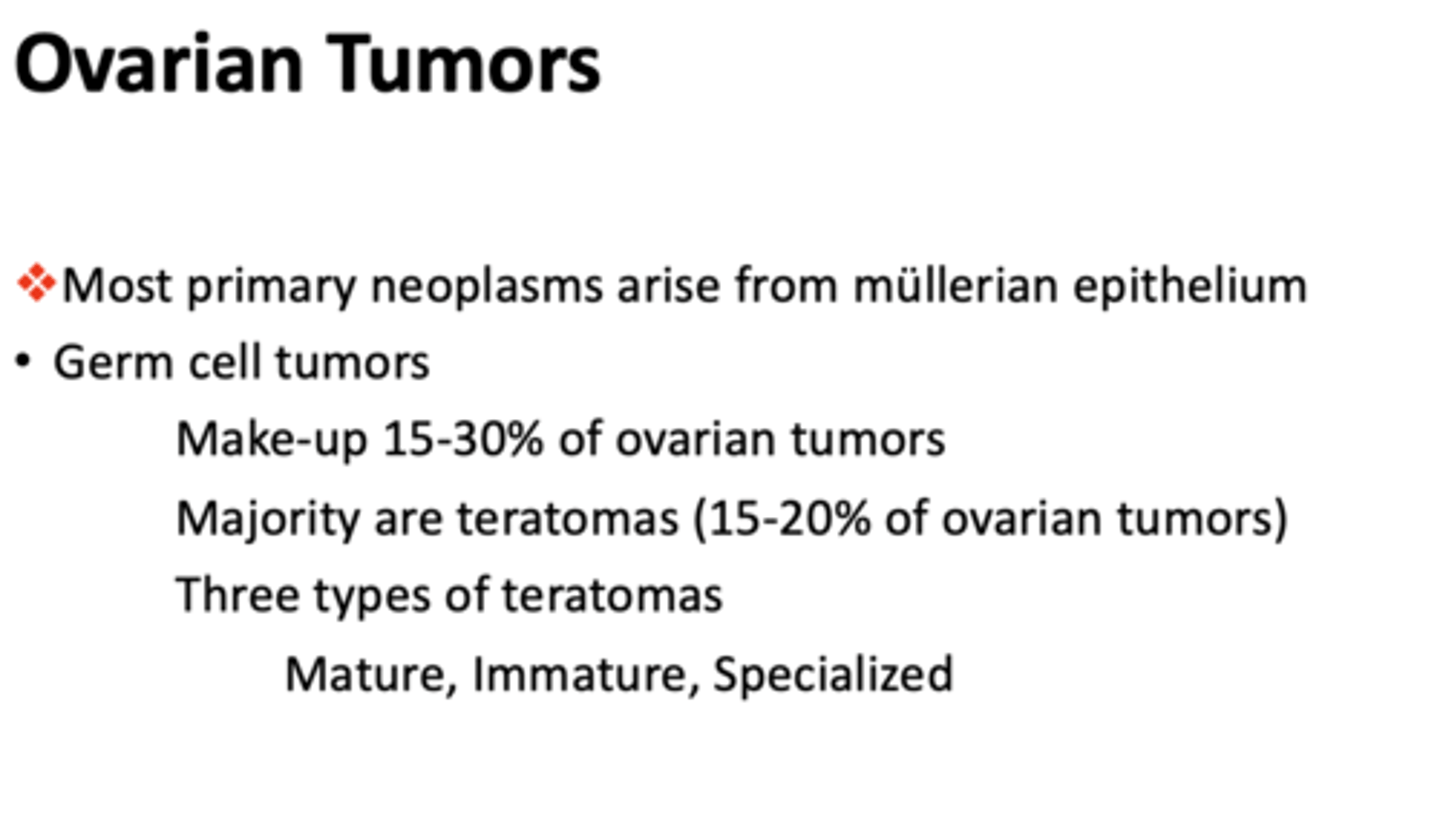
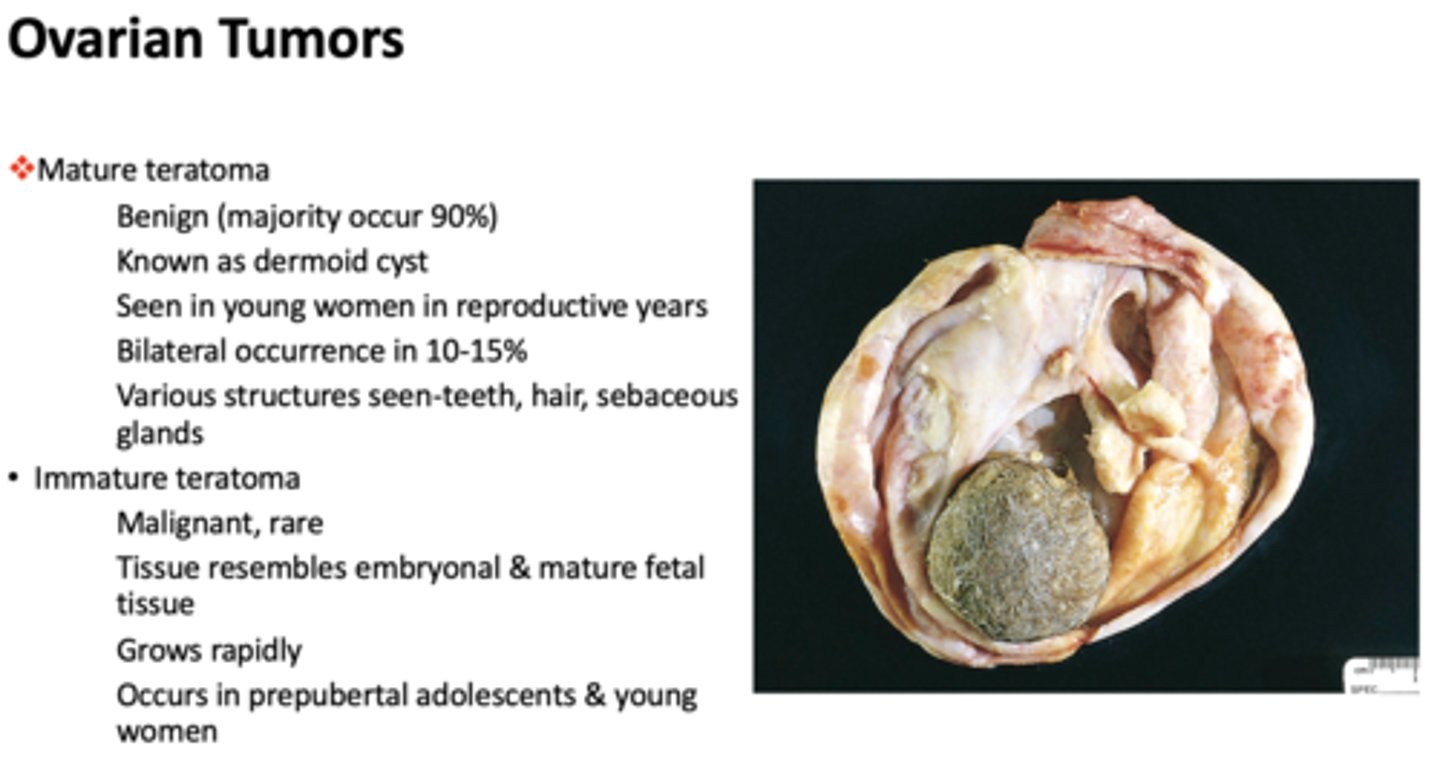
What has the following characteristics:
- Benign ovarian tumor (majority occur 90%)
- Known as dermoid cysts
- Seen in young women in reproductive years
- Bilateral occurrence in 10-15%
- Various structures seen: teeth, hair, sebaceous glands
mature teratoma
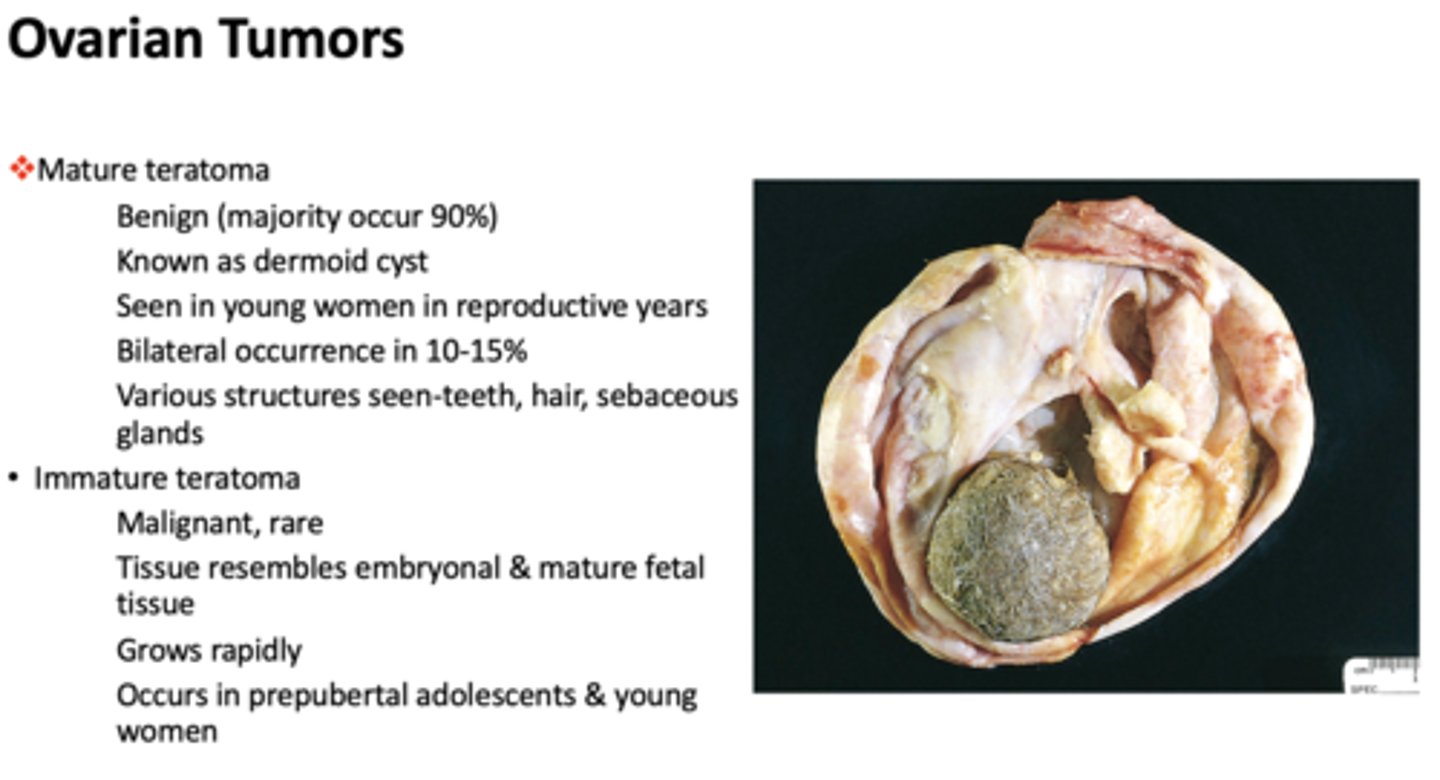
What has the following characteristics:
- Malignant, rare
- Tissue resembles embryonal & mature fetal tissue
- Grows rapidly
- Occurs in prepubertal adolescents & young women
Immature teratoma
which two locations most commonly metastasize to the ovaries?
- Breast
- GI

What metastatic tumor of ovaries?
- Can be bilateral
- Usually GI carcinoma-comprised of signet-ring cells
Krukenberg tumor

What has the following characteristics:
- Maternal endothelial dysfunction
- Reduced placental flow to the fetus which may result in hypoxia
- Occurs in last trimester after 34 weeks and seen in first pregnancies
preeclampsia

What is characterized by:
- Hypertension
- Edema
- Proteinuria
and symptoms disappear after placenta delivered?
preeclampsia

What has the following characteristics:
- Maternal endothelial dysfunction
- Result of preeclampsia
- Present with hypertension, edema, proteinuria, convulsions (seizures)
eclampsia
